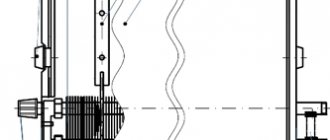
General structure of a bimetallic and aluminum radiator
To understand them, you first need to understand how each of these types of radiators works.
Aluminum radiator
Consists of homogeneous aluminum metal. Not pure, but alloyed with silicon for strength. It is cast in a special mold in sections or, less often, in blocks. The sections are screwed together using a threaded connection using a gasket to seal the joint. The design of the section itself is designed in such a way that when assembled, several sections form petals with convection passages for better heat transfer.
Bimetallic radiator
As already mentioned, it is similar in appearance to aluminum, but there is a difference in the device. The internal part of the radiator section consists of horizontal and vertical steel pipes. Horizontal pipes are larger in diameter than vertical pipes. The outside of the pipes is “clad” in aluminum. The design of the aluminum “fur coat” is also ribbed, like that of all-aluminum ones. Hence the external similarity. The sections are also screwed together using a threaded connection using a gasket. The individual tubes of the sections form a system of tubes in the form of a collector, which is designed to circulate coolant through it. Since steel is much stronger than aluminum, bimetallic radiators can withstand much greater pressure and water hammer.
What types of radiators are there and how do they differ?
By design, all hydraulic heating devices can be divided into four main types: sectional, panel, tubular (this includes heated towel rails) and convectors.
Sectional heating devices
Such devices consist of separate heating elements-sections. Sectional heating devices can be made of aluminum, cast iron, steel, as well as so-called bimetallic ones (having an aluminum body and a steel pipe through which the coolant moves). The sections are connected to each other using nipples, and seals are installed between the sections. More often, gaskets are made of rubber, which is normal when using water as a coolant, but is unacceptable when using antifreeze as a coolant, because rubber can be destroyed by its aggressive influence (in such cases, special seals are used in modern heating devices).
Panel (non-sectional) heating devices
These are mainly steel panel radiators. The design of a panel radiator is, roughly speaking, two steel sheets welded together (usually 1.25 mm thick) with vertical channels in which the coolant circulates. To increase the heated surface, and, as a result, heat transfer, steel U-shaped ribs are welded to the back side of the panel.
Tubular heating devices
In most cases, the design of such radiators consists of vertically arranged curved steel tubes connecting the upper and lower collectors. It is worth noting that steel tubular radiators are usually the most expensive type of radiator (in terms of 1 kW).
Convectors (or plate heaters)
A convector, figuratively speaking, is one or several pipes (through which the coolant moves) with metal “ribs-plates” “put on” them. The air passes through the convector from bottom to top, heating up from numerous warm fins. Such heating pipes are usually made of steel or copper. In some convectors, the amount of heat flow is regulated by a special damper, by opening or closing which you can increase or decrease the flow of moving heated air. The design of the convector can be completely open or closed with a decorative casing (in wall-mounted and baseboard versions). Convectors built into the floor are covered with a decorative grille.
How to distinguish when purchasing
Now, knowing the design of both radiators, they won’t sell you aluminum radiators under the guise of bimetallic ones.
- Pay attention to the place of the radiator where there is a thread for connecting the sections. In a bimetallic radiator, threads are cut into a steel pipe. Therefore, steel differs from aluminum in color; you can often observe the boundary of the two metals, again in the area of the thread (but sometimes this transition is not visible)
- Compare the weight of a bimetallic radiator with the weight of an aluminum radiator with the same size and equal number of sections. Steel is heavier than aluminum, so the weight of one section of bimetal can weigh up to half a kilogram more than its “double”. But in general, this difference will be sensitive even without the use of scales.
How to distinguish an already installed radiator
Imagine a situation where you hired a team to install a heating system, they installed it completely, they purchased all the materials themselves. You missed the moment when the radiators were not yet installed. Doubts have crept into your mind whether they installed aluminum batteries instead of bimetallic ones. This fact needs to be verified to dispel all doubts.
To do this, take a magnet, preferably neodymium. He is much stronger than others. But it can also be ordinary. Bring the magnet somewhere on the edge of the radiator closer to its center, instead of as close as possible to the intended passage of the metal pipe. Steel is attracted to a magnet; aluminum does not have this property. Therefore, a bimetallic radiator will experience a slight attraction, since the magnet will not be located close to the pipe, but at some distance due to the aluminum shell surrounding it.
By the way, you can use a magnet on an uninstalled radiator by bringing it to the thread for connection. The effect of attraction will be clearly felt here if it is a bimetal.
Now knowing the differences in the design features and properties of these types of radiators, it will be impossible to deceive you and you will feel their warmth in your home for many years to come.
There are many heating radiators on the market, the differences of which lie in the material of manufacture, design features, methods of connecting sections to each other and many other parameters that affect the reliability and durability of the products. However, most often the controversy arises around aluminum batteries and their bimetallic analogues. At first glance, they are ideally suited to the conditions of city apartments. However, there are significant differences between these two types of radiators that you need to know before making a purchase. So, which radiators are better, and how does a bimetallic battery differ from an aluminum one?

