When a car's heating system fails, a common cause of problems is a faulty heater core. Therefore, there is an urgent need to replace this element on your car. The procedure for changing the stove element itself may differ depending on the design features of the car. But the key issue here is the right choice. The main dispute is over aluminum and copper products. It is not always possible to give a definite answer to which radiator is better - aluminum or copper. To do this, you need to study their features, strengths and weaknesses. This will allow you to give an objective assessment of the devices and understand whether there is an obvious leader among them.
Recommendations for choosing a radiator.
How it works
First you need to understand how the heater cores in your car function. The heat inside the cabin comes from the running engine. This is a kind of side effect of the operation of the power unit. It generates heat, which engineers have learned to use for the benefit of humans, that is, to heat the interior of the car with it. The heat itself is created as a result of the combustion of the air-fuel mixture and friction between the surfaces of engine elements. To remove this heat from the heated components of the motor, its design includes a cooling system. One of its functions is to heat the car interior.
A logical conclusion follows from this. The hotter the engine is, the warmer it can be inside the cabin. The coolant becomes hot, removing heat from the engine, and passes into the heater core. Here the fan comes into operation, blowing air through the heated radiator and distributing it throughout the car. To be more precise, around the cabin. The driver and passengers can regulate the temperature of the supplied hot air using deflectors and a tap, which are located on the line between the power unit of the car and the stove itself. This is the simplest shut-off type valve, which has a mechanical or electrical drive type. With its help, the amount of cooling liquid passing through the heating system is regulated.
If you raise the temperature on the control unit, the tap will open more. When the temperature decreases, the opposite effect occurs. Its functionality directly affects the operation of the machine's stove. If the system cannot provide full passage for the coolant heated by the engine, then the driver and passengers will feel cold. The temperature outside plays a big role. In the case of a serviceable and well-functioning heater, even it will not be able to warm up the interior as much as possible if the outside temperature is at a very low level. The colder it is outside, the more difficult it is for the stove to warm up the interior.

Radiator design
It is important to consider that the car has two radiators at once. One of them is included in the heating system and is in many ways similar to its older brother installed in the cooling system. Their functions are also similar. Only the cooling radiator mainly transfers the selected heat to the atmosphere, and the small one (heating radiator) is intended for the interior. Both devices provide for the presence of 2 tanks connected by tubes to each other. The plates necessary to increase the cooled area are mounted to them. The more plates the device has, the higher its heat transfer rate will be.
Therefore, when choosing a new heating radiator, you should definitely pay attention to the number of plates present. If their density is high, then the heat transfer will be at a high level. The main difference between them is the material of manufacture. The choice in favor of a copper or aluminum option is not so clear-cut. You should study in detail the characteristics and features of the two options in order to understand which one would be better to choose in each specific case.
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the bottom connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, coolant is supplied to the radiator on one side and removed from the other.
Bottom connection of heating radiators for single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply and where the return is connected is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Heating radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are many more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected into two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option #1. Diagonal connection
This connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard and this is how manufacturers test their heating devices and the data in the thermal power passport for such a connection. All other connection types transfer heat less efficiently.
Diagonal diagram for connecting heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option #2. Unilateral
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return from below. This option is convenient when the riser runs on the side of the heating device, which often happens in apartments, because this type of connection usually predominates. When the coolant is supplied from below, this scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to position the pipes.
Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%. But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or will remain cold at all. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extenders are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle. The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, thereby improving heat transfer.
Option #3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, saddle connections for heating radiators are the least effective. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal from an aesthetic point of view. And so that losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation, this type of connection should not be made, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, it’s not even worse than the side one. It’s just that at a certain speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
Date: September 25, 2021
Advantages and disadvantages of copper devices
Let's start with copper. Many people call them the preferred choice because they have better technical characteristics. But there are also disadvantages here. Let's start with the advantages. These include:
- Thermal conductivity. This is one of the main arguments that speaks in favor of copper and against aluminum. Copper devices are characterized by greater thermal conductivity compared to competitors. As you already understood from the above, the higher the radiator’s thermal conductivity, the higher the quality of its work in heating the interior.
- Suitability for repair. Copper is a rather unique material. It is both lightweight and yet resists damage from minor impacts and dents. Therefore, it is much easier to repair in case of emergency situations. The experience of car owners clearly shows that in case of cracks or damage to the tubes, you can easily solder them with your own hands or seek help from specialists. With such a repair, the thermal conductivity does not change, and therefore partial failure does not force you to throw away the radiator and buy a new one in its place.
- Copper tank. Copper radiators are equipped with tanks made of similar material. This is considered a significant advantage, since such design features help improve the performance characteristics of the product.
