Types of OLM
This includes asbestos and metal.
Asbestos sheets are characterized by withstanding prolonged heating up to +500 °C. Poorly conductive of heat, they do not lose strength and are used to construct fire-resistant walls.
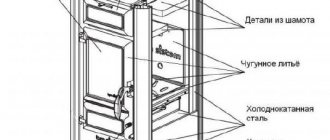
Steel plates in the form of elements of stoves and fireplaces are placed in front of the doors of these heating systems.
Fire-resistant sheet materials for stove and fireplace protective screens
Protective screens made of steel sheets are mostly used for metal combustion products to insulate their side walls. They are installed at a distance of up to 5 cm from the walls of the heating device and reduce thermal radiation.
Screens can be side or front. With their help, the temperature on the outer surfaces of combustion systems is reduced to +100 °C, which improves fire safety. Installation of convenient protective screens is simple and is carried out by attaching them to the floor using special legs.
Side protective screen
Fire resistant wall cladding
As an option, to protect the surrounding space from heating operating heating products, it is possible to create heat-reflecting cladding. It is equipped to avoid ignition if the wall of the room fits tightly to the stove or fireplace surface and becomes excessively hot.
Heat-resistant screens for sauna stoves. Part 1
Reflective trim
It is effective to use cladding consisting of fire-resistant sheets in combination with non-flammable thermal insulation composites.
Fire-resistant sheet materials are mounted on top of thermal insulation; it is preferable to use stainless steel sheets for such cladding, since galvanized steel sheets can release toxic substances into the air when heated. To make the protection more effective, the steel sheet is polished to a mirror finish: this way, heat rays are reflected better from the metal, and the wall heats up even less.
Wall cladding with mineralite slabs
There is a whole range of OLM for cladding:
- basalt cardboard, made of basalt fiber, provides good heat and sound insulation;
- asbestos cardboard is durable and strong;
- mineralite; protective screens for stoves and fireplaces are also made from its sheets.
Cladding with cladding
Facing the mineralite surface with soapstone tiles
The following fire-resistant sheet materials are used for it:
- fire-resistant plasterboard - it is made with the addition of fiberglass and does not deform under the influence of thermal radiation;
- mineralite, it is also characterized by high moisture resistance and the ability not to collapse under the influence of elevated temperatures;
- The glass-magnesium sheet is made of fiberglass (in which the magnesium substance acts as a binder), it is able to withstand high temperatures.
Heat-resistant screens for sauna stoves. Part 2
Wall cladding with sheet fire-resistant material
To ensure the fireproof condition of the room, you need to wisely select the material for covering the walls near which the heating structure is located.
And vermiculite panels are ranked among the most effective OLM. Moreover, such slabs are used to ensure fire safety in various premises, including enterprises in the nuclear and oil refining industries.
Among the advantages of fire-resistant vermiculite boards are:
Vermiculite boards
- environmental friendliness;
- fire resistance;
- thermal insulation;
- sound insulation;
- aesthetic appearance, which allows them to be used in prominent places.
Where are they used?
Vermiculite panels, due to their excellent performance qualities, can be used in many areas.
Scheme of thermal protection of a wall and fireplace lining with a vermiculite slab
- For thermal insulation of fireplaces and stoves.
- For fire protection of structures made of different materials.
- To ensure that various objects can withstand fire hazards.
- For guaranteed fire resistance of various indoor items, including stoves and fireplaces.
Vermiculite boards, as representatives of OLM, are installed simply and quickly and do not require professional training. Processing them on all sides of a stove or fireplace ensures protection of the room from the effects of fire and high temperatures, and therefore such fire-resistant sheet materials are optimal in solving the problem associated with the fire safety of the room.
All samples of fire-resistant sheet materials for stoves and fireplaces are modern, high-quality products. In addition to fire protection, they provide heating devices with resistance to various types of damage, including mechanical and chemical.
Types and rules for the manufacture of fireproof cladding
Fire walls can be created using sheathing made from non-combustible materials. Today, 2 variants of such designs are used:
- reflective coverings;
- sheathing with cladding.
To produce reflective protection, thermal insulation material is attached to the wooden surface of the walls, which is covered with a steel sheet. A few years ago, galvanized and stainless steel sheets were used equally widely. However, studies have shown that when heated, galvanized steel can release harmful substances, so it is preferable to build fire walls from stainless steel.
In order for the reflective effect to be as intense as possible, the surface of the sheet must be well polished (almost to a mirror finish).

