Heat exchanger and its types
The heat exchanger works as an intermediary device between two environments that have different temperatures. There are devices of regenerative and recuperative types, differing in their operating principles.
Regenerative heat exchangers have one working surface, with which liquid media come into contact in turn. Recuperative devices have a wall made of heat-conducting material that separates moving media from each other. Devices of this type have become widespread in industry.
Types of recuperative heat exchangers:
- Plate - prefabricated modifications from connected modular plates with adhesive-free heat-resistant gaskets between them (the most popular option);
- Shell and tube - welded or brazed structures made of pipes forming a lattice;
- Twisted - equipped with concentric coils, the coolant is directed through a spiral pipe and the interpipe space;
- Spiral - metal structures, made of thin metal sheets rolled into a kind of spiral;
- With water or air operating principle.
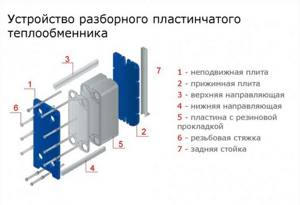
Design
The design elements of a plate heat exchanger include:
- two plates (fixed and pressure);
- inlet and outlet pipes with connections of different types;
- a set of hermetically connected plates, guides, threaded hardware;
- stand for installation in a heating system.
The main working element of the design is plates made of inert materials for transferring energy between coolants. Made by stamping, they are resistant to corrosion and any aggressive environment.
When assembled, the heat exchanger consists of plates tightly (hermetically) adjacent to each other. At their junction, channels (slits) are formed. The thickness of the plates varies from 0.4 to 1 mm. They do not differ in shape and are made of stainless steel, less often of titanium and other expensive alloys. The material requirements are determined by the tasks for which the heat exchanger is intended.
Rubber or polymer composites are most often used as an insulating material. When choosing, you should take into account the severity of operating conditions, temperature range, and type of working environment.
Recommended types of polymers depending on the characteristics of the active media:
- water and glycol – EPDM;
- oil and oil-containing coolants – Nitril;
- high temperature environment, steam – Viton.
Plates and channel types
The most important components in heat exchangers are plates, thanks to which an effective heat exchange process is carried out. They are produced with different corrugation angles (30° and 60°), which makes it possible to more accurately select the layout of heat exchangers for each specific task, taking into account the cost, size and hydraulic resistance requirements of the customer. Two types of plates can form three types of channels between themselves:
- TL is a rigid channel formed by two plates with groove angles of 30°. It has the best heat transfer properties (high heat transfer coefficient), but also the highest hydraulic resistance of the three.
- TK is a soft channel formed by two plates with groove angles of 60°. It has weaker heat transfer properties (low heat transfer coefficient), but also the lowest hydraulic resistance of the three.
- TM is the middle channel formed by one plate with a corrugation angle of 30° and one plate with a corrugation angle of 60°. It is distinguished by intermediate (between hard and soft channels) heat transfer properties (heat transfer coefficient) and hydraulic resistance.
Main types of plate heat exchangers, their purpose and advantages:
Collapsible (the design consists of a package of plates and rubber seals):
- low production and installation costs;
- adjustable, easily customizable performance;
- simple, cheap operation, quick repair;
- reliability, minimal downtime;
- low energy intensity;
- possibility of processing.
Scope of application of a plate heat exchanger with a collapsible design: heating systems, swimming pools, refrigeration and climate control equipment, hot water supply, heating stations.
Brazed (solid design with soldered plates, no rubber gaskets):
- compactness and low cost;
- optimal performance/cost ratio;
- fast and cheap installation and assembly;
- reliability and reliability.

Scope of application of brazed structures: refrigeration units, compressors and turbine units, air conditioners and fans, industrial installations for various purposes.
Welded and semi-welded (connected using welds):
- simple compact design without sealing gaskets;
- adjustable flow;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- maximum temperature range;
- permissible pressure up to 4 MPa, temperature up to 300 °C;
- ease of installation;
- resistance to abrasive and aggressive substances;
- reliability and long service life.

Scope of application of welded and semi-welded units: food, chemical and pharmaceutical industries, air conditioning and refrigeration systems, including in industry and medicine, operation of heat pumps and hot water supply systems.
Plate heat exchangers - technical characteristics
The plate heat exchanger has fairly high power ratings. The coolant temperature mode can reach 180 degrees. Reliable plate heat exchangers are widely used in the fields of heating, energy, food industry, climate control, refrigeration and ventilation equipment.