How to distinguish devices visually
External factors often mislead buyers. The batteries have a similar appearance - metal rectangles with flat ribs and the same number of sections. To distinguish devices with an identical number of elements, you can pick them up right in the store. Aluminum ones will be lighter.
The second way to check is with a magnet, regular or neodymium. The product must be moved from the edge to the center. The steel surface will create a slight attraction.
When choosing radiators made of aluminum and bimetal, you need to compare several factors - cost, installation features, heated area. Owners of private houses can opt for aluminum options; in apartments, bimetallic ones are justified.
Where are aluminum radiators used?
The main condition for life support in any apartment or private house is the presence of a heating system. The coolant, which is heated by autonomous heating equipment or in the boiler circuits of the central boiler room, circulates through pipes and radiators. And through convection or thermal radiation, heat spreads throughout the room.
Aluminum radiators have the best price-quality ratio. They are installed both in centralized heating systems and in individual ones. But we must keep in mind that aluminum radiators react to the presence of acids and alkalis in the coolant.

According to their design, they are sectional or panel. Most often you can see sectional products on sale that are connected using nipples. To seal the joints, special gaskets are used. According to the technical characteristics stated by the manufacturers, different models of aluminum radiators can withstand pressure from 6 to 18 atmospheres. Some models have stated limits of 25 atmospheres. This is important when installing products in central heating systems. When choosing and comparing how heating batteries differ from each other, these parameters must be clarified in advance.
Which radiators are better: aluminum or bimetallic?