The following can be used as a heat insulator fixed under steel:
- basalt wool, which has good thermal insulation characteristics and absolute environmental safety;
- basalt cardboard, the base of which includes basalt fiber;
- asbestos cardboard, characterized by good fire-resistant qualities;
- mineralite, made specifically for shielding surfaces.
Fire walls sheathed with steel sheets are quite simple to install. The main thing is to remember what each layer of cladding should consist of:
- wall;
- a gap of 2-3 cm, providing ventilation between the wooden surface and the heat insulator;
- thermal insulation material (at least 1-2 cm thick);
- sheet of steel.
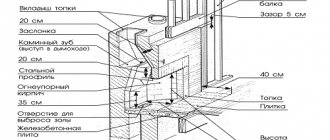
The distance from the furnace body to the steel sheet must be at least 38 cm. It is recommended to use ceramic bushings for fastening materials. They are not exposed to heat and do not deform, ensuring the safety of the ventilation gap between the heat insulator and the wood.
When the distance between the heater and the wall is less than 38 cm, it is necessary to use a double layer of fire-resistant material. The best choice would be mineralite. It is secured with ceramic bushings with a gap of 2-3 cm from the wooden wall and covered with stainless steel.
Classification
Fire-resistant products are available in various forms: in plates, sheets, rolls and there is a group of unformatted materials. In addition, it is divided into types according to other characteristics:
By size and shape:
- wedges and straights of small, normal and large sizes;
- shaped simple, large-block, complex, weighing more than 60 kilograms;
- laboratory or industrial use.
By production method:
- production of refractory materials by sawing rocks from blanks;
- cast, made using liquid casting technology;
- production from plastic masses with subsequent additional pressing;
- formatting by pressing from powders;
- made by hot pressing;
- manufactured by thermoplastic pressing;
- formatted from hot melt.
According to deformation temperatures:
- from 1580 degrees C to 1770 degrees C - ordinary fireproof;
- up to 2 thousand degrees C – highly fire-resistant;
- up to 3 thousand degrees C – materials with the highest fire resistance;
- more than 3 thousand degrees C – super-fire-resistant.
By degree of porosity:
- the pores are open, their volume does not exceed 3% - especially dense;
- pores open up to 10% - highly dense;
- pores are open, volume up to 16% is dense;
- pores are open, up to 20% are compacted;
- pores are open, up to 30% - medium dense;
- total porosity up to 45% - low density;
- total porosity up to 75% - highly porous;
- total porosity more than 75% - ultra-porous.
Varieties by composition:
- oxygen-free;
- siliceous;
- silicon carbide;
- aluminosilicate;
- carbon oxides;
- glass-magnesite;
- aluminous;
- carbon;
- magnesium;
- oxide;
- magnesian-calcareous;
- zirconium;
- limestone;
- chromium;
- magnesia-silicate.

