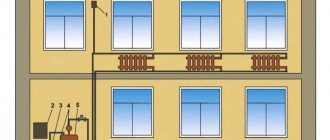
One-story private houses are beautiful and comfortable; many people prefer to build one-story country houses and cottages. After construction, the question arises of organizing the heating of a one-story private house, which we will discuss in detail in this article.
The heating options themselves are overwhelming. But which one is right for you? Let's try to figure it out.
Heat consumption for ventilation
To find out how much heat a private house loses as a whole, you need to add up the losses of all its rooms.
But that’s not all, because we must also take into account the heating of the ventilation air, which is also provided by the heating system. In order not to go into the jungle of complex calculations, it is proposed to find out this heat consumption using a simple formula: Qair = cm (tв – tн), where:
- Qair – required amount of heat for ventilation, W;
- m – amount of air by mass, defined as the internal volume of the building multiplied by the density of the air mixture, kg;
- (tв – tн) – as in the previous formula;
- с – heat capacity of air masses, is taken equal to 0.28 W / (kg ºС).
To determine the heat demand for the entire building, it remains to add the value of QTP for the house as a whole with the value of Qair. The boiler power is taken with a reserve for the optimal operating mode, that is, with a coefficient of 1.3. Here you need to take into account an important point: if you plan to use a heat generator not only for heating, but also for heating water for domestic hot water supply, then the power reserve must be increased. The boiler must operate effectively in 2 directions at once, and therefore the safety factor must be taken at least 1.5.
Nuances and subtleties
Those who want to make homemade heating should remember that they should use only those types of pipes that have a small diameter, since only they can maintain high water temperatures and effectively create and maintain the necessary temperature conditions in the Russian climate.
However, they also have their disadvantages. In particular, due to the small diameter of the pipes, installation of water heating cannot be carried out without first carrying out a major overhaul of the entire room. In addition, as for the water heating system itself, it requires constant heating of the coolant.
Therefore, if you forgot to drain the water from the pipes of your private house in the winter and left it for a long time, then you should expect trouble, since under the influence of low temperatures the pipes may simply break. As a result, upon your return you will be forced to repair the entire water heating system, since the main part of the pipeline will be damaged.
But even if you remember to drain water from heating pipes that have a small diameter, they can still suffer from corrosion, since the presence of air will take place, which will lead to the formation of internal condensation on the walls of the pipeline.
Water heating of a country house means an affordable cost of materials for installation and further operation, as well as good results in creating warmth and comfort in the house.
Ethylene glycol
It is worth knowing that ethylene glycol is very dangerous, so it should be used with extreme caution. So, if the walls of the system are damaged, the consequences can be very tragic.
So its use in double-circuit boilers is undesirable. In addition, ethylene glycol is strictly prohibited from being used in cases with open expansion tanks, since if it enters the human body (especially a substance with the third hazard class), it will negatively affect health. Although it is impossible to recognize it by smell due to its absence, there is only a slight sweetish aftertaste. So all this is very dangerous and requires caution.
Today, almost all antifreezes in the world are made based on ethylene glycol. Its cost is approximately 80 rubles per kilogram.
Types of water heating systems in a private house
There are several types of water heating for private homes. Here we mean standard heating systems using radiators, heated floors and baseboard heating. Individual types can be combined with each other, which allows achieving effective heating. For example, ordinary radiators are installed in bedrooms and living rooms, and heated floors are often installed in bathrooms and toilets - an excellent solution for those who cannot stand the cold and do not like cold tiles. Let's look at the individual types of heating and their advantages.
Radiator
Radiator heating systems are timeless classics. The principle of their operation is to transfer heat from the coolant through radiators installed in the premises. Such heating systems are installed in the vast majority of buildings for various purposes - residential, industrial, administrative, utility and many others. They are relatively easy to install - just stretch the pipes and connect radiators to them.
Previously, water heating in a private house involved the installation of bulky cast-iron radiators. Over time, they were replaced by lighter and thinner steel radiators made of corrosion-resistant steel. Later, aluminum batteries were introduced - they are lightweight, cheap and durable. For a private home, this is the most ideal battery option.
The main advantage of radiator systems is that they do not require pouring concrete screeds to install them. The entire installation comes down to installing the boiler and radiators with their subsequent connection. Radiators provide effective heating of rooms and do not interfere with interior design, especially if they are modern aluminum multi-section radiators.
