Old metal pipelines in heat supply systems are being replaced by products made from more practical and convenient materials. The most popular today are metal-plastic, polyethylene and polypropylene pipes with brass and bronze connecting elements.
Metal-plastic pipes for heating are characterized by excellent hygienic, hydraulic and temperature properties. They cope excellently with the functions of heating and water supply.
Installation of a heating system with metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic pipes easily change shape and are quite convenient to install.
An additional advantage is that there is no need for expensive tools; they have an attractive appearance, so painting the system is not required. You can even do without special scissors (replace with a hacksaw) and a pipe bender (a spring is enough). In order to bend metal-plastic heating pipes, various pipe benders and external or internal springs (mandrels) are used. The bending radius depends on the outer diameter of the product, but cannot exceed four diameters.
Follow installation with detachable fittings
Detachable (threaded and compression) fittings are quite expensive, but without them it is impossible to create connections between pipes and devices. If necessary, these elements can be dismantled and installed again (in compression ones, the crimp ring must be replaced).
Regardless of the fitting used, you first need to cut a piece of pipe to the desired length, calibrate the end and remove the chamfer. When cutting, maintain perpendicularity to the axis. Both the presence of a chamfer and unevenness during cutting can lead to a violation of the tightness of the connection.
If the fitting is threaded (coupling, tee, cross), then it is enough to screw the pipes to its ends. If it is compression, then it is equipped with a special nut, which should be tightened with a wrench immediately after the pipe is inserted into the fitting. Both threaded and compression ones do not require the use of special tools during installation, but they must be monitored during operation, since such connections tend to relax. They are used for open installation, as well as for connecting to manifolds, installing radiators and connecting to valves.
Sequence with press fittings
If it is necessary to monolith metal-plastic pipes for heating, installation is carried out using press fittings that cannot be disassembled and do not require maintenance during operation. In this case, you cannot do without a press tool that compresses the sleeve around the fitting.
When installing a heating system, you can use fittings made of plastic, bronze and brass.
Metal-plastic heating pipes have not only advantages, but also disadvantages:
- the “layer cake” design is weakened by repeated deformations caused by temperature fluctuations;
- the cross-section of the fitting is narrower than the cross-section of the pipes;
- high-quality fittings are very expensive;
- counterfeit materials create problems during operation of the heating system;
- metal-plastic is unstable in relation to ultraviolet rays, mechanical and thermal influences.
The cost of high-quality metal-plastic cannot be less than 90 rubles per meter. This should be taken into account when purchasing. For example, metal-plastic pipes for heating rehau with a diameter of 16 mm cost 119 rubles per meter, with a diameter of 40 mm - 959 rubles per meter.
Installation of heating and water supply systems has become significantly easier with the advent of a new building material on the market - metal-plastic pipes. They have a number of advantages: they bend easily and reliably retain their given shape, are resistant to corrosion, do not require painting, have a lower noise level of liquid flow, are light in weight, and the flow area does not narrow during the entire period of operation.

Polyethylene is inert towards aggressive environments, and metal-plastic pipes are not subject to corrosion.
Regardless of what diameters of metal-plastic pipes are used in installation, the expansion coefficient of the material is always the same.
This ensures the reliability and durability of the pipeline
It is important that these products can come into contact with any materials, including concrete. They have proven themselves well in the Russian climate and can work without insulation at a temperature of -25°C
They are sold in coils and measured in linear meters. Flexible, allowing installation without the use of special tools.
What technical characteristics do different types of metal-plastic pipes have?
All types of metal-plastic pipes for heating have their own sizes and permissible load levels. The scope of application of metal-plastic pipes also depends on the technical parameters:
- In residential buildings, when installing a pipeline or heating system, pipes with an external cross-section of 16, 20 and 26 mm are used. For large objects, types with a diameter of 32 and 40 mm can be used.
- The diameter of the pipe corresponds to a certain wall thickness: a pipe with a diameter of 16 mm has a wall thickness of 2 mm, and pipes with a diameter of 20 mm have a wall thickness of 2.25 mm.
- The outer diameter also affects the thickness of the aluminum layer (in the range of 0.19–0.3 mm).
- Metal-plastic pipes are manufactured in lengths from 50 to 200 meters and, depending on the diameter, have different weights. So, one meter of pipe with a diameter of 16 mm weighs 115 g, and a pipe with a diameter of 63 mm will weigh 1.2 kg.
Metal-plastic pipes are supplied in coils and sold by the meter.
It is worth mentioning what technical characteristics allow you to fearlessly operate various types of metal-plastic pipes:
1. Temperature indicators:
operating temperature +95 °C, short-term maximum +130 °C, maximum minimum – +39 °C.
2. Working pressure
(depending on temperature):
- at an operating temperature of +95 °C – a pressure of 10 bar is allowed;
- a temperature of +25 °C allows the line to be operated at a pressure of 25 bar;
- at a temperature of +20 °C, operation of the pipe with a pressure of up to 80-94 bar is allowed (a higher pressure value will compromise the integrity of the pipes).
3. Pipe bending radius indicator:
- with manual bending, a radius of 80–125 mm is allowed;
- If a pipe bender is used, the pipe can be bent to a radius of 45–95 mm. The bending radius is also affected by the diameter of the pipe.