Basalt fireproof insulator
Classification of materials NG
Taking care of the safety of buildings under construction and in operation, the state develops standards and building codes, classifying building materials for fire hazard.
Their properties are taken into account:
- flammability;
- flammability;
- the time it takes for the flame to spread across the surface;
- ability to generate smoke;
- release of toxic components;
- explosiveness.
All materials used in the construction industry are divided into (NG) non-flammable and (D) combustible. The first ones resist destructive fire, they cannot be ignited by sparks or chemical processes (reactions), they are resistant to high temperatures.
Documentation regulating the requirements for non-combustible materials
According to GOST 30244-94 and SNIP 21-01-97, those building materials that demonstrate the following results during testing are considered non-flammable:
- give a temperature increase of up to 50 degrees Celsius;
- the sample loses up to 50% of its mass during the experiment;
- demonstrates stable flame combustion for no more than 10 seconds.
Experimental studies are carried out with samples in a special oven. If at least one parameter is outside the permissible limits, the material is considered flammable.
In turn, flammable building materials are divided into the following groups: low-flammable (G1), moderately flammable (G2), normally flammable (G3) and highly flammable (G4). The flammability index of slabs for finishing ceilings and walls depends on the base underlying the manufactured product. The base can be made from organic or inorganic raw materials.
Wood is an organic raw material; it is used for the manufacture of sheets of wood-fiber, particle boards, plywood, and when antipyrines are added to their composition, the materials become resistant to fire. True, pyrine retardants do not prevent products from catching fire if they remain in a fire for a long time.
Non-flammable panels are made from inorganic raw materials.
Peculiarities
First of all, it is very important to list the main features of fire-resistant sheets, which can help both in the choice of material and in its installation.
- Fireproof. Since in baths, saunas and places where stoves and heating equipment are located, the heating power can reach 300-400 degrees, it is very important to install especially resistant sheets. There are several types of them, but they all have one feature - protecting the environment from high temperature heating. This minimizes the risk of fire and other situations that are prevented by compliance with safety requirements.
- Resistance to environmental conditions. Since most slabs and their varieties are made of chemicals, they are protected from the effects of alkalis, acids and other elements that deform the surface of ordinary materials. In addition, manufacturers create raw materials that prevent the formation of fungus and mold, and are also resistant to dirt. This feature makes maintenance of fire-resistant sheets simpler and less expensive.
- Strength. The chemical compounds that serve as the basis for covering high-temperature equipment are quite dense and meet the required strength requirements relative to different installation methods. Some types of slabs have high resistance to physical damage, which makes them more reliable and durable.
- Soundproofing. This is not a feature of all, but only of some types of refractory materials. As a rule, soundproofing materials have a dense filled internal structure, which is how this effect is achieved. This choice is preferable for those who deal with noisy heating equipment, the operation of which can be inconvenient.
Installation
To ensure that the oven door closes tightly, a fireproof cord is installed in a special groove around the perimeter. To fix the seal in this groove, use high-temperature silicone sealant. Before applying it, the groove must be thoroughly cleaned of the remnants of the old fire-resistant cord and sealant. After the seal is installed, it is necessary to close the door, pressing it with a locking device and leave in this position for 2-3 hours. During this time, the sealant will polymerize, and the cord will take the required shape and position in the groove.
If it is necessary to protect combustible structures from metal chimneys passing through them, a fire-resistant cord is used somewhat differently. In this case, they wrap it around a metal pipe in the place where it will cross partitions or ceilings. The cord is wound in several layers. The width of the winding should be such as to provide protection for another 5-7 cm outside the building structure. In this case, the fire-resistant cord will also work as a heat insulator.
Fireproof materials for walls around furnaces
When firing a stove or igniting a fireplace, their body becomes very hot, transferring this temperature to the surrounding surfaces.
In accordance with fire safety techniques, it is necessary to insulate the furnace body from adjacent surfaces using fire-resistant materials if a safe distance is not maintained.
This is a distance equal to 30 cm for a brick stove, more than 1 meter for a metal stove and 70 cm for a metal-lined stove. If it is impossible to dissipate heat naturally in a room (especially a small area), fire-resistant materials are used for the walls around the stoves.
Heat-resistant materials for finishing walls near the stove: types
Refractory materials can be divided into several types depending on the type of raw material:
- Materials with organic elements, for example, polystyrene foam boards. The fire resistance rating is not very high, so they are used to protect against slight heat.
- Materials with inorganic components are used to insulate both wooden walls and brick and concrete walls. These are stone wool, basalt slabs, fiberglass, fiber cement slabs, polypropylene, honeycomb plastics, vermiculite panels, foamed perlite.
- Mixed materials: asbestos cardboard, asbestos-lime and silica refractories.
Protective screens
Oven protective screens
In addition to sheet materials, protective fireproof screens are used to insulate the side walls of the furnace and are installed at a distance of 1-5 cm from its body. They are distinguished from sheets by their multilayer structure. Screens made of cast iron and also stainless steel are widely used, including those combined with non-flammable plates in the outer layer.
The polished mirror surface of the steel screen reflects heat with softer and more gentle flows. The slabs inside the screen are held together using heat-resistant mastic, glue, mortar, and sealant that have high heat resistance.
Heat-resistant mastic has a fire-resistant composition that can withstand over 1100 degrees; it is also resistant to moisture, has bactericidal properties, and can be used as a facing solution. There are not only side but also front screens. Installation of such fire protection is done by attaching it to the floor near the stove; the screen itself is equipped with special legs.
In addition to steel fireproof screens, brick ones are used in the form of a wall that separates the stove body from the flammable surface. The brick screen is installed at a distance of 5 to 15 cm from the walls of the stove, and at the same distance from the flammable surface. Its height can reach the ceiling, or it can be equal to the height of the stove.
Wall cladding
Fireproof sheet materials for stoves and fireplaces
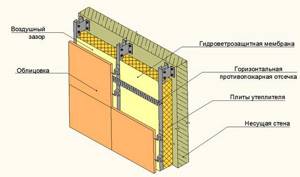
The refractory cladding of the walls around the stove is divided into reflective and cladding. The first type usually consists of metal sheets with heat-resistant thermal insulation materials.
The insulation is attached to the wooden wall, then covered on the outside with a sheet of stainless steel, polished to a mirror finish. Between the sheathing and the wooden wall it is necessary to provide ventilated gaps of 2-3 cm in size.
In this case, the refractory sheets are attached through ceramic bushings. The following are used as thermal insulation:
- Minerite
- Basalt cardboard
- Asbestos cardboard
If the stove is located at an unsafe distance from the wall, you can use a double layer of thermal insulation, which is secured through bushings and covered with a sheet.
Sheathing with cladding gives the protected surface an aesthetic appearance. Ceramic, terracotta, clinker tiles, and porcelain tiles, which are attached to refractory, are often used as facing materials. However, the tiles do not serve as thermal insulation. It is attached on top of the heat-resistant sheet. For the fire-resistant layer the following are used:
- Fireproof drywall is drywall with fiberglass added. Resistant to deformation and strong thermal radiation.
- Minerite
- Glass-magnesium sheet made from fiberglass.
Refractory materials for furnace lining
Fireclay materials for lining furnaces, namely brick and mortar, make it possible to create a protective fireproof screen both around the firebox and around the body of the metal furnace. The difference between a kiln brick screen and a lining screen is that the lining is a protective casing located close to the walls of the kiln.
Natural stone for finishing
Fireclay can withstand temperatures up to 1300 degrees. Today, in addition to bricks and mortar, there is also fireclay coating, glue, and mastic, which can be applied even while the stove or fireplace is operating.
Their composition includes microscopic fireclay fibers and binding substances; they line the entire surface of the furnace and seal individual cracks.
In addition, materials such as kaolin paper, kaolin cardboard, in the form of rolls and also kaolin wool in separate pieces are produced for lining.
Wall cladding with sheet refractory material (PVTN)
Vermiculite board
Properly selected material for wall cladding ensures high fire safety of the room. One of the most effective for achieving this task are vermiculite panels. Vermiculite fire-resistant boards for walls are widely used to ensure fire safety of various types of premises. Their reliability is so high that this material is used in the nuclear and oil refining industries.
Advantages
The use of fire-resistant vermiculite boards allows achieving high levels of:
- environmental friendliness;
- fire resistance;
- thermal insulation;
- soundproofing;
- aesthetics.
The last point is especially worth noting. Experts know how difficult it can be to find a material that would equally satisfy the requirements of fire safety and aesthetics. Fireproof vermiculite boards are just the kind of material that is protective and at the same time has an attractive appearance. Therefore, it can be safely used in prominent places.
Areas of use
Vermiculite board near the furnace
Excellent performance characteristics allow these fireproof boards to be used in the following areas:
- thermal insulation of fireplaces and stoves;
- fire protection for structures made of various materials;
- ensuring fire hazard for a wide range of objects;
- ensuring fire resistance of various elements of premises.
All this is achieved thanks to the high quality, reliability and efficiency of vermiculite panels, which are the optimal solution for achieving fire safety in a room.
When are sheet fireproof materials used?
It is not always necessary to use protective materials, but only in cases where the fire-safe distance from the stove surface to flammable objects is not maintained. If the distance is large enough, the wood does not heat up enough to cause a fire.
Modern standards require that a brick stove be located at least 32 cm from the wall, a non-lined metal stove at least 1 m, and a lined metal stove at least 70 cm.
For a spacious room, such requirements are quite feasible. But in a small home steam room it is not possible to provide a distance of 1 m. Therefore, fire safety can only be achieved with the help of fire-resistant screens and cladding.
Requirements
Fireproof materials must reliably protect the home from any fires, withstand numerous heating-cooling cycles for a long time without deformation, and be environmentally inert so that no harmful substances enter the room when heated.
They must have:
- fire resistance sufficient to ensure safety;
- low thermal conductivity;
- constancy of shape and volume when heated;
- chemical resistance;
- slag resistance;
- low ability to absorb moisture;
- increased strength.