Warm floor
Water floor heating in a private house can operate both in independent mode and in auxiliary mode. In independent mode, there is no need to lay pipes with radiators, and all the heat is emitted by the floors. Thanks to this, children can play on such floors without fear; they will not be blown or draughty. Do your feet constantly get cold? Then you will definitely like always warm floors. In auxiliary mode they work as a complement to radiator systems.
Underfloor heating systems are good in kitchens, bathrooms and toilets. where there are often eternally cold tiles on the floor. Installing heating will help make the floors warm and comfortable. For example, in the bathroom you no longer have to stand barefoot on cold tiles. The same applies to the toilet. If you have a tiled floor in your kitchen, feel free to install heated floor systems here too. Another place where a warm floor will become an attribute of comfort is the bedroom - you must admit, it’s not pleasant to crawl out from under a warm blanket and put your heels on cold floors.
Warm floors are characterized by a low coolant temperature, not exceeding +55 degrees, which allows the creation of economical heating systems. But the need to make concrete screeds and go through walls and door frames is a significant disadvantage. It is best to consider the need to install the system at the stage of building a house.
Skirting
Modern heating systems, built on the basis of classic aluminum radiators, are distinguished by the fact that the heat from them spreads only upward - due to natural convection. As a result, all the warm air rises and cold air comes in to take its place. It is not surprising that household members’ feet begin to freeze. The only advantage is the absence of cold from the windows, as it is carried away by convection to the ceiling. But what to do with heating? Shouldn't we lower the radiators to the very floor?
The way out of the situation is baseboard heating systems. Small-sized radiators made of brass or aluminum are used here. The coolant is supplied using small diameter plastic pipes. The system is complemented by taps, air vents and other necessary accessories.
All this is laid in a special plastic plinth - the air entering here is heated and heats the walls above. Next, the room is warmed by infrared radiation from the heated walls and floors. There are no drafts blowing across the floor in heated rooms. Here, not only the walls are heated, but also the floors themselves, making the rooms warm and comfortable.
The advantage of baseboard heating is that it can be installed at any stage, even after construction is completed. Disadvantages - high installation cost and a lot of requirements for the placement of skirting boards and other elements. Simultaneous installation of all types of systems described is also allowed.
Radiators or water convectors, which is better?
Convectors are based on the principle of heating a room through air flow. It heats up as it passes through the body of the heating installation. In turn, radiators heat the room by radiating heat from the surface body.
Radiators have gained great popularity. Their operating principle can be compared to the operation of a Russian stove.
Convectors are heating panels; they heat a space using the movement of cold and warm air masses. The convector includes a pipe in which the coolant is located. The pipe is framed by ribs, plates that heat the surrounding space. The plates are often made of copper or steel. Convectors are divided into external and built-in. The first type of convectors is mounted on the wall, the second can be mounted along the floor or wall. Convectors also include warm baseboards. This device is an excellent solution for people who do not want to depend on public heating systems.
Convectors are used as additional and main heating; they are especially indispensable in places where standard radiators are not used. For example, built-in convectors in the floor are also located along sliding doors and glass walls. Convectors heat a room much faster and cool it down faster. The devices are durable in use.
If it is better for you when heating a private house when the room warms up faster and more evenly, then install convectors. The most common options are steel radiators (60% convection) or copper-aluminum (90% convection). If these points are not important, then install regular radiators.
DIY heating schemes in a private house
How effective the heating will be depends on the characteristics of the mounted circuit. A do-it-yourself heating scheme in a private house can be implemented in different ways. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the available options to choose the best option.
You can always choose the appropriate option
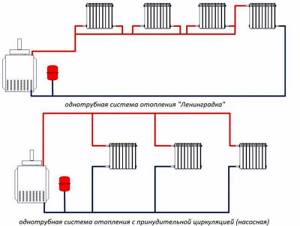
Do-it-yourself diagram of a single-pipe heating system for a private house
The single-pipe scheme assumes that the coolant from the boiler begins to move along a single line, and then returns back through it. Radiators are connected to the main line at both ends. A correctly installed one-pipe heating system for a private house with your own hands works as follows:
- The coolant heats up to +75÷85°C and begins to move through the pipeline. Having reached the first radiator, part of the hot water fills the battery, and the rest continues to move through the pipes;
- after passing through the radiator and releasing heat into the surrounding space, the water mixes with the coolant, reducing its temperature by a couple of degrees;
- On the next radiator the situation repeats. As a result, significantly cooled water enters the last battery, which reduces the amount of heat given off.