Other indicators that affect the performance characteristics of different types of metal-plastic pipes:
- oxygen diffusion – 0 g/m³;
- tensile strength (transverse) – 2880 N;
- level of linear expansion – 0.26x10-4 1/°С;
- thermal conductivity – 0.43 W/m*K;
- roughness level – 0.07;
- The service life depends on the temperature of the transported liquid: at +95 °C - service life - 25 years, at +20 °C - 50 years.
The cost of various types of metal-plastic pipes for heating is in the range: 35-950 rubles per linear meter and depends on the material of manufacture, outer diameter and thickness of the inner wall.

Diameters of metal-plastic pipes
These are the most popular metal-plastic products for wiring heating and water supply systems in city apartments. Lime and rust do not accumulate in them and do not block the passage of the working environment. The fittings for them are the most inexpensive, which is the determining factor in the choice. 16 mm products are often used as outlets for faucets in the bathroom and kitchen, when installing meters, while the main pipelines can be made with larger diameter products.
20*2, where 20 is the outer diameter, 2 is the wall thickness, and the internal section is 16 mm;
A variety of fittings allow for competent and technologically correct wiring of systems.
These metal-plastic products are traditionally used in the installation of “warm floor” systems. The fittings on them are more expensive, but the throughput is higher than the previous ones. Therefore, if the water pressure is unstable, it is better to use them for installing hot and cold water supply systems than 16 mm metal-plastic pipes. Especially if you need to run a long route. Withstand pressure up to 10 bar, which corresponds to the characteristics of steel products.
20*26, where 20 is the internal section, and 26 is the external. Wall thickness - 0.3 cm;
Often used for installation of risers and underfloor heating systems. They are the preferred choice when installing engineering systems in a private home, since for autonomous heating and water supply it is necessary to provide a higher throughput due to possible surges in internal pressure.
26*32, where 26 is the inner diameter and 32 is the outer diameter. Wall thickness - 0.3 cm;
Large diameter products are the basis of any heating and water supply systems. They are used as risers and the main pipeline in low-pressure conditions, since, thanks to their high throughput, they ensure the uninterrupted supply of a large amount of liquid.
32*40, where 32 mm is the internal section, and 40 mm is the external. Wall thickness - 0.39 cm;
They are used to create networks of central and individual heating and water supply, central air conditioning, and in water treatment systems. They are used to assemble long routes for engineering systems in industrial and civil construction.
40*50, where the internal section is 40 mm and the external section is 48 mm. Wall thickness - 0.4 mm.
One of the common materials for manufacturing is metal-plastic. This is a modern material that has excellent qualities for use in heating systems.
This gives them incomparable advantages over pipes made from other materials:
- they do not require painting;
- ease of installation - no welding machine is required for operation;
- they can be walled into the wall and poured into the floor;
- they are lightweight, there is little waste during installation;
- their throughput is almost 1.5 times higher than that of metal pipes;
- stray currents will not be able to pass through them;
- have an aesthetic appearance;
- they are easy to replace, repair, or install an additional element into the heating system (for example, an additional radiator).
Metal-plastic pipes also have minor disadvantages:
- high price for pipes and fittings for them;
- they are sensitive to defrosting;
- service life is reduced by 2 times when used in systems with high operating temperatures (about 95° C);
- the presence of many threaded connections requires careful insulation, otherwise the pipes will leak.
A metal-plastic pipe is a pipe made of modern composite material. An aluminum pipe runs inside, surrounded on both sides by plastic.
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of heating pipes
Each pipe material has characteristics unique to it, which means advantages and disadvantages.
Metal pipes
Metal pipes are the oldest version of pipeline elements, and are still actively used both for heating private houses and for creating city communications.
Since iron is highly susceptible to corrosion, galvanized pipes or their corrosion-resistant steel grades should be used.
The widespread use of these products at present is partly due to adherence to traditions in the design of heating circuits, but there is also a rational explanation.
The advantages of using metal (steel, cast iron, copper) heating pipes:
- ease of pipeline installation;
- resistance of products to elevated temperatures;
- resistance to mechanical stress of any kind;
- good thermal conductivity;
- the ability to use a minimum of fasteners due to the inherent rigidity of metal;
- plasticity of pipes, which makes it possible to bend products;
- a wide range of fittings - connecting, corner, etc.;
- resistance to high internal pressure in the heating system;
- the ability to use pipes made of different metals;
- durability and reliability of the assembled structure (for steel pipes - up to 50 years, for copper pipes - over 100 years).
Disadvantages of metal products:
- heavy weight, in some cases making it impossible to work alone;
- the need to weld elements, requiring a qualified welder or skills in working with a welding machine;
- installation of a metal pipeline takes more time;
- roughness of the inner surface of the pipes, which means the possibility of sedimentation;
- the threat of corrosion of elements, requiring the avoidance of hidden pipe laying;
- the need to periodically paint products to avoid external damage;
- large heat losses in cold rooms.
