Vermiculite insulation features and application
Composition and processing of vermiculite
Vermiculite contains several components connected by one chemical formula. It contains the most silicon - about 35%; there is also 10% magnesium, iron, potassium, calcium, etc.
Natural vermiculite comes in the form of large, scaly crystals. When exposed to high temperature, they are transformed into winding twisted threads-columns, increasing in volume up to 10 times.
When the material is heated above 1000 degrees, expanded vermiculite is obtained - a light bulk material, brownish, golden in color.
Hygroscopicity
The main distinguishing feature of expanded vermiculite (hereinafter simply vermiculite) is its high hygroscopicity. 100 grams of material can absorb up to 500 ml of water. But vermiculite dissolves just as easily with water.

In fact, it is a natural hydraulic accumulator. Therefore, it is mainly used in crop production, as a soil additive.
Thermal insulation
Another feature of the material is its high thermal insulation qualities. The thermal conductivity coefficient of bulk vermiculite is in the range of 0.05 – 0.07 W/ (m*K) depending on the size of the fractions and compaction density. This makes it possible to use the material as an effective insulation material.
1 mm, 120 kg/m3 – 0.059
2 mm, 110 kg/m3 – 0.057
4 mm, 95 kg/m3 - 0.054
8 mm, 65 kg/m3 – 0.052
The use of vermiculite as insulation
It is effective to use vermiculite as bulk insulation for thermal insulation of floors and ceilings. And also for filling various cavities in walls, partitions, pipeline ducts....

When used on attic floors, reliable waterproofing on the roof side is required, as well as covering the material layer with a vapor-permeable membrane (paper layer). On the side of the room, there should be a vapor barrier film under the material
During installation, special attention is paid to ensuring continuity
Special Use
Rigid slabs are made from vermiculite. They are more expensive, but can be used instead of mineral wool, as they have similar characteristics to it.
What is vermiculite and what are its main characteristics
Although vermiculite, as an insulation material, is a mineral of natural origin, its beneficial properties, surprisingly, were recognized not so long ago. It was described as a rock only at the end of the 19th century, but it took almost another century for the characteristic features of this mineral to be put at the service of man.
In fact, natural vermiculite is a rock of the silicate class, a group of hydromicas. It differs from ordinary mica in the increased content of water bound in the crystal lattice and the low level of bonds between the layers of the material. Thus, the common molecule of the original, natural vermiculite includes four water molecules “attached” to it.

Fragment of hydromica - raw material for the production of expanded vermiculite
In its normal state, it is a fairly hard rock, with a high density, reaching 2400÷2700 kg/m³, resistant to abrasion, but easily stratified into plates. Its melting point is about 1350 °C. But an interesting feature of the mineral was noticed and used - if it is not brought to melting, but heated to temperatures of the order of 900÷1000 ° C, then the material completely changes its crystal structure. Thin plates swell - increase in size 15-25 times and turn into porous worm-shaped columns or even thin threads with a pronounced golden or silver tint. Apparently, this is where the accepted name of the mineral came from – vermiculite, from the Latin “vermiculus”, which literally means “worm”.
The result is expanded vermiculite - precisely the material that is subsequently widely used in a variety of sectors of construction, industry and agriculture. The air-filled structure has a very low density - it is much lighter than water, and its specific gravity becomes only from 60 to 130 kg/m³.

When fired at high temperatures, pieces of mica turn into layered “worms”
Currently, the production of expanded vermiculite is put on an industrial basis. Our country has rich deposits of the necessary mica rocks - in the Murmansk, Chelyabinsk, Irkutsk regions, in the Krasnodar and Primorsky Territories.
The production cycle consists of several stages. This is raw material sorting, enrichment (removal of ballast impurities), crushing into fine fractions and roasting. The firing process takes a matter of minutes - and then the expanded columns go through the stage of crushing to the desired fraction, followed by sorting, packaging and shipment to consumers.