Aluminum radiators appeared 30 years ago and immediately won a significant market share from the usual steel and cast iron batteries. These products gained popularity due to their unique appearance, increased heat transfer and low weight. In terms of heat transfer, aluminum batteries are the undoubted leaders, but due to the behavior of the material from which the product is made, the use of these devices is not always possible.
Construction of aluminum radiators
Aluminum heaters are produced using two technologies:
- The finished product is cast in molds.
- The radiator is assembled using the extrusion method.
In the first option, a monolithic product is obtained that perfectly withstands network pressure due to the absence of connecting seams and connections.
In the second option, aluminum profile blanks are used, which are processed using a press. The individual sections obtained in this way are connected into a battery by welding. To ensure tightness, the sections are connected using seals and special gaskets.
A prefabricated radiator is cheaper than its monolithic counterpart, but, subject to the requirements of production technology, it has the same strength characteristics. The advantages of monolithic models include the ability to operate the product without additional maintenance, while prefabricated models are subject to periodic technical inspection and maintenance work.
Characteristics
Aluminum is a metal with a high degree of thermal conductivity. This feature allows you to create a powerful heat wave from the battery, which is evenly distributed throughout the space of the heated room in the apartment.
Thermal power is measured in W and is, for a single section of an aluminum battery, at least 180 W. This product weighs within 2 kg, thickness does not exceed 110 mm. To completely fill such a radiator you will need 0.4 liters of liquid. The maximum limit on the carrier temperature is +90oC.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of aluminum batteries include the following:
- thanks to the rapid heating of the material, the process of heating the room occurs quickly (for living rooms, 15-20 minutes are enough to obtain a comfortable temperature), which allows for significant (up to 35%) savings on heating fluid costs;
- To regulate the flow of coolant, each product has a special thermal valve, which allows you to reduce or increase the flow of liquid in the radiator, which also leads to
- saving heating resources;
- aluminum radiators look very attractive in appearance, even elegant - small, but powerful in terms of heat transfer, the products fit perfectly into the interior of a private house, cottage, or
- administrative premises;
- if necessary, the owner of a private house can independently add sections to already installed prefabricated heating radiators (it is better for professionals to work with cast models);
- Due to their small size and weight, these products are easy to install in any room and on any surface.
Aluminum radiators also have negative qualities. These include the following points:
- aluminum not only heats up quickly, but also cools down quickly, which is why in order to maintain a comfortable atmosphere in the room it is necessary to constantly maintain the required level of coolant supply;
- radiators made from this metal cannot withstand high pressure in the heating network, so they are not suitable for use in apartment buildings - they are more often installed in wooden country cottages or in small autonomous buildings;
- prefabricated structures are equipped with rubber gaskets; over time, these elements wear out and require replacement, which creates certain inconvenience for the owners; also, this feature does not allow the use of the types of batteries in question when using special liquids with an aggressive chemical composition, such as antifreeze, as a coolant;
- if the coolant has a high content of alkaline compounds, destruction of the material and failure of the radiator occurs, therefore it is advisable to use aluminum products in small private buildings where problems with excessive concentration of foreign substances in the water do not exist;
- When water and aluminum combine, a weak process of gas formation occurs, therefore, to bleed air and remove plugs, Mayevsky taps must be installed on the products.
Mayevsky crane.
Bimetallic radiators
Bimetal radiators are visually no different from aluminum products. They are also compact and aesthetic, but due to the use of steel in the structure, the weight of bimetal heaters is slightly greater.
Which radiators are better - aluminum or bimetallic - can be understood if you understand the structure of each system and compare them.
Thus, thanks to the reinforcement of the product structure with a steel base, bimetallic radiators can withstand higher coolant pressure without damage, which significantly expands the scope of their application.
Device
To obtain a high-quality radiator using two metals, steel and aluminum, a complex casting process using high pressure is required. Thanks to the distribution of metal under pressure in the mold, a tight bond of two different materials is achieved, which is necessary for high-quality heat transfer.
The steel core absorbs the pressure of the coolant and, through contact with the aluminum shell, transfers energy into the room.
Comparison of aluminum and bimetallic radiators
Externally, both types of heaters are absolutely identical, and an untrained consumer will not be able to distinguish an aluminum product from a similar one made of two metals. These types of batteries differ only in parameters:
- The heat transfer of aluminum radiators is higher than that of bimetallic ones;
- the ability to resist network pressure is almost twice as high for bimetallic products;
- the ability to resist corrosion is higher for bimetallic radiators in which the core is cast from stainless steel;
- the service life of aluminum products is about 10 years, and bimetallic radiators are designed for 25 years;
- the cost of bimetallic devices is 30% higher.
How to distinguish an aluminum radiator from a bimetallic one
Knowing the differences between the batteries in question, you can easily determine which product is offered in the store. It is necessary to pay attention to the following points:
- the connecting thread in the bimetallic radiator is made of steel;
- the weight of a bimetallic battery, with the same dimensions, will be significantly higher than an aluminum radiator;
- the easiest way is to check the material with a magnet: a magnet will not be attracted to a product cast entirely from non-ferrous metal - this method of checking is convenient for determining
- material of the already installed battery.
Positive properties of aluminum batteries
Aluminum radiators are light and durable, easy to transport and install. In addition, they also have a number of important advantages:
- small sizes (shorter in width compared to cast iron);
- very high level of heat transfer;
- operating pressure corresponding to the needs of modern heating systems;
- you can select a product with a certain number of sections according to the heated area;
- good heat transfer, which means efficiency;
- the ability to adjust the temperature using built-in thermostats;
- excellent aesthetic appearance.

The advantages of aluminum radiators over bimetallic ones are their lower price, which is very important for the consumer.
Cons of aluminum radiators
Any product has some pros and cons. Consumers have to weigh the pros and cons when they compare the differences between heating radiators.
The disadvantages of aluminum radiators are the following:
- high demands on the coolant: it should not contain acids or alkalis;
- all aluminum radiators must have air venting devices in order to promptly remove air pockets;
- aluminum radiators are connected to the heating system only using aluminum pipes;
- weak points - connections of sections that can leak under load;
- heat is distributed unevenly, the hottest places are the fins of the radiators;
- The service life of an aluminum product is about 15 years.

If you handle the aluminum product carelessly during installation, it can be damaged, since the material is quite fragile. Therefore, this work should be done by a professional. The listed disadvantages help to understand the difference between an aluminum radiator and a bimetallic radiator.
Application for various heating purposes

After considering the main characteristics, pros and cons of the devices, you can decide on the option for the heating system.
Apartment heating main
Bimetallic models were created for use in urban environments. The water poured into the pipes has an aggressive chemical composition that does not affect the quality of the steel core. The element also provides resistance to hydrodynamic shock and pressure fluctuations. The small cross-section of the water channels allows the batteries to be quickly filled with water from a centralized boiler room.
A private house

The best option is aluminum devices that require high-quality coolant. The batteries are easy to operate under conditions of minimum pressure from 2 to 3 atm, and to regulate the temperature they can be equipped with a thermostat.
Country cottage
For heating in winter it is better to use aluminum modifications. They will provide maximum heat transfer, unlike bimetallic ones, which are expensive and will break quickly.
Features of a bimetallic radiator
Bimetallic radiators are a new technology for manufacturing heating products. To know how to distinguish bimetallic radiators from aluminum ones, you need to understand their internal structure, which combines materials with different performance characteristics: aluminum and stainless steel. The bimetallic radiator successfully takes into account the positive aspects of these two metals.
What are bimetallic radiators? Structurally, these are steel pipes with aluminum sections. Such products are considered most suitable for installation in central and individual heating systems.
The sections are made of aluminum, so they have maximum efficiency and instantly transfer heat to the room. When asked how aluminum batteries differ from bimetallic ones, they always compare the price - for bimetallic ones it is much higher.