The scheme and procedure for installing single-pipe heating involves building up a section of radiators, starting from the second one from the boiler, in order to ensure uniform heating of all rooms of a private house. Water heating works quite efficiently if it contains no more than 5 batteries. In a multi-story building, several risers are often installed. This vertical scheme assumes the presence of stably operating 3÷4 batteries.
The one-pipe model is not always effective
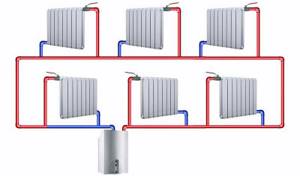
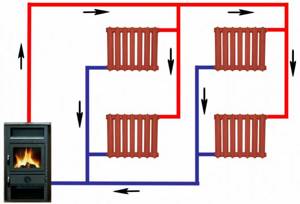
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
A stable and reliable option that supplies radiators located in different rooms with coolant heated to the same temperature. Heated water moves through one pipe, and cooled water returns through another.
Depending on the chosen wiring, the two-pipe circuit can be:
- Tupikova. The coolant supplied through the corresponding branch fills all radiators, and returns through the return branch. Balancing allows for uniform heating of all batteries;
- Along the way. Loop-shaped heating scheme for a country house. When performing the installation yourself, you should ensure that the coolant along the main and return branches moves in the same direction. Suitable for a fairly long circuit;
- Collector. A suitable option for a large private house. To power each radiator, a separate two-pipe branch is used, connected to the distribution comb.
Dual-circuit circuit allows better heating of all rooms
Scheme of water heating of a two-story house
When installing a system in a two-story building, a gravity-flow scheme is rarely chosen. Here, the best choice is water heating in a private house with forced circulation. The circuit can be one-, two-pipe or beam.

The scheme is selected individually
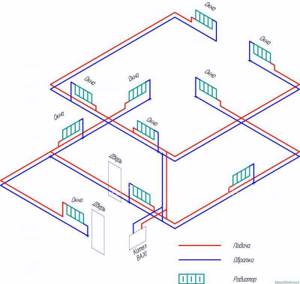
Collector heating circuit for a one-story house with forced circulation
The collector (radiant) water heating system includes a collector, which is a device used to collect coolant. Two pipes are connected to each radiator: forward and return. This heating scheme with forced circulation of a one-story house makes it possible to best hide the pipes being laid. Moreover, each room can have its own temperature.
A special cabinet is used to place the collector. The disadvantage of this scheme is the increased cost due to the need to purchase new equipment.

The collector circuit will be expensive
Types of heating with gravity circulation
There are four gravity heating schemes. When choosing a specific type, the desired network performance and house features are taken into account. After selecting the scheme, a hydraulic calculation is made, determined with the diameter of the distribution pipes and the parameters of the heating equipment.
Closed system
The closed circuit of the heating system of a private house with natural circulation works according to the following principle:
- After heating, the coolant expands and displaces water from the circuit.
- This liquid enters a closed expansion tank. Such a tank consists of two chambers (water and gas), separated by an elastic membrane. It is completely sealed.
- As a result of liquid entering the water chamber, the membrane is forced into the cavity of the gas compartment, which increases the pressure there.
- After cooling the coolant in the network, the pressure in the pipeline decreases. Due to gas pressure, the membrane squeezes the coolant back into the circuit.
For smooth operation of the network, it is important to correctly calculate the volume of expansion capacity. If we are talking about a large house with an extensive heating system, then you will need a large tank
Open system
Natural circulation is more often used in an open heating system of a private house. It differs from the previous scheme in the design of the compensation tank. You can make a tank with your own hands from an ordinary steel or plastic barrel. A container of the required size is installed under the ceiling of the house or in an insulated attic.
The main disadvantage of the scheme is in an open container, through which oxygen penetrates into the circuit, promoting corrosion of heating devices and pipes. Another disadvantage is that the system often becomes air-filled, which forces Mayevsky taps to be installed on each battery.
Single pipe system
This scheme is used infrequently because it cannot boast of efficiency. Due to the sequential connection of all radiators to the circuit, coolant with a lower temperature enters each subsequent device. This contributes to uneven heating of the house, forcing the number of sections in the radiators to increase as they move away from the boiler.
The advantages of single-pipe wiring are simple installation and low consumption of materials. Complex hydraulic calculations are not required to set up the network. The disadvantages of this scheme are that rooms far from the heating equipment are less heated. Considering that additional sections will have to be installed, the savings on pipes are insignificant.