Prepackaged expanded vermiculite
Vermiculite produced at enterprises must comply with certain standards introduced by GOST 12865-67. So, it is divided into:
- large - grains ranging in size from 5 to 10 mm;
- average - from 0.6 to 5 mm.
– fine – grains up to 0.5 mm.
Expert opinion: Afanasyev E.V.
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
Typically, consumers are supplied with three different grades of material - 200, 150 and 100, in which the numbers indicate the upper limit of the bulk density of the material (kg/m³). The density itself and, accordingly, the insulating qualities of vermiculite depend on the size of the fraction. For example, without going beyond GOST, manufacturing plants offer material with the following parameters:
| Average fraction size, mm | Average bulk density of the material, kg/m³ | Average thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m×°С | |
| at a temperature of +25 °C | at a temperature of +100 °C | ||
| 0,5 | up to 130 | 0,056 | 0,062 |
| 1,0 | up to 120 | 0,052 | 0,059 |
| 2,0 | up to 110 | 0,051 | 0,057 |
| 4,0 | up to 95 | 0,048 | 0,054 |
| 8,0 | up to 65 | 0,046 | 0,052 |
Vermiculite has now become widely used in construction, as it has a number of advantages:
- The low coefficient of thermal conductivity allows the use of vermiculite as an effective thermal insulator for building structures. In terms of these indicators, the material is quite comparable to other popular insulation materials, for example, mineral wool or expanded polystyrene, but significantly surpasses them in its other characteristics.
- The operating temperature range is extremely wide. Thus, vermiculite itself, and many construction materials based on it, can withstand freezing below -200 °C and heating up to 900 ÷ 1000 °C. The material itself is absolutely non-flammable and does not contain any additives that could contribute to combustion or the spread of fire. When heated, vermiculite does not emit any gases that are dangerous to the human respiratory system. These qualities are used to create effective fire barriers or protect metal structures of buildings and structures.

One of the tasks of vermiculite is fire protection of metal structures
- The pronounced granular and at the same time layered structure of vermiculite becomes an excellent soundproofing barrier. Both airborne and impact noises are attenuated in the thickness of the material, and a building structure (wall or ceiling) insulated with vermiculite or made on its basis will not be a transmission “membrane” that propagates sound waves further. The sound absorption coefficient at a frequency of 1 kHz reaches from 0.56 (for material with a minimum fraction of 0.5 mm) to 0.7÷0.8 (with a fraction of 4÷8 mm).
- Despite the layered and seemingly unstable structure, vermiculite grains are highly durable. So, if we compare it with another expanded material - perlite sand, then vermiculite is not afraid of transportation, vibration, it does not shrink, does not break into small fractions, and does not generate dust.
- The material is chemically resistant and completely inert - it can withstand the effects of all known acids, alkalis, organic solvents or other technical liquids used in construction without any loss of its qualities.
- A very special property of the material is its pronounced adsorbing ability and the highest moisture absorption. Thus, vermiculite is capable of absorbing a volume of water that is five times its own weight. This, of course, can also be attributed to the shortcomings of the material. However, vermiculite just as easily releases moisture into the atmosphere, without losing its qualities at all.
By the way, the adsorbing properties of vermiculite are actively used for filtration systems, for cleaning soil and water bodies from oil stains and for other similar purposes.
An advantage can be considered that condensation drops never form on the insulating layer of vermiculite - water is absorbed into the porous structure, and when conditions are normalized, the moisture evaporates freely. Thus, the material helps maintain optimal temperature and humidity balance in the premises. However, this feature of the material should be taken into account when planning the insulation of building structures.
- The material has the highest biological resistance. Despite its porous structure and pronounced water absorption, it never decomposes and does not undergo rotting or decay processes. Vermiculite does not become a breeding ground for any forms of life - no pockets of mold appear in it, insects do not make nests, and rodents avoid it.
- The material does not cause allergic reactions even in people prone to such manifestations. Research shows that vermiculite is even capable of reflecting a certain part of the radioactive spectrum.
- The material is not subject to “aging” - over time it does not lose any of its specific qualities, neither under the influence of moisture, nor under the influence of extremely low or high temperatures.
- Finally, the expanded vermiculite itself has excellent flowability. When filling cavities in building structures with it, it is able to completely fill the entire volume without leaving any air voids.
The conditional disadvantages of the material include only two positions:
- The already mentioned high hygroscopicity of the material. When using vermiculite in bulk form, it is necessary to provide reliable waterproofing and the possibility of free evaporation of moisture. This is achieved by correct placement of vapor barrier and vapor permeable diffuse membranes.
- Quite a high cost of the material. Thus, the price of vermiculite is several times higher than that of other bulk mineral insulation materials - expanded clay or perlite sand. The cost of one cubic meter of material can reach 6.5 ÷ 7 thousand rubles. This, of course, somewhat limits its widespread use for thermal insulation of private houses. True, the advantages and durability of vermiculite fully justify such costs.
Nomenclature