The technology for its production is complex. High-quality products are cast under high pressure. To reduce cost, manufacturers sometimes use welding, which does not greatly affect the strength of the radiator.
For reference. The manufacturing technology of bimetallic radiators allows them to be installed in systems with any operating pressure, since the internal part of the product is made of high-quality steel.
The main difference between bimetallic radiators and steel ones is that they are reliably protected from corrosion by an aluminum casing.
Performance characteristics
When choosing high-quality heating equipment, you must pay attention to operating parameters. Classic bimetallic radiators have the following technical characteristics:
- The heat output level ranges from 100 to 190 W. The aluminum shell has excellent performance.
- The maximum temperature can reach 1000 °C.
- Working pressure is 40 atm. This is due to its high strength - the presence of a steel core. System rupture is possible only if the pressure exceeds 90 atm. Such batteries can be used even under water hammer conditions.
Radiators from well-known manufacturers can boast optimal performance parameters. In this case, they have a warranty period of 15 years.
The inner layer consists of a durable steel core, which includes upper and lower manifolds, which have a specific H-shape. The parts are connected to each other by a heat pipe through which heated liquid circulates. The outer layer is a decorative shell made of several plates. Sectional products have reliable sealed fastenings inside
The battery can not only be increased, but also decreased, which is very important for achieving optimal operating parameters

For a private home
The final thermal characteristics depend on the material of manufacture. There are two common options:
- Aluminum, steel - radiators do not always have a core in the form of a pipe, as they are equipped with steel-reinforced channels. This option has optimal heat transfer performance. There are never any blockages in them.
- Aluminum, copper - products have excellent performance properties. The difference between copper is that it has high thermal conductivity and is also not susceptible to corrosive processes. The radiator has high power.
Bimetallic products are factory equipped with small channels, which allows you to save on heating your home. The production technology is quite complex, since casting is performed under high pressure. Some models are made using spot welding. All parts are connected using threaded nipples.
Several interesting secrets for choosing a quality device are presented in the video:
Advantages of bimetallic batteries
An important advantage that allows you to save energy resources is the small internal volume of the bimetallic radiator. This means that these devices require a small amount of coolant. This does not affect the intensity of air heating in the heated room. The aesthetic appearance of the products will fit perfectly into any interior.
List of advantages of bimetallic radiators:
- The product can withstand any pressure in the system;
- when comparing how bimetallic heating radiators differ from aluminum ones, it should be noted that they can be installed in heating systems with any acid-base balance of the coolant;
- the connections of the sections are very reliable (paronite seals are used);
- large margin of safety of the product;
- the appearance does not deteriorate over time due to durable coloring;
- bimetallic radiators serve for more than a quarter of a century due to the use of steel pipes in the design;
- have maximum heat transfer due to aluminum fins.

For reference. Installing such radiators is not difficult. If necessary, you can build up additional sections without removing the already installed radiator. This is very convenient when the heating system has already been installed, but the decision has been made to enlarge the radiator.
Comparison of the fundamental differences between aluminum and bimetallic radiators
In appearance, both presented radiators are very similar to each other. They are made in the form of metal rectangles, their ribs have a flat shape. The number of sections for both types of structures ranges from 6 to 12 pieces. Their heat transfer is also almost on par with each other, amounting to approximately 170-200 W.
Today it is very popular to play up every household detail of a room, turning it into a fashion accessory. The same applies to bimetallic batteries installed in your home. The outer coating of the products is always painted in neutral white or gray colors. However, you can improve standard store-bought options yourself by covering them with specialized bright paint. Apply a pattern that you like to the radiator and breathe a special atmosphere into the room.

Color options from the manufacturer

Heating radiator decor option
Important! Before purchasing paint, consult with specialists. It is important to choose one that is non-toxic and heat resistant to ensure your health remains safe.
So, let’s summarize and name the main difference in the operation of batteries made of aluminum and bimetal:
- Aluminum batteries are well suited for installation in country cottages and ordinary private houses. This is where it is necessary to obtain maximum heat transfer from radiators, especially in winter. Provided there is low pressure and high quality coolant, this is an ideal option for heating country houses equipped with an autonomous heating system. There is no point in installing bimetallic sections, as they can quickly fail;
- Bimetallic batteries were developed specifically for operation in the conditions of a city centralized heating network. Admixtures of aggressive chemicals have long been added to the water circulating through them to reduce heat loss. The steel core of bimetallic installations easily copes with these impurities, and also withstands hydrodynamic shocks and pressure drops in the system. That is why it is better to use this type for installation in an apartment, office, etc.
Video - choosing between a bimetallic and aluminum radiator
Differences between bimetallic radiators and aluminum ones
When it is advised to buy cheaper models, many of the models’ shortcomings are not taken into account. Therefore, sometimes you have to “pay twice” and redo the entire heating system from scratch.