Polypropylene pipes
Advantages of pipelines made of polypropylene pipes:
- smooth inner surface, virtually eliminating the possibility of blockages;
- light weight, allowing installation without unnecessary effort, including alone, and in addition, safe for houses built on shifting soils;
- there is no threat of corrosion, so such pipes can be laid in walls in a closed way;
- there is no need to paint products;
- if the required temperature level is maintained, the pipeline will last at least 20 years;
- the structure is easy to wash and clean;
- low cost of production - for the same money you can build a pipeline of much greater length than from metal.
Disadvantages of such pipes:
- you need a special welding machine to connect structural elements;
- pipes cannot be bent, fittings must be used;
- maximum temperature threshold - 70°C (short-term - up to 90°C);
- instability to mechanical stress;
- sagging in extended areas (more fasteners should be used during installation).
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes
The advantages of such products:
- high operating temperature threshold for plastic – up to 90°C;
- increased density of the manufacturing material, providing good mechanical stability and protection against leaks;
- pipes made of this material can be bent when heated and unbent in the same way (memory effect);
- smoothness of the inner surface, preventing the formation of blockages;
- small expansion coefficient, which does not require the installation of compensators;
- light weight, making it possible to freely assemble the pipeline;
- ease of installation (press fittings are used);
- durability of products - the service life of such a pipeline is at least 50 years.
Such pipes have no disadvantages; they can be used both for installing the pipeline as a whole and in combination with other materials.
Metal-plastic pipes
Such pipes combine the best properties of metal and polymer products: a smooth inner surface, metal reinforcement that provides strength, and an outer layer that does not require painting.
Disadvantages of products:
- high cost of associated fittings;
- deformation due to freezing - such pipes must be used in houses for permanent residence, otherwise an unused pipeline will become unusable over the winter.
The choice of pipes for the installation of heating systems is practically unlimited, and the quality of the assembled circuit depends primarily on the correct decision of the designer and the conscientious implementation of all stages of system assembly.
Application area
Due to the technical characteristics of metal-plastic, the material has found application in pipelines for cold and hot water supply, as well as sewage.
It is used for various heating systems:
- Underfloor heating device "warm floor".
- Connection to wall-mounted radiator radiators.
- Heating of soil in closed greenhouse complexes and greenhouses.
- Water heating device for swimming pools.
- Laying protective screens for power cables.
- Compressed air supply.
Metal-plastic products can be found in air conditioning systems and in transport routes for the movement of gaseous and liquid substances.
Design and properties of metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic is not an alloy, but a combination of materials. The walls of metal-plastic pipes are a sandwich of thin aluminum enclosed between protective layers of polymer: cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), low-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP). The layers are securely glued together with a special compound.
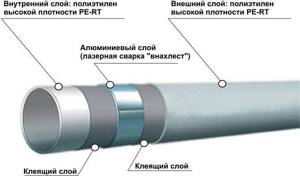
The aluminum layer strengthens the pipes, and the plastic on the internal and external surfaces protects the metal from chemically active elements contained in transported substances and the external environment.
Subject to operating conditions, metal-plastic pipes have the following properties:
- elasticity and flexibility within the established bending radius - using a pipe bender it is possible to bend pipes with a radius from 5 to 18 cm, manually - from 8 to 55 cm;
- resistance to short-term temperature increases up to +110 degrees;
- resistance to short-term pressure surges up to 80-90 bar.
These properties make it possible to use metal-plastic products for equipment of cold and hot water supply systems and heating circuits.
Installation and wiring of the system - installation
To construct a heating circuit in a private house, you need to take into account some details. There are different system wiring diagrams
It is important to choose and design the most optimal option. Media circulation can be natural or forced
In some cases, the first option is convenient, in others, the second.
Natural circulation occurs due to changes in liquid density. A hot medium is characterized by a lower density. The water going the other way is denser. Thus, the heated liquid rises along the riser and moves along horizontal lines. They are mounted at a slight angle of no more than five degrees. The slope allows the carrier to move by gravity.

A heating scheme based on natural circulation is considered the simplest. To perform its installation you do not need to have high qualifications. But it is only suitable for small buildings. The length of the highway in this case should not exceed thirty meters. The disadvantages of this scheme include low pressure inside the system and the need to use channels of large cross-section.
Forced circulation implies the presence of a special circulation pump. Its function is to ensure the movement of media along the highway. When implementing a scheme with forced fluid movement, there is no need to create an inclination of the contour. One of its disadvantages is the energy dependence of the system. If there is a power outage, the movement of media in the system will be difficult. Therefore, it is advisable that the house have its own generator.
The wiring happens:
- Single-pipe.
- Two-pipe.
The first option is implemented through sequential flow of the medium through all radiators. This scheme is economical. To implement it, a minimum number of pipes and fittings for them will be required.
To do this, you need to use the so-called “Leningrad” wiring diagram.
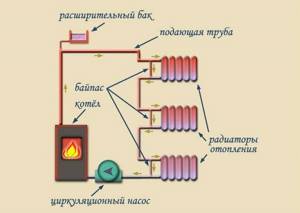
It involves installing bypass pipes and shut-off valves on each radiator. This principle allows for uninterrupted circulation of the carrier when any battery is cut off.
Installing a two-pipe heating circuit in a private house involves connecting reverse and forward current to each radiator. This approximately doubles the channel consumption. But the implementation of this option allows you to regulate the heat transfer in each battery. Thus, it will be possible to adjust the temperature in each individual room.