VVF means Expanded Fractionated Vermiculite. Grade 100 means that the volumetric bulk density of vermiculite is no more than 100 kg/m³.
St. Petersburg Mica Factory offers expanded vermiculite:
Most thermal insulators have one or more flaws - they are either fire hazardous, expensive, or not environmentally friendly. In search of the optimal option, developers are often interested in the idea of using vermiculite in this role - a layered mineral that, at high temperatures, changes its structure and acquires new properties, which at first glance are quite suitable for insulating a building. How versatile is this insulation, does it have any disadvantages, and how to use it correctly?
Properties of expanded clay
- high strength
- fire resistant
- frost-resistant
- does not contain harmful impurities;
- does not absorb water;
- durable
- does not lose its properties and is not destroyed when frozen
- not subject to rotting
Absolutely safe for humans and the environment.
Expanded clay is a product of rapid firing of low-melting clays. From Greek, the word “expanded clay” is translated as “burnt clay,” which is absolutely true. Despite heat treatment, it not only does not lose the properties inherent in the clay itself, but also acquires additional ones, becoming porous.

Photo: Properties of expanded clay material. Application area
On their basis, expanded clay concrete blocks are made, the thermal insulation and mechanical properties of which allow them to be used for the thermal insulation construction of floors, walls, ceilings, foundations and basements. Thanks to the expanded clay filler, these blocks also acquire its properties. They are lightweight, durable, fireproof, acid resistant, etc.
Distinctive characteristics
Insulation has become so widespread due to its qualities. In bulk form, it is a substance of silver or golden color. The mineral does not decompose and has no odor.
Properties
Expanded vermiculite has a porous structure, so its volumetric weight ranges from 100-300 kg/m³. The material also has the following characteristics:

- density – 65–150 kg/m³;
- coefficient of thermal expansion - 0.000014;
- hardness – 1–1.5;
- sound absorption coefficient – 0.7–0.8;
- thermal conductivity – 0.05–0.09 W/m*K;
- melting point - 1350°C.
The elastic structure makes it possible to obtain heat-insulating boards from bulk raw materials by pressing.
Benefits of filler
Compared to other bulk thermal insulation materials, vermiculite has high qualities:
- high thermal insulation properties;
- biological resistance, it is not susceptible to rotting and mold;
- operating temperature is in the range of 260–1100°C;
- good fluidity allows you to fill voids of any shape;
- does not emit any gases when exposed to high temperatures;
- chemical inertness, does not react with acids and alkalis;
- high sound insulation;
- long service life - more than 60 years.