To prevent this from happening, you need to know how heating radiators differ and what are their similarities:
- Bimetallic aluminum radiators are very similar in shape: flat rectangular white casings.
- Radiator models can consist of several sections. You can select the appropriate number of sections to suit the size of the heated area.
- The fundamental difference between aluminum heating radiators and bimetallic ones is that during operation, aluminum ones can be destroyed if the coolant pressure is higher than permissible according to technical characteristics (on average, 12 atmospheres). Bimetallic radiators can withstand voltage three times higher.
- Since steel is heavier than aluminum, bimetallic radiators weigh more. When there are many sections, the difference is significant: 1 section of a bimetallic battery is 0.5 kg heavier than an aluminum one.
- The service life of a bimetallic device is at least 25 years; for an aluminum device, 15 is the limit.
Popular types of radiators
Bulky cast iron batteries are slowly becoming a thing of the past, being replaced by elegant radiators. Such designs give off excellent heat and look attractive.
The cost of the products is relatively high, but taking into account the long-term service, the investment pays off in the long term. By updating the heating system, the consumer will find out which heating radiators are best for a private home
There are bimetallic and aluminum sections available in stores, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Pros and cons of aluminum heating radiators
Neat and attractive aluminum batteries include several sections connected by nipples and sealed with special gaskets. The inner side has a ribbed surface, increasing the heat transfer area to 0.5 m2. According to the manufacturing method, they are divided into solid cast and extruded. The first ones are more expensive and more durable, the second ones are light and budget-friendly.

Let's look at the main advantages and disadvantages of such radiators:
The disadvantage of such models is considered to be poor tolerance to pressure surges and fragility during water hammer. The working pressure of an aluminum radiator is 6-16 atmospheres, less often 20. Needless to say, the installation of aluminum radiators in multi-storey buildings is not recommended, because it is difficult to control the centralized heating supply. In private construction, such a problem does not arise, because a separate heating system (HS) is not subject to uncontrolled changes in operating pressure and water hammer. In terms of heat transfer, an aluminum product leaves other types of heating structures far behind. One sectional unit emits up to 200 W of thermal energy: part transmits convection heat, while the second transmits infrared radiation. There is also minimal thermal inertia, which is extremely useful in a private home. Almost immediately after starting the system, the room becomes more comfortable. The most common coolant is plain water. The product is available, but at the same time, the salts and other components contained in the water react aggressively with the aluminum surface
Due to the chemical activity, it is extremely important to monitor the pH status. An indicator that exceeds 8 units is detrimental to the radiator - it will be “eaten up” by corrosion
Hydrogen is also released which can cause a fire or battery explosion. Air should be removed from the sections in a timely manner. The maximum coolant temperature should not exceed 110 degrees, which is also a disadvantage of aluminum radiators.
Bimetallic radiators - a combination of the best qualities of metals
First, let's figure out how bimetallic heating radiators differ from aluminum ones? The main difference is the bimetal’s resistance to pressure changes. This allows radiators to be used universally both in apartment buildings and in private homes. Bimetallic radiators are reliable in conditions of water hammer. This is ensured by an internal steel or copper core through which the coolant moves. This structure allows you to withstand operating pressure within 20-40 atmospheres. Here is a list of other benefits:
- Low requirements for coolant. Steel and copper are not as susceptible to chemical composition, therefore, oxidation and corrosion processes do not develop as quickly as in an aluminum battery.
- The highest temperature of the coolant is 130 degrees.
- Durability - service life is on average 1.5-2 times higher than that of aluminum.
Bimetallic radiators still have some disadvantages compared to single-component metal products. Heat transfer rates are lower: depending on the manufacturer, the difference can reach a 5-fold value in favor of aluminum. The price for one section made of bimetal is higher, which is also not considered an advantage.
Conclusions from comparative characteristics
When purchasing radiators, you need to take into account the main performance characteristics: the ability to withstand significant pressure drops, resistance to corrosion processes, the strength of section connections and, ultimately, the durability of the product.
Aluminum ones can be installed in private households, where it is possible to control the quality of the coolant and the pressure in the system. They will serve well for many years. Home owners will receive good quality at an affordable price. However, you should not install such radiators in houses where antifreeze is supposed to be used as a coolant.
Structural differences and appearance
Cast iron
Let's start with cast iron radiators, which today have changed their design, but, as before, have wide water channels and are made up of several cast sections. Heat-resistant gaskets made of rubber or paronite, which are placed between the sections, provide the necessary tightness. The length of the finished radiator is determined by the number of sections, the height varies from 0.35 to 1.5 meters, and the depth can be 0.5 meters or several centimeters. Depending on the volume of the room, you can select the desired radiator size, and it is possible to modify it (for example, remove an extra section or add several new ones).