Two-pipe system
It is much more profitable to do two-pipe wiring. In this case, supply and return pipelines are laid, and all heating devices are connected to the circuit in parallel. Thanks to this, coolant with the same temperature reaches all batteries, and the house warms up evenly.
Positive aspects of using a two-pipe scheme:
- Uniform heating of a building with a large area and several floors.
- There is no need to install additional sections on radiators to adjust heat transfer.
- It’s easier to set up and regulate the network. You can adjust the heating temperature in each room and repair batteries without stopping the network.
- For wiring, pipes of a smaller cross-section are used than with a single-pipe scheme.
Installation diagrams for a heating system in a private house
In practice, two types of systems are used - diagrams (or types of pipe layout), namely:
- single-pipe;
- two-pipe.
Each of them has its own advantages, disadvantages and is used in different cases.
Single pipe system
This type of wiring is cheaper and simpler. The system is built in the form of a ring - all batteries are connected in series with each other, and hot water moves from one radiator to another, then goes back into the boiler.
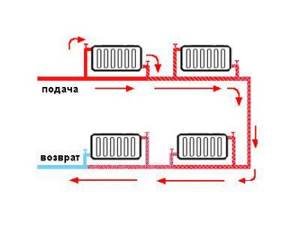
As can be seen in the figure, all batteries are connected in series, and the coolant passes through each of them.
This heating scheme is very economical in its implementation, it is easy to install and design. But it has one significant drawback. It is so significant that many refuse such wiring and prefer the more expensive and complex one - two-pipe. The problem is that as the coolant moves, it will gradually cool down. Until the last battery, the water will flow slightly warm. If you increase the boiler power, the first radiator will heat the air too much. This uneven heat distribution forces us to abandon a simple and cheap single-pipe system.
You can try to get out of a difficult situation by increasing the number of sections of the last radiator, but this is not always effective. This suggests the conclusion that single-pipe wiring can be used in the case when the number of batteries connected in series is no more than three.
Some people get out of the situation in the following way: they connect a pump to the boiler, thereby forcing the water to move forcibly. The liquid does not have time to cool and passes through all the radiators, almost without losing temperature. But even in this case, you will face some inconveniences:
- the pump costs money, which means the costs of installing the system increase;
- electricity consumption increases as the pump runs on electricity;
- if the electricity is turned off, there will be no pressure in the system, which means there will be no heat.
Conclusion. A single-pipe system is effective only for small houses with 1-2 rooms, where a small number of radiators are used. Despite its simplicity and reliability, it does not justify itself in country houses, where it is necessary to install more than three radiators in the entire living area.
Two-pipe system
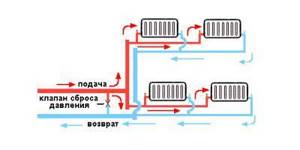
Hot water is supplied through one pipeline, and cooled water through another. This ensures uniform heat distribution across all batteries.
Such heating distribution in a private house will be much more efficient and better than a single-pipe one. Although it is more expensive to make and more difficult to install, it allows you to distribute heat evenly across all batteries, which will help create comfortable conditions. Unlike the single-pipe system, in this installation a pipe with hot water is supplied under each radiator, and the cooled liquid is discharged through the return line into the boiler. Since the coolant is supplied to all batteries at once, the latter heat up equally.
This system is not much more complicated than the first; you will have to buy more materials, since pipes will have to be connected to each radiator.
A two-pipe system can operate according to two schemes:
- collector;
- ray.
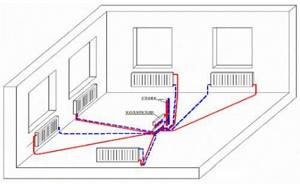
The beam wiring option is older. In this option, the supply pipe is installed at the top of the house, after which pipes are laid out for each battery. Thanks to this design, the circuit received the name - beam.
The first scheme works as follows: in the attic it is necessary to install a collector (a special device consisting of many pipes), which distributes the coolant through the heating pipes. In the same place you need to install shut-off valves that will cut off the circuits. This design is quite convenient; it facilitates the repair of the entire line and even an individual radiator. Although the scheme is reliable, it has one significant drawback - complex installation with a large number of materials (shut-off valves, pipes, sensors, control devices). The collector layout of heating pipes is similar to the radial one, but more complex and efficient.
Unlike a one-pipe system, a two-pipe system does not require additional forced circulation of coolant. It shows high efficiency even without a pump.
Bottom wiring
Here the coolant-conducting pipe is installed directly under the window sill, and the return pipe is installed near the floor.
