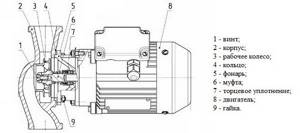
Design and principle of operation of the circulation pump
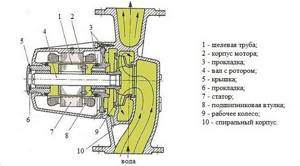
The design of the circulation pump is an implementation of the standard design of a centrifugal machine. The main structural components include:
- pump housing;
- a rotor that transmits rotation from the engine shaft to the turbine block;
- turbine impeller with inclined blades, which is also called an impeller;
- means of sealing, insulation from water or coolant;
- the main electrical circuit that switches operating modes and monitors engine parameters.
Circulation pumps can have different body shapes and locations of outlet and inlet pipes. This is done so that the device can be easily installed and maintained under the operating conditions for which it was designed. In particular, the selection of a pump can be made according to the type of connection: with a flange, a threaded connection, or a nut.
The circulation pump has small dimensions. It is often built directly into the internal cavity of the housing of domestic gas heating boilers. Safety devices can be installed with the pump. The small size of the blower is easy to understand if you consider the purpose of circulation pumps. They do not require record liquid supply power. In fact, they literally move water horizontally.
The task of circulation pumps is to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipelines. If a collector group of a warm floor is considered, the blower is busy creating a flow of very small volume as such, since no significant gravitational forces exist in a heating circuit of this type.
The principle of operation of a circulation pump can be illustrated by several points.
- The coolant enters the inlet pipe.
- When the engine is turned on, the rotational torque is transmitted through the rotor to the turbine wheel.
- Rotating, the wheel moves water with inclined blades, which moves to the edge of the disk under the influence of mechanics (distribution of forces along an inclined plane), as well as due to centrifugal force.
- As you approach the edge of the disk, the speed of the water flow increases, as does its pressure.
- The liquid is discharged into the outlet pipe.
As water or coolant moves to the edge of the turbine wheel, a vacuum arises in the inlet pipe; it captures a new portion of the working fluid for transportation.
Important! The circulation pump of a gas or solid fuel boiler is capable of effectively servicing a certain length of pipelines, pumping the volume of coolant stated in the characteristics. If greater performance and pressure are required, it is not necessary to buy a separate, external supercharger. An additional pump can be installed in the system, which will create the necessary flow or help raise water to the second floor. The same is done when building a distributed, zoned floor heating system.
Both a conventional home heating system and a dual pump heating system can use different types of blowers. The main difference between the models offered on the market is the engineering solution of the rotor-turbine zone.
Glandless Rotor Pumps
Glandless circulation pumps are the most common type of blower for the heating system of a private house or apartment. The devices are so named due to the fact that the operation of the units occurs directly in the coolant.
- The rotor is placed in a special glass with sealing or vortex protection against leaks.
- During operation, rotor parts, including plain bearings, are in water or coolant.
- Continuous lubrication and cooling of structural parts occurs.
Thanks to these operating features, wet systems are characterized by stability, no need for maintenance, and low noise.
To prevent air from entering the rotor area, the pump is equipped with exhaust outlets. The upper one is designed for operation of the automated system, and gas is released through the one located in the front part of the housing during commissioning operations or adjustments.
Important! Operating a pump with a wet rotor when air gets into the pipelines causes sharply increasing wear of moving parts, overheating, jamming or irreparable damage to equipment. The presence of abrasive particles in the coolant is not recommended. Therefore, a glandless water pump should only be installed in a closed heating system.
Dry rotor pumps
The pump with a dry rotor is designed with careful isolation of the turbine block from leaks. The system has a number of advantages and disadvantages.
- The advantage of dry systems is better cooling - most components do not come into contact with hot coolant in the heating system.
- Dry pumps are noisier.
- The overall level of reliability of pumps with a dry rotor is lower due to the larger number of seals and lack of constant lubrication.
However, the main advantage of dry-type superchargers is that they are not afraid of airing . They are also less bothered by the abrasive suspension in the water - only the turbine suffers from it, which has a much higher failure life than the rotor unit with its plain bearings. Therefore, such blowers should be chosen if an open heating system with a circulation pump is being built.