Environmentally friendly mica does not contain heavy metals and has a neutral pH value. In case of fire, it does not emit toxic gases, which puts it one step above all mineral representatives.
Flaws
Laying insulation requires the installation of a waterproofing layer. This is due to the fact that hydromica in its swollen state is capable of absorbing large amounts of moisture. Also, the material has a high cost, but this factor is relevant only for products in the form of slabs. Loose granular filler is inexpensive.
Areas of application
Discovered relatively recently, the mineral vermiculite and its derivatives have found many different applications today:
- Ecology, oil and chemical industries. Few people can answer when asked about vermiculite that it is an excellent sorbent capable of binding alkalis and acids. This property allows it to be used to neutralize a variety of chemicals in industries, as well as to limit oil spills.
- Nuclear industry and energy. It is used as an absorber of radioactive elements such as cobalt-58, strontium-90 and cesium-137, and also as a reflector of gamma radiation.
- Automotive and aviation industry. A variety of sound-absorbing and heat-insulating materials and products are made from vermiculite.
- In industrial and civil construction vermiculite is used as follows:
insulation, as well as sound and heat insulators for roofs and floors;

- for backfilling as insulating material into hollow panels;
- as a component of various plasters, lightweight concrete and dry building mixtures;
- in the manufacture of concrete and cement blocks, as well as heat-insulating mastics as a filler;
- in the production of fire-resistant and heat-resistant slabs, panels and other wall materials;
- when installing self-leveling floors.
5. In industrial and private plant growing and horticulture. Let's take a closer look at how vermiculite is used for plants.
Scope of use
The advantages of the material include its versatility. It is used for different purposes in different forms.
- As a backfill insulation for frame structures and for well masonry. In this case, there is no need to protect it from moisture.
- In the form of insulating backfill for floors, attics, and roofs.
- The material is added to masonry mortars when the walls of a house are built from cellular concrete blocks.
- Raw materials are added to plaster mortars to provide sound and heat insulation for walls inside and outside, as well as partitions.
- The properties and internal structure of the insulation allows the material to be used in the form of slabs and plaster to protect metal or other load-bearing structures from fire.
- Adding backfill to the floor screed solution.
- As a filler for decorative plaster.
- Use in agriculture to improve the soil, fertilize it and mulch plantings.
Technologies for laying vermiculite building materials
Work with mineral insulation is not difficult or harmful - in terms of the degree of impact on the human body, vermiculite coating, according to GOST 12.1.007-76, belongs to class IV (low-hazard substances). To prevent dust from getting into the eyes and respiratory system, before using vermiculite, the worker should protect them with goggles and a respirator. Provided the building material is stored in dry, indoor areas, its shelf life is unlimited.

Thermal insulation of house enclosing structures with backfill vermiculite
To protect the attic ceiling and the surface of the pitched roof from heat leaks, you need to follow a simple algorithm:
- Cover the inner lining with an overlapping vapor-proof film, which will prevent moisture from entering the vermiculite from the inside.
- Pour dry vermiculite into the resulting cavities in the roof frame.
- Lay a windproof super-diffusion membrane on top of it, the purpose of which is to prevent the material from weathering and at the same time allow vapors to circulate freely.
- Install the counter-lattice and lay the roof covering.
The insulation scheme for attic floors is, in principle, similar:
- Reliable waterproofing is laid on the lining between the beams.
- A log system is installed in a layer of 100–150 mm.
- Bulk insulation for the floor is introduced, which must be immediately covered with a vapor-permeable film.
- After installing the plank or plywood covering, the floor is ready for finishing.
- To reduce the cost of the material, vermiculite can be mixed with sawdust in a ratio of 1:1 or 3:2.