Nuances of choice
A wide variety of species often makes you doubt the correctness of your choice. To avoid problems and to avoid regretting your decision, you need to decide on the material that will protect the walls next to the stove, chimney or fireplace.
For finishing walls around stoves and in boiler rooms
Fireproof finishing of walls around furnaces and in boiler rooms is prescribed by fire safety rules and is mandatory.
- Fire-resistant plasterboard panels can be used as a basis for cladding walls near the stove.
- Using fireclay bricks and/or mortar, create fireproof protection in the form of a screen near the furnace. The surface inside the furnace is laid out (lined) with bricks, and cracks and cracks are sealed with mortar.
- But the most effective protection for surfaces adjacent to fireplaces and stoves is made of stainless steel. Steel sheets are used to construct fireproof screens. They are mounted at a distance of 1-5 cm from the body of the stove or fireplace.
- Thermal protection can be further increased by fiberglass laid under steel sheets.
- Cast iron screens are also popular.
- Basalt rolls and mats, flexible and lightweight, are also used for shielding stoves and fireplaces.
- Terracotta or porcelain tiles are ideal for fire protection of boiler rooms, as well as baths. They do not deform or burn, and are also easy to maintain - they are easy to clean and wash. Due to their high decorative properties, they can also be used to decorate various surfaces.