Advice! The danger of an open heating system for a circular pump is the likelihood of airing, hydraulic surges and the formation of an abrasive suspension in the coolant. Due to contact with air, water is constantly saturated with oxygen, oxidation processes are accelerated, especially if steel pipes or heating radiators are used. The amount of rust in the coolant increases. In such conditions, the use of a pump with a dry rotor is recommended.
Variable Speed Pumps
The speed of the pump in a heating system plays a big role. By changing it you can achieve:
- optimal operating mode of heating equipment;
- stabilizing the temperature of all radiators, regardless of their distance from the boiler;
- reducing the temperature of the coolant while maintaining constant heating efficiency, since with a higher circulation rate the water loses less energy in each pass.
Today, various technical pump solutions are available on the market. Home heating can use a single-speed model, the performance of which must be selected in accordance with the characteristics of the boiler and the total volume of coolant. Two, three, four-speed models are available. Their work is based on changing the switching circuit of the motor's pole pairs.

A more technologically advanced, but also significantly expensive solution is frequency control. This type of pump does not provide stepwise switching, but smooth speed control. This allows you to very finely tune the operation of the heating circuit.
Selecting the right unit
To ensure long-term uninterrupted operation of the system, it is better to entrust the selection of equipment to a professional technician.
- low energy consumption,
- durability,
- uniform heat distribution,
- noiselessness,
- automatic regulation of maximum and minimum pressure,
- sufficient water flow in the heating system.
To do this, it is necessary to calculate the following parameters: the total length of the system line, the material and diameter of the pipes. Take into account the type of heating units and quantity, types of control and shut-off equipment, automation characteristics. The heating circulation pump, which has the function of regulating the frequency and speed of the rotary shaft, is characterized by reduced energy consumption, noiselessness, and durability. An automatic change in the speed occurs when the temperature of the water (glycol mixture) decreases or increases. Retrofitting the device with air vents eliminates the problem of air locks.
Among the many models, professional craftsmen call a popular, cost-effective, low-noise device a Wilo circular pump (Wilo Top and Wilo-Stratos), which has a wet rotor installed inside the coolant pipeline. The low weight of the device allows it to be mounted on the pipe surface without additional supports. The models are high-performance, universal: suitable for any heating system. Popular domestic units are linear units TsVTs, Livgidromash.
Choose a heating pump model that has two or three operating modes, and through testing you will find the optimal option for heating the room.
Approximate circulation calculation: for an area up to 250 sq. m. – the circulated volume of water is 3.5 cubic meters. m. per hour, at a pressure pressure of 0.4 atm.
Increasing the area to 350 sq. m. requires 4.5 cubic meters. m per hour and 0.6 atm.
If the area exceeds 350 sq. m, close to 800 sq. m. you need permission up to 10 cubic meters. m., at 0.8 atm.
When the room in the house is larger, it is necessary to install an additional pump in the heating system.
The correct installation of the pump influences the smooth functioning of the device.
The use of circulation pumps in home heating
Since some features of the operation of water circulation pumps in various heating schemes have already been mentioned above, we should touch upon the main features of their organization in more detail. It is worth noting that in any case, the supercharger is installed on the return pipe; if home heating involves raising the liquid to the second floor, another instance of the supercharger is installed there.
Closed system
The most important feature of a closed heating system is sealing. Here:
- the coolant does not come into contact with the air in the room;
- inside the sealed pipeline system the pressure is higher than atmospheric;
- The expansion tank is built according to the hydraulic compensator circuit, with a membrane and an air area that creates back pressure and compensates for the expansion of the coolant when heated.
On a note! For a closed circuit, you can make an expansion tank with your own hands. Its capacity is calculated using simple formulas and depends on the total volume of water in the system.
There are many advantages to a closed heating system. This includes the ability to desalt the coolant to ensure zero sediment and scale on the boiler heat exchanger, and to fill in antifreeze to prevent freezing, and the ability to use a wide range of compounds and substances to transfer heat, from an aqueous-alcohol solution to machine oil.