Filling the walls with vermiculite is possible at the stage of their construction using frame or well technology or during the process of external insulation. To do this, as the load-bearing wall and facing layer are erected, the space between them is filled with vermiculite granules with light tamping. The approximate layer thickness is 100 mm (for Moscow). Additional vapor and waterproofing is not required, ventilation gaps in the external wall are also not needed.
Another way to create an insulated wall is to fill the cavities of building blocks with vermiculite. The thermal insulation effect of such a design increases sharply, and the free exchange of vapor in the wall is not disturbed, and it remains light and breathable. If necessary, the outer wall can be further insulated if it is built from concrete panels based on quick-hardening cement with the addition of loose wall insulation.
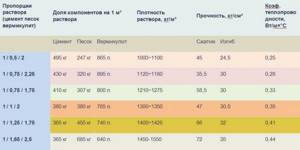
Proportions of solutions for screeds
Insulation with dry vermiculite is a rather expensive solution, so in private construction they prefer to add this material to construction and finishing mixtures. To prepare a solution for a thermally insulated screed, you need to stock up on standard M400 Portland cement, sand and fine- or medium-fraction vermiculite. Due to its high water absorption, the solution must be used within 30 minutes after mixing.
For reliable insulation of the floor above an unheated space, 100 mm of screed is usually sufficient, and for interfloor ceilings, 30 mm is sufficient. It must be remembered that the poured floor, due to the small mass fraction of cement, is not frost-resistant, therefore such screeds are recommended only for heated rooms.
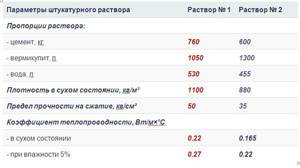
Recipe for plaster mortars for exterior use
To plaster the walls from the inside, you can use the same composition, but for their external treatment, the proportions of the solution must be slightly changed. Both external and internal plasters have high vapor permeability, facilitating normal self-regulation of the internal microclimate. Warm plasters based on vermiculite have a natural golden or silver tint, but if desired, pigment of the desired shade can be added to their composition.
Plaster for interior decoration: C – cement, I – lime, G – clay, V – vermiculite
When laying walls, it is advisable to use modern thermal insulation materials (gas, foam blocks, vermiculite concrete), and the seams between them should be made of masonry mortar with a low thermal conductivity coefficient. You can knead it using the same vermiculite, having previously decided on the optimal composition.
Thus, the demand for vermiculite in construction is obvious: excellent manufacturability and a unique combination of properties bring vermiculite backfills and slabs to the forefront among fire-resistant insulation materials. The only significant obstacle to expanding the scope of their application is the high price, but increased production gives hope that this will soon be eliminated.
Features of use
For effective thermal insulation, the insulation layer must create the required thermal resistance value. In the central zone of the Russian Federation, this value is taken to be approximately 3.5-3.8 m2*K/W. It turns out that the vermiculite layer to achieve the desired effect should be at least 17.5 cm for a fraction of 1 mm.
To save material, they use one trick: mix vermiculite with sawdust in a ratio of 1:1 or 6:4. Mineral insulation prevents sawdust from caking and ensures free removal of moisture from it.
Sawdust adds volume to the insulation layer without significantly reducing its overall thermal resistance. Sawdust is much easier to obtain, and its cost is insignificant. In combination with vermiculite, their disadvantages are leveled out, and the bottom line is savings on insulation.
Combine the materials on site, mixing them until smooth with a hand mixer and a drill attachment. Alternatively, sawdust and vermiculite in the required proportions are placed in a pneumatic pump for delivery through an air duct to the installation site. During delivery they will be sufficiently mixed.
Properties of vermiculite insulation
Vermiculite insulation is a material that is widely used in construction and finishing work during the construction of new buildings, and carrying out major and ongoing repairs of old buildings. It is used in the form of pressed slabs, as a filler and as an additive to plaster mixtures. It is used for insulating walls, floors, attics and ceilings. Insulation with vermiculite is carried out during the construction of pipeline systems and highways for various purposes, which significantly extends their service life. This has a positive effect on the operation of equipment and pipeline fittings installed for the smooth functioning of the entire system.
Technological features