Disadvantages of the high thermal conductivity of copper and its alloys
Copper has a much higher cost than brass or aluminum. At the same time, this metal has its disadvantages, which are directly related to its advantages. High thermal conductivity leads to the need to create special conditions during cutting, welding and soldering of copper elements. Since copper elements need to be heated much more concentrated compared to steel. Also, preliminary and concomitant heating of the part is often required.
Don’t forget that copper pipes require careful insulation if they make up the main line or distribution of the heating system. Which leads to an increase in the cost of network installation compared to options when other materials are used.

Example of thermal insulation of copper pipes
Difficulties also arise with gas welding of copper: this process will require more powerful torches. When welding metal 8–10 mm thick, two or three torches will be required. While one torch is used for welding, the other is heating the part. In general, welding work with copper requires increased costs for consumables.
It should also be said about the need to use special tools. So, to cut brass and bronze up to 15 cm thick, you will need a cutter capable of working with high-chromium steel 30 cm thick. Moreover, the same tool is enough to work with pure copper only 5 cm thick.

Plasma cutting of copper
Pros and cons of aluminum radiators
By comparing the strengths and weaknesses of devices, you can understand their main differences. After all, the difference between copper and aluminum radiators lies in their main characteristics. What is considered an objective advantage for one person turns out to be a serious disadvantage for another. Just look at the pros and cons of aluminum products and you will understand the difference between them.
Let's start with the positive aspects of aluminum as a material for the manufacture of car heater radiators.
- Price. While cost was considered a disadvantage of copper radiators, here it is a serious advantage. If we compare the price tags for both products, aluminum ones will win by about 2 times. Much depends on the manufacturer, but still the difference in cost remains significant. The buyer can save a lot. Because of this, aluminum units have such a large audience.
- Heat dissipation. Provided that the number of plates is increased, that is, the cooling area becomes larger, aluminum will not be much inferior to copper in terms of heat transfer. Therefore, in this component they are practically the same. But remember that aluminum ones are cheaper.
- Range. A huge proportion of modern cars that have been produced over the past few years are equipped with aluminum units from the factory. Because of this, the number of their analogues and original spare parts offered by different manufacturers is growing. The copper versions have a more modest choice.
We're done with the benefits. Let's move on to the other side of the coin. Aluminum is not doing so well. The stated advantages are beyond doubt. But still, motorists make a choice in favor of copper after they have studied the main disadvantages of the design option under consideration.

Therefore, the disadvantages should definitely be pointed out. This clearly shows the differences between the elements. The main disadvantages include:
- Thermal conductivity indicators. This is a very important drawback that literally negates all the objective positive qualities of the devices. If the driver needs to get the most efficient radiator so that the heating system works efficiently and fully warms up the interior, he will not look in the direction of aluminum.
- Repairability
Approximately the same conclusions can be drawn regarding these devices, which are made from two different materials.
Which conducts heat better: aluminum or copper?
Today, radiators are made from a variety of materials, the most common being steel, stainless steel and aluminum.
Always have doubts about which radiator to choose for installation in your home? Obviously, this depends on personal taste, as well as on the requirements that you have set for yourself regarding the quality of the heating of the room.
Aluminum is by far the most environmentally friendly material and has a huge number of advantages.
How to choose a heating radiator: expert advice
In this article we will not consider cast iron radiators, because... they are losing popularity among buyers.
Let's focus on the most popular models.
The material will tell you in detail about the advantages of aluminum and steel batteries.
Aluminum radiators are lightweight
Aluminum radiators are lighter than traditional steel or cast iron radiators, this fact makes it possible to place such a radiator on any wall in the room.
Aluminum batteries can be hung on the wall, even in situations where the thickness does not allow for deep fastening.
This significantly saves the cost of paying for construction work, since they can be hung very quickly and reliably.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the range of heating radiators presented in online stores; on the manufacturers' websites you can buy aluminum radiators from leading European manufacturers (ESPERADO, FERROLI, GLOBAL, FARAL, FONDITAL) with a 10-year guarantee!
Aluminum is a corrosion resistant material
Aluminum is not subject to corrosion, which makes it an ideal material for the production of radiators that are intended to be installed in areas such as bathrooms and kitchens where there is high humidity.
Aluminum conducts heat well
Aluminum heats up quickly, making it an excellent heat conductor.
Aluminum radiators have a low water content, which means that once turned on, such devices give an intense burst of heat and heat up rooms quite quickly.
By installing aluminum radiators, you can quickly achieve the required temperature in the rooms, as they have the shortest response time.