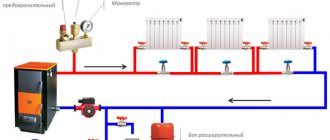
The diagram of a closed heating system with a single-pipe and two-pipe type pump is as follows:
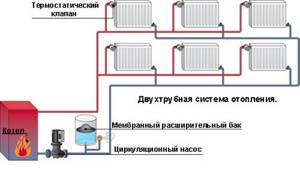
When installing Mayevsky nuts on heating radiators, the circuit settings are improved; a separate air exhaust system and fuses in front of the circulation pump are not needed.
Important! A closed heating system, built without tilting the pipes or maintaining the level of the main coolant flow lines, does not work without a circulation pump. It also does not function when the power is turned off.
Open heating system
The external characteristics of an open system are similar to a closed one: the same pipelines, heating radiators, expansion tank. But there are fundamental differences in the mechanics of work.
- The main driving force of the coolant is gravitational. The heated water rises up the accelerating pipe; to increase circulation, it is recommended to make it as long as possible.
- The supply and return pipes are placed at an angle.
- The expansion tank is open type. In it, the coolant comes into contact with air.
- The pressure inside an open heating system is equal to atmospheric pressure.
- The circulation pump installed on the return flow acts as a circulation amplifier. Its task is also to compensate for the shortcomings of the pipeline system: excessive hydraulic resistance due to excessive joints and turns, violation of inclination angles, etc.
An open heating system requires maintenance, in particular, constant topping up of coolant to compensate for evaporation from the open tank. Also, corrosion processes are constantly occurring in the network of pipelines and radiators, due to which the water is saturated with abrasive particles, and it is recommended to install a circulation pump with a dry rotor.
The diagram of an open heating system looks like this:
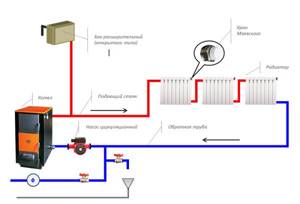
An open heating system with the correct angles of inclination and sufficient height of the acceleration pipe can be operated even when the power supply is turned off (the circulation pump stops working). For this purpose, a bypass is made in the pipeline structure. The heating circuit looks like this:
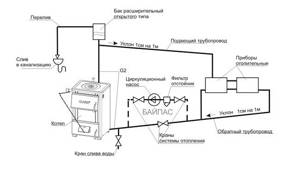
If the power supply is interrupted, it is enough to open the tap on the bypass loop so that the system continues to operate on a gravitational circulation circuit. This unit also makes the initial heating start-up easier.
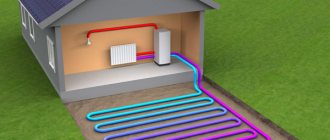
Warm floor system
In a heated floor system, correct calculation of the circulation pump and selection of a reliable model guarantee stable operation of the system. Without forced water injection, such a structure simply cannot work. The pump installation principle is as follows:
- Hot water from the boiler is supplied to the inlet pipe, which is mixed through the mixer block with the return flow of the heated floor;
- The supply manifold for the heated floor is connected to the outlet pipe of the pump.
The distribution and control unit for a heated floor looks like this:

The system works according to the following principle.
- At the pump inlet, a main thermostat is installed that controls the mixing unit. It can receive data from an external source, such as remote sensors in the room.
- Hot water at a set temperature enters the supply manifold and is distributed through the underfloor heating network.
- The return return has a lower temperature than the supply from the boiler.
- The thermostat, using a mixer assembly, changes the proportions of the hot flow of the boiler and the cooled return flow.
- Through the pump, water of the set temperature is supplied to the input distribution manifold of the heated floor.
Important! In such a structure there is no gravitational component of circulation. Therefore, when the power and pump are turned off, the heated floor simply does not work.
Electrical connection options
An electric pump for heating has the only drawback: in the event of an emergency power outage, the circulation will stop, so it is necessary to design the system with the expectation of additional use of the natural flow of coolant.
The pump box is equipped with three contacts, marked as phase, ground, zero, which are connected to the socket with a cable and plug, or the cable line from the meter runs directly to the device. Manually starting the device increases energy consumption, wear of the mechanism and parts, so it is better to make the connection to electricity automatic - through a thermostat.