The pressure in the pipes is not very high, so pumps have to be used. Airing is possible. To avoid this drawback, Mayevsky cranes should be installed on the floor. If the house is multi-story, then this tap should be located on each floor.
The wiring can be laid only to the doorway or two heating systems independent of each other can be installed on both sides of the door.
The expansion tank is easy to install anywhere. If it is closed, then it can be placed in rooms rather than in the attic, which is convenient. Bottom wiring is not noticeable
This is important if you care about the wiring fitting into the decor of your room.
Boiler selection
for water heating at the dacha depends on the variety of energy sources available at the dacha. If the dacha community has a gas main, then it is better to choose a gas boiler - this is the most economical option. The boiler can also be electric, or run on diesel fuel or coal
It is worth paying attention to the fact that boilers can be single-circuit - intended only for heating the room, and double-circuit - coping not only with heating a country house, but also used for heating water
An example of a solid fuel heating boiler with a water circuit.
In a country house, the wiring can be made open or hidden under the floor, which will help to install heated floors, which are very popular today. If the house is only at the construction stage, then it is preferable to place the heating system under the floor. And if the house is already ready, then the pipelines are installed along the internal walls.
Installation
Effective water heating in a country house can involve two types of piping:
with a vertical riser - all systems are connected to a single riser;
with horizontal drain.
The horizontal scheme is better than other options in terms of self-installation, and is cheaper to install, but there is a risk of air accumulation and the formation of air locks. The horizontal type is also used for installing warm water floors.
Subtypes
Vertical
A special feature of this heating scheme is that water flows simultaneously into all radiators, which are located vertically at different levels. For more precise heating settings, thermostats and balance valves are used.
Horizontal
This heating scheme differs in that the coolant flows simultaneously into all radiators, which are located on the same level. In this case, all their outputs are connected to one tap. With the help of a return element, the coolant returns to the boiler.
Horizontal distribution
The outputs of all radiators are connected to the boiler. An example is heated floors.
Features of installation of water heating
The use of water as a coolant is due to the fact that this liquid has a very good heat capacity and is able to effectively receive and release heat. Water heating has been used in homes for a long time. Over the past time, the principle has remained the same, but the connection diagrams for heating elements have undergone serious modernization. However, for the construction of water heating, all the same materials and devices are used as a hundred years ago, only improved:
- power plants. They can be stoves or boilers running on electricity or gas;
- pipes of various diameters. Today, in addition to metal pipes, plastic and metal-plastic ones are actively used;
- heating radiators made of cast iron, steel or aluminum;
When purchasing radiators, choose trusted manufacturers
- various shut-off valves, without which it is impossible to build water heating for a private house with your own hands. Its connection diagram is quite simple;
- expansion tank to compensate for excess pressure in the system;
- a circulation pump, which is included, for example, in the heating circuit of a one-story house with forced circulation.
This is an almost exhaustive list of the equipment that you will need to make water heating for a private house with your own hands. There are three schemes for installing and connecting radiators:
- Using one pipe.
- Using two pipes.
- Using collectors.
Single-pipe heating system with circulation pump
Based on the type of coolant supply, all schemes can be divided into heating with natural water flow and forced. Natural circulation occurs due to changes in water temperature. Hot liquid rises because it has less density, while cold liquid flows down. The forced type of circulation occurs due to pumps that are built into the pipeline or located directly in the boiler.
A stove with a water circuit for heating a house: implementation options. Stove heating, heating and cooking stoves, fireplace stoves, advantages, design, implementation options. Calculation, materials, installation.
Efficiency of forced circulation schemes
The prevailing part of modern heating systems can function fully only when artificial circulation is created, that is, one in which the coolant moves within the network due to the operation of the circulation pump.
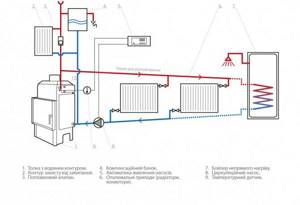
Diagram of a heating system with a gas boiler in a 2-story house: equipment and metering devices are installed on the first floor (in the basement, in the basement), in a specially equipped room with good sound insulation (+)
There are prerequisites for installing forced circulation in a building with several floors:
- installation of a pipeline with a smaller diameter, which facilitates the assembly of the wiring as a whole;
- providing zonal regulation (along with or instead of general regulation);
- the presence of 2nd and higher floors does not affect the heating efficiency;
- reducing the coolant temperature without changing heat transfer parameters;
- possibility of using inexpensive plastic pipes.