The main characteristics of the unit will vary depending on the type of design and model:
| Soldered | Collapsible | Semi-welded | Welded | |
| Highest temperature | 220°C | 200°C | 350°C | 900°C |
| Highest pressure reading | 25 bar | 25 bar | 55 bar | 100 bar |
| Highest power rating | 5 MW | 75 MW | 75 MW | 100 MW |
| Efficiency | 90% | 95% | 85% | 85% |
| Guarantee period | 20 years | 20 years | 10-15 years | 10-15 years |
The standard technical parameters of plate devices include:
- The material of the plates is most often thin sheet steel AISI304 or AISI316, titanium, alloys 254 SMO, Hastelloy (nickel-based).
- The maximum temperature of the coolant for which the plates are designed is 180°C.
- Maximum medium pressure – 25 kgf/sq.cm.
- Heat exchange surface area – 0.1-2100 sq.m.
- The number of plates is 7-10 pieces or more, depending on the scope of application.
When choosing a specific model, it is advisable to take into account the operating conditions - more power requires more plates. Their number determines the performance and beneficial effect of the heat supply or cooling system.
MIT Sealed Plate Heat Exchanger Specifications
| Type | 504 | 513 | 514 | 521 | 522 | 617 |
| Width, mm | 200 | 360 | 360 | 460 | 460 | 337 |
| Height, mm | 480 | 930 | 930 | 1090 | 1090 | 1047 |
| Depth, mm | 200-400 | 250-1000 | 250-1000 | 250-1500 | 250-1500 | 250-1250 |
| Horizontal axis range, mm | 70 | 140 | 140 | 210 | 210 | 150 |
| Vertical axis range, mm | 381 | 640 | 640 | 720 | 720 | 800 |
| Max. Working pressure, bar | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Test pressure, bar | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Weight, kg | 23+0.25n | 98+0.75n | 98+0.75n | 225+1.1n | 225+1.1n | 116+0.91n |
| Connection diameter | 1 1/4″ Threaded | 2″ Threaded or rebated | 2″ Threaded or rebated | 4″ Seam | 4″ Seam | 2 1/2″ Threaded or rebated |
More detailed information on technical characteristics can be found in this catalog
MIT Welded Plate Heat Exchanger Specifications
| Type | VZ-012 | VZ-014 | VZ-020 | VZ-027 | VZ-030 |
| Width, mm | 72 | 77 | 72 | 111 | 95 |
| Height, mm | 186 | 207 | 314 | 311 | 325 |
| Depth, (min-max) | 7+2.3n | 7+2.3n | 7+2.3n | 9+2.4n | 9+1.5n |
| Horizontal axis range, mm | 40 | 42 | 42 | 50 | 39 |
| Vertical axis range, mm | 154 | 172 | 278 | 250 | 269 |
| Max. Working pressure, bar | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Test pressure, bar | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Weight, kg | 0.6+0.044n | 0.7+0.06n | 1.1+0.09n | 1.2+0.013n | 1+0.09n |
More detailed information on technical characteristics can be found in this catalog
Industry Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers
At municipal facilities
Plate heat exchangers help solve a wide range of problems: heating water for hot water supply, boilers and swimming pools, ventilation systems and heated floors. They are often used as part of an independent circuit of a heating system powered by a combined heat and power plant or central heating station. In this case, the temperature should not exceed 180 °C, pressure – 16 kPa.
In the food industry
Heat exchangers as an element of cooling, evaporation and pasteurizing equipment are indispensable in the production of dairy products, sugar, vegetable oils, beer, and alcohol. The most popular modifications in the food industry are dismountable and soldered.
Metallurgy and shipbuilding
Many technological processes in metallurgy are associated with strong heating of structures and units. Heat exchangers cool equipment and fluids, hydraulic lubricants and pickling solutions. In shipbuilding, heat exchangers are used to cool the engine, as part of the heating system and hot water supply.
Oil and gas industry
Heat exchangers are needed to cool hot substances and heat liquids. They are part of network complexes, water treatment systems and low-pressure apparatuses. In oil and gas production, titanium structures with a sheet of up to 0.7 mm and a seal made of NBR or Viton polymers are in demand.
Technical specifications and Questionnaire by industry:
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for the refrigeration industry;
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for energy and oil and gas;
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for heat supply and housing and communal services;
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for the processing industry;
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for marine use;
- Specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for pharmaceuticals;
- Technical specifications for calculating a heat exchanger for mechanical engineering and metallurgy;
Technical advantages of the design
If we compare the technical parameters with shell-and-tube models, we can highlight the following features of collapsible plate structures:
- Increased heat transfer index (3-5 instead of 1);
- The permissible temperature difference of working media is only 1-2% (in shell-and-tube structures 5-10 degrees);
- It is possible to arbitrarily change the surface area by simply adding and removing plates;
- During assembly, welding and rolling are not required due to the collapsible design;
- Easier maintenance, inspection, troubleshooting, convenient access to internal elements, replacement and washing of plates;
- 8 times less time required for disassembly (15 minutes instead of 2 hours);
- Simple and quick replacement of seals (no glue is used);
- Instant leak detection without disassembling the device;
- Non-corrosion and vibration resistant;
- Failure-free operation life before major repairs is 20 years (shell-and-tube models require repairs after 5-10 years);
- Plate units benefit in weight and size;
- No thermal insulation or special foundation is required.
