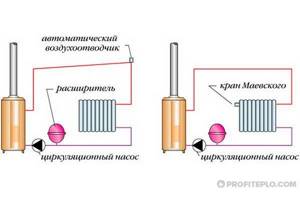
To remove air pockets from heating systems, manually controlled devices are traditionally used - drain valves, Mayevsky taps. Also widely used is an automatic air vent, which vents gases accumulated in a pipeline with a coolant liquid, without human intervention.
Automatic air vents for heating systems
Design and operating principle
The automatic air valve for heating systems has a simple and reliable design. The hollow metal body is equipped with a connecting pipe, which is located at the bottom or side, depending on the version of the product. In the inner chamber of the device there is a float made of polymer resin. The float is connected by a lever rod to a needle valve that closes the hole in the upper part of the air vent cover.
When removing the plug using a manual valve, you need to control the process in order to shut off the device in time - the air will be completely released when a trickle of coolant flows through the vent. Installing an automatic air vent eliminates the hassle of servicing the heating system.
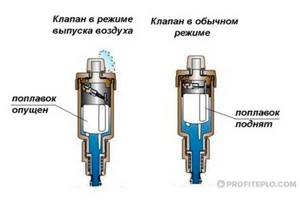
The operating principle of the device is based on the use of gravity - a hollow float is lighter than water, but heavier than air. In the normal state, the air extractor is filled with coolant, due to which the float is in the upper position, pressing the needle valve. Over time, the coolant is displaced from the internal chamber of the device by accumulating gas.
As a result, the float falls down under the influence of gravity, opening the valve slightly. The accumulated air under the pressure of the liquid in the heating system comes out through the hole in the drain body, and the chamber is again filled with coolant, which raises the float, automatically closing the valve.
Float ventilators serve to remove air pockets and also help speed up the draining of coolant from the system during maintenance or repair work. Due to a decrease in the coolant level in the circuit, the valves automatically open, and the air entering through them causes the liquid to drain faster.
Reasons for airing the system
Air in the heating circuit negatively affects the function and durability of the system. Oxygen reacts with steel and causes corrosion. Air locks interfere with the normal movement of the coolant, blocking the heating of the upper part of the radiators or entire heating devices. The presence of air bubbles in the coolant leads to premature wear of the moving parts of circulation pumps.
Air-filled heating system
There are several reasons for the formation of air jams
:
- Using water from a water supply system as a coolant that has not undergone special treatment to remove dissolved air. When heated, gases leave the liquid medium and accumulate at the upper points of the pipeline and batteries.
- Excessively fast filling of the system with coolant or its supply is not from the lowest point. In such a situation, the liquid does not have time to displace air from all corners of the installed system.
- Loss of system tightness due to installation errors or damage to elements.
- The use of polymer pipes that do not have a barrier coating, which prevents the penetration of oxygen molecules into the coolant.
- Errors when developing a project or arranging a system (incorrectly chosen angle of inclination of pipes, etc.).
- Air entering the system during repairs that require dismantling circuit elements.
Note! If an air lock regularly forms in one of the sections of the pipeline and it is necessary to increase the pressure in the system in order to move it to the air vent, it is recommended to install an additional automatic air bleeder in the problem area.
How to remove excess air from a battery
Before you bleed air from the heating system, you need to thoroughly understand the features of this procedure and prepare all the necessary tools and materials.
Let's look at how to remove air from the heating system in more detail. For this work, you will need a special key with which you can open the air valve on the radiator. A radiator wrench is best. It is sold at any hardware store. If a modern battery is installed, you can take a simple screwdriver. It is also necessary to prepare a container into which the coolant will be drained. And also have a couple of rags nearby in case of unexpected situations. The algorithm for how to properly bleed air from the heating system is given below:
Inspect the battery and find a small valve (or Mayevsky tap, as it is most often called). Install it at the top of the radiator. Sometimes there are several such devices. But often they get by with just one valve. Turn off the tap until you hear air hissing.
You must unscrew it carefully and smoothly. Place a container under the valve.
You need to wait until all the accumulated air comes out. When the water comes out in a thin stream and stops bubbling, it means that the air has left the system.
Some experts advise draining about 2-3 buckets of water after water without gases begins to flow. This is done for reinsurance so that you don’t have to perform similar operations again. Turn the tap back on.