Vermiculite in the form of slabs and in bulk.
Vermiculite is an environmentally friendly material created by nature. Belongs to the minerals of the hydromica group. It has a crystalline form of golden brown, yellowish or bronze color. It was found that when vermiculite plates are heated, they transform into threads or worm-like columns. Actually, this property made it possible to give the material such a name, because vermiculite means worm in Latin. After examining its physicochemical properties obtained after heating, vermiculite insulation began to be used in various industries, agriculture and construction. Also read: “Choosing the best insulation for the roof.”
The main advantages of the material include:
- fire resistance (1350 0 C);
- density (not higher than 150 kg/m3);
- low thermal conductivity (no more than 0.12 W/m*K);
- resistance to aggressive environments, bacteria and does not form mold on the surface;
- hygroscopicity;
- ability to absorb sound (sound absorption coefficient up to 0.8);
- environmental friendliness;
- service life (60 years).
Before pouring antifreeze into the heating system of your home, you need to clean the pipes and radiators from all kinds of contaminants.
Here you can read what equipment is needed to pump the heating system with antifreeze (antifreeze liquid).
Methods for insulating walls with vermiculite

View of a wall plastered with mortar containing vermiculite.
Vermiculite insulation of walls is carried out during the construction of new buildings and old buildings constructed from different materials. Thermal insulation in bulk form can serve as a filler in the manufacture of heat-resistant concrete and is used for plastering surfaces. It is produced in different fractions (from 0.5 to 12 mm) and is sold in retail chains in paper bags, most often weighing 25 kg.
Granular vermiculite can be poured into inter-wall voids. The pressed slabs are secured using special fasteners and can be cut before installation. The slabs can serve as good insulation when lining fireplaces, stoves, chimneys and pipes. Vermiculite for ceiling insulation additionally performs soundproofing functions in multi-story buildings.
Vermiculite insulation, the properties of which remain unchanged regardless of its type, is also used for plastering vertical surfaces. To do this, it is added to concrete mixtures in certain proportions. You can make them yourself or buy ready-made ones. Comprehensive home insulation with vermiculite (walls, floors, attic) will save on heating bills.
The method for installing an electric heating boiler consists of two parts: inserting the circuit and connecting to the network.
Vermiculite insulation of floors and attics
The technology for insulating floors and attics with vermiculite is the same. In this case, the thermal insulation is protected with special films. A vapor barrier should be installed on the side of the warm room, and waterproofing on the side of the street or unheated attic.
When performing thermal insulation with vermiculite, the presence of waterproofing and vapor barrier is mandatory
It is extremely important to place these protective layers correctly
Insulation of a pitched roof