For pipe
To avoid fire, chimney outlets must be reliably thermally insulated. For this purpose, mullite-silica boards and cardboard are used, which are excellent for processing. You can cut holes in them of any configuration for chimney pipes and other structural elements of stoves.

For the bath
The walls of the baths are finished with heat-resistant materials so that they have fire-resistant properties. For this use:
- “pie” made of a metal reflective coating and a heat-insulating gasket;
- superizol;
- fire-resistant plasterboard;
- glass magnesite;
- minerite;
- terracotta tiles.

Fire protection for sauna stoves is also provided by products made from foamed vermiculite. For the layer between the first rows of the stove masonry and the wooden floor, vermiculite boards are preferable, since they are stronger than cardboard.
During the construction of stoves, professional stove makers traditionally use fireclay bricks, which can withstand fairly high temperatures and sudden cooling. Modern material - lightweight fireproof fireclay - perfectly absorbs solutions mixed with cement and clay.
For the fireplace
The main product used for facing the fireplace, along with fire-resistant plasterboard, is fire-resistant ceramics:
- terracotta tiles or majolica as its variety;
- tiles;
- clinker tiles;
- porcelain stoneware
All of them are moisture resistant and resistant to temperature changes. Choose tiles marked A - they are of higher quality than tiles marked B.

Overview of species
Previously, asbestos or asbestos-containing sheet slabs were widely used to decorate walls near stoves. But today these products are not used in residential and industrial premises, because when heated strongly, asbestos releases carcinogenic substances that are harmful to people, and especially to small children.