The advantage of using a thermostat is the regulation of the switching time: the pump of the Wilo heating system starts working only when the water is heated, and does not allow cold water to run idle.
Operating principle: the thermostat is attached to the pipe, measures the temperature of the heat pipe, and starts the mechanism of the unit.
If it was not possible to buy a device special for pipes, you can connect the circulation pump to electricity using a room household thermostat, which has an external temperature measurement sensor attached to the pipe.
In the absence of electricity, use a backup UPS source that provides uninterrupted power to the heating pump: car batteries, or a set of batteries in a compact cabinet.
The connection follows the following diagram: the home electricity line is connected to the UPS, then connected to the pump and boiler. Connection conditions:
- Do not allow the power cable to come into contact with hot parts of the device - motor, housing, pipe;
- Avoid wetting the terminal box;
- if the box is on the side, connection is allowed from below;
- the cable must be heat-resistant;
- be sure to ground.
If you equip the pipe with a thermostat, energy losses during pump operation will be reduced.
Circulation pump calculation
The circulation pump in the heating system of a house must solve the main task: to ensure sufficient pumping of the working fluid to release the normal amount. That is, pump through the pipes such a volume of coolant that, when cooled in one cycle, will transfer to the air in the rooms the energy specified in SNiP (at least).
When calculating, the norms for the coldest time of the year are used. Namely, with heat transfer requirements at the level of 173-177 W/sq.m in outdoor air temperatures from -25 to -35 degrees. This standard is valid for one- and two-story buildings. In houses of greater height, an output of 100 W/sq.m is assumed.
Based on these indicators, the power of the main heater, electric, gas, liquid or solid fuel boiler is calculated, first of all. The main parameter of the circulation pump, flow or performance, is quickly and conveniently calculated based on the characteristics of the heater. To do this, it is enough to divide the boiler power in Watts by the temperature delta, the rate of water cooling in one operating cycle. This is the difference between supply and return. In practice, it is taken equal to 20-25, since at the boiler outlet the coolant is 80-95%, and after passing through the batteries it is from 60 to 70 degrees Celsius.
However, calculating pump performance is only half the battle. Its characteristics should be sufficient to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the entire network of pipes inside the house. It is reduced to the pump pressure parameter in the following ratio: 100 Pa/m corresponds to 0.01 m.
To calculate the hydraulic resistance of the pipe network inside the house, its number of storeys is ignored. The reason is simple: the length of the water lift pipes from the boiler is almost always equal to the length of the return pipe. To calculate hydraulic resistance, special formulas are usually used that take into account all the features of the distribution network.
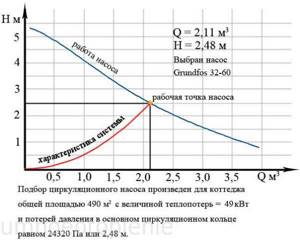
Example of calculation of a circulation pump
There is also a simplified calculation option. The following assumptions are used in the calculation:
- one meter of straight pipe creates a resistance of 100 to 150 Pa per meter, depending on the material;
- the use of fittings increases the network resistance by 30%;
- When using three-way mixers, you need to add another 20% of the direct resistance to the final result.
The calculation procedure looks like this: first measure the total length of the pipes. Multiplying it by the normalized resistance gives the basic result. Then losses are added to it. That is, they add percentages for fittings, faucets, and turns. If the network is built using a single-pipe scheme and thermostatic valves are used in the radiators, 70% of the base resistance value is added to the final result.
There is an opinion that the target parameters of the circulation pump obtained as a result of calculations describe the technical maximum. But in practice, you can take a device with underestimated performance. However, a simplified calculation means a fairly serious gap in the final results. Many factors remain unaccounted for.
The advice can be given quite simple: buy a circulation pump with a speed controller. It will allow you to empirically select parameters if the device operates in constant mode.
Why do you need a bypass?