When insulating the floor, waterproofing is placed under the vermiculite.
With such insulation, it is important to correctly select the thickness of the vermiculite poured. It depends on temperature conditions and ranges from 10 to 20 cm
The technology for insulating a pitched roof is as follows:
- a vapor barrier film is laid on the rafters;
- granular vermiculite is poured in;
- covered with a layer of waterproofing and a counter-lattice;
- the roof is spreading;
- Internal lining is carried out with any material.
Vermiculite insulation, the properties of which have been well studied, is a modern material that has a wide range of applications.
Characteristics of vermiculite
The main characteristics of expanded vermiculite are presented in the table:
| Fraction, mm | Thermal conductivity, W/m*K | Volumetric weight, kg/m 3 | Humidity, % | Sound absorption coefficient, at a frequency of 1 kHz |
| 0.5 | 0.053 | 144 | 3 | 0,56-0,6 |
| 1 | 0.05 | 125 | 4 | 0,6-0,65 |
| 2 | 0.49 | 100 | 4 | 0,7-0,8 |
| 4 | 0.48 | 94 | 5 | Same |
| 8 | 0.045 | 87 | 3 | Same |
- The thermal conductivity of the coarse fraction mineral approaches the values of mineral wool and extruded polystyrene foam, which makes its consumption in various insulating fills economical. It must be borne in mind that the thermal insulation characteristics of slab vermiculite are deteriorated due to the use of a large proportion of cement in them.
- Hygroscopicity is the ability to retain moisture; this quality makes the material in demand in agriculture and brings additional troubles to builders, since in order to maintain its thermal insulating properties, careful waterproofing of the insulation and ventilation are necessary to allow water vapor to escape.
- The sound absorption of vermiculite makes it possible to use slabs and plasters in soundproofing structures.
- Fire resistance – the melting point of the mineral is above 1300 degrees, which makes it suitable for insulating hot pipes, chimneys, furnace fireboxes or fireplaces.
- Environmental friendliness - the raw materials and expanded vermiculite do not emit gases harmful to humans, do not pollute the environment, are not radioactive, and do not cause allergies.
- Unattractive to rodents, due to its hygroscopicity it absorbs marks and becomes unattractive to them.
- Resistance to aggressive environments and bacteria.
- Durability of use up to 60 years.
Vermiculite insulation is a high-quality, harmless and affordable heat insulator for residential, public and industrial construction.
Vermiculite area of application, pros and cons, installation features
When solving the pressing issue of thermal insulation of a home, one has to face the problem of choosing a thermal insulation material.
The range on the market is quite wide, but almost every option has significant drawbacks. In one case, the flammability deters, in the other, the high hygroscopicity rate.
The article discusses the characteristics and advantages of vermiculite, which is the golden mean of price and quality.
Description and scope of vermiculite
Vermiculite is a natural crystalline mineral with a layered structure. Belongs to the group of hydromicas. It contains: silicon, iron, magnesium, calcium and other mineral components.
The main advantages due to which the material is used in construction are resistance to aggressive influences, high acidity, retains its integrity for a long time, and does not decompose.
Many gardeners are familiar with vermiculite; it is often used as a mulching material, a substrate component, and an aerator. It is not used so often in construction work, although its properties and physical characteristics are of great interest for this field of activity. Among the developed areas:
• production of paint and varnish products, soft roofing;
• when installing a “warm floor” system;
• as a filler for heat-insulating and decorative plaster mixtures;
• for insulation of individual areas in the house (chimney, floor, roof, etc.);
• as a component of a screed mixture.
Vermiculite has good insulating characteristics, due to which it is used in regions with warm climates as backfill in three-layer walls to prevent overheating of the house, and in northern regions - for thermal protection of housing.
The ground in the regions of the middle zone and the Urals freezes strongly in winter, which often causes cracks to form in the concrete bowls of swimming pools. Vermiculite helps correct the situation. It is poured to the bottom, as well as into the cavity between the bowl and the edge of the trench during the construction process.
Insulation is produced in the form of backfill, compressed slabs, blocks, pipe segments, and liners.
Pros and cons of vermiculite
To appreciate the material, you need to familiarize yourself with its advantages and disadvantages.
Among the main advantages of vermiculite:
• environmental friendliness, during operation no toxic substances are released during heating;
• low thermal conductivity (0.055–0.098 W/m•°C);
• fire resistance (operating temperature range from minus 260° to plus 1200°);
• does not shrink over time;
• has good vapor permeability, which eliminates the formation of condensation in the room;
• resistance to microbiological processes, rodents and insects do not show interest in the material;
Advantages
Vermiculite is a mineral based on plate-like crystals united into three-dimensional groups. It is durable and, unlike mineral wool, is not subject to destruction, does not compress, and does not precipitate under its own weight. This makes it a much better insulation material than expanded clay or perlite, to which it is essentially closer.
In terms of thermal conductivity, it is on par with the most commonly used mineral wool, has the same fire and environmental resistance, but does not compress over time. Sound insulation characteristics are noticeably better than any of the listed materials. The main advantage is its low cost and availability.