In addition to Mayevsky taps, automated air vents are often used for heating systems, which bleed off excess air on their own. Such automatic units are compact and reliable. But at the same time you need to be extremely careful. After all, the valve operates without supervision. And the slightest violation in the process can cause flooding of the attic or riser.
Some nuances
There are situations when craftsmen, when installing a heating system, do not install special valves to release excess air.
Let's look at how to bleed air from a heating battery in this case. To work, you will need an adjustable or gas wrench. Use it to unscrew the plug. This needs to be done very slowly. Sometimes the plug won't come off. Most often this happens if the battery is cast iron. In this case, you need to apply a special lubricant to the threads and try again after some time. When the plug is unscrewed, the same algorithm of actions is performed as with a regular tap. When the plug is screwed into place, you must remember to wrap either FUM tape or flax around the thread. This will avoid leaks and make the connection tight.
If air has accumulated in the heating system of a private house, the water will have to be drained using an expansion tank.
This container is always located at the highest point of the heating system. When the water is drained, you need to wait a little and then unscrew the tap on the expansion tank. Usually, when the battery temperature rises, the plug comes out on its own. If such actions are unsuccessful, then the water in the circuit should be brought to a boil. In this case, the plug will definitely come out.
How often should I bleed?
Knowing how to bleed air from a heating system can prevent and solve many problems.
But how often should such a procedure be carried out for preventive purposes? As a rule, this should be done at the beginning of the heating season. Twice is enough (the first time for checking, the second for control). Of course, if the system has defects or is faulty, then the number of descents may be greater. If the apartment has aluminum radiators. then before starting the system it is necessary to drain the water. This will help increase battery life significantly.
Types of automatic air vents
Depending on the manufacturing option, the automatic float air vent can be straight, angular or radiator. Models differ in appearance and installation location, but the principle of air bleed is the same.
Devices with straight connection
A straight air vent is the most popular version of the device, since it is suitable for installation on the upper ends of vertical risers, on underfloor heating manifolds, as part of a safety group, on circulation pumps. Using a tee, it can be cut into a problem section of the pipeline if a small slope angle provokes the occurrence of air pockets.
Design of a direct automatic air vent with a pipe
Radiator and corner models
The corner air vent is designed for installation in hard-to-reach places. For example, due to the pipe located on the side of the housing, the device can be connected to the threaded end of a horizontal pipeline of a dead-end branch of the heating system. If necessary, corner automatic air vents in the heating system can be used instead of straight ones.
Instead of a Mayevsky manual tap, standard corner automatic drain valves can be installed on radiators to remove frequently occurring air pockets from radiators. However, a more rational approach is to use special radiator automatic air vents. This model also has an angular design, but differs from the standard one in its threaded design - it is suitable for connecting the device directly to the radiator, without using an adapter.
Technical specifications
Air vents for heating systems operating in automatic mode have different connecting diameters. Russian heating systems use devices with 1/2” and 3/4” threaded connections. The most common thread is 1/2”, which is also known as DN15 (connecting size is 15 mm).
The following characteristics are also taken into account when choosing:
:
- operating pressure (standard 10 atm, there are models with an indicator of 16 atm);
- operating temperature of the environment (standard up to 110-120°C);
- type of threaded connection - external or internal thread.
Pay attention to the case material. Reliable devices are made from high-quality plumbing brass. Silumin products are characterized by increased fragility.

Technical data of automatic air vent
For a house with an autonomous heating supply, any heating system air bleeder with the required type of thread is suitable. It is more difficult to select a device for radiators connected to the central heating network - it is important to check with the housing department or other organization responsible for the house about the operating parameters of the system.
Where does the air in the system come from?
Practice shows that it is impossible to ideally isolate a water heating network from the external environment. Air penetrates the coolant in various ways and gradually accumulates in certain places - the upper corners of the batteries, turns of highways and highest points. By the way, the latter should be equipped with automatic bleed valves shown in the photo (air vents).

Types of automatic air vents
Air enters the heating system in the following ways:
- Along with water. It's no secret that most homeowners replenish the lack of coolant directly from the water supply. And from there comes water saturated with dissolved oxygen.
- As a result of chemical reactions. Again, water that is not properly demineralized reacts with the metal and aluminum alloy of the radiators, releasing oxygen.