The main advantage is a significant saving in energy costs during the heating season and, as a wonderful bonus, saving money, since aluminum radiators can be turned off while you are away from the house, and when you return home, turn them on and quickly get a warm home without spending a long time waiting.
Aluminum radiators come in a wide range of designs and colors
There is a common belief that efficient heat cannot be beautiful and original. Fortunately, the days when design must give way to superior performance are over.
Aluminum radiators have a diverse range of designs and offer even the most demanding buyer a decent choice.
You can choose your own finishing color that will perfectly match the style of your home, the shape of the radiator will be one hundred percent in harmony with your home or office atmosphere.
Style sacrifice? Absolutely not when you choose aluminum radiators for your home!
Stainless steel
The use of steel for the production of heat exchangers allows us to obtain durable products, which are mainly used for individual heating systems in houses and cottages.
Due to the ability to control the quality of the coolant and the pressure in the system, steel appliances will be an excellent choice for autonomous heating systems.
Provided that high-quality coolant is supplied and the working fluid pressure is moderate, such devices will last more than 30 years.
Steel radiators have low thermal inertia, which means there will be no problems with rapid changes in room temperature. In addition to low thermal inertia, steel radiators have other advantages:
Where to choose
The question of choice still remains open. But you need to try to answer it as objectively as possible. Despite the shortcomings mentioned, when choosing a radiator several years ago, everyone would definitely have opted for a copper product. Such designs were objectively better and could ensure excellent performance of the entire heating system of the car. But now the situation is different. There are many manufacturers, but there are no truly high-quality copper elements as they used to be. This is due to the desire to reduce the cost of production.
As a result, all sorts of impurities began to be added to copper, which negatively affect strength, quality, thermal conductivity and other aspects that have always been considered the main advantages. Therefore, it is more logical to choose aluminum. This material does not need to be reduced in price due to impurities, therefore it actually completely retains its advantages. And car owners say the disadvantages are not so significant, since the radiator is still a consumable item that can be changed every few years.
Under current conditions, aluminum is objectively better than copper. But if you manage to find the highest quality product without any admixtures of other metals, then you can safely opt for a copper stove radiator. But what you should categorically refuse is painted heating radiators. The presence of a layer of paint significantly reduces heat transfer. In addition, when the paint coating heats up, it begins to emit an unpleasant odor that enters the interior of the car. Try to carefully monitor the heating system to prevent clogging of the channels. If they turn out to be clogged, the fact of what material these elements of the car heating system are made of will no longer play any role.
Manufacturers
If you have been able to determine for yourself which radiator is better, then all that remains is to resolve the issue with the manufacturer. Copper and aluminum are actively used in the production of their products by various companies that create components for automotive heating systems. There are a lot of good manufacturers, but everyone has their own experience in working with certain factories. It is impossible to objectively determine the best company. Some people speak well of them, others were not particularly pleased. The question is quite subjective.
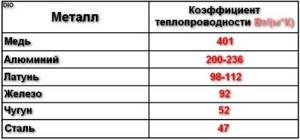
What is thermal conductivity
This term means the ability of various materials to exchange energy , which in this case is represented by heat. In this case, energy transfer passes from the hotter part to the colder part and occurs due to:
- Molecules
- Atoms.
- Electrons and other particles of the metal structure.
The thermal conductivity of stainless steel will differ significantly from that of another metal - for example, the thermal conductivity of copper will be different than that of steel.
To indicate this indicator, a special value is used, called the thermal conductivity coefficient. It is characterized by the amount of heat that can pass through a material in a certain unit of time.
Indicators for steel
Thermal conductivity can vary significantly depending on the chemical composition of the metal. The coefficient of this value will be different for steel and copper. In addition, with an increase or decrease in carbon concentration, the indicator under consideration also changes.
There are other features of thermal conductivity:
- For steel that does not have impurities, the value is 70 W/(m* K).
- Carbon and high-alloy steels have much lower conductivity. Due to an increase in the concentration of impurities, it is significantly reduced.
- The thermal effect itself can also affect the structure of the metal. As a rule, after heating, the structure changes its conductivity value, which is associated with a change in the crystal lattice.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of aluminum is much higher, which is due to the lower density of this material. The thermal conductivity of brass also differs from that of steel.
Specific heat capacity of aluminum
The specific heat capacity of aluminum depends significantly on temperature and at room temperature is about 904 J/(kg deg) , which is significantly higher than the specific (mass) heat capacity of other common metals, such as copper and iron.
Below is a comparative table of the specific heat capacities of these metals. The heat capacity values in the table are in the temperature range from -223 to 927°C.