Asbestos dust, which enters the lungs and also causes serious illness, is also dangerous.
- Today, fire-resistant plasterboard panels are considered the best fireproof materials for this purpose. The maximum temperature for their use exceeds 1400 degrees. Fire resistance – up to 30 minutes of fire resistance; they do not ignite within 1 hour, even if the fire has already started.

- Fiber cement mineralite boards are multifunctional and environmentally friendly. They are made from cement - gray or white - with the addition of cellulose. They are characterized by high heat resistance, strength and impact resistance, and work well in humid atmospheres.

- Stainless steel, or clad steel, is a very popular, although expensive, material. Formally, steel does not belong to refractories, but it has the highest heat reflection coefficient compared to analogues and does not lose its properties due to temperature changes.

- Refractory made from basalt fiber (mats or rolls coated with aluminum) does not ignite or undergo deformation when heated to 900°C; it is also completely hygroscopic.

- Superisol is universal, practical and durable - it is a special fire-resistant (up to 1100 degrees) material. It is made from calcium silicate, which makes it environmentally friendly and has a low specific gravity.

- Porcelain stoneware or terracotta tiles are not only fireproof, but also excellent decorative material, chemically inert, environmentally friendly, vapor-proof and durable. Terracotta tiles have an increased ability to transfer heat, and porcelain tiles are resistant to cracking.

- Refractory made from xylolite fiber also meets environmental requirements. It is produced in leaf form. The material is technologically advanced and moisture resistant.

- Widely used fireclay refractories have high heat resistance - up to 1300°C. This versatile material is also very beautiful, resembling sandstone in appearance. There are different types of it offered on the market - fireclay bricks, coating, glue, mortar and mastic.

- A modern, reliable fire-retardant material is slabs made of expanded vermiculite, characterized by high heat resistance – up to 800-900 degrees. They do not rot, are not susceptible to microbes, are not to the taste of rodents, and also meet environmental requirements.

- Fireproof boards made of mullite-silica fiber have high chemical resistance to alkalis and acids. They have no analogues in their fire-resistant properties.

- Glass magnesite is a heat-resistant composite material based on magnesium chloride and magnesium oxide. It has increased moisture resistance, density and strength, is lightweight and technologically advanced to use. Magnesium glass sheets are often used as an alternative to fire-resistant plasterboard.

Kinds
Sheet materials are produced in the form of panels and slabs of different sizes and are used for cladding and shielding surfaces from heat. The most common fire-resistant sheet materials in use are:
- fiber cement slabs
made of lightweight concrete with synthetic fiber, do not contain asbestos fiber; - asbestos cardboard
– based on chrysolite asbestos, can withstand temperatures above 500° C, has a high level of mechanical resistance to damage and alkalis; - basalt cardboard and boards
are environmentally friendly material, not dangerous to work with, based on basalt raw materials. Used at temperatures above 900° C, sometimes supplemented with a reflective foil coating; - mineralite slabs
- this material does not burn at all, is impact-resistant, moisture-resistant, has high sound insulation, and does not support bacteria or mold. Minerite is universal in use; - glass-magnesium sheets
- made of glass fabric and a magnesium binder; - sheets of fire-resistant plasterboard
- contains fiberglass; - vermiculite decorative panels
- are made in the form of panels with different textures (have a decorative appearance), can withstand temperatures up to 1200° C. They are fixed using heat-resistant mastic.
Areas of application
Fireproof sheets are most often used when lining heating equipment, for example, boilers and stoves in a bathhouse or sauna. The main reason for the demand is the fact that the equipment can be located close to the walls. To prevent high temperatures from affecting them, installation in the form of cladding and the creation of protective screens is required. They cover the entire space from which heat can spread. These processes have their own characteristics and differ in technological sequence, but most slabs are installed in a similar way.
At the same time, the structural cladding depends on specific conditions, for example, the location of the stove/boiler, their size, as well as the material of the room itself.
In addition to private and domestic use, fire-resistant sheets are used in production and industrial areas. Some premises that contain any explosives inside need safety and protection. It is these materials that help prevent the spread of fire in cases of fuel ignition.