- The pipeline network of a private house was initially designed or installed with errors - there are no slopes and loops are made that face upward and are not equipped with automatic valves. It is difficult to remove air accumulations from such places even at the stage of filling with coolant.
- A small amount of oxygen penetrates the walls of plastic pipes, despite the special layer (oxygen barrier).
- As a result of repairs with dismantling of pipeline fittings and partial or complete drainage of water.
- When microcracks appear in the rubber membrane of the expansion tank.
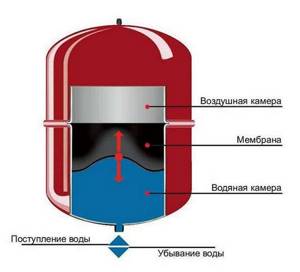
When cracks occur in the membrane, gas mixes with water
Note. Water taken from wells and shallow wells is prone to chemical reactions, since it is saturated with active salts of magnesium and calcium.
Also, a situation often arises when, after a long period of inactivity during the off-season, the pressure in a closed heating system decreases due to air ingress. Draining it is quite simple: you just need to add a couple of liters of water. A similar effect occurs in open-type systems if you stop the boiler and circulation pump, wait a couple of days and start the heating again. As the liquid cools, it contracts, allowing air to enter the lines.
As for the centralized heat supply systems of apartment buildings, air penetrates into them exclusively along with the coolant or when the network is filled at the beginning of the season. How to deal with this - read below.
Example from practice. It was necessary to remove air pockets from the open heating system every day due to a completely clogged mud trap. A working pump created a vacuum in front of itself and thus drew oxygen into the pipelines through the slightest leaks.
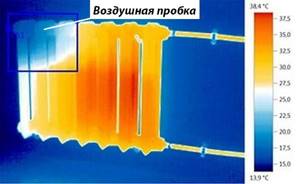
The thermal image shows the area of the heating device where an air bubble usually lingers.
Where are air vents installed?
Given how the automatic air vent works, the device is designed to be installed
:
- At the highest points of heating circuits (top of vertical risers, etc.), where air bubbles from the coolant tend to enter.
- At the ends of dead-end pipeline branches.
- As part of the safety group for boiler piping (primarily solid fuel) in a closed-type heating system. The automatic air vent is mounted on the manifold along with a pressure gauge and an emergency valve. The device helps to bleed air when the water jacket of a boiler unit is filled with coolant or quickly drain water from it when emptying a heat generator cut off from the heating circuit.
- On the circulation pump in order to improve its operation, if the design of the unit provides for the installation of a device for releasing air. Pumping airy coolant impairs the operation of the pump, an air lock causes it to stop, and the impeller and bearings wear out faster. The air vent also removes steam from the overheated coolant.
- On the pipeline of a working system if an area is detected where air constantly accumulates (this happens, in particular, if the angle of inclination of the pipes is not observed).
- For heating devices.
How to remove air from the system
The easiest way, and if the system is made correctly, is to go to the valve, open it, release the air until water flows, and close it. I’ve been doing this in my system for over ten years now and I’m happy with everything.
This is Mayevsky's crane. He should probably be given a Nobel Prize for this invention! You need to operate this valve as follows. We hold the white part with one hand, because it will dangle and water will splash our walls. With our second hand we unscrew the screw in the middle. How do we hold a mug into which the water will be drained? Right! Third hand!

This is an improved faucet (see my complaints about the standard one). Please note, there is no guarantee that after screwing on, the hole will point straight down. But still better than normal. I wonder if the standard crane was invented by the genius Mayevsky, then who invented this crane? But, by the way, Mayevsky is an unknown hero. Someone came up with an idea and off it went.
If the system is gravity-flowing and there are no valves for bleeding air, but there are slopes, then you need to wait until the air comes out on its own through the expansion tank. In this case, there should be no circulation in the system. The system must be cold. You can wait a long time. It could be a day, three days, or a week. It all depends on the length of the lines, the diameter of the pipes and the steepness of the slopes. This expectation is also typical when filling the system from above. In other words, if your system is working, but poorly, and you would like the bubbles to come out on their own, then you need to turn off the boiler, turn off the motor, if there is one, and let the system cool. The heating system has circulation and this circulation will interfere with the exit of air in those areas where the circulation and exit of bubbles go in different directions.