According to the table, it can be seen that the value of the specific heat capacity of aluminum is significantly higher than the value of this property for copper and iron , therefore this property of aluminum, such as the ability to accumulate heat well, is widely used in industry and heating engineering, making this metal irreplaceable.
Tables of the thermophysical properties of Ag silver are presented depending on temperature (in the range from -223 to 1327°C). The tables give properties such as density ρ
, specific heat of silver
C p
, thermal conductivity
λ
, electrical resistivity
ρ
and thermal diffusivity
a
.
The reliability of auxiliary materials should be as low as the main material. From a hacking point of view, there is a limited amount of water that can be installed. Chemical composition design is also important for materials operating at elevated temperatures.
Usually the welding properties of the weld are selected. Additional materials are supplied in the form of beads, tubes, tapes, electrodes and the like. Due to the high quality requirements for welded connections with adjacent materials, their properties are classified in the relevant standards and required with appropriate certification. Therefore, manufacturers guarantee the required properties, but all precautions must be taken for the recommended storage and use of auxiliary materials.
Silver is a rather heavy metal - its density at room temperature is 10493 kg/m3.
When silver is heated, its density decreases as the metal expands and its volume increases. At a temperature of 962°C, silver begins to melt. The density of liquid silver at the melting point is 9320 kg/m 3 .
Area exposed to heat
In the case of thermally untreated and cold-formed materials, there is a change in recrystallization and heat recovery during mashing. In addition, a coarse grain structure can also be formed. Thus, the deterrent state is the least affected by the crop.
Heat-treated alloys mainly retain their strength by atomization or dissolution of precipitated phases. The sensitivity of the curing material significantly influences the degree of strength loss. Once harvested, most materials cannot maintain the cooling rate required to create suitable aging conditions, so that the strength of the untreated base material can no longer be achieved.
Silver has a relatively low heat capacity compared to . For example, the heat capacity is 904 J/(kg deg), copper - 385 J/(kg deg). The specific heat of silver increases when heated. Its behavior for this metal in the solid state is similar to that for copper, but the jumps in heat capacity during melting have opposite directions. Overall, growth C p
to the melting point compared to the classical value is about 30%.
These alloys are known for their low sensitivity to cure, that is, the strength achieved after aging is slightly dependent on the rate of cure. This means that cooling this material results in air cooling to achieve strength values as in this moderate condition.
This type of alloy is therefore called self-synchronizing. If necessary, please ensure that you have gained the necessary knowledge from this paragraph. Aluminum in various minerals forms 8% of the earth's crust, which is the third most abundant element of oxygen and silicon. Aluminum is non-magnetic and is often used in magnetic X-ray machines to prevent magnetic field damage. This is because aluminum reacts with oxygen to form a thin protective oxide layer. Aluminum is 100% recyclable and does not lose its original properties in this process. Recycled aluminum requires 5 percent of the energy required to produce primary aluminum. About 75 percent of all aluminum ever produced is still used in Europe, with about 70 percent of aluminum cans being recycled and used cans becoming new in less than 60 days.
- Aluminum does not occur naturally in its metallic form.
- Aluminum is not corrosion resistant and corrosion resistant.
Effect of carbon concentration
The carbon concentration in steel affects the amount of heat transfer:
- Low carbon steels have a high conductivity index. That is why they are used in the manufacture of pipes, which are then used to create the heating system pipeline. The coefficient value varies from 54 to 47 W/(m* K).
- The average coefficient for common carbon steels is a value from 50 to 90 W/(m* K). That is why such material is used in the manufacture of parts for various mechanisms.
- For metals that do not contain various impurities, the coefficient is 64 W/(m* K). This value does not change significantly under thermal influence.
Thus, the considered indicator for alloyed alloys may vary depending on the operating temperature.
Is it possible to increase the thermal conductivity of copper?
Copper is widely used in the creation of microcircuits for electronic devices and is designed to remove heat from parts heated by electric current. When trying to increase the speed of modern computers, developers were faced with the problem of cooling processors and other parts. One of the solutions was to split the processor into several cores. However, this method of combating overheating has exhausted itself, and now it is necessary to look for new conductors with higher thermal and electrical conductivity.
One solution to this problem is the recently discovered element graphene. Thanks to graphene deposition, the thermal conductivity of the copper element increases by 25%. However, the invention is still at the development level.
Importance in everyday life and production
Why is it important to consider thermal conductivity? A similar value is indicated in various tables for each metal and is taken into account in the following cases:
- In the manufacture of various heat exchangers. Heat is one of the important carriers of energy. It is used to provide comfortable living conditions in residential and other premises. When creating heating radiators and boilers, it is important to ensure rapid and complete heat transfer from the coolant to the end consumer.