Heat exchanger in chiller
Chiller is a refrigeration machine used to cool water. The process takes place in a double-circuit radiator. Boiling freon is pumped through one - cold - circuit, and a cooled medium is pumped through the other - hot - circuit. The temperature decrease occurs as a result of heat exchange between the coolant and the refrigerant through the metal wall separating their flows.
The intensity of heat transfer is determined by:
* physical characteristics of the liquid - density, viscosity, heat capacity. They are taken into account when calculating the main thermophysical criteria of Prandtl and Nusselt (Pr, Nu)
* the nature of the flow – laminar or turbulent. It is described by the Reynolds number (Re)
* the area of the walls through which heat exchange occurs.
The last parameter has the greatest impact on the efficiency of using the heat exchanger. This influences the choice of its design.
A variety of heat exchange devices are used not only as part of refrigeration machines. They are also part of thermal systems where water-to-water heat exchange is required. That is, heating or cooling one stream by another in various technological processes.
Operating principle and design of a plate heat exchanger
Each of the plates has two holes for the coolant and seal:
- for supplying and discharging heated coolant;
- for hermetic connection of plates and insulation of coolants due to compact seals.
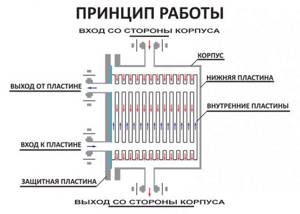
A characteristic feature and advantage of a plate heat exchanger is that the movement of the coolant is accompanied by flow turbulence, which dramatically enhances the exchange of thermal energy. The resistance is minimal, which reduces the formation of scale. Due to repeated and intense heat exchange, the operating efficiency and efficiency of a plate heat exchanger are among the highest.
Consequences of incorrect heat exchanger selection
For long-term trouble-free operation, it is important to choose a model that will be optimal for specific environments, temperature conditions, power and load frequency. Only a specialist can choose the option that meets all the criteria. Contacting professionals guarantees no breakdowns throughout the entire service life of the device. There is no need for frequent servicing and repairs. The correct choice of system eliminates the common problem of glassy scale, which leads to device failure.
Automation and connection
When installing equipment, it is important to consider that the heat exchanger always works as an element of the system. It is not used as a stand-alone device. Together with the heat exchanger, the system uses the following equipment: check valves, shut-off valves (a set of gate valves, dampers), control and measuring devices - pressure gauges, thermometers, circulation pumps and other types of instruments and units.
Appearance of the device
Any heat exchanger has technical characteristics:
- maximum operating temperature, for example 200 °C;
- maximum operating pressure, for example 30 bar;
- test pressure, for example 43 bar.
The country of origin is indicated, a technical passport in the manufacturer’s language, a diagram, contours are indicated. If necessary, the passport can be translated into Russian. The design and operating principle of a heat exchanger from different manufacturers can sometimes be slightly different. But the essence remains the same.
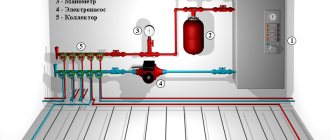
The heat exchanger circuits for heating can be located either vertically or diagonally. This does not affect the principle of operation. The simplest device is a diagonal arrangement. In this case, the heat exchanger must be mounted strictly in a vertical position.
Hot water from the central heating system will flow from top to bottom into the heat exchanger, transferring its heat to the autonomous system through the separation system. At the entrance it will be very hot water, at the exit it will be water with a dropped temperature. In the circuit of an autonomous system, the coolant will flow from bottom to top. At the bottom, the water heats up slightly, and the closer to the top, the stronger the heating will be. Due to such a device, it will be easier for the system to work.
The process of supplying water to the heat exchanger is carried out using forced circulation. The thermal power plant operates on its own pumps. And the autonomous floor heating system in the apartment will operate on its own circulation pump.
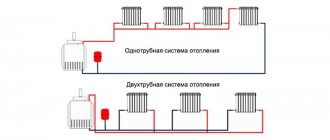
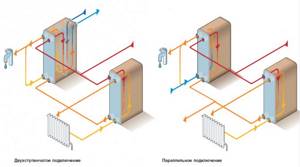
Connection options for a plate heat exchanger, their advantages and disadvantages.
