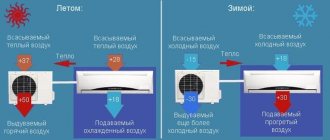
Air conditioner characteristics
In the technical documentation, manufacturers indicate several power indicators: when operating for cooling, heating and, in fact, electricity consumption. The first two characteristics are not taken into account when calculating how much the air conditioner will consume; on their basis, a suitable unit is selected so that it can cope with maintaining the microclimate in a room of a given area and volume.
The air conditioner consumes approximately 3 times less cooling power. This figure is exactly what is used when calculating energy consumption. On average, it is not 2-3 kilowatts, but only 0.8, which is less than an iron or electric kettle, but more than a computer or plasma TV.
Estimated cost of duct air conditioners.
The price of a set consisting of outdoor and indoor units of a ducted air conditioner directly depends on the air pressure it provides, cooling power, manufacturer, and additional functions. The price for low-pressure air conditioners starts from 25,000 rubles. and higher, for medium-pressure - from 35,000 rubles, for high-pressure - from 120,000 rubles. Prices for inverter duct air conditioners, which can be smoothly and accurately adjusted, are one and a half to two times higher than for non-inverter ones. If they have automatic modes, the price also increases. The price for design, purchase, and installation of a high-pressure inverter ducted air conditioner can reach up to 1,000,000 rubles.
What to consider
The climate control system has a heat pump. It pumps warm air from indoors to outdoors. To operate, it needs to use the right amount of electrical energy. Each split system has two indicators: consuming and cooling-heating power.
By looking at the technical data sheet of a particular split system model, you can see the power characteristics indicated by the manufacturer for cooling, heating, and the electricity consumption of the device itself. The first two indicators are not taken into account when calculating the electricity consumption of an air conditioner. Based on their indicators, they choose the appropriate model for a particular room.
Let's look at it in detail:
- consumer power - a value that shows the amount of energy consumed by equipment from the electrical network;
- cooling-heating power is a value indicating the amount of useful work performed.
Both of these indicators are calculated in Watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). The indicators of generated heat or cold are designated in the technical data sheet as COP and EER, respectively. The readings are inversely proportional to each other. The higher the final figure, the lower the electricity consumption, and vice versa.
Energy Efficiency in Cooling Mode (EER)
| Energy class | Index |
| A | 3.20 EER |
| B | 3.20 EER 3.00 |
| C | 3.00 EER 2.80 |
| D | 2.80 EER 2.60 |
| E | 2.60 EER 2.40 |
| F | 2.40 EER 2.20 |
| G | 2.20 EER |
Energy efficiency in heating mode (COP)
| Energy class | Index |
| A | 3.60 COP |
| B | 3.60 COP 3.40 |
| C | 3.40 COP 3.20 |
| D | 3.20 COP 2.80 |
| E | 2.80 COP 2.60 |
| F | 2.60 COP 2.40 |
| G | 2.40 COP |
You need to understand that the indicators indicated by the manufacturer may differ from those that actually exist. Calculations are carried out at the factory with doors and windows closed, in contrast to apartment conditions, which are not entirely ideal.
The positive point in this matter is that any equipment will consume approximately 3 times less electricity than it produces, since electrical consumption is only needed for refrigerant circulation.
Types and types of air conditioners
Selecting an air conditioner for a home, office or industrial enterprise begins with choosing the appropriate type of device. This is important to achieve the desired temperature and extend the life of the device. Main types of air conditioners:
- Wall-mounted split systems – have two blocks and are highly reliable;
- Multi-split systems - several indoor units are combined into a common system, several rooms are cooled at once;
Home multi-split system Source gaudisp.ru
- Mobile air conditioners – not fixed, can be carried;
- Window air conditioners are mounted on the window.
The listed systems relate to household air conditioners - they can be used at home or in a small office. For large premises, other types of air conditioners are used; they are called industrial and commercial.
How much electricity does an air conditioner consume per hour?
There is a formula for calculation: the rated power of the split system divided by the EER coefficient. All this data is indicated in the instruction manual.
EER indicates how many times a device's power consumption is lower than its performance. The coefficient depends on the energy efficiency class. Most modern systems have class A, which corresponds to EER >3.20.
For example, the cold performance of an air conditioner is 2.5 kW, class A. We calculate its consumption per hour: 2.5 / 3.20 = 0.78 kilowatts.
Roughly speaking, a split system spends three times less than it produces. Therefore, to the question of how much an air conditioner consumes, the answer will be as follows:
- “sevens” – 0.65-0.75 kW/h;
- “nines” - about 0.78-0.88 kW/h;
- “twelve” - 0.96-1 kW/h.
Please note that the system does not operate continuously. When it reaches the desired temperature, it will turn off.
If the model is inverter, when the specified parameters are reached, the compressor will reduce speed to a minimum without turning off. Maintaining the temperature requires less energy than full cooling.
Manufacturers of inverter air conditioners claim that their devices consume 40% less electricity than conventional models. Thus, the inverter “nine” consumes approximately 500 W per hour.
Factors of influence
Let's consider several points that directly affect the level of energy consumption of a split system. It is important to understand that we will be talking about inverter devices that can regulate the number of compressor revolutions. Non-inverter models operate stably with maximum energy consumption, therefore the energy consumption is always the same.
Influencing factors:
- Compressor functionality Inverter split units operate continuously without turning off. After the set temperature is reached, the compressor reduces speed to a level sufficient to maintain the desired parameters. The lower the speed, the lower the energy consumption. In this way, an economical operating mode is achieved, which is not available for non-inverter models that operate on-off.
- Temperature difference. The higher the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air, the more electricity will be required to cool the indoor environment.
- Cooling rate. The more you need to cool the air, the higher the energy costs.
- Functional mode. Each mode has a programmed time interval during which it operates. With longer operation, power consumption also increases.
What are the nuances of designing air conditioning systems?
Features of determining network power
In general, the electrical network is designed so that its operation does not require special knowledge. It is enough to follow some rules, the main one of which is to prevent overload.
Important! Failure to comply with the rules for using the electrical network can lead to failure and even fire
It is important to note that the technical characteristics of the outlet and the household appliance differ from each other:
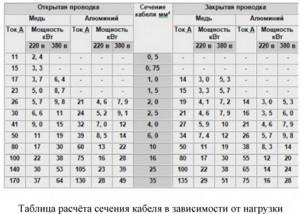
- In sockets, the maximum permissible alternating current is measured in Amperes: in the old housing stock of Russia it is 6 A, in Europe - 10 or 16 A;
- The power of connected devices is measured in Watts.