The installation of a circulation pump in the heating system is carried out in the presence of electricity. To ensure that the water supply does not stop during a power outage, the pump is mounted on a bypass, blocking its inlets with ball shut-off valves. Open and close the fittings along the edges of the bypass when turning the device on and off, directing the water flow in the required direction. In cold weather, the pump is turned on and the coolant is released into the bypass pipe. In summer (or without power supply), the liquid flows by gravity through a straight pipe.
Other parameters for pump selection
In addition to the key parameters, when choosing a specific model, you need to pay attention to a number of its important characteristics.
Working temperature
The documentation for the pump indicates at what coolant temperature it can operate. For most manufacturers, especially models in the budget segment, this figure is overestimated. So, if 90% is stated on an inexpensive device, in practice it will be able to operate without failure with a coolant of 70-80 degrees Celsius.
The key requirement here is to match the parameters of the heater and the heating network as a whole . In a heated floor system, the water temperature is quite low. As well as in several other schemes. But when using a heating boiler, you will either need to buy a fairly expensive pump, or regulate the water temperature at the inlet of the pipe network.
High-quality and reliable circulation units have acceptable working fluid parameters of 110-130 degrees. The cost of such solutions is high. However, users have minimal complaints about their reliability.

Operating pressure
In one- and two-story houses, the pressure in the heating network usually does not exceed 2 atm. Very rarely this parameter is from 3 to 4 atm. A pump correctly calculated according to the pressure characteristic will cope with the task assigned to it. However, if you need to choose an inexpensive circulator, you should pay close attention to its operating pressure indicator.
Protection systems
Automatic protection is an extremely useful option for the circulation pump. It significantly extends the service life of the device or blocks the occurrence of emergency situations. Two types of protection are common today.
- From overheating. A thermocouple that monitors the temperature of the electric motor will automatically turn off the pump if it overheats.
- From dry running. Particularly important in models with a wet rotor. It will prevent the engine from overheating.
In addition to caring for the engine, dry running protection plays another role. It stops the pump, thereby preventing the impeller and seals from failing. Jamming and damage are excluded.
Number of speeds
With correct calculation, it does not matter how many speeds the circulator has. But if you want to optimize the operation of the system, achieve lower noise levels and save energy, you should pay attention to three-mode models. This is an affordable home option.

Circulation pump Grundfos ALPHA2 32-40, 3 speeds
More complex pumps can have more speeds or be electronically controlled by an external signal, providing smooth power delivery and fully controlled flow.
Structural design
When talking about structural design, we mean the dimensions of the fittings, dimensions and material of the housing. Regarding the latter, everything is simple. Cast iron housings are strong, durable, and promote better heat removal from the engine. Inexpensive plastic ones are practical and acceptable for pumps installed in places where they are not subject to temperature changes or mechanical damage.
The fittings should ideally correspond to the network parameters. That is, for a 25 mm plastic pipe, a pump with the same characteristics is selected. Larger fitting diameter is allowed. The pump can be connected using various types of adapters. But a smaller diameter is not allowed.
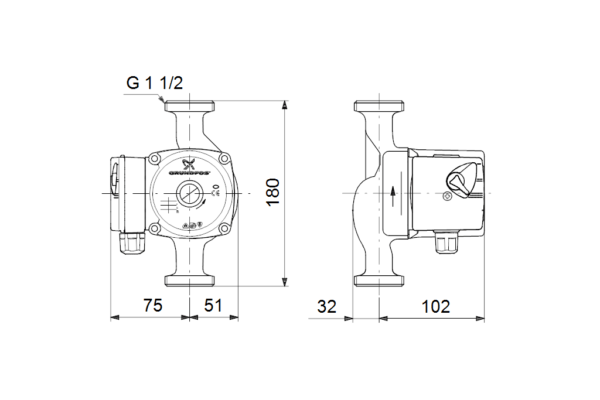
Pump dimensions are standardized
The dimensions of a standard pump are standardized. This is 180 mm between the connection points on the fittings. All bypasses and surges that are offered in stores are designed for this exact size. There are more compact solutions for placement inside equipment or in limited space. The length of this pump is 130 mm.
Device
There are 2 types of pumps for heating systems: “wet” and “dry”. The design and principle of operation of each of them has its own characteristics, which should be examined in more detail:
"Wet"
The design of this type of pump does not imply contact between the pumped water and the rotor, since the pump is separated from the electric motor using O-rings made of metal or ceramic.