Some building structures are made entirely of low-fire-resistant plastic and its derivatives, so the immediate space is sometimes sheathed with fire-resistant sheets. And also rooms in which there are a large number of communications, for example, server stations, are lined with protective slabs that prevent the transfer of fire from one type of equipment to another.
Don't forget about fireplaces. This decorative element also requires proper installation and operation.
At the same time, vermiculite boards, which have a decorative component, can be used in finishing rooms that are more demanding in terms of protection from high temperatures.
Today there are many similar materials on the domestic market, so their choice depends on the specific properties and advantages that the sheets are endowed with.

Fireproof protection options
A simplified classification of fire-resistant materials allows us to divide the entire range of fire-resistant products:
- Refractory refractories;
- Materials with increased resistance to high temperatures.
The latter are more commonly known as fire-resistant sheet materials, but in essence, they are effective non-flammable heat insulators that can withstand short-term contact with a hot surface or an open flame. They are used to protect flammable substances and structures from accidental short contact with a fire source. To facilitate installation, they are most often manufactured in sheet or roll form. Unlike furnace refractories in the form of blocks and bricks, refractory materials in the form of flat sheets are not designed to bear the load; their main task is to screen and reflect powerful heat flows emitted by the hot walls of the firebox.

The first category is used as materials for stoves and fireplaces. Refractory material consists of ceramic, composite blocks and slabs sintered from refractory chemical compounds that can withstand prolonged contact with an open flame, temperatures of more than one and a half thousand degrees, without loss of load-bearing capacity and strength.

Plate, sheet and roll refractory materials
The slab and sheet form is very convenient for cladding the walls of the room in which there is a stove, fireplace or cast iron heating boiler. The most popular protective materials used for wall cladding are:
- Fireproof boards and cardboards based on pressed asbestos and glass fibers. The cheapest and most accessible material can withstand heating up to 700°C. The average fire protection is 30 minutes of open flame;
- Vermiculite boards have heat resistance up to 800-900°C, but at the same time they are chemically inert and do not decompose under the influence of moisture and organic solvents. Vermiculite cardboard or a plate can be used to protect the bathhouse;

- Minerite fire-resistant boards and sheets are popular due to their successful combination of fire-resistant and mechanical properties. White cement is used as the matrix of the refractory material;
- Magnesite sheets are characterized by high resistance to high temperatures and aggressive substances;
- Rolled materials made of fire-resistant basalt fiber, with a sprayed heat-reflecting coating of aluminum, can withstand heating up to 900°C. Lightweight and flexible fire-resistant fabric is ideal for shielding apartment wood-burning fireplaces and stoves;
- Porcelain and terracotta tiles. They have good fire-resistant qualities and allow water vapor to pass through well. The slabs are easy to wash, clean from soot and dirt, and do not age over decades of intense heating, so they are often used as thermal protection for walls and floors in bathhouses and boiler rooms.

For your information! Although sheet metal is not technically a fireproof material, stainless or clad steel makes the most effective fire-retardant coating for walls and floors adjacent to fireplaces and stoves.

Of all the listed means, steel has the highest coefficient of heat reflection and is not afraid of temperature changes, therefore it is often used as heat shields for stoves, fireplaces, and boilers.

Not all fire-resistant materials are equally suitable for cladding the walls of a room. For example, thermal insulation boards made from pressed basalt fiber cannot be used. In the production of certain brands of basalt slabs, formaldehyde resins are used. Under the influence of thermal radiation, the surface of the refractory cladding can heat up to 300°C, which leads to intense release of toxic and noxious substances.
Fireproof materials and methods of their use
Asbestos
- a common fireproof material that can withstand prolonged heating up to 450-500 °C. At the same time, it almost does not lose its strength. Asbestos is a material that conducts heat poorly.
It is produced in different forms, including in the form of sheets. Widely used where furnaces are used, for thermal insulation of objects prone to fire, for the construction of fire-resistant walls and ceilings, etc.