To calculate, you will need the formula: P = U*I, where:
P - power,
U - voltage in Volts,
I is the current strength in Amperes.
The voltage of a working outlet is 220-230 Volts; the current can be measured with a multimeter.

To determine the current strength in the outlet, you should use a multimeter
Calculation methods and formulas
It is quite logical for a scrupulous user not to trust the numbers obtained from an online calculator. To check the result of calculating the power of the unit, use the simplified methodology offered by refrigeration equipment manufacturers.
So, the required cold performance of a household air conditioner is calculated using the formula:

Explanation of symbols:
- Qtp – heat flow penetrating into the room from the street through building structures (walls, floors and ceilings), kW;
- Ql – heat release from apartment residents, kW;
- Qbp – heat input from household appliances, kW.
It is easy to find out the heat transfer of household electrical appliances - look at the product data sheet and find the characteristics of the electrical power consumed. Almost all of the energy consumed is converted into heat.

The compressor of a home refrigerator converts almost all consumed electricity into heat, but operates in periodic mode
Heat gains from people are determined by regulatory documents:
- 100 Wh from a person at rest;
- 130 Wh - while walking or doing light work;
- 200 W/h - for heavy physical activity.
For calculations, the first value is accepted - 0.1 kW. It remains to determine the amount of heat penetrating from the outside through the walls using the formula:
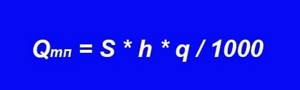
- S – quadrature of the cooled room, m²;
- h – ceiling height, m;
- q – specific thermal characteristic related to the volume of the room, W/m³.
The formula allows you to perform an enlarged calculation of heat inflows through the external fences of a private house or apartment using the specific characteristic q. Its values are taken as follows:
- The room is located on the shady side of the building, the window area does not exceed 2 m², q = 30 W/m³.
- With average illumination and glazing area, a specific characteristic of 35 W/m³ is taken.
- The room is located on the sunny side or has many translucent structures, q = 40 W/m³.
Having determined the heat input from all sources, add up the resulting numbers using the first formula. Compare the results of your manual calculation with those of an online calculator.

A large glass area means an increase in the cooling capacity of the air conditioner.
When it is necessary to take into account the heat input from ventilation air, the cooling capacity of the unit increases by 15-30% depending on the exchange rate. When updating the air environment once per hour, multiply the calculation result by a factor of 1.16-1.2.
Other Important Factors
There are other parameters that affect the waste of electricity when operating a split system.
- Compressor potential (at lower rotation speeds, less energy is consumed). The most profitable are inverter models.
- The actual electricity consumption of the air conditioner will be shown by the temperature difference (outdoors versus indoors). The costs of heating a room in forty-degree frost will be much higher than for cooling a room in the unbearable summer heat.
- Cooling loads in a split system.
- Various additional functions of the device.
Characteristics of the power parameter of split systems
The power of the air conditioning system is calculated for an already cooled room based on the amount of heat influx as a result of adding the thermal power on all sides of its inflow. These are the floor, walls, ventilation, ceiling, lighting.
The rated power of the installed air conditioning device is as close as possible to the optimal power of the system.
The optimal power of the air conditioning device is equated to the amount of heat inflow into an already cooled room on a sunny day; when it is necessary to calculate the maximum number of individuals in the working area, with actively working equipment, and open doorways, it is necessary to take into account all the possible influx of warm air into the room being used.
Ideally, you need to take an air conditioner with an inverter. It can operate over a fairly wide operating range. It is known that the frequency of device starts greatly influences the degree of its wear and the efficiency of the duration of its active operation.
Calculation of air conditioner power by room area
When calculating energy consumption, the area, not the volume, of the building being cooled is taken into account. This is due to the fact that cold air still sinks. Whatever the height of the ceilings, the cooled air will still accumulate near the floor of the room.
The following table is good for calculating the power of an air conditioner:
| sq. m | 16 | 20 | 26 | 35 | 37 | 30 | 52 | 70 | 80 |
| thousand BTU | 5 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 30 |
| kW | 1.6 | 2 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 4 | 5.2 | 7 | 8 |
However, it is necessary to take into account a large number of related factors and coefficients:
- the size of the family or other group of people in the room;
- the amount of heat generated by the people themselves in the room (this depends on the amount and intensity of physical labor, as well as on whether people wear outerwear);
- distance from floor to ceiling;
- the presence of other heat-producing devices and apparatus (TV, computer);
- the amount of heat entering the windows with the light of the sun.
Most online calculators for selecting air conditioner power take these parameters into account.
For example, below are calculations that require knowledge of such parameters as:
- coefficient from 30 to 40 W/cubic. m to take into account the heat generated by the room itself due to the area of the walls, ceiling and floor, as well as depending on the presence of solar radiation;
- the heat generated by the owners of the house is from 0.1 kW to 0.2 kW (for an adult), depending on physical activity.

Let’s try, as an example, to select a cooling unit with the following parameters:
- living area – 25 sq. m;
- ceiling height – 2.55 m;
- family of 3;
- computer and TV in one room;
- The windows face north.
Here are instructions for calculations:
- First, let's calculate the heat release of the room itself using the formula: Area x Height x Internal heat release coefficient of the building. Here's the calculation: 25 x 2.55 x 30 = 1.9 kW.
- Let us further assume that all the inhabitants of the refrigerated space behave calmly and mostly relax at home: 0.1 x 3 = 0.3 kW.
- Now let’s include the heat emission from the computer and TV into the calculations. The PC has a power supply with a nominal power of 0.3 kW, and the TV has a power supply of 0.2 kW. Let's assume that it is quite possible for one of the family members to watch TV and someone else to use the computer: 0.3 + 0.2 = 0.5 kW.
- We add up all the obtained values: 1.9 + 0.3 + 0.5 = 2.7 kW.
How to calculate the power consumption of an air conditioner for a room
You can calculate the power of the air conditioner both for a room and for any household premises yourself.
Let's take a room: area 20 sq. m, ceiling height 3 m, accommodates 1 person, has a computer, TV and refrigerator. The room is sunny, office equipment works alternately.
Calculation:
- Heat inflows into the room are the sum of the walls and ceiling Q1, from the person Q2 and from the equipment that produces heat Q3.
- In the solar room, to determine Q1, q 20x3x40/1000 = 2.4 kW is used. Q2 is assumed to be 0.1 kW in a quiet state. Q3 is determined by the sum of the heat emission of a computer, as the most expensive - 0.3 kW and a refrigerator 30% of the power of 150 W - 0.05 kW. Heat dissipation – 2.4 kW + 0.1 kW + 0.35 kW = 2.85 kW.