Alternatives with the same properties are perlite and ecowool. However, perlite is inferior in cost and availability, and ecowool is significantly inferior in terms of fire safety and over time gets into the room in the form of cellulose dust.
Application of expanded clay gravel
| Indicators | Fractions of expanded clay gravel, mm | ||
| 8/20 | 4/10 | 0/4 | |
| Thermal insulation of pitched roofs | + | ||
| Thermal insulation and creation of a slope of flat roofs, lawns on terraces | + | ||
| Production of ultra-light concrete and light ceramic concrete blocks | + | + | + |
| Thermal insulation and sound insulation of floors and ceilings | + | + | |
| Thermal insulation and reduction of foundation depth | + | + | |
| Soil thermal insulation | + | + | |
| Thermal insulation and drainage in earthen embankments of roads laid in water-saturated soils | + | + | |
| Hydroponics, creating an optimal microclimate for the root system of plants | + | + | |
| As a dry backfill for gypsum fiber board floors to improve the heat and sound insulation properties of the floor | + | ||
| Production of warm solution | + | ||
| Production of facade and paving slabs | + |
Expanded clay will also be useful for those who lay heating networks near their home. Firstly, you will be sure that your pipes are heating you, and not the cold ground. Secondly, in the event of an accident, you will not have to dig long and tediously in search of a leak. Thirdly, after a successful repair, nothing prevents you from using the material again, and it will not lose its properties.
Expanded clay can be used not only in construction. With its help, they improve paths in their summer cottages and even increase the yield of fruit trees, creating a kind of drainage system for their roots. The same applies to indoor flowers and plants. For these purposes, expanded clay is used that is smaller in size.
The use of expanded clay as a concrete filler when pouring a foundation is not recommended. In this case, it is better to use any crushed stone, be it crushed stone or granite. Expanded clay is bad in this quality because it has smooth rounded edges, and this does not prevent the occurrence of shear (shear-fracture) work on the concrete mass. And the foundation must specifically exclude cracks (shifts) of the tape in the cross section.
Using vermiculite for mixtures and solutions
Mixtures for masonry and plaster are produced from fine-grained vermiculite. They are sold ready-made. Another option is to make the raw materials yourself. You will need cement, sand and insulation. The ratios are: 1:0.5:2 or 1:1.25:1.75. At the output, the plaster will have a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.24–0.4 W/m*K.
Reinforced concrete floors can be insulated with a screed containing vermiculite. In addition to thermal insulation, the layer will protect the rooms from noise. The technology for forming the screed does not change.
However, since the insulation is hygroscopic, it is not recommended to use it for very damp rooms, basements, or foundations.
Otherwise, vermiculite is a universal, environmentally friendly and practical material, used both in the process of building a house and in the finished building. It is easy to work with, and its long service life will allow you not to think about changing the insulation for many years.
Scope of expanded clay
In addition, expanded clay is also used as insulation, but it must be a highly porous material, and before using it as a backfill insulation, calculations that are not very complex, but accessible only to specialists, should be made. Regarding its capabilities in the field of heat conservation, we will only say that as a backfill option it is inferior to other insulation materials. The calculated thickness of expanded clay backfill with a density of 600 kg/m3 is approximately 40 cm. This is not entirely effective.
At the same time, used in the manufacture of expanded clay concrete blocks, it significantly increases their heat-saving characteristics.
Expanded clay is also actively used in the construction of dry screeds. Nowadays this method is very popular, as it allows you to get a solid base for laminate, linoleum, and cork in the shortest possible time, literally in a flash.
Also, due to its unique properties, including immunity to moisture and frost, it is actively used for filling the foundation during the construction of various buildings and structures. This makes it possible to reduce the depth of the foundation by almost 2 times - from 1.5 m to 0.8 m, which leads not only to savings in building materials, but also to the prevention of freezing of the soil near the foundation of the building. The latter is fraught with distortion of the doors and window frames of the building.
What else is vermiculite used for?
This material is part of heat-insulating plasters, which are used for external and internal work. Due to the high capillary porosity of vermiculite, plasters based on it acquire the properties of anti-condensation, low thermal conductivity and a significant level of fire resistance. The use of such plaster for finishing work will provide an exemplary surface quality that resists cracking well and has a beautiful texture.
Disadvantages of expanded vermiculite as insulation
Among the disadvantages of the material, its susceptibility to moisture should be noted. It is able to absorb it in a volume 4 times greater than its own. But vermiculite gives it away just as easily, which cannot be said about other insulation materials. Therefore, when using this material as insulation when constructing a roof, the technology requires good ventilation.
We hope that our brief review will help developers decide on the choice of material for home insulation.
- Wall kit