The disadvantages include the availability of power supply - interruptions are possible, but they can be easily avoided by using backup UPSs. The problem of louder noise can also be solved by installing a layer of sound insulation in the boiler room.
Scheme of water heating with forced circulation: 1 – gas or electric boiler; 2 – riser; 3 – pipe to the expansion tank; 4 – riser for draining; 5 – upper horizontal wiring; 6 – expansion tank; 7 – circulation pump; 8 – return line
The most suitable place for inserting the circulation pump is where the temperature drops to a minimum, that is, directly in front of the boiler, on the return line.
Single pipe connection
Installing heating using the single-pipe method is the least expensive, while at the same time, installing it in two pipes will be the most effective, especially if the rooms in the house are large. The advantages of such a scheme are as follows:
- Easy installation and repair;
- Cost-effective;
- Possibility of laying the main line at floor level;
- Using the system in a one-story and two-story house;
- Possibility of forced or natural circulation.
With a single-pipe system, water moves from one radiator to another through a pipe, and upon reaching the last radiator it cools down greatly. Such a system cannot be adjusted.
Connection options.
Tips for installing a home heating system
The heating installation begins with the installation of radiators in pre-prepared places under windows or on corner external walls. The devices are hung on special hooks attached to the structure itself or the plasterboard finish. The unused lower outlet of the radiator is closed with a plug, and a Mayevsky valve is screwed in from above.
The pipeline network is installed according to the assembly technology of certain plastic pipes. To protect you from mistakes, here are some general recommendations:
- When installing polypropylene, take into account the thermal elongation of pipes. When turning, the knee should not rest against the wall, otherwise, after starting the heating, the line will bend like a saber.
- It is better to lay the wiring in an open way (excluding collector circuits). Try not to hide the joints behind the sheathing or embed them in the screed; use them to secure pipes.
- Mains and connections located inside the cement screed must be protected with a layer of thermal insulation.
- If for any reason a loop has formed in the pipeline, facing upward, install an automatic air vent on it.
- It is advisable to install horizontal sections with a slight slope (1-2 mm per linear meter) for better emptying and removal of air bubbles. Gravity flow schemes provide for slopes from 3 to 10 mm per 1 m.p.
- Place the membrane expansion tank on the return line near the boiler. Provide a valve to shut off the container in the event of a malfunction.
Application of gas boilers
Boilers used in a water system can use different types of fuel. The most common and convenient to use is gas equipment - although it can only be installed if a central gas supply is connected to the house. In addition, among the disadvantages of gas boilers is the need for their regular monitoring by the relevant utility services.
But such a system has the following advantages over others:
- Easy to install and operate.
- High efficiency in the use of energy resources. On average, gas costs are 30–40% lower than using liquid fuel or electricity.
- Fast heating of rooms with coolant. Within an hour, the temperature in rooms with a water heating system, in which the heat source is a gas boiler, will increase noticeably.
- Environmentally friendly use of gas.
- The ability to automate the process, including programming the required temperature and hot water heating.
How to make water heating for a private house with your own hands - step-by-step diagram
Step 1: Project
To begin, select a suitable diagram and display it on paper. Consider the area of the rooms, the position of radiators, pipelines, their sizes, etc. Such a sketch will help to correctly calculate the amount of consumables. Special programs will greatly simplify all calculations.
Step 2: Accessories
Let's briefly look at what a boiler, batteries and pipes can look like. Depending on the fuel used, types of heating units are gas, electric, solid fuel and combined. Gas devices can rightfully be called a favorite among these options. Water boilers come with a pump (for a forced heating scheme for a private house) or without it (natural circulation), and both types can be installed with your own hands. The dual-circuit unit has proven itself to be excellent, providing not only heat in the house, but also hot water.
Steel batteries are affordable, but at the same time they are susceptible to corrosion, and if you plan to drain the coolant, their service life will be significantly reduced. Cast iron, on the contrary, can be said to be an eternal material. It takes a long time to heat up, but also retains heat for a long time. But the heavy weight, not very attractive appearance and high cost have significantly reduced the popularity of this material. Cast iron batteries were replaced by aluminum ones. Their appearance is very attractive, they heat up quickly and are resistant to corrosion. However, aluminum does not tolerate sudden changes in pressure. Bimetallic resistors are famous for their excellent heat dissipation, however, their anti-corrosion properties remain the same as those of aluminum.