- Using Q range (-5~+15)% you need to look for an air conditioner with a cooling capacity of 2.7 - 3.3 kW.
- We select a model of suitable power from the table.
When independently choosing a climate system based on cooling power, you must take into account that the power of the air conditioner may not be in kilowatts, but in units of BTU/hour, this indicator corresponds to the British inch/pound measurement system. You can use a plate that connects the model range with the power of the air conditioner, according to the British and international systems.
| Row | BTU | kW | Row | BTU | kW |
| 7 | 7000 | 2,1 | 36 | 36000 | 10,6 |
| 9 | 9000 | 2,6 | 42 | 42000 | 12,3 |
| 12 | 12000 | 3,5 | 48 | 48000 | 14,0 |
| 18 | 18000 | 5,3 | 54 | 54000 | 15,8 |
| 24 | 24000 | 7,0 | 56 | 56000 | 16,4 |
| 28 | 28000 | 8,2 | 60 | 60000 | 17,6 |
Knowing the cooling capacity, you can always determine how much power the air conditioner consumes in units of measurement.
It is important to choose the right split system, window or floor air conditioner. Excessive power consumption can lead to disruption. Thus, calculations for a small room allow you to select a mobile unit, wall and window air conditioners. Floor-ceiling and duct fggfhfns are used if the area is more than 26 square meters. meters.
How much will summer comfort cost?
If we assume that the start-stop “nine”, which is not particularly economical, will be turned on 8 hours a day, in moderately hot weather, and its power consumption is 0.8 kilowatts, then the daily electricity consumption will be approximately 6.4 kW/hour. Multiplying this number by the average cost of a kilowatt of electricity of 4.32 rubles, we get 28 rubles. In this case, the monthly expense will be 840 rubles (28x30=840).
According to manufacturers, an inverter air conditioner consumes 40% less electricity. This means that it will no longer consume 0.8 kilowatts, but approximately 0.5. At the same time, it will cool in the same way as a start-stop. As for the daily electricity consumption, it will be 17 rubles for 8 hours and 510 rubles per month (17x30=510).
Energy Saving
The user asks a logical question about how to save energy: what can I do to pay less?
Everything will depend on various factors. On average, split systems with a power of two to three and a half kilowatts consume from half to one and a half kilowatts per hour.
Before installing an air conditioner, it is important to analyze the following parameters:
- what is the power consumption of the device, is the outlet designed for these indicators;
- what load will the electrical wiring withstand;
- parameters of meter safety plugs.
To avoid wasting money, you should choose the right device. There is a significant difference in the energy consumption of household, semi-industrial and industrial air conditioners. In addition to connection difficulties, industrial and semi-industrial air conditioners will consume several hundred kilowatts per month. While ordinary household air conditioners can cope with their responsibilities.
Cost of owning an air conditioner and ways to save
So, as we see, owning an air conditioner is not a cheap pleasure, but, in principle, not so expensive, considering what we get in return: coolness and comfort in our rooms during the hot summer months.
In addition, the cost of operating an air conditioner can be optimized in several simple ways:
- You can reduce the costs associated with operating your air conditioner by regularly and thoroughly cleaning the ventilation ducts. In this case, their cross-country ability will be higher, as will the cooling effect, so you will turn on the device less often, which will save on energy bills;
- Another good way to reduce costs is to seal your windows and doors and install blinds that block out strong sunlight. This way, the air-conditioned room will heat up less, which means you will use it less often;
- Another way to save money is to not open windows during the summer season. Unfortunately, many homeowners forget about this, although when the windows are open, the entire cooling efficiency of the rooms is reduced to zero. The rooms can be ventilated in the evening or morning, but during the day (in the heat) it is better not to do this and use only air conditioning;
- Another way to optimize the cost of operating an air conditioner is to slightly increase the temperature in the device’s thermostat. Remember: the lower the temperature on the thermostat, the higher the cost of using the air conditioner;
- If you have several air conditioners in your home, experts advise turning off the fans installed in the rooms while they are running. Thanks to this solution, the air conditioner will cool the rooms more efficiently, and you can save several thousand rubles a year.
Calculation example
Let's say we have a store with an area of 36 square meters. located in the shady side of the building. There are two sellers working, and, let’s say, a couple of buyers are constantly coming and going. It contains:
- one chest freezer Snezh MLP-500 (power consumption 3.24 kW/24 hours!!!);
- one refrigeration cabinet PREMIER SHVUP1TU-1.4K (power consumption 0.982 kW/h);
- TWO refrigerated display cases Cryspi Octava U New 1800 (power consumption of one 0.23 kW/h);
- one refrigerated display case Cryspi Octava 1200 (power consumption 0.2 kW/h).
At the same time, their cooling capacities are as follows:
- Snezh MLP-500 – 0.245 kW;
- PREMIER SHVUP1TU-1.4K – 0.919 kW;
- Cryspi Octava U New 1800 – 0.299 kW;
- Cryspi Octava 1200 – 0.264 kW.
The total cooling capacity of the five devices is 2.026 kW. At 36 sq.m. area will require 3.6 kW of air conditioning cooling power, and for four people another 0.4 kW. Summing up these figures, to provide such a pavilion you will need an air conditioner with a cooling capacity of 6.026 kW, i.e. “twenty-four” (its cooling power will be approximately 7 kW).
This is how the arithmetic turned out - if there was no store with refrigerators in a room with such an area, then an air conditioner of “twelve” power would have managed.
PS Those who are very “bothered” may ask additional questions - like, you need to take into account that in hot weather refrigerators are continuously filled with warm food, or something like the refrigerator compressor works periodically (you can apply its operating coefficient). My opinion is that these are all minor errors that can be ignored.
Saving tips
There are several ways to save energy:
- Choose an inverter type of air conditioner or with an inverter compressor.
- Keep an eye on the filters and heat exchanger; if they are dirty, it takes longer for air to enter the room.
- After use, turn it off and unplug it from the socket (since even in this state it consumes electricity).
- If you don't need it, turn it off.
- Do not open windows and doors so that the converted (cooled or heated) air does not escape into the street.
Popular Features
Possibility of ventilation (fresh air supply)
In fact, only a ducted air conditioner has the ability to ventilate a room, due to its technical features. But most household air conditioners operate in this mode simply as a “Fan”. The fan of the indoor unit turns on, but the compressor simply does not turn on in this mode. It is used to smoothly distribute air around the perimeter of the room, for example in the winter, when warm air accumulates near the radiators and near the ceiling.
Although some modern models are still equipped with such a function, which actually takes fresh air from the street and lets it into the room, these are quite expensive and rare models that cost quite a lot and have complex installation.