There are several types of two-pipe wiring:
- lower vertical;
- top vertical;
- horizontal.
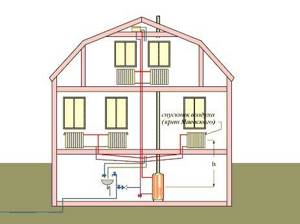
Lower vertical wiring involves running a supply circuit along the floor of the lower floor of a building or its basement. Then, from the main line through the risers, the carrier goes up and enters the radiators. From each device there is a “return”, delivering the cooled liquid to the boiler. When implementing this scheme, you need to install an expansion tank. There is also a need to install Mayevsky taps on all heating devices located on the upper floors.
The upper vertical wiring is arranged differently. Fluid from the heating unit goes into the attic. The carrier then moves down through several risers. It goes through all the radiators and returns to the unit along the main circuit. To remove air from this system, an expansion tank is needed. This scheme is more effective than the previous one. Because there is a higher pressure inside the system.
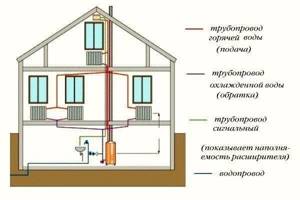
The horizontal two-pipe type wiring diagram with forced circulation is the most popular. It comes in three varieties:
- with radial distribution (1);
- with associated movement of liquid (2);
- dead-end (3).
The radial distribution option consists of connecting each battery to a boiler. This operating principle is the most convenient. Heat is distributed evenly in all rooms.
The option with a parallel movement of liquid is quite convenient. All lines going to the radiators are of equal length. Adjustment of such a system is quite simple and convenient. To install this wiring you need to purchase a significant number of channels.
The last option is implemented by using a small number of channels. The downside is the significant length of the circuit from the distant battery, which complicates the adjustment of the functioning of the system.
Heating systems: their types and installation rules
Before installing a heating system in a house, you should first decide how the coolant (in most cases it is water or non-freezing antifreeze liquid) will circulate through it. Because both the choice of heating boiler and the choice of pipes directly depend on this step.
At the moment, there are the following types of boilers used for heating private houses:
- gas - one of the most popular, powered by natural gas;
- solid fuel - also very popular, can run on various types of solid fuel (coal, firewood, peat);
- liquid fuel (diesel) – less popular compared to others and run on liquid fuel (usually diesel fuel);
- electric - optimal in conditions of lack of gas, because they run on electricity;
- combined ones are universal and can operate on different types of fuel.
As a rule, the following option for dividing heating systems is generally accepted:
- with natural circulation, in which the coolant moves due to the temperature difference: hot water rises and, gradually cooling, naturally falls down;
- with forced circulation, in which the movement of the coolant occurs due to the connected circulation pump.
The first option allows the heating system to operate only using a gas boiler, without additional installations. But, at the same time, its installation will require complex calculations, calculation and compliance with the required slopes and a strictly defined distance between the pipes.

In this regard, a forced circulation heating system has a number of advantages and is considered more efficient. A pump installed separately or built into the boiler provides the necessary pressure in the system, regardless of the presence or absence of a slope or the length of communications. Even in this case, you can install heating pipes of small diameter, which provides additional opportunities for interior design.
The pressure created in a heating system with natural circulation is usually 1.5 - 2 bar, and in a system with forced circulation - 2 - 4 bar.
Its main advantages include the absence of high temperatures and pressure, as well as the possibility of using thin metal or flexible corrugated foil pipes. But despite this, this system also has disadvantages. So, due to the strong noise and overall dimensions of such pipes, installation and installation in the wall may not always be possible.

After you have been able to decide on the type of heating system to be installed and choose the most suitable option, you should familiarize yourself with some points that are important to consider when installing it.
So, the rules for installing heating systems are as follows:
It is necessary to maintain the recommended distance between communications and not install additional objects (shut-off valves, strainer) between the boiler and the safety group (pressure gauge, relief valve, automatic air vent). In a network with a forced heating system, a strainer can be installed in front of the pump. Pipes should be selected based on the type of boiler. Different types of pipes can be combined, but you must carefully study their markings and manufacturer’s recommendations. When connecting a large number of radiators, double-circuit wiring should be done and large-diameter pipes should be installed. It is important to provide for the installation and removal of combustion products to the outside if required by the boiler design.
Now we will tell you in detail about what types of heating pipes there are, what main characteristics and properties they have.
Central or autonomous heating
However, first you should decide whether such pipes can be used at all for central and autonomous heating systems. In fact, such systems are operated under different conditions, and this cannot but affect the recommendations for choosing one or another type of pipe for heating premises. Thus, in autonomous heating systems, the pressure averages from 1.5 to 2.5 kgf/cm2 at temperatures from 40 to 75 degrees Celsius. At the same time, in centralized networks, the coolant pressure in the pipes is from 4 to 5 kgf/cm2 at temperatures from 40 to 95 degrees.