Types of cast iron heating radiators.
It is worth mentioning the models of radiators artistically cast from cast iron. They not only perfectly warm the room, but are also able to give it charm and charm. Such radiators with skillfully molded patterns on their surface are produced mainly by foreign manufacturers. Like any piece of art, such devices cost a lot of money.

Several types of artistic cast iron heating radiators.
Bimetal
The body of bimetallic radiators is aluminum, its shape is ribbed. This is how it is designed for better heat transfer. A durable steel core is hidden under the body - this refers to “real” bimetallic radiators. However, there are also semi-bimetallic (or pseudo-bimetallic) radiators - their difference is that only the vertical channels of the radiator are reinforced with steel. The rest of it is made of aluminum. Such a device costs 20 percent less than a completely bimetallic one, and produces more heat. But it is less reliable and durable, and using it in a centralized network is highly undesirable.
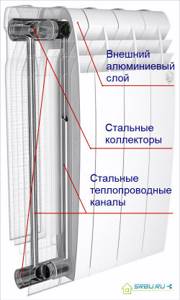
Construction of a bimetallic heating radiator.
Like cast iron radiators, their bimetallic counterparts are usually sectional, which allows them to be modified. Models with an even number of sections are usually sold. A small segment of the market is occupied by monolithic models that cannot be disassembled, assembled or improved. The design of all bimetal radiators is very attractive.
Appearance: Cast iron + — | Bimetal +
Let's compare the heat transfer of radiators
Cast iron. Let's start again with traditional cast iron radiators. They are so slow that sometimes you can freeze while waiting for a cold room to warm up. But on the other hand, such radiators take a long time to cool down - and this is a completely different matter. After all, there are often cases when the heating is turned off. Due to an accident or repair, for example. And you can still warm up for a long time near the cast iron battery.
The great advantage of cast iron products is that they heat the room not only by convection, but also by radiation. That is, when they are turned on, in addition to the air, objects close to the batteries also become warm. As for the thermal power, it is usually given for one section and ranges from 100 to 160 watts. These are average values and may vary between models.
Bimetal. The good thing about these radiators is that they heat up instantly. However, they cool down just as quickly, alas. Heating in them is carried out mainly by the principle of convection - the radiative component is much smaller. This is some minus. The thermal power of sectional models is comparable to cast iron products. This figure ranges from 150 to 180 watts (on average). If we compare the rate of heating of the room, then they certainly outperform cast iron ones.
Heat dissipation: Cast iron + - | Bimetal +
Ability to hold pressure
In a traditional central heating system, typical of multi-storey buildings, the pressure is by no means stable. Sometimes even water hammer occurs. After all, according to the rules, the taps of circulation pumps should turn on smoothly, but often workers do not follow these rules. And when the hot water is suddenly turned off, its pressure in the entire system jumps so much that many batteries burst. Therefore, apartment residents should definitely choose radiators with a good pressure reserve.
Cast iron radiators can withstand 9-12 atmospheres of pressure. This may be sufficient until a strong water hammer occurs. If it does happen, then the brittle cast iron, unfortunately, may burst. Therefore, if you look from this point of view, whether cast iron or bimetallic radiators are better, then it is better, of course, to play it safe and take a bimetallic one.
Resistance to poor quality coolant
Another disadvantage of central heating is the dubious quality of the coolant. The hot water coming from the pipes to the radiators is neither clean nor chemically neutral. It also contains a considerable amount of tiny grains of sand and pebbles that can act on the internal walls of the battery like an abrasive.
Cast iron is chemically absolutely “calm”, so a high level of alkalis or acids in hot water will not harm it. And in the summer, when the water is completely drained from the system, it will not rust. But she doesn’t like small abrasive pebbles - they wear away gradually. However, if the radiator walls are quite thick, this is not so critical.
Bimetal is also resistant to chemically active water during the heating season. However, in the summer, when water is drained from the system for repair and maintenance work, air appears in the radiators, and the steel core may be attacked by corrosion. So bimetal is slightly less durable than cast iron.
Poor quality coolant: Cast iron + | Bimetallic + —
Heating using a convector
Convector heating is a heating method using more modern types of heaters.
The principle of operation of the convector is different in that it uses natural air circulation to heat the room. Today, the main types of convectors are water and electric.
Water convector.
Their main feature is that they need to be connected to pipes with a coolant - hot water, which heats the air around them. At first glance, they are similar to central heating radiators, however, their main difference is the use of the convection principle for heating.
Radiators use several surfaces (sections) to distribute thermal radiation. For a water convector, this is a pipe on which metal plates are installed. They are heated by the coolant (in this case, hot water) and release heat into the air due to convection.