Air dehumidification
In dehumidification mode, the air conditioner reduces the amount of moisture in the air. Recommended for regions with high humidity. It is worth noting that the air dehumidification mode accompanies its cooling. This is due to the principle of its operation. Warm air comes into contact with the cold heat exchanger, as a result of which condensation is released from the air, which goes into the drain hose of the device. Thus, there is less moisture in the air.
Air cleaning
Air purification often comes as an additional function to an air conditioner, although in fact it is already present in every device, but to a different degree. To clean the air, a filter is placed in front of the heat exchanger in the air supply channel. Thus, all the debris (fluff, hair, wool and other large particles) settles there. In air conditioners with an air purification function, an additional fine filter is installed, which cleans the air from small particles such as dust, pollen and even some harmful microorganisms.
Night mode
In night mode, the device, to reduce noise, switches to a reduced fan speed mode and slowly increases the air temperature by several degrees. Thus, creating more comfortable sleeping conditions.

Air conditioner functions
Technical condition of the air conditioner
The efficiency of an air conditioner very much depends on its technical condition and can sometimes drop almost to zero if the air conditioner is dirty or malfunctioning.
Air conditioner dirty
If the filters, fan and heat exchangers of the external and internal units of the split system are dirty, then the efficiency of the air conditioner decreases.
Moreover, if the pollution is very strong, then it is noticeable to the eye - the air conditioner blows “warm air”, and if it is not too strong, then no, but the air conditioner still treacherously increases the electricity meter.
The main recommendation in this case is to clean the filters more often.
Filters must be washed under running, not hot water; if necessary, you can use neutral detergents, such as dishwashing detergent.
The amount of freon in the air conditioner
The cooling efficiency of a room air conditioner also depends on the presence of freon in its refrigeration circuit.
Moreover, its quantity should be optimal for the refrigeration system.
The efficiency of the air conditioner drops both when freon leaks and when it is refilled!
The “bigger is better” principle does not apply to an air conditioner.
And even if the air conditioner cools normally, this does not mean that it is operating in its optimal mode.
The only way out for a non-specialist in this case would be to carry out regular maintenance.
Those who want to learn how to diagnose and repair an air conditioner on their own can study our constantly updated section “Do-it-yourself air conditioner repair”
Thermal insulation of copper tubes
The external and internal blocks of the split system are connected by tubes through which freon circulates; its temperature is much lower than the ambient temperature and therefore losses also occur through them.
And the longer the route, the greater the heat loss.
Thermal insulation on the tubes may not be partially applied during installation; birds love to peck at it, using it to insulate their nests, and it also loses its properties over time.
So you need to monitor the integrity of the thermal insulation and restore it.
Air circulation in the room
Since the air conditioner operates on a principle similar to that of a refrigerator, the constant flow of cold or hot air forces the device to work with increased load. This directly affects electricity consumption – it increases.
How much electricity does an air conditioner consume?
Power consumption shows how much electricity the device consumes per hour
The air conditioner's passport indicates 2 powers: consumed and productive. The first shows how much electricity the device consumes per hour.
The second is the efficiency of using power consumption. It is always more than consumed, since in an air conditioner energy is spent only on the operation of the pump and fans blowing the evaporators.
For heating
To determine energy consumption for heating a room, 2 parameters are used: productive power and efficiency coefficient COP.
To obtain the amount of electricity consumption for 1 hour, you need to divide the productive capacity by the COP.
The coefficient can be found in the device passport or in the table below.
| Energy efficiency factor | Energy efficiency class | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
| EER (heating) | 3.2 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| COP (cooling) | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
For example. An air conditioner with energy consumption class A (for this class COP = 3.60), with a productive capacity of 2.2 kW, will consume 0.6 kW of electricity in 1 hour. For 1 month, when operating 8 hours a day, it will consume 144 kW of electricity.
For cooling
When cooling the air, the air conditioning compressor may turn off when the desired temperature is reached
The energy consumption of a split system operating in air cooling mode is calculated using a similar principle, with one difference: instead of COP, the EER coefficient is used.
Unlike operation in heating mode, when cooling the air, the air conditioning compressor can turn off when the desired temperature is reached. This keeps energy consumption to a minimum.
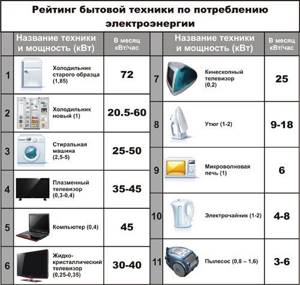
Rating
Listed below are popular models of split systems that have already proven themselves well among buyers.
Ballu BSVP-07HN1
Designed for 21 square meters, it has proven itself among buyers. It is distinguished by its low price, low electricity consumption (class A), and also fairly compact dimensions. A split can work not only for cooling, but also to heat an apartment in the off-season, that is, when the outside air temperature is down to -7. Useful modes include dehumidification, self-diagnosis, ventilation, night, and timer. With a low price tag, the manufacturer equipped the device with saving settings (they will not be lost when the power is turned off), the ability to direct the flow, a motion sensor, a system that prevents the formation of ice, and a deodorizing filter. Power – 2.2 kW. Price – from 13,500 rubles. (2 store).
An inverter model with 21 square meters from a brand that is considered one of the best in the segment. The device is not budget, but this is explained by the name and inverter motor. The system is quite compact and has a beautiful appearance. The noise level is very low - 21 dB. Functions include dehumidification, self-diagnosis, anti-ice system, timer, heating, saving settings in case of failure, flow control. Unlike many competitors, it can be turned on for heating at -15 degrees. As a rule, the lower threshold of most devices is 0. Another interesting point is that there are very few inverter sevens on the market. As a rule, they are produced starting from a capacity of 27 square meters. Thus, this model has practically no competitors. Price – from 39,200 rubles. (2nd store - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, 3rd store).