Note that the factory characteristics of metal-plastic pipes meet even such stringent requirements that are established for central heating. However, as always, there are a few “buts”. For example, in autonomous heating systems - during normal operation - water hammer is practically eliminated. At the same time, anything can happen in centralized heating networks, including the actions of an inexperienced mechanic. So, if you quickly open the house valves, the pressure can briefly rise to 25 atmospheres. Meanwhile, for metal-plastic pipes the maximum operating pressure is only from 10 to 16 kgf/cm2.
Moreover, during severe frosts, if residents of an apartment building complain about the cold, mechanics often remove the nozzle in the elevator unit and turn off the suction to increase heating efficiency. And as a result of this, hot water enters the pipes and radiators directly from the supply heating main, the temperature of which sometimes reaches 150 degrees Celsius. However, even despite all these nuances, metal-plastic pipes for central heating are still used.
We recommend: How to choose a microprocessor controller for two central heating pumps?

Installation of heating from metal-plastic pipes
There are 3 known ways to connect metal-plastic pipes to each other:
- threaded or collet connection. It is detachable and used as a dynamic option. If necessary, you can disconnect/connect one or another branch of the network;
- compression or conditionally detachable connection. It can also be disconnected or reconnected, but this is associated with certain difficulties;
— press fitting, a fixed connection technology that does not imply the possibility of disassembling and reassembling the unit.
Installing heating using metal-plastic pipes is easy to do yourself, since it does not require special knowledge or complex equipment. The heating system is designed in accordance with the location of the rooms, the boiler, the location of the radiators and some other factors. You can choose a collector, one- or two-pipe scheme, with top or bottom hot water supply.
The most economical is the single-pipe scheme, but the temperature of the radiators will decrease as they move away from the boiler. To distribute heat evenly between the radiators, a collector circuit should be installed. But its installation will require more material. Two-pipe is a compromise solution: heat distribution is more uniform than in the case of single-pipe distribution, and fewer pipes are required than in a manifold circuit.
Installation of a heating system based on metal-plastic pipes is carried out taking into account the following rules:
— work should be carried out at an ambient temperature of at least +10 °C;
- if the pipes were stored at lower temperatures before installation, they must be allowed to warm up to the specified temperature;
— installation of pipes should be carried out only after the final finishing of the wall surface;
— pipes should be cut only with special scissors;
— do not allow pipes to break when bending;
— attach the pipes to the hay using clamps or clips.
Flaws
Along with an impressive list of positive technical characteristics, metal-plastic heating pipes also have disadvantages:
- Disadvantage 1. With sudden temperature changes, and these happen very often, the joints may leak. This happens due to the fact that aluminum and polyethylene have different rates of expansion from heat. Plastic expands faster than aluminum. This deficiency negatively affects the integrity of the joints.
- Disadvantage 2. Such products can be bent, but only in certain quantities and to a specific radius. Repeated bending leads to destruction of the aluminum layer, and as a result, the polyethylene layer is destroyed.
IMPORTANT! One of the disadvantages is that they cannot be bent or twisted about their own axis
Restrictions on the use of MP materials
- Central heating system network, with elevator units;
- Premises with fire safety category “G”;
- For a main line with a pressure above 10 bar, if there are pipes of small diameter;
- Places located near heat sources with radiation temperatures above 150 degrees.
Connecting MP products with fittings
For any pipeline containing metal-plastic pipes, the connection with fittings is a very important point. There are three main types:
- Detachable;
- Compression;
- Press fittings.
Detachable. They are the most expensive, and with their help the elements can be connected to other devices or fittings multiple times, because they have threaded connections.
Compression. They are difficult to undock; if necessary, change the crimp ring.
Press fittings. They don't understand at all. They permanently seal the system. This can be considered a disadvantage.
Compression and detachable fittings are used for open-type heating lines; such connections must be accessible. But press fittings do not require further maintenance after installation, so they can be used for a hidden network.
The connection is allowed with fittings made of various materials:
- Plastic;
- Brass;
- Bronze.
Installation of metal-plastic pipes in the heating system
Simplicity and ease of installation is a very attractive factor. MP pipe products have excellent bendability and take on various shapes. The workpieces are connected using threaded connections, therefore, neither a pipe bender nor a soldering iron is needed for this work.
- Cutting scissors are used to prepare workpieces of the required size;
- At the edges of the workpieces, remove sharp protrusions so that they do not later damage the rubber seals;
- An O-ring installed on the fitting makes a seal;
- A nut and a clamp are placed on the workpiece;
- Use a calibrator to flare the end of the pipe and place it on the fitting;
- The fitting fitting is aligned and the clamp clamp is returned;
- The fitting nut is tightened and the workpiece can be connected to the system.
Metal-plastic pipes for heating, the characteristics of which were discussed above, have become an indispensable part of any household pipeline system.
Of the varieties of plastic modifications provided, these metal-plastic ones have gained the greatest popularity.
What is taken into account when choosing pipe diameter
Heat generator power. It is taken as a basis and determined individually for each building. What does the owner focus on when purchasing a boiler?
For the total area of all heated premises. This is exactly what the manager at the point of sale will definitely clarify if the buyer has questions about this item.
Coolant speed. If it is less than 0.25 m/sec, then there is a risk of airing the system and causing traffic jams on the highway. Exceeding the value of 1.5 is fraught with “noise” in the highway.
This is especially noticeable when the pipes are metal, and even laid in an open way. But in any case, the movement of the coolant along the route will be clearly audible.