In addition, the power of convector heating can be controlled by installing control valves, and the heating strength can be adjusted in each room of the house separately.
Advantages of water convectors:
- They heat the room quite efficiently.
- More economical than radiators.
- Silent.
- They do not require electricity.
- They come in different sizes and placement methods (wall-mounted, floor-mounted).
The disadvantages include the complexity of installation - the need to lay a pipe with coolant, as well as the not very fast process of heating the room.
Thus, a water convector is more convenient in comparison with heating radiators in terms of its characteristics, if it is possible to connect pipes with hot water to it.
Electric convector.
This device is the most modern. An electric convector passes cold air through a heating element inside the housing, when heated, it rises, and thus ensures natural circulation of warm air in the room. They are controlled using a thermostat that regulates the temperature.
This type of heater allows you to do without complex installation or pipe laying - you just need to plug it into an outlet, and the device is ready for use.
Advantages of electric convectors:
- When placed correctly, they heat the room efficiently and evenly.
- They do not require complex installation, you only need a nearby outlet.
- Silent.
- Compact, mobile, can be installed on the floor or mounted on the wall. This is why they are better than radiators.
- They can work for a long time without the risk of breakdown.
- Fireproof. Branded models have overheating protection, which turns off the device when tipped over. Also, thanks to the low temperature of the body, you can’t get burned on them, so you don’t have to be afraid to install them in a child’s room.
- You can combine several convectors into a single system, which will make it easier to control the temperature in different rooms.
- Inverter devices with an electric thermostat are quite economical, as they work by maintaining the required temperature.
- Modern models can be controlled via the Internet or mobile devices.
- They have a more affordable price compared to radiators, and you can also save on installation.
The only disadvantage of using an electric convector is the cost of electricity.
However, they can be reduced if you use an inverter type of device. Therefore, today an electric convector is the simplest, most efficient and convenient heating device.
Maximum coolant temperature and its fluctuations
And the temperature of the coolant in our heating systems is not stable. Sometimes the pipes are barely warm, sometimes they are hot, like fire. It is important for us how the radiators will behave in the latter case, whether they can withstand too hot water. The indicators for this parameter are as follows. For a cast iron radiator, the coolant can heat up to 110 degrees. Hot water flowing through the pipes of a bimetallic radiator core can have a temperature of up to 130 degrees. But in general, both types of radiators tolerate temperature changes well. The only thing is that due to the difference in expansion of steel and aluminum, with a sharp change in temperature, you can hear small crackling sounds from the bimetallic radiator.
Maximum coolant temperature: Cast iron + | Bimetal +
Types of radiators
The properties of the equipment and its ability to withstand negative phenomena depend primarily on the type of material.
Cast iron
A Soviet classic, familiar to every resident of high-rise buildings, because they were everywhere. They often meet even now. Bulky structures that have to be painted regularly to maintain a decent appearance.
And yet, many homeowners are in no hurry to part with old cast iron products for central heating and buy new models that are on the market. Before revealing the secret of such popularity, let's name their disadvantages:
- heaviness - it will take a lot of effort to bring in such a colossus. In addition, it is unlikely that you will be able to install it yourself;
- cast iron is fragile, which is why it does not always withstand strong water hammer;
- high price.
As you can see, there are not many disadvantages. But the advantages of cast iron samples are presented in abundance:
- serve up to 50 years;
- copes well with pressure up to 12 atmospheres (which is often more than enough);
- keep warm for a long time;
- please with efficient heat transfer;
- almost do not rust.
Such devices today are produced not only in the usual design. There are simply stunningly beautiful specimens that fit perfectly into the retro style, as well as quite modern, laconic forms.
To prevent the surface from having to be repainted regularly, a protective paint is applied to it, which does not have to be renewed.
Steel
They look beautiful and are inexpensive. Another positive aspect is the low weight and productive heat output. There are panel and tubular steel radiators.
Panel specimens look like two plates, between which water passes in steel contours. They fit perfectly into the interior as they look very presentable.
Tubular ones consist of several parts welded together and are similar to classic batteries (though their shapes are much more varied). As a rule, they are more expensive than panel ones.
Everything would be fine, but this option is not suitable for an apartment: such products can withstand no more than 10 atmospheres, and if this value is exceeded, they can burst and leak. In addition, without filling with liquid, they often begin to rust.