Automatic air vents should be installed at the highest heating points. They should not be included in the security group. Now strange security groups like tridents have appeared. There is a pressure gauge on one tooth, an emergency valve on the other, and an air vent on the third. I consider this trident a stupid and arrogant move to extract extra money from us. The air vent on this trident is superfluous. It was turned on in order to extract extra money from us. There is no air at the outlet of the boiler. Air accumulates at the highest points. But the boiler is not this top point. The boiler is, one might say, a continuation of the return flow. But there is no air in the return.

The air duct is superfluous, but what a beautiful detail!
Is it possible to expel the air with strong water pressure?
Theoretically it is possible, in practice it is very difficult. To do this, you need a powerful pump with high pressure (more than two atmospheres). In this way, air can only be expelled from an open system. Also, there should not be too many branches in the system, or those branches that are not driven through must be closed. Usually with this method the expansion tank overflows heavily. You need a lot of experience and skill to use this method.
Expelling air by draining water
But this is the most popular way to “bleed” gravity systems. A large volume of water is drained from below while simultaneously being poured from above. The bubble is thus shifted, broken and removed from the place where it was stuck. This method is personified by the torment of the Russian people (I don’t know about other peoples) with gravity-fed open heating.
I hope for a successful solution to the problems of air jams in your heating. Dmitry Belkin.
Article created 09/14/2015
What type of radiators require air vents?
Automatic radiator models are primarily intended for aluminum heating devices in which gas formation occurs due to contact of the coolant with the metal. It is also recommended to equip partially bimetallic radiators with an air vent valve. Fully bimetallic batteries have a steel core, which allows the installation of a manual valve.

Types of radiators for heating systems
Steel panel heating devices are equipped with a standard Mayevsky manual tap; a drain valve is mounted on cast iron radiators and tubular steel radiators.
Note! Do not smoke or light a fire near an aluminum battery equipped with an automatic valve for releasing gases. The device releases explosive hydrogen generated during a chemical reaction.
What and how to bleed air from a heating radiator
In order to control the gas contamination of the system both in an apartment and in a private house, use a manual or automatic air release valve. They should be discussed in more detail.
- Automatic air valve;
- Air separator;
- Mayevsky crane.
The automatic air valve is capable of independently releasing air that has accumulated in the radiator. It consists of a brass body, float, articulated arm and valve. A special cap protects against leakage, and the protection located under the spring protects against the ingress of external contaminants.
The system works on the following principle:
- While there is no air, the float keeps the valve closed;
- As gas accumulates, the float begins to descend and gradually open the valve;
- The accumulation of air leaves the compartments, and the system returns to its original state.
It is important to note the fact that all automatic versions are equipped with connectors that are suitable for a screwdriver or octagonal keys. Thanks to this shape, you can open the valve even in manual mode if the automatic mode suddenly breaks down
As for the air separator, this system is a little more complicated. The principle of its operation is to absorb air, turn it into bubbles and remove it out. Most often, separators are combined with sludge, which is capable of trapping dirt, sand or rust. If we talk about the design, it is presented in the form of a metal cylinder, which includes an air vent at the top and a valve at the bottom, which serves to discharge foreign contaminants. Inside such an installation there is a mesh that creates a vortex flow.
The same method is used when there is a water circuit that is connected to heating. The release in the water supply is carried out as a bleed. That is, a stream of air or water with impurities can be released through the bleeder.
Installation principles
The automatic air release device is installed vertically - for both straight and corner models, the cap covering the outlet is directed upward. A ball valve or shut-off valve must be installed in the pipeline before the drain valve.
Attention! An exception is the air vent in the boiler safety group - there should be no shut-off valves between this unit and the boiler pipe.
A shut-off check valve allows you to clean the air vent or replace a faulty device without draining all the coolant from the circuit. The automatic air vent with a check valve is easy to use.
When installing an automatic Mayevsky crane, use a wrench rather than an adjustable wrench to control the tightening force of the fasteners. In this case, you should not hold the device by the body, so as not to break it. Hold the air vent by the hexagon under the cylindrical chamber.
Where does air constantly come from in the heating system?
This question is asked quite often and I don’t know the exact answer to it. Just guesses.
Air can be taken from the water itself, in which it is somehow present. If there is a lot of water, then there will be a lot of air. After freshly filling the heating with water, air is actively released for several months.
Air can collect in dead ends, such as closed expansion tanks, and escape gradually. Through the same water. This process is even longer. Hang closed expansion tanks upside down, as I described in the article about open and closed heating systems.