Practice has proven that for a private building (with an autonomous heating circuit) you should focus on an indicator in the range from 0.3 to 0.7. This is the optimal value for any system.
Circuit configuration. In private houses, when installing it, as a rule (regardless of the circuit), all the “threads” are connected to the collector. Each of them is “loaded” with a certain number of radiators.
There is no point in purchasing pipes of the same diameter for all lines, given that the larger the cross-section of the workpiece, the higher the price of 1 running meter.
Pipe diameter. The outer one does not play a special role, since products made from different materials have differences in wall thickness. This parameter only indicates the ease of fastening the product. The internal diameter is about the throughput of the route. It is he who is decisive.
Pipe diameters are usually indicated in inches. For us, this is an unusual (non-metric) system, so you should know the rules for converting quantities. The ratio of inches to centimeters is ½.54 (or 25.4 mm). Pipe material – metal-plastic, steel, PP, PE.
Specifics of the structure. First of all, this relates to the effectiveness of its thermal insulation - what materials it is assembled from, what method is used, and so on.
How to connect pipes
Before installing the flange, you need to check it for the presence of various sharp parts, burrs, corners - all of them can damage the plastic pipe. When purchasing, check the flange for defects; they should not have cracks or unevenness at the joints.

High-quality pipeline connection
Let's look at how to properly connect metal-plastic pipes without threads:
- Before starting work, you need to make an even cut on plastic pipes using special scissors;
- After this, a selected flange of suitable diameter is put on the cut;
- Next, a durable rubber gasket is threaded under the flange to ensure a strong and tight connection;
- A flange is also placed on the metal pipe and is bolted to the flange connection of the plastic pipe.
To prevent sewerage connected in this way from leaking, the connection points must be treated with sealants
Also pay attention to the tightening force of the flanges. They need to be tightened firmly enough with the bolts, but do not pinch the plastic so that it does not crack under pressure.

Pipe flange
Gears are very convenient for making rotary transitions in the pipeline system. They are most often used in private construction work; they are used to connect plastic pipes with common metal pipes.
To make a threaded connection, you will need a fitting.
- At the designated junction of pipes made of different materials, the coupling is removed from the metal transition. It happens to many owners that there is no coupling in these places, in which case the main pipe is simply cut;
- To carry out the work, you will need a thread cutter - this is a special device similar to a hand cutter; it will make a thread on the cut section of the pipe;
- When working on a riser, you need to make no more than 5 turns of thread, and only 3 of them are treated with sealants and sealing tapes;
- Before covering the threads with sealants, you need to clear them of chips;
- On any hand-threaded pipes, the fitting must be screwed on only by hand. If you use special clamps, you can damage the non-standard thread and you will have to cut the pipe even further, which will shorten it;
- The fitting is simply pushed onto a PVC, PP or PE pipe;
- All that remains is to carry out welding work at the places where the fitting and plastic are attached using a special inverter.
Work is carried out similarly when heating, if you need to connect plastic pipes with metal taps. You will also need to cut a thread on one end (metal) and weld an adapter on the other. In this case, you will need an American faucet.

Fitting for copper and plastic pipe
Naturally, a flange connection is much more difficult to implement than a fitting connection, but it is considered more reliable. Do not forget to seal threaded connections with special devices: self-adhesive tapes, jute, resins.
Tips on how to make connecting plastic pipes to metal ones as simple as possible:
- Work according to the project;
- Consult with specialists; your pipeline may require a special approach and selection of adapters;
- Before starting work, be sure to turn off the water in the riser;
- Periodically check connections for leaks or physical damage;
- Metal fasteners must be treated with protective mastics, which will help prevent the appearance of rust at the attachment points of flanges and fittings.
How to choose a metal-plastic pipe to replace an old water supply
The market offers metal-plastic pipes for water supply at a variety of prices. There are pipes at very low prices, but do not rush to purchase cheap products. The choice of pipes for arranging a water supply system should be approached with special care. After all, this work is being done for a long time and the system must be reliable. Experts advise:
- First of all, the pipe should look perfectly glued when cut, i.e. visually you should not observe delaminations.
- It is recommended to purchase pipes with a metal layer thickness of at least 0.3 mm, but not more than 0.55 mm. A layer that is too thin is easily destroyed, while a layer that is too thick deprives the pipe of flexibility and ease of installation.
- Buy pipes made using high-quality polyethylene.
It is not advisable to purchase pipes marked HDPE, PE-HD and PE-RS. They are the cheapest, but, unfortunately, the most fragile.
- It is preferable to choose models with butt welding, which is performed with a laser, which is considered more reliable.
- Buy building materials in specialized stores; if the quality of the product is inadequate, you can always hold the seller accountable. While a product purchased from a random merchant on the market is sometimes impossible to return, since the merchant may simply disappear.
Metal-plastic pipes are in great demand today, but the choice is always up to the buyer. The market offers various solutions for arranging pipeline systems; in each specific case, it is better to enlist the support of specialists, and even better to entrust the installation work to a specialized company that provides a warranty on the material and work performed. In addition, specialists will give you comprehensive advice on the operation of newly installed systems.