Aluminum
Light weight and reasonable price. This is the main reason for buying aluminum items. They have a better heat transfer coefficient and can last from 15 to 25 years, but only under conditions of constant low pressure and good quality media. But, as we remember, a centralized system cannot satisfy these requests.
They cannot withstand high pressure and leak. Such structures are also sensitive to water quality and are destroyed by a chemical reaction with the release of oxygen. So, alas, it is better for residents of high-rise buildings to refuse them.
Bimetallic
Consists of an aluminum casing and an internal part made of steel or copper. They can easily withstand temperatures up to 130 degrees and pressures up to 30 atmospheres.
The enamel coating provides an aesthetic appearance: such a device will easily fit into any environment. They are also treated inside and outside with anti-corrosion agents, which keeps them intact for a long time.
There are two types of such radiators.
- Sectional – you can add or reduce the number of segments.
- Monolithic - capable of withstanding pressure up to 100 atm, and therefore are characterized by a large margin of safety.
It is this type that is recommended to be chosen for an apartment building, as it is the most reliable. But the cost of such models is higher than others.
Copper
A rare guest in our stores. This is explained by the high cost of the metal. Although in operation they show themselves to be quite acceptable:
- quickly heat the room, thanks to increased efficiency;
- are not afraid of water hammer up to 25 atmospheres;
- resistant to high coolant temperatures;
- do not need painting or processing;
- do not rust and serve for a long time.
Among the weaknesses, additional requirements for the materials of supply lines and connecting elements can be noted: they must be made of copper or brass. Otherwise, the copper will react with other metal, leading to corrosion and destruction.
However, the design of such items is still quite specific and they cannot fit into any interior, which is clearly visible in the photo.
Which radiators are easier to install?
There is nothing to argue about here - naturally, with cast iron there will be more problems during installation and transportation. And one person cannot lift such a battery, and special brackets are needed for it - especially strong, and a plasterboard wall will not support it.
And one more thing: when purchasing cheap domestic radiators, you need to be prepared for the fact that they will additionally need painting and broaching.
But working with bimetallic radiators is, one might say, a pleasure. They are so light and neat that hanging them (and on any surface) is not difficult. And if ease of installation is your first priority, then the answer to the question of which is better - bimetallic radiators or cast iron ones is clear. Of course, bimetal.
Ease of installation: Cast iron - | Bimetal +
Let's talk about the difference in the price of radiators
Cast iron is undoubtedly cheaper, especially when produced domestically. So, the cheapest section of the MC model, for example, costs only about 300 rubles. However, only classic models will have such a “tasty” price. But retro-style radiators made by artistic casting are several times more expensive. Similar models from the Konner brand cost from 2,000 rubles (for one section).
Sectional models of bimetallic radiators will be slightly more expensive than similar cast iron ones. For example, one radiator section from Rifar (Russia) will cost at least 500 rubles. The price of a section of the same Italian radiator starts from 600-700 rubles.
Price: Cast iron + | Bimetallic -
We draw conclusions and decide on the type of radiator
Now, after comparing cast iron and bimetallic radiators, we can confidently say that in old apartment buildings up to five floors high, cast iron radiators are a good option. They can withstand the pressure supplied to the system. Naturally, if there are no powerful water hammers. But here you have a choice, and if finances allow, then of course you can install a more stylish bimetal.
If the apartment is located in a high-rise building, then the working pressure of the coolant will be significantly higher. Therefore, in this case, it is more reasonable to install bimetallic heating devices that have a longer pressure life.
Well, one more thing. If you previously had cast iron radiators in your apartment, you can replace them with more modern cast iron radiators and bimetallic products. But after steel or aluminum it is definitely better to install bimetal.
Having an autonomous heating system, you can install any of the radiators, but as a rule, in such systems it is most advisable to use steel or aluminum radiators.
Steel radiators
Radiators made of steel are quite popular both in Europe and in our open spaces. If you prefer simplicity and practicality, then the option with steel radiators is for you. Why? The point is in the simple designs and shapes of such batteries . Steel radiators do not have (or almost no) hard-to-reach places, which means they are easy to care for. Like aluminum radiators, they do not need to be painted.
A steel radiator is, as a rule, a plate (or two) with vertical channels filled with a minimum amount of coolant. This circumstance allows radiators to quickly respond to your heat needs when you regulate the temperature in the heating system. The less water in the radiator tanks, the faster it heats up, the less fuel is consumed by the heating boiler. Steel radiators have high efficiency.