By modern standards, an inexpensive 27 square model from a popular and high-quality brand from Japan. Electricity consumption – 2.6 kW, low noise level – 26 dB. Among the modes are self-diagnosis, prevention of ice formation, night mode, and the ability to select the air direction. Can be used for heating down to -7 degrees. The system does not have a display, but all settings and parameters are displayed on the remote control. Price – from 27,000 rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Inverter air conditioner for 27 square meters and consumption of 2.5 kW. Received all modern functions - timer, adjustment of air flow direction, anti-ice systems, restart with specified parameters after a failure, self-diagnosis. Optionally, you can buy a module for control via Wi-Fi. That is, using this control unit you can turn on cooling or heating remotely from your smartphone. The system operates for heating at -15 degrees. Noise – 20 dB. The purchase price is from 33.5 thousand rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Despite the inverter motor, this model has a very affordable price tag, which may be a reason to buy it. Designed for an area of up to 36 square meters. Noise level - 19 dB. Electricity consumption – 3.6 kW. The system operates for heating down to -5 degrees. A plus is the double cleaning filter. It is possible to direct the air flow and set a timer. It is equipped with a motion sensor, that is, it will start working if a person enters the room. Price – from 35,900 rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Consumption calculations
Many people mistakenly believe that an air conditioner consumes a lot of energy, but in comparison with other devices that are plugged in for months, the amount of electricity consumed by climate control equipment turns out to be less. For example, the energy consumption of a household-grade air conditioner for a standard room with an area of 15-20 m2 ranges from 0.3 to 1 kW (minimum and maximum). It should be taken into account that the climate control equipment does not operate constantly, but is turned on only to maintain the temperature in the apartment within certain limits, and if you add up the energy consumption per month, the amount does not come out too large.
There is no universal formula that answers the question with 100% accuracy of how many kilowatts the equipment will consume. And, first of all, because, again, it is impossible to predict the temperature set in the room (at the same time as that outside). We also do not know how often the device is planned to be turned on. However, approximate calculations of how much energy will be spent can be made - for this you need to take the daily rate of expenditure as a sample.
The expected operation time of a conventional split system operating on the start-stop principle can be 6 hours. If the indicated demand is 800 W per hour, then 4.8 kW will be consumed per day. This means that a day of cooling will cost 21 rubles (at a price of 4.32 rubles per kW/h). This means 630 rubles per month, which will need to be added to electricity costs.
These data can increase significantly if the device needs to operate 24 hours a day (for example, if the apartment is located on the sunny side).
Selection and calculation of power
The basis for the maximum performance of a device is its power. If the equipment is insufficiently powerful, the consumer will receive a poorly functioning air cooling system. A high-power air conditioner consumes more electricity and is more expensive to install and operate.
Currently there are 3 types of calculations:
First calculation: Approximate calculation
To calculate, you need to know the area of the room. Based on the area, a calculation is made. So, for 1 kilowatt of power there are 10 square meters of space with a standard ceiling height of 2.5-3 meters. This amounts to 30 cubic meters of room volume. When calculating, you should also take into account the following nuances:
- A large number of people in the room
- Availability of panoramic windows
- A large number of office and office equipment in the room
- Sunny side
If these factors are present, 20 percent of the power should be added to each in the calculation.
So, for a room with an area of 10 square meters, you should purchase equipment with a power of 1 kW.
Second calculation: Accurate
If the room has a non-standard shape or a large area, it makes sense to make a more accurate calculation of the power of the equipment. Errors in this calculation method will lead to the purchase of unnecessarily expensive equipment with significant costs for its installation and operation.
How to calculate which air conditioner is needed using the precision measurement method? To do this, there is a formula with which you can calculate the maximum effective power of the equipment:
Q = S * h * q
Where Q is the calculated power (measured in W)
S – room area (sq.m)
h – ceiling height (m)
q – illumination coefficient (W/cub.m)
By default, for rooms with average illumination, a coefficient of 0.035 is applied (35 W per cubic meter)
For rooms located on the sunny side, a coefficient of 0.04 is applied (40 W per cubic meter)
The coefficient of the room located in the shade is 0.03 (30 W per cubic meter)
When calculating, you should also take into account the number of people who will use the room. Because Heat flows also come from people. 1 person generates 0.1 kW of heat in normal conditions. In a state of fear, stress, excitement, heat transfer is 0.3 kW.
The operation of electrical appliances should also be included in the formula. A computer, printer, scanner, and copier each emit 0.3 kW of heat. Calculation of the heat transfer of the remaining equipment is carried out taking into account their passport data: heat transfer = heat flows declared in the documents divided by 3.
When calculating power using the formula, you should take into account all the above nuances and sum them up.
It is worth noting that this method is suitable for permanent structures. A room with transparent walls, a plastic roof or a metal room is not suitable for this calculation system. The walls and ceiling of such rooms give off a large amount of heat, so calculating the effective power in this case is quite difficult.
Third calculation: Accurate calculation made by specialists
Is it expensive to maintain an air conditioner?
The cost of operating an air conditioner in a detached house consists of several factors:
- electricity consumption;
- filter replacement;
- the cost of periodic inspection and cleaning of the entire installation.
The main point to start with is calculating the energy consumption of the air conditioner, because the cost of electricity will be the most significant expense for the homeowner.
Electricity costs
Electricity costs depend on the power consumption of the air conditioner. Let's take, for example, the power of a standard air conditioner, which consumes 2.5 kW/h when turned on (this type of device is used in rooms up to 25 sq. m.). This air conditioner model, operating 6 hours a day, will consume 15 kW of electricity.
How much will this cost the home owner? In the Moscow region, the cost of a kilowatt hour from 2021 on a single-phase tariff is 5.56 rubles per 1 kW/h, on a two-phase tariff - 6.39 rubles per 1 kW/h during the day, and 2.41 kW/h at night. We don’t know what tariff will be used, but it’s obvious that no one will use the air conditioner at night, so for ease of calculations, we’ll round these data closer to the upper limit and take the cost of electricity as 6 rubles per 1 kW/h.
It is easy to calculate that if you use the air conditioner only in the summer months (from June to August inclusive), turning it on for an average of 6 hours every day, the homeowner's expenses will be:
(2.5 kW/h x 6) x 6 rubles per 1 kW/h x 90 = 8100 rubles
The amount is not small, but still such a case will be typical only for a very hot summer, when every day will be clear and sunny.
Still, in the Moscow region, summer is mostly cloudy, so let's see what happens if the air conditioner turns on not every summer day, but every other day:
(2.5 kW/h x 6) x 6 rubles per 1 kW/h x 45 = 4050 rubles
Let’s say there will be not one, but three air conditioners in the house (for example, one for the living room, and one for each of the 2 bedrooms). Moreover, for the hall there will be the same air conditioner as in the examples above, and for the bedrooms - less power, consuming 1.5 kW per hour:
(2.5 kW/h x 6) + (1.5 kW/h x 6) + (1.5 kW/h x 6) x 6 rubles per 1 kW/h x 45 = 8910 rubles
That is, all electricity costs will amount to 10 thousand rubles per season. Considering that in this case several rooms of the house will be cooled at once every second summer day for 6 hours, the amount, in general, looks acceptable.