DIY installation features
Self-installation of an individual heating system has its own characteristics and nuances. Most questions arise regarding the issues of giving the desired shape to the pipe line and the choice of connection methods.
How to bend a pipe
The most optimal way to bend a pipe is to use a special device - a pipe bender. If this is not available, an alternative method of bending is used by heating with a construction hairdryer. It should be remembered that, unlike steel, metal-plastic is a more fragile material and therefore the bending radius is equal to seven times the diameter of the pipes being connected. If the bending angle is smaller, it is best to install an elbow fitting.
Connection methods
With an open installation method, experienced plumbers recommend connecting individual sections of the thermal distribution with compression fittings. If pipes are laid in a hidden way, for example, in a floor structure, press fittings or crimp couplings are used.
Detachable connections are installed only with open heating pipelines.
Overview of fittings for metal-plastic systems
To prepare for work, it is important to cut the pipes into sections of the required length, and all cuts must be made strictly at right angles. If the pipe is deformed during the cutting process, it must be leveled with a gauge (it will also help remove the internal chamfer)

To connect metal-plastic pipes of different categories into a single structure, connecting elements are used - fittings that differ in design, size and fastening methods
To install the structure, various types of fasteners are used - fittings; we will dwell on them separately.
Option #1: collet
Push-in fittings, consisting of a body, a ferrule, and a rubber gasket, have a detachable design, so they can be used several times. The thread of the parts allows them to be combined with household appliances.
To connect the connecting elements to the pipe, you need to put a nut and a ring in series. Insert the resulting structure into the fitting and tighten the nut. To make it easier for the pipe to pass into the connecting element, it is advisable to wet it.
Option #2: compression
Parts widely used for connecting pipes, which can be called conditionally detachable
Before installation, it is important to ensure the presence of o-rings and dielectric gaskets, which should be located on the shank of the part
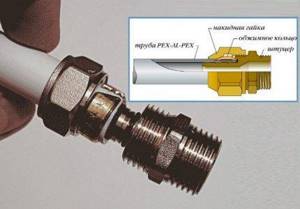
Compression fittings are widely used in the construction of metal-plastic structures. They allow you to easily create connections without the use of special tools
To connect, a nut and a ferrule are put on the end of the pipe (if it has the shape of a cone, then the process is carried out on the narrower side of the part). After this, the shank is inserted into the pipe (this requires some effort), and in order to seal, the part is covered with tow, flax, and sealant.
The next step is to put the union nut on the fitting body and tighten it. It is convenient to do this with the help of two keys: one of them fixes the part, the other tightens the nut.
This method is quite easy and does not require the use of special equipment, however, it is not advisable to use it for hidden wiring, since it requires checking the connection.
Option #3: push fittings
Convenient connecting elements that do not require special tools for fastening. For installation, it is enough to insert the product into the connecting part, and the end of the pipe should be visible in the inspection window.
Immediately upon completion of installation, thanks to the included water jet, the fitting wedge is pushed forward, forming a clamp that prevents leakage.
This method allows you to quickly and easily create the required structure, ensuring high-quality, durable connections. Almost the only drawback of push fittings is their high cost.
Option #4: press fittings
These elements are used to create permanent connections using press jaws or similar devices.

Press fittings create tight, long-lasting connections, but can only be used once. In addition, to work with such elements you will need press pliers.
To connect using press fittings, you need to calibrate the part by removing the fez from it, after which the sleeve is put on it and the fitting is inserted. The sleeve is grabbed by press jaws, after which the part is firmly clamped by bringing the handle together.
This element can only be used once, but the fasteners mounted with it are quite tight and reliable, making them suitable for hidden wiring.
Installation of press fittings is carried out in the following order:
Installation of pipes from different types of materials
To connect elements, one of which is made of metal and the other of metal-plastic, special fittings are designed, one end of which is equipped with a thread, and the other with a socket.
For installation, a metal pipe needs to be threaded, wrapped in tow, lubricated with soap or silicone, and then the fitting is put on by hand. After its second end is connected to the plastic element, the thread is completely tightened using a wrench.
Assortment of fittings of different shapes
For ease of installation, the connecting elements can have different shapes. The most common are:
- adapters for connecting pipes with different diameters;
- tees providing branches from the central pipe;
- corners for changing the direction of flow;
- water sockets (installation elbows);
- crosspieces that allow you to organize different flow directions for 4 pipes.
Press fittings can have a special configuration (couplings, triangles, tees).
Connection methods
There are several ways to connect such pipes; two main ones are used for heating systems:
- using compression fittings;
- using press fittings.
The first method is good because the use of compression fittings greatly simplifies all work. These fittings do not require any special tools, with the exception of the aforementioned scissors.
In addition to these, you may need:
- a set of open-end wrenches or an adjustable wrench;
- FUM tape;
- calibrator
FUM tape can be replaced with regular tow with a special sealant.
As for fittings, they can be of various shapes:
- corners;
- tees;
- adapters and so on.
All fittings have a fitting at their end that contains one or more O-rings. In addition, there is a clamping ring and a union nut, which presses the pipe and fitting together.
Before connecting the pipe and fitting, the ring and nut from this fitting are put on the pipe. Now you need a calibrator. It serves to create an even round shape at the end of the pipe. If this shape is not in place, then during the process of securing the fitting and pipe, the O-rings on the fitting may simply become damaged, which will lead to a leak.