The steel pipeline has lost its former glory due to its short service life. It has been replaced by modern polypropylene. Easy installation, the ability to create a “solid” structure, reasonable cost and reliability - all these are undeniable advantages. Copper pipes also have good characteristics, but their cost is not affordable for everyone.
Step 3: Boiler
Water heating in a private house is designed in such a way that the medium is heated by a boiler. This scheme is the most optimal in the absence of centralized supply. Therefore, when choosing a place to install the boiler, you should take into account the location of the gas pipeline entry or the presence of electrical wiring. If we are talking about a solid fuel unit, then additional installation of the chimney is necessary. If you prefer natural circulation of the coolant, then position the heating unit so that the return inlet is as low as possible. In this case, a basement is ideal.
Step 4: Installation of radiators
Batteries are placed under windows or near doorways. The design of the fastening depends on the material of the resistors and the number of sections. The heavier they are, the more reliable fixation they need. A gap of at least 10 cm should be left between the radiators and the window sills, and more than 6 cm to the floor. By installing shut-off valves on each element, you can regulate the amount of coolant in the radiators, and the air valve will help avoid unwanted traffic jams.
Step 5: Wiring
The boiler will be the starting point for the installation of the pipeline. In this case, you should adhere to the scheme chosen and sketched on paper. If the pipes are visible, then we are talking about open wiring. On the one hand, the aesthetic side suffers, but on the other, any leak will remain visible, and to replace the damaged element, you do not need to disassemble the box. The pipeline can also be hidden, walled up in the wall, sheathed with plasterboard, etc. At this stage, batteries and additional equipment (pump, filters, safety unit, expansion tank, etc.) are connected.
Pros and cons of different types of coolants
Depending on the coolant, heating can be water, air, or electric. Some cottages are heated using open flames - fireplaces or stoves. Each type of coolant has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Water systems consist of a boiler, pipes and radiators. The cold coolant is heated in the boiler, then flows through pipes into radiators, where it gives off heat to the surrounding air. The cooled water is fed into the boiler and the cycle repeats again.
If the system is combined with underfloor heating, then the coolant flows from the radiators into the second circuit and only then returns to the heating device. The boiler itself can operate on gas, electricity, solid or liquid fuel.

Water heating with radiators
The principle of operation of the air system is simple: cold air enters the heat generator, from where it is supplied through air ducts to the rooms of the cottage. Warm flows displace cold ones, which also enter the heat generator, and the cycle repeats.
The air circulation mode can be natural or forced. In the first case, the heating in the cottage is disrupted if the windows or doors are open. And in the second you have to use electric fans.
To heat the cottage, you can use convectors, heaters or any type of electric heated floor (cable, carbon, etc.). These systems are the easiest to maintain because they are usually fully automated.
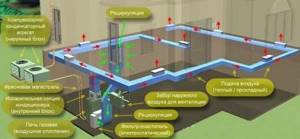
Scheme of air heating with a gas furnace
Electric heating of a cottage will cost much more than other types of heating. Another disadvantage: in the event of an accident, the house may be left without electricity and heating at the same time.
A stove or fireplace may be a good option for a small space, but it is unlikely to be suitable for a house with several rooms. In addition, you will have to give up the idea of organizing a convenient hot water system.

Autonomous heating of a private house
DIY heating system installation
Installation work should begin with the installation of the heating boiler. If the equipment power does not exceed 60 kW, you can install the device in the kitchen; if it is higher, a separate room should be allocated for the boiler. Heat sources that burn different types of fuel must have air flow. In addition, it is necessary to ensure the removal of combustion products. This can be done with the help of a properly equipped chimney.
When installing a heating boiler, certain rules must be followed. The distance to the nearest equipment and walls must be at least 0.7 m. The wiring of units that operate on different types of fuel is practically the same. The figure shows an option for piping a gas boiler with a forced circulation system.
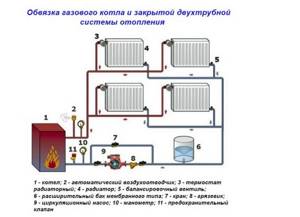
This tying method is used most often. Other schemes provide for the presence of their own pumps to ensure continuous circulation of the heated coolant.
If solid fuel heat generators are used to service the heating system, the following nuances must be taken into account when connecting them: due to the inertia of the device, the coolant may overheat and boil. To avoid unpleasant situations, it is necessary to install a circulation pump on the return line. An additional security system is also installed, which consists of the following elements:
- safety valve;
- automatic air vent;
- pressure gauge
An important function is performed by the safety valve, because it is responsible for relieving excess pressure in cases where the coolant overheats. The most effective piping scheme for a solid fuel boiler is shown in the figure below.