Of course, all the calculations given are approximate. In practice, these figures can vary greatly, both positive and negative, depending on the intensity of use of the air conditioner, temperature, number of sunny days, etc. Many homeowners use air conditioners not only in the summer months, but already from April-May and ending in September-October.
Another important factor is also the electricity tariff you choose and the presence of intermediaries in the chain (if you are not directly connected) or, conversely, discounts from suppliers. Although, as practice shows, a simple single-phase tariff remains the most profitable for the operation of an air conditioner (because rarely anyone uses it at night).
Costs associated with cleaning and maintaining the air conditioner
When installing a home air conditioner, you should also consider the cost of having it professionally serviced. It will be better if this is done by a qualified company that knows all the features of the installed equipment plus will provide a guarantee on spare parts and labor.
What is included in the maintenance of such devices:
- Professional diagnosis of problems;
- Cleaning the air conditioner from dust, plaque, mold and other contaminants;
- Refilling with freon and replacing filters;
- Repair and restoration of damaged / burnt out parts;
- Checking and cleaning of all blocks and drainage systems, coarse and fine filters;
- Antibacterial treatment and prevention
Cleaning and maintenance of the air conditioner should be carried out regularly: preferably at least once every 1-2 years. As a rule, homeowners order this service before the start of the summer season. The cost of such work largely depends on the specifics of the device’s operation, but on average it ranges from 2 to 4 thousand rubles per device.
Calculation of cooling capacity by square meters
So, the same split system model is available in several variations, designed for different room volumes. Naturally, each manufacturer labels its products so that everything is clear to sales representatives, installers and end customers. But if the first ones know how to navigate the notations, then not all consumers have such information.
The number highlighted in the marking will tell us the cooling power
Devices are marked according to their cooling performance. This parameter is expressed in kWTU, one unit of which per hour is 293 W. The photo above shows an example of such marking - all data is contained in the exact name of the model. What options could there be:
07 – the power of the device will be 2 kW. Such a device can be installed in a room of 18-20 square meters
Please note that 7 units are indicated, not 0.7 units, otherwise you will get confused in the calculations;
09 – here the power increases to 2.5/2.6 kW. Manufacturers recommend them for rooms no more than 26 square meters; 12 – is the most powerful option for household split systems
It can effectively cool a room up to 35 square meters.
When choosing an air conditioner, the individual characteristics of the room will be of great importance.
However, a pure calculation by square meters is fraught with inaccuracies, which the seller is unlikely to tell you about in the store, since he himself may not know, or simply does not want to waste extra time, since you may not have the necessary data at hand. Now we are hinting at the height of the ceilings in your rooms, because it is logical that in rooms with ceilings of 2.7 and 3.4 m there will be different volumes of air, and the difference is significant.
For this reason, the following adjustments need to be made to the methodology described above:
- If the ceiling in the room is no higher than 3 m, then 100 W of cooling energy per square meter will be enough to effectively cool it.
- From 3 to 3.4 m this parameter increases and is already 120 W;
- 3.4-4 m – 140 W per meter;
- Above 4 m – 160 W.
There are no higher values, since higher ceilings are usually not installed in residential premises - industrial split systems are used there.
Industrial split systems
The specified cooling energy parameters are designed for a room in which there are no additional sources of temp, which we humans are also. Therefore, when making an accurate calculation, you should definitely calculate how many people on average can be in a refrigerated room. We also add household appliances: TVs, computers, stoves (if you need to install the system in the kitchen) and so on.
The calculation here is rough and average, but it still helps to significantly improve the result. For one resident and one household appliance, an average of 300 W of thermal energy is released into the surrounding space.
Let's give a simple example of calculation. Let's take a hypothetical room of 20 square meters, in which there are always two people, one of whom works on a computer, and the other just lies on the sofa and relaxes. The ceilings in the room are no higher than 3 m, which means we take 100 W per unit area. As a result, we get 2 kW from the area of the room and another 900 W from people and equipment. Total - 2.9 kW. To cool such a room, according to calculations, we will need 09,10 or 12 according to product labeling.
When choosing an air conditioner, it is important to consider the height of the ceilings
Air conditioner energy efficiency classes
The energy efficiency class of the air conditioner is indicated in the technical data sheet by the value COP - heating mode and EER - cooling.
Energy efficiency classes of split systems:
- A – COP – 3.60, EER – 3.20.
- B – COP – 3.40/3.60, EER – 3.20/3.00.
- C – COP 3.20/3.40, EER 2.80/3.00.
- D – COP 2.80/3.20, EER 2.60/2.80.
- E – COP 2.60/2.80, EER 2.40/2.60.
- F – COP 2.40/2.60, EER 2.20/2.40.
- G – COP 2.40, EER 2.20.
Which energy efficiency class is better?
Air conditioners of classes A, A+, A++, A+++ are considered energy efficient, the coefficient of which is equal to or higher than 3.2.
As a rule, the higher the class, the more rational the energy consumption. Such devices are more expensive, but they are more economical to operate.
Precision air conditioners: types, installation, maintenance
Additional parameters to consider when choosing an air conditioner
Solving this problem is not difficult. You can ventilate the room with the air conditioner on at any time, but you should not forget to close the entrance door to the room (so as not to create drafts). It is also necessary to take this nuance into account when calculating the power of the system. For this purpose Q1
increase by 20% to compensate for the heat load from the supply air. It is necessary to understand that with an increase in power, electricity costs will also increase. For this reason, air conditioners are not recommended for use when ventilating rooms. At the highest possible temperature (summer heat), the air conditioner may not maintain the set temperature, since the heat influx may be too strong.
If the cooled room is located on the top floor, where there is no attic, then heat from the heated roof will be transferred into the room. Heat inflows from the ceiling will be much higher than from the walls, so we increase the power of Q1
by 15%.
The large glass area of the windows also plays a significant role. It's pretty easy to follow. It is enough to measure the temperature in the sunny room and compare it with the others. During the usual calculation, the presence of a window in a room with an area of up to 2 m2 is provided. If the glazing area exceeds the permissible value. Then for every square meter of glazing an average of 100-200 W is added.
An inverter air conditioner is well suited to operate over a wide range of heat loads. It has variable cooling power, so it is able to create comfortable conditions in a given room.
Nominal and optimal power of the air conditioner
The rated power refers to the average performance of the air conditioner when operating in cold conditions. But in each individual case it is necessary to calculate the optimal power, which ideally should coincide as much as possible with the first.