Steel is widely used in furnace production
. It is used in different forms (angle, channel, wire, etc.). You can’t do without sheet steel either. Thus, elements of furnaces are made from it, sheets of metal are laid in front of the furnace doors, and it is also used for ovens. In the latter case, the steel must be clean, absolutely free from rust.
Classification of furnace refractories
GOSTs and specifications for the production of refractories classify materials according to their chemical basis, the most widely used:
- Silica refractories are made from quartz and high-purity rocks with a high content of silicon oxide. The most famous representative of refractory materials is the Dinas brand with a quartz content of up to 95%;
- Sintered blocks based on aluminum oxide, with an oxide content of 28 to 90%, these include furnace fireclay and mullite fused blocks. Such materials are used for combustion chambers of fossil fuel stoves;
- Magnesia refractories made by sintering metal oxides at very high temperatures.
Important! Quartz and magnesia refractory materials are designed to withstand very high temperatures. Some brands are able to withstand heating up to almost 2000°C for many months in an aggressive environment.

But they are practically not used in household stoves and fireplaces. The reason is quite simple - despite high mechanical strength and durability, very heavy and dense dinases and mullites cannot withstand sudden temperature changes. When starting up an industrial furnace, heating to operating temperature is often performed at a rate of no more than 1°C per hour. Otherwise, internal thermal stresses split the refractory blocks with many cracks. Therefore, such materials are practically unsuitable for domestic purposes.

The exception is certain brands of highly porous fireclay. For household brick kilns, the industry produces special lightweight fireclay fireclay, which absorbs masonry mortars based on clay and cement well.

Industrial refractory powder or scrap is added to fatty clays to increase the heat resistance of pipe coatings and concrete structures. Before the advent of fire-resistant impregnations, powdered rocks with a high content of silicon and magnesium were added to clay for fire-retardant coatings on stove pipes and the bases of wooden log houses and buildings. Such clay not only increased fire resistance, but was also an effective preservative. Pine and oak piles and subfloors with similar coating stood on the ground for 20-30 years without signs of damage by rot and insects.
OLM production
The production of refractory materials begins with the preparation of raw materials. Often workers manually pick out contaminants and impurities from it. Next, the raw materials are crushed and sifted. Then the powder and additives are mixed in strictly defined dosages. The mixture is formatted, dried under natural or special conditions, and fired.
You should understand! OLM are made from natural and artificial raw materials. The most compatible chemical and mineral substances are selected. The structure, density, porosity and strength of the required parameters are formed using a specific technology.

Fire-resistant products differ according to the types of raw materials:
- Organic components. Such products are made from mineral raw materials and are able to withstand significant temperatures. But not all types. For example, expanded polystyrene is characterized by a low resistance to heat and fire, but it can be used to make a stove or fireplace with low heat.
- Inorganic components. This is the largest group of products, the range of fire resistance of which is large. The category includes mineral and basalt slabs, fiberglass, cellular concrete, vermiculite, honeycomb plastic, perlite. The cost of such products is not high - from 300 rubles per 1 m2.
- Composite compositions. This group includes asbestos-based products: asbestos-lime and asbestos-cement materials. This also includes foamed silica products and some others.
Installation Tips
Minerite slabs can be fastened with screws; To increase reliability, 2 plates are used. In this case, the mineralite sheet should not fit tightly to the insulated surface. An air gap is left, since this material is subject to thermal deformation and increases in size. Or a mineralite sheet is attached to a heat-resistant substrate, which increases the effectiveness of thermal protection.

Steel plates inside the protective screen are connected with heat-resistant materials, for example, heat-resistant mastic, stable at temperatures exceeding 1100 ° C, heat-resistant glue or sealant. On the market, along with side ones, they offer frontal protective screens. They are attached to the floor near the stove. Sometimes, instead of metal screens, walls are built of fireclay bricks, which separate the furnace body from the space of the room.

Refractories in the form of plates and sheets are very technologically advanced for thermal insulation of premises. So, fire-resistant drywall is attached with screws or glue.
To work with fireclay bricks, use solutions based on light clays with a small addition of sand. Fireclay clays are reliable and durable in use; they hold masonry together well.
At the same time, professional stove makers use special heat-resistant adhesives for laying fireclay refractories, which are characterized by low shrinkage and the formation of thin seams. All this also works to increase the strength and durability of the structure.