If you have a special air trap in the form of a vertical pipe with an automatic air vent at the end, then this can also be a source of bubbles. The fact is that automatic air vents often “freeze” and stop venting air. Then the tube is filled with air and the bubbles accumulated in the tube are torn off from below by the air flow and carried into the system. In this case, I say that bubbles begin to circulate throughout the system.
If you have an exceptionally strong circulator installed and there is a small hole in the system, then I think air may be sucked into the hole due to the Venturi effect. I have observed this many times in a water supply system, when there is a hole from which water does not flow, but into which air is sucked in by the flow of water. That is, if you turn off the water, water flows out of the hole. And if you open the water at the end, the water stops flowing from the hole. But in reality, I have never seen this in heating systems. In heating systems, the water speed is not so high. But this does not mean that this can never happen.
Personally, in my heating system, the air stops bothering me about six months after freshly filling the heating with water. I don't have automatic air vents. All valves are manual only. But my system is small and my house is small.
Tips and tricks
As you know, the more complex the equipment, the higher its cost, while such a device is less reliable. Therefore, in order for the hydrofloor to work properly, you need to buy and install high-quality components.
Today there is a huge range of kits for installing water floors on the market. When choosing, you should carefully read their characteristics and features.
You can use a mechanically driven device, which is reasonably priced. In addition, the operation has been proven by many years of practice, so it rarely breaks down. Devices with a sulfur drive are more expensive, and there are more elements that can fail in this design.

When choosing a device for bleeding air, experts recommend paying attention to Mayevsky taps - they are reliable, durable and do not need adjustment.
Automatic devices have a more complex design and are more expensive. In addition, they become unusable when dirty.
As you can see, air locks lead to malfunctions, but this problem is easy to solve. The main thing is to bleed the air from the pipeline in time, and this must be done correctly and regularly.
Causes of air
The main reason why water circuits become airy is violations during the preparation of the project; during installation work; due to the use of the floor.
The accumulation of air masses in the coil is caused by:
- Inaccurate calculation of thermal load;
- Errors made when calculating the size and number of loops, as well as the diameter of the pipes;
- Incorrect selection of pump, safety and control components;
- Laying a highway with a large number of differences in height;
- Not high quality material;
- Poor installation - lack of tightness of joints and threaded connections;
- Violations of the rules when the floor is first launched;
- Failure to comply with the temperature level during operation;
- Depressurization of the pipeline due to a breakdown or defect;
- Impaired fluid circulation in the circuit, which is caused by a decrease in pressure due to a pump malfunction;
- Breakdown of the automatic air vent, as well as the safety and shut-off valve;
- The release of gases when heating the coolant contained in it.
Important! Before starting the device for the first time, you should remove air from the heated floor circuits.
How to prevent air locks from occurring?
The main disadvantage of water floors is the formation of air pockets, otherwise they have excellent performance characteristics and are easy to use.
Even despite the correct installation work, the water system can become airborne during operation. To prevent this, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Conduct regular preventive inspections of the structure for defects and leaks;
- monitor the level of temperature and pressure of the coolant, since sudden jumps lead to blockage of pipes;
- periodically pump air in the pump housing and manifold;
- if you cannot service the device or replace faulty equipment yourself, you should invite specialists;
- install the circulation pump only for water supply, this will prevent air from entering the pipeline due to the fault of the pump;
- install a separator on the return hose in front of the manifold, with its help it will be possible to expel air;
- the coolant should not be drained from the hydrofloor pipeline, since small air blockages can be easily removed using a separator or manifold valves;
- To set up the collector, it is better to invite a specialist.
For your information! If a circulation pump is used, it is recommended to connect it to an uninterruptible power supply, in which case the water flow in the floor loops will remain unchanged.
What is needed for the air valve to work properly?

With a properly functioning system, the smell of the sewer does not enter the apartments, since the water in the bend of the siphon interferes with the movement of sewer gases. This phenomenon is called water lock. But if the water seal breaks, the pressure will change sharply, push out the water, and gases will penetrate into the room.
An air valve is a device that neutralizes possible pressure drops in pipes. For it to work properly, you need to choose a suitable model for the main riser and install it correctly.
What is an air valve for?