Nominal values are selected by manufacturers for each type of cooling device:
- Window units usually have the following standard positions: 5, 7, 9, 12, 18, 24;
- Wall splits correspond to the following model range: 7, 9, 12, 18, 24. Sometimes some brands produce non-standard models with the following nominal values: 8, 10, 13, 28, 30;
- The cassettes go in this order: 18, 24, 28, 36, 48, 60. Non-standard row: 34, 43, 50, 54;
- Channel splits begin the power range with model 12 and sometimes end with 200;
- Console installations have the following variety: 18, 24, 28, 36, 48, 60. In a non-standard version: 28, 34, 43, 50, 54;
- Columns start at 30 and go up to 100 or more.
This list is not accidental. This has already taken into account the selection of an air conditioner and its power based on the area of the room, the height of the ceilings, and the heat flow from household equipment, electric lighting, people, roof and walls, open windows and ventilation.
Standard formulas for calculating suitable power
To calculate the total power of a fusion system, the indicators of the main factors are added up:
- An indicator of heat gain, depending on the area of the room, ceiling height and number of windows. To do this, calculate: area*ceiling height*illuminance factor/1000. The illumination factor is selected as follows: 30 for darkened rooms, 35 for moderately lit rooms, 40 for strongly lit rooms.
- An indicator of heat release from human bodies. 0.1 kW for each person, if there is no need to engage in physical activity in this room.
- Heat inflows from household appliances. The average figure is calculated at 30% of the power consumed by the device. For example, a computer with a power of 0.9 kW allocates 0.3 kW, etc.
After adding up all the indicators, the average power required by the air conditioner in a particular room is obtained.
Calculation taking into account additional parameters
The usual calculation of air conditioner power, which is described above, most often gives fairly accurate results, but it would be useful to know about some additional parameters that are sometimes not taken into account, but have a strong influence on the required power of the device. The required air conditioner power increases with each of the following factors:
- An influx of fresh air from a slightly open window. The way we calculated the power of the air conditioner assumes that the air conditioner will operate with the windows closed and no fresh air will enter the room. Most often, the operating instructions say that the air conditioner must operate with the windows closed, otherwise an additional heat load will be created when outside air enters the room.
When the window is open, the situation is different; the volume of air entering through it is not standardized and therefore the additional heat load will be unknown. You can try to solve this problem using this method - set the window to winter ventilation mode (open the window slightly) and close the door. In this way, drafts will be eliminated in the room, but at the same time a small amount of fresh air will fall into the room.
It is worth noting that the instructions do not provide for operating the air conditioner with the window slightly open, therefore normal operation of the device cannot be guaranteed in such a situation. If you do use the air conditioner in this mode, then it is worth considering that in this case, electricity consumption will increase by 10-15%.
- Guaranteed 18-20 °C. Most buyers wonder: is air conditioning dangerous to health? The instructions clearly state that the temperature difference between inside and outside should not be very large. For example, if the temperature outside is 35-40 °C, then it is preferable to maintain the temperature in the room at least 25-27 °C. Based on this, in order for the room to have the minimum possible temperature of 18°C, it is necessary that the outside air have a temperature of no more than 28.5°C.
- Top floor. In the case when the apartment is on the top floor and there is no technical floor or attic above it, then the heated roof will transfer heat inside the room. A dark-colored horizontal roof receives many times more heat than light-colored walls. Based on this, heat inflows from the ceiling will be higher than will be taken into account in the usual calculation, therefore power consumption will need to be increased by about 12-20%.
- Increased glass area. During normal calculations, it is assumed that the room has one standard window (with a glazing area of 1.5-2.0 m2). Based on the degree of sunlight, the power of the air conditioner changes by 15% more or less from the average. In the case where the glazing size is larger than the standard value, then the power of the device should be increased.
Since conventional calculations take into account the standard glazing area (2*2), then in order to compensate for additional heat inflows for each square meter of glazing over 2 sq m, you should add 200-300 W in strong lighting, 100-200 W in average insolation value and 50-100 W for shaded rooms.
So, if the room:
- located on the sunny side;
- the room has a large amount of office equipment;
- there are a large number of people in it;
- it has panoramic windows,
then they add an additional 20% of the required power.
In the case when, taking into account additional parameters, the calculated power has increased, it is recommended to choose an inverter air conditioner. Such a unit has variable cooling capacity and therefore, if installed, it will cope more efficiently with a wide range of heat loads.
Consultants at santehnikportal.ru do not recommend choosing a conventional air conditioner with increased power, since in a small room it can create uncomfortable conditions due to the specifics of its work.
Thus, calculating the power of an air conditioner allows you to select a device with optimal cooling capacity to create a comfortable microclimate in the room. The larger the area of the room, the greater the power of the device should be. But the greater its performance, the more electricity the device consumes. Therefore, select equipment with the power necessary and sufficient for effective work.
Determination of power by room volume
The most correct way to calculate the cooling power of air conditioners is by the specific amount of cold per 1 m3 of room volume, especially if its area is within 70 m2. For calculation, it is recommended to take the value of specific power q equal to:
- 30 W/m3 in shaded areas;
- 35 W/m3 for rooms with average illumination;
- 40 W/m3 in rooms on the sunny side of the building.
The required power to compensate for heat gain through building structures is calculated using the formula:
Q1 = qx V, where V is the volume of the room in m3.
Since there are people and household appliances in the building, which also emit heat, it is necessary to add to the obtained value Q1 the amount of heat generated by people Q2 (in accordance with the standards) and from household appliances Q3. The last value is taken depending on the purpose of the household equipment:
- From a computer - 250-300 W.
- From home or office equipment - in the amount of 30% of the consumed electrical power.
Now let's calculate the power of the air conditioner using the formula:
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3
In our example, the ceiling height is assumed to be 2.7 m, the volume will be 20 m2 x 2.7 m = 54 m3. Taking the average specific cooling capacity equal to 35 W/m3, we calculate Q1 = 35 x 54 = 1890 W. Now we should add here the heat from a person with a computer, respectively, Q2 = 130 W and Q3 = 300 W:
Q = 1890 + 130 + 300 = 2320 W.
Operating modes
The electricity consumption of an air conditioner is related to how it works, so let's look at this issue first. Temperature conversion occurs thanks to a heat pump, and it, in turn, works by pumping coolant with a compressor and changing pressure in the lines. The coolant (freon) changes from liquid to gaseous state in the indoor or outdoor unit, depending on how it operates: in cooling or heating mode.
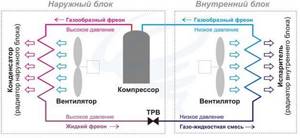
After reaching the set temperature (it is set by the user from the control panel), the system goes into standby mode. When the ambient temperature goes beyond the set limits, it goes into operation mode again. This reduces energy consumption.