After calibration, the pipe is put on the fitting. Next, the clamping ring and the union nut are pulled into place, which is screwed along the thread until it stops. Tow or FUM tape is pre-wound on the ring.
The nut is tightened with not very much effort. If you apply too much force, the nut will simply burst or strip the thread. Tightening should be continued until a characteristic metal squeak appears.
Related article: DIY window frame: designs
Regarding the use of press fittings, installation can be divided into two types, although the division should be considered conditional:
- using crimp couplings;
- using press fittings.
This method requires a special tool, for example, press jaws. Such a tool can be mechanical or hydraulic. It is worth noting that each type of press fitting requires the use of its own type of tool, which differs in design and principle of operation. For example, push-on press fittings require a special expander.
In addition to this tool, you will also need the one listed above.
Installation process
As we said above, most negative reviews about metal-plastic pipelines are associated with errors made during installation of the system. Therefore, before starting the actual installation, you need to study the manufacturers’ recommendations and read the instructions for installing the heating circuit from the products in question.
Before installation begins, a diagram of the future highway is drawn up. The location of the threads and other necessary components is placed on the house plan. After this, they calculate the volumes of materials that will be required to solve the problem.
The step-by-step installation looks like this:
- A piece of pipe is cut off with scissors.
- The calibrator is used to align the inlet pipe for connection to the fitting.
- The press fitting is mounted and clamped using crimping pliers.
If you have purchased high-quality metal-plastic pipes, it is permissible to use a spring pipe bender. In this case, the minimum bending radius must be carefully observed. It directly depends on the cross-sectional index of the product.
Basic rules for installing metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic pipes are highly sensitive to mechanical damage, temperature influences, and do not tolerate direct exposure to ultraviolet rays. Therefore, open laying of metal-polymer pipes is possible only in those places where the presence of these factors is excluded.
In order to easily repair concealed metal-plastic pipes with screw fittings, it is necessary to provide inspection hatches at the joints. These elements should not have sharp edges.
Metal-plastic pipes are laid through building structures using sleeves. There should be a gap of 3-5 mm between the inner surface of the sleeve and the outer side of the pipe, which is created using a soft, non-flammable material that allows longitudinal movement of the pipe.
Therefore, sharp objects should not be used when unpacking pipes. Marks can only be drawn with a marker or pencil.
For the installation of press fittings, reliable equipment is used, which eliminates the creation of poor-quality connections.
Installation of metal-plastic pipes - video materials will help you cope with this process - should be carried out using hangers and supports offered by pipe manufacturers. When using metal fasteners, the pipe is protected with gaskets made of soft materials.
To solve the question of how to repair a metal-plastic pipe, you can choose one of the options:
- to eliminate a leak, it is necessary to cut out a piece of pipe and install a new one using a connecting fitting;
- if the leakage area is small, you can install only a connecting fitting without buying a new pipe;
- The leak can be sealed by installing a flange with a gasket or sealed with epoxy glue or sealant.
Metal-plastic pipes are the most versatile among polymer pipes; they are reliable in operation, easy to install and have an aesthetically attractive appearance. It is these properties that explain the growth of their popularity.
Tools and materials for laying pipes
Laying metal-polymer systems requires a minimum of devices and materials, but it is better to choose high-quality devices and pipes.
Pipeline installation accessories
To create a structure made of metal-plastic, a very modest set of tools is enough: a pipe cutter, a simple pipe bender, press pliers, a sliding and spanner wrench.

To install a metal-plastic system with your own hands, you need a minimum of tools, which can be purchased in a set or separately from a construction supermarket.
To separate measured sections of pipe from the coil, it is advisable to stock up on a pipe cutter designed for cutting metal-plastic pipes. Since metal-plastic is a fairly malleable material, it can be cut with a hacksaw or even a sharp knife.
However, ideal perpendicularity of the lines, without which it is difficult to obtain a tight connection, can only be achieved by using a special cutter.
Different types of wrenches are important for installing and assembling threaded connections on pipeline fittings. If absolutely necessary, you can get by with one spanner, but for comfortable work it is better to use two spanners and one adjustable wrench.
A gauge is an important tool for creating an accurate and tight connection between a pipe and a fitting: it allows you to center the cut plane and chamfer the inside of the product.
The pipe bender allows you to change the configuration of the element, so you can save on corner fittings
It is especially important to have this tool if the design involves a large number of angular mates
Before starting work, we advise you to familiarize yourself with the rules and specifics of crimping metal-plastic pipes.
What materials will be needed?
To lay the pipeline, it is important to stock up on the following components:
- pipes (coils, measured sections);
- various fitting options (bends, tees, corners), with the help of which individual sections of pipes are transformed into a single system;
- fastening elements - dismountable clamps and clips, with the help of which metal-plastic structures are fixed to supporting surfaces, most often on the wall.
It is important to select all the necessary materials and tools in advance so that you can carry out all the work smoothly. This article will introduce you to the range of metal-plastic products for pipeline assembly.
This article will introduce you to the range of metal-plastic products for pipeline assembly.
Date: September 25, 2021