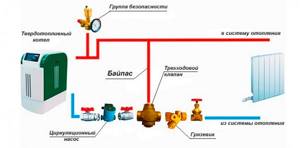
Another problem that is often encountered when operating a heating system with solid fuel boilers is the accumulation of condensate on the elements of the unit. This happens due to cold water entering the hot cut. To prevent condensation of the coolant, a three-way valve and a bypass are installed in the systems.
Installation of heating pipes
It is impossible to install a heating system in a private house without a pipeline. In old houses there are cast iron pipes from the last century. They boast a long service life, durability and reliability. However, today such products are used extremely rarely, because they have been almost completely replaced by lighter, more convenient and cheaper pipes that can be made from the following materials:
- steel;
- copper;
- stainless steel;
- polypropylene;
- polyethylene;
- metal-plastic.
Selection and installation of radiators
Previously, traditional, cast-iron, not very aesthetic batteries were available, which were used in every private house or high-rise buildings. Today, in specialized heating equipment stores there are so many models of radiators, they all differ from each other in price, technical characteristics, and appearance, that it may be difficult to choose. As a rule, these products are classified depending on the material from which they are made.
- Aluminum batteries are lightweight, durable, reliable, and have excellent heat transfer performance. The products are made from solid alloy, which ensures their durability;
- Bimetallic radiators are used primarily in central heating systems. Internally they are equipped with a tubular steel frame;
- Steel panel batteries are the best option, which experts recommend for use when installing a heating system in a private home. To regulate the air temperature in the room, you can install thermostatic valves;
- Cast iron heating radiators are available in a wide range today. These are not Soviet “accordions”, but durable, safe and reliable products, which are characterized by an attractive design.
The type of heating system and type of coolant depends on the number of floors and area of the house, the availability of one or another fuel. You can install a heating system in a private home with your own hands, if you follow the recommendations for selecting and installing equipment.
(no votes yet)
How the coolant is circulated
The heat carrier can be:
- antifreeze;
- alcohol solution;
- water.
Circulation can be either “natural” or forced. There may be several pumps. Also only one pump is used.
Features of “natural” circulation
Due to the special properties of the liquid, gravity expands as the temperature rises.
When water cools, density increases. The water then rushes towards the departure point. This leads to the closure of the circuit.

Recommended material: high quality polypropylene
The pressure can be provided:
difference in installation (the heating installation is mounted lower. This usually happens in the basement area or in the basement)
The lower the height difference, the lower the speed at which the coolant moves; temperature difference (the difference in the room and inside the system itself is taken into account). The warmer the house, the slower the heated water moves.
In order to reduce the resistance of the pipes, it is recommended to place the horizontal sections slightly at an angle. You should focus on the movement of water.
The circulation speed depends on the following indicators:
| Index | Description |
| Features of the scheme | One of the important criteria is the number of connections. The best effect can be achieved against the background of linear placement of heating units. |
| Pipe diameter (routing) | It is recommended to choose models with a large internal cross-section. This will help reduce resistance when moving fluid. |
| Material used | Recommended material is polypropylene. It has higher throughput. The material is also resistant to corrosion and lime deposits. The most undesirable material is metal-plastic. |
If the installation was done correctly, it can last for several decades.
One of the main disadvantages is the limitation of the circuit length, up to 30 meters. The liquid moves along the line very slowly. Against this background, the liquid in the radiators also heats up slowly.
Features of forced circulation
The slow flow rate of the coolant can be increased using a pump. Thanks to this, even with a small diameter of the line, fairly fast heating is ensured.
The type of system for forced advancement is closed. Air access is not provided. The expansion tank is the only area where important processes take place. The best choice is sealing.

Pressure gauges help regulate pressure
To ensure pressure stability and safe operation of the entire system, the following are used:
- air exhaust device. You can find it in the expansion tank. Its main purpose is to extract the air formed during the boiling process of water;
- fuse. If the pressure is very high, it causes excess water to be removed “automatically”;
- pressure gauges. Designed to regulate and control pressure in the internal part of the circuit.
It is recommended to install a pump next to the boiler, on the return circuit. This helps reduce the adverse effects of heated liquid on the rubber gaskets of the installation. This increases its service life. Repairs are not required for very long.
If the system is equipped with a circulation pump, its operation is affected by alternating current. To ensure proper operation, it is recommended to install a bypass. This will help ensure the system transitions to another mode.