In multi-storey buildings, the riser is placed on the roof - this is considered a proven and simple method of ventilation. However, the installation of pipes is often done incorrectly, and the system does not fulfill its tasks: gases accumulating in the sewer system do not escape outside, but enter the living space.
Returning along the riser, they disrupt the pressure level in the pipes, while strange sounds are heard in the rooms, and when the water seal breaks, a putrid smell of hydrogen sulfide appears. In the worst case, siphons break and foul-smelling slurry rushes out.
Note! Sewage gases are dangerous to human health because they contain methane, bacteria, fungal spores and various microorganisms.
And the air valve, which is correctly called an aerator, creates a barrier that prevents sewer gases from entering the apartment. When the pressure in the pipes increases, the valve blocks the system, and when the pressure decreases, it automatically removes the valve.
It neutralizes violent processes in the pipeline and protects apartments from sewer odors, dirty wastewater, and also removes strange sounds.
Operating principle
To understand the principle of operation of the aerator, you need to know its structure. Air valves, differing in the fastening mechanism, have the same design:
- the case is made of hard polymers, sealed, the top cover is removable so that the device can be inspected and cleaned, there is a rubber gasket for a tight fit of the cover;
- an inlet on the housing through which air is supplied;
- a valve equipped with an opening and closing mechanism - a membrane or a single-acting rod.
We recommend that you read: Vacuum valve for sewage systems
When the pressure in the pipes is normal (equal to or greater than atmospheric pressure), it keeps the valve closed, pressing it from the inside so that sewer gases do not enter the apartment.
When the water descends, a vacuum occurs (pressure below atmospheric pressure), the valve opens, letting air in, and the air equalizes the pressure. After this, the valve on the aerator closes automatically.
Classification of air valves
There are several types of aerators, depending on the characteristics of the work, the diameter of the pipe and the method of fastening.
According to the principle of operation, the gradation is as follows:
- automatic aerator copes with low water pressure and small volumes of air, suitable for small private buildings;
- kinetic works only at low pressures - it is designed to prevent the accumulation of a large volume of air during the draining process when the system is filled with water;
- combined combines the capabilities of automatic and kinetic.
The pipeline is laid both horizontally and vertically, and in addition, the pipes have different diameters. When choosing an aerator, you need to consider these nuances:
- the air intake valve has a diameter of 20 cm, is equipped with a filter that does not allow solid particles from the water into the system, but is placed in front of the horizontal pipeline pump;
- ball is designed for pipes with a small diameter running horizontally;
- The wafer aerator is light and compact, installed in vertical and horizontal pipelines, available in corner and pass-through types;
- the return one is intended for large-diameter pipes, it can be simple (for systems protected from water hammer) and shockless (with a damper).
Note! Large diameter air valves often break because their parts hit each other violently during operation. And to avoid this, a damper must be installed on the valve - a special muffler that dampens water hammer.
And according to the method of fastening, aerators are divided into:
- welding - for aggressive environments, this method is not used in residential premises;
- coupling - for pipes with a small diameter (equipped with a check valve, which is secured with a threaded coupling);
- Wafer valves do not have a fastening element; they are fixed between flanges in the pipeline (for a small sewer system).
Features of the location of the air valve
The place where the aerator is mounted may vary when installed in private residential buildings and apartments in apartment buildings. But in both cases it is important to comply with the necessary general conditions:
- install the device in a section of the pipe where the membrane will be protected from dirt, which interferes with the seal and reduces the efficiency of the valve;
- installing the aerator in places of free air circulation is an important condition for normal functioning;
- the operation of the aerator is accompanied by sounds, some valves “grunt”, and therefore the installation location needs to be somewhere where it will not irritate the ears.
Installation location of the aerator in apartments
In apartments, air valves are installed on any section of the pipeline: a tee is built into the system, a vertical pipe is placed on it, and a valve is placed on it. But it is better to do this 20-30 cm above the axis of the main sewer pipe so that the aerator does not become clogged.
Aerators in a private house
In private houses, the situation is different: an autonomous treatment station is made unventilated - a drain pipe is led into the attic, and an air valve is mounted on top of it, but it is important that this attic is not residential and is heated (if the aerator freezes, its membrane will lose its tightness and the sewer will not be able to retain the smell).
If two families live in a private house, the valve can be installed on an auxiliary riser, but at least one of them (auxiliary or main) must be led to the roof.