Independent single-stage parallel circuit.
Pros:
- Economical installation, saving space;
- Simplicity of design.
Minuses:
- There is no heating of the cold coolant.
Two-stage mixed scheme.
Pros:
- By heating the incoming coolant with reverse flow, efficiency increases by 40%.
Minuses:
- When designing a hot water supply system, you need to connect two heat exchangers at once, which makes the solution more expensive.
Two-stage sequential circuit.
Pros:
- The network load is stabilized and the efficiency of coolant use increases.
- Costs are reduced by 60% compared to a parallel scheme and by 20-25% compared to a mixed one.
Minuses:
- Impossibility of 100% automation.
Flaws
Plate heat exchangers have practically no disadvantages, but there is one drawback - with poor-quality coolant, they can reduce their productivity relatively quickly. This happens due to rapid contamination of the internal surfaces of the heat exchanger.

Therefore, a clean working environment must be used. This is not always possible, which does not allow the devices to be installed at all sites.
Selection of plate heat exchanger
To choose the right plate heat exchanger, it is necessary to calculate its technical parameters.
The following data is used as a basis:
- - DHW connection diagram;
- — thermal load (power);
- — data on the heating medium:
- inlet temperature (for winter/summer), in °C;
- outlet temperature (for winter/summer), in °C;
- medium consumption (if there is no data on power), in cubic meters. m/hour;
- permissible pressure loss (atm);
- — data on the heated medium:
- input temperature (winter/summer), in °C;
- output temperature (winter/summer), in °C;
- medium consumption (if there is no data on power), in cubic meters. m/hour;
- permissible pressure loss (in atm.);
- power reserve (in %).
Calculation example
Plate heat exchangers belong to individual engineering equipment, which is separately selected, configured and adapted for each object. Tell us the specific technical parameters for your project, and we will immediately calculate what equipment is needed in your case.
To leave us calculation data, fill out the online application form on the website, write or call. Below we provide a list of the main parameters that are needed to calculate a plate heat exchanger.
- Power (load) – the amount of thermal energy required for heating and hot water supply of the facility (measured in Gcal/hour, kcal/hour, kW/hour).
- Temperature graphs - what temperature the heating network gives and takes back, what temperature mark needs to be reached.
You can view these characteristics in the contract with the heating network. There are technical conditions and temperature charts, as well as the power allocated for heating and hot water supply.
Based on the data you provide, we calculate the heat exchanger and inform you about its cost and delivery conditions. We provide a detailed calculation, technical description of the required device, indicating the dimensions and weight of the plate heat exchanger.
Calculation from our company is made using professional clipping software
User manual
Each factory plate heat exchanger must be accompanied by detailed operating instructions containing all the necessary information. Below are some basic provisions relevant to all types of VET.
PHE installation
- The location of the unit must provide easy access to the main components for maintenance.
- The fastening of supply and discharge lines must be rigid and airtight.
- The heat exchanger should be installed on a strictly horizontal concrete or metal base with sufficient load-bearing capacity.
Commissioning works
- Before starting the unit, it is necessary to check its tightness according to the recommendations given in the technical data sheet of the product.
- During the initial startup of the installation, the rate of temperature increase should not exceed 250 C/h, and the pressure in the system should not exceed 10 MPa/min.
- The procedure and scope of commissioning work must clearly comply with the list given in the unit’s passport.
Unit operation
- When using PHE, it is not allowed to exceed the temperature and pressure of the working medium. Overheating or increased pressure can lead to serious damage or complete failure of the unit.
- To ensure intensive heat exchange between working media and increase the efficiency of the installation, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of cleaning working media from mechanical impurities and harmful chemical compounds.
- Regular maintenance and timely replacement of damaged elements will significantly extend the service life of the device and increase its performance.
Advantages of ordering a plate heat exchanger from us:
- Accurate calculation of the heat exchanger. We select adapted equipment for your project.
- Objective price guarantee. By optimizing the power of equipment, we do not inflate the price.
- We process applications promptly.
- We organize the production, delivery and connection of plate heat exchangers on favorable terms.
- We offer wholesale prices through direct cooperation with leading manufacturers.
- We bear full responsibility for meeting deadlines and quality of equipment.
Call us, we will help you solve your problem, calculate and design the device, organize delivery and installation. We offer Russian-made plate heat exchangers with high efficiency and favorable technical parameters and characteristics. The catalog provides approximate descriptions of models, purposes and operating features of plate-type heat exchangers.