It follows: the split system does not operate constantly, but periodically. In standby mode, it consumes virtually no electricity. The current consumed in this state is necessary for the operation of the control system. The compressor consumes the most current, followed by fans.
Specifications
Let us immediately note that the average intensity indicator of a standard household cooling device is in the range from one and a half to eight W, which is optimal for those rooms whose area does not exceed 100 m2.
Let us clarify that before calculating the power of the air conditioner, you need to understand that it can be electric and that which characterizes the cooling process. The first indicator shows how much energy (kW) the device consumes during its operation. This amount is paid by consumers according to the meter. The second characteristic shows the amount of resources that are spent on transferring thermal energy from the apartment (office) to the street - this is precisely the essence of the cooling process.
Power consumption and cooling capacity
Power consumption - electricity consumption per unit of time (also in kW). The energy consumed is spent on removing some heat from the room to the outside. The magnitude of the cooling capacity is usually several times higher than the power consumption precisely because the heat is not absorbed by the device, but is removed to the street.
Through the total ratio of these two quantities, one can judge the energy efficiency (EER) of the air conditioner, that is, its efficiency in terms of energy consumption. Manufacturers distinguish seven energy efficiency classes, among which devices corresponding to class A are considered the most profitable equipment. They spend the least amount of energy on their work. An important indicator in this case will be annual consumption.
But when talking about selecting the power of an air conditioner, experts mean precisely its cooling capacity, the values of which correspond to the total amount of heat from all heat sources in the room.
As already mentioned, this value has two designations: BTU (BTU) and kW. The first is a British thermal unit, corresponding to 0.293 watts. In labeling, different brands indicate this characteristic differently. Typically, rated power values in BTU are multiples of 1000. If the numbers 7 (07), 9 (09), 12, 18 and so on appear in the marking code or technical documentation, then these are the rated power values, where 7 = 7000 BTU, 9=9000 BTU and further down the list. Experts, accordingly, call them “seven”, “nine”, “dvenashka”, “eighteenth”.
How much do household and industrial air conditioners consume?
The difference between how many kilowatts air conditioners for domestic and industrial use can consume is very large. Household models serving an area of up to 25 m² often consume less than 1 kW with other average indicators. Typically, air conditioners installed in apartments do not exceed a consumption of 2.4 kW or 2400 W. They have a single-phase connection. For semi-industrial devices (duct, column, cassette) and even more so for industrial ones (chillers, server cabinets and the like), electricity consumption can reach hundreds of kW. As a rule, they have a three-phase connection.
Household refrigeration devices most often do not require a separate power cable, and can be plugged into a regular outlet. For the rest, it is necessary to lay a separate wire with a larger cross-section.
Also pay attention to which outlet is allocated for power. Old Soviet sockets may not be able to handle a load of more than 1 kW.
Required power of a household air conditioner
For domestic needs, a unit with a capacity of 30 BTU is usually sufficient, which equates to 8 kilowatts. Such a monster is capable of effectively cooling an area of approximately 80 square meters. m. Devices of higher power are considered industrial and have a large set of parameters that influence the determination of effective cooling power.
Since household appliances are most often represented by split systems, the lowest possible power is 2 kW. The window option can be even more economical, with a power of 1.5 kW, but it is only suitable for a very small room.
The air conditioner does not work - the causes of the problem
In order to save time and nerves, you should consider simple reasons leading to equipment failure:
- The batteries in the remote control have run out. They should be replaced and try to turn on the unit.
- The remote control is out of range of the equipment sensors.
- The plug does not fit tightly and the air conditioner is not receiving power.
- The device works slowly and does not cool the apartment sufficiently: there are many people gathered in the room or devices that emit heat are turned on, open windows in the heat do not allow the device to work fully.
- The device turns off shortly after starting operation: the set temperature has been reached, the sensor needs to be reconfigured for stronger cooling.
- An obstacle has appeared in the path of the air flow, such as furniture, which needs to be removed to ensure the normal passage of warm air and the exit of cold air.

The air conditioner does not turn on at sub-zero temperatures
After checking trivial operating errors, you can move on to more serious breakdowns. They occur due to systematic violation of the rules for using climate control equipment. One of these mistakes is turning on the device for heating in cold weather. An air conditioner can only heat a house in the off-season - in spring or autumn, when the temperature outside is above zero. In winter, it can be turned on in cooling mode if the external unit is equipped with a winter kit - heating the drainage and crankcase.
Additional parameters to consider when choosing an air conditioner
There are many factors that have a significant impact when choosing an air conditioner. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the role of fresh air flow when opening a window. The simplified method for calculating air conditioner power does not take into account opening windows for ventilation. This is due to the fact that even the operating instructions for the system indicate that the air conditioner should only operate with the windows closed. In turn, this creates certain inconveniences, since windows can only be ventilated when the device is turned off. Solving this problem is not difficult. You can ventilate the room with the air conditioner on at any time, but you should not forget to close the entrance door to the room (so as not to create drafts). It is also necessary to take this nuance into account when calculating the power of the system. For this purpose Q1
increase by 20% to compensate for the heat load from the supply air. It is necessary to understand that with an increase in power, electricity costs will also increase. For this reason, air conditioners are not recommended for use when ventilating rooms. At the highest possible temperature (summer heat), the air conditioner may not maintain the set temperature, since the heat influx may be too strong.
If the cooled room is located on the top floor, where there is no attic, then heat from the heated roof will be transferred into the room. Heat inflows from the ceiling will be much higher than from the walls, so we increase the power of Q1
by 15%.
The large glass area of the windows also plays a significant role. It's pretty easy to follow. It is enough to measure the temperature in the sunny room and compare it with the others. During the usual calculation, the presence of a window in a room with an area of up to 2 m2 is provided. If the glazing area exceeds the permissible value. Then for every square meter of glazing an average of 100-200 W is added.
An inverter air conditioner is well suited to operate over a wide range of heat loads. It has variable cooling power, so it is able to create comfortable conditions in a given room.
ELECTRICITY CONSUMPTION DEPENDING ON POWER
| Model\Working area m2 | Model cooling capacity, kW | Amount of energy consumed, kW/hour |
| 7, up to 20m2 | 2.0kW | 0.7 kW/hour |
| 9, up to 25m2 | 2.5kW | 0.8 kW\hour |
| 12, up to 35m2 | 3.5kW | 1.0kW/hour |
| 18, up to 50m2 | 5.0kW | 1.4 kW\hour |
It is important to know!
The numbers are approximate, because premium segment models are definitely more economical than inexpensive models. From year to year, the leaders of the climate control market are improving compressors, the shape of fans, and changing heat exchangers to achieve maximum energy efficiency.