- In the manufacture of outlet elements. You can often encounter a situation where you need to remove heat rather than supply it. An example is the case of heat removal from the cutting edge of a tool or gear teeth. To ensure that the metal does not lose its basic performance qualities, rapid removal of thermal energy is ensured.
- When creating insulating layers. In some cases, the material should not conduct thermal energy transfer. For such operating conditions, a metal is selected that has a low heat conductivity coefficient.
Specific heat capacity of multicomponent special alloys
The specific (mass) heat capacity of multicomponent special alloys is given in the table at temperatures from 0 to 1300ºС. Heat capacity dimension cal/(g deg). Heat capacity of special alloys: alumel, bell metal, Wood's alloy, Invar, Lipowitz alloy, Manganin, Monel, Rose alloy, phosphorus bronze, chromel, Na-K alloy, Pb - Bi alloy, Pb - Bi - Sn, Zn - Sn - Ni - Fe - Mn.

Operating principle of the heater
To make the right choice, you need to know the principle of operation of the heating system in a car.
Heat enters the car interior from the engine, this is a side effect of its operation. Heat is generated as a result of fuel combustion and from rubbing surfaces. To remove heat from very hot parts, the engine is equipped with a cooling system, an integral part of which is interior heating. Therefore, the hotter the engine gets, the better the heating. Hot coolant is supplied to the heater core, and the fan, passing air through it, dissipates heat throughout the cabin.
The temperature of the air leaving the deflectors is regulated by a tap located on the line between the motor and the stove. This is a regular shut-off valve with a mechanical or electrical drive; it regulates the amount of coolant that passes through the heater (by increasing the temperature on the control unit, the valve opens more; by decreasing the temperature, it closes). How the stove will work greatly depends on its operation. If it does not work correctly (does not fully open the passage for liquid), then it will be cold in the cabin.

Also an important factor is the temperature “overboard”; even a well-functioning heater in cold weather will heat a little worse, since the liquid does not heat up enough, because of this the heating becomes insufficient. The thermostat has a big influence: if it doesn’t work correctly, then don’t install any radiator, and cold air will blow from the deflectors. First you need to check the proper functioning of the entire system as a whole, and then think about replacement.
Device
The radiator of the heating system is similar to its older brother from the cooling system. And their functions are similar, only the large one releases heat into the atmosphere, and the small one into the cabin. Both have two tanks in their design, which are connected to each other by tubes. Plates are attached to the tubes by soldering, increasing the cooling area (the more plates, the greater the heat transfer). Therefore, when choosing, you need to pay special attention to the number of plates. This can be done by placing both copies together and visually inspecting the density of the plates. Which radiator has a higher density, the heat transfer is higher. Liquid inlet and outlet pipes are attached to one of the tanks. Some models are equipped with places for attaching to a car.
Copper stove radiator
- Copper has greater thermal conductivity than aluminum. And with an increase in thermal conductivity, heating improves.
- Maintainability. Copper is soft and will not be damaged by minor dents. Even if cracks appear, burst tubes can be soldered, leaving thermal conductivity unchanged.
- The copper radiator is equipped with a tank made of the same material, which significantly improves its performance characteristics.
Flaws

This type has only one drawback - its price.
Aluminum radiator
- The first and most important advantage will be its price. It is almost two times smaller than that of its copper counterpart.
- With an increased number of plates (increased cooling area), the heat transfer will be less than that of copper, but not so significantly.
- Prevalence in the new car market. Cars of recent years produced in our country are equipped with aluminum radiators.
Flaws
- The low thermal conductivity of the material is the biggest disadvantage.
- Non-repairability: if the tubes are damaged, they cannot be soldered, and the entire assembly has to be replaced. A plastic tank can be damaged by the slightest blow. Some copies may have a crack in the tank out of the box. There are “craftsmen” who change tanks, but this is unreliable, and there is a high probability of failure of the entire stove.
- Susceptibility to corrosion. Aluminum is more susceptible to corrosion, which leads to poor heat transfer and the formation of smudges and failure of the entire interior heating system.

Summarizing all of the above, we can say that both types are clogged with dirt equally, both from the inside and the outside. And while it is possible to wash the outside of the device, doing it properly inside is problematic. And if the cooling system of your engine is clean (the engine has been overhauled or a new car has been done), then it is better to choose a copper option, if this is possible for your model. Well, if the condition of the water jacket is unknown, it is better to take an aluminum one and replace it after a few seasons with the same cheap option.