During the operation of the devices, these rings rotate relative to each other, and an almost imperceptible layer of water film forms between their surfaces.
It is this that ensures reliable sealing of the connections due to the difference in pressure in the heating system and the general atmospheric pressure.
This type of circulation pump does not lose its performance characteristics for at least 3 years.
This is due to the fact that over time, the O-rings rub against each other even more, so the reliability of their connection only increases, and does not decrease.
The pump is also characterized by complete silent operation, compactness, long continuous operation, economical energy consumption, ease of repair and use.
Depending on the power, “wet” structures are equipped with single- or three-phase electric motors. Cooling and lubrication of engine parts is provided by coolant.
Also, the design of this pump provides for a flange connection or thread, which significantly simplifies and speeds up the installation of the structure.
But, despite all the advantages, these pumps have a significant drawback - low efficiency. It is less than 50 percent.
This is due to the fact that it is impossible to attach a large diameter rotor to it, since in this case there will be no sealing of the connections. Therefore, such devices are most often used only in domestic conditions.
"Dry"
The main difference between this type of device and the previous one is that the pump is at least 80%. However, the device is characterized by a high noise level, so it is best to install them in rooms with high-quality sound insulation.
In addition, pumps of this type must be kept perfectly clean. This is due to the fact that during their operation, air turbulence is formed, which can attract dust particles.
This provokes a violation of the tightness of the seal rings. Therefore, it is important to carefully remove dust in the room where the pump is installed, and also monitor the quality of the coolant.
There are 3 types of dry type pumps:
- Horizontal. They are also called “console”. Their design assumes a horizontal engine arrangement, the presence of a discharge and suction pipe.
- Vertical. The engine in them, accordingly, is located vertically, and the pipes are mounted in the same axis.
- Block options consist of individual blocks.
Now let's look at the elements that make up the circulation pump:
- Frame. It is made of metal elements that are reliably protected from corrosion: steel, cast iron, bronze, brass. Also on the body there is a so-called “snail” - an important element that is used to connect the device to the pipes.
- Rotor. This is the main working steel, which is made of alloy or ceramic steel.
- A shaft equipped with a wheel and blades. It carries out the coolant circulation process: it sucks in water and moves it along the circuit.
- Electric motor (UPS).
Its power depends on the specific model of the device.
Source: https://stroy-podskazka.ru/vodosnabzhenie/nasosnaya-stanciya/cirkulyacionnaya/
Pump marking
All the data the user needs is contained in the markings on the front panel. The numbers on the circulation pump mean:
- type of device (most often it is UP - circulation);
- speed control type (not specified - single-speed, S - step switching, E - smooth frequency control);
- diameter of the pipes (indicated in millimeters, means the internal dimension of the pipe);
- pressure in decimeters or meters (may differ among different manufacturers);
- installation dimensions.
The pump marking also contains information about the types of connections of the inlet and outlet pipes. The complete coding scheme and word order looks like this:

Responsible manufacturers always follow standard labeling rules. However, individual companies may not indicate some of the data, for example, installation dimensions. You need to find it out directly from the documentation for the device.
It is worth choosing a pump only from trusted brands. Reliable devices are also available in the mid-price category. And if you need the highest quality and have the opportunity to pay one and a half to two times more, you should pay attention to products from the GRUNDOFS and WILO brands.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
About the design and installation rules of the pump in the video:
Features of installing circulation equipment in a heating system are demonstrated in the video:
Having become familiar with the operating principle of circulation equipment and the main differences between wet and dry type, you can choose the most suitable option for your heating system. If you wish, you can install the pump yourself. To do this, you should follow the rules and useful recommendations for installing circulation equipment.
Do you have personal experience installing similar equipment? Please share it with our readers. Tell us about the installation nuances that you know. Leave your comments, ask questions, share your experience in the comments section.
Pros and cons of such systems
Now let's look at what a water pump will give us and what it will deprive us of.
Advantages of a system with a pump.
- There will be virtually no requirements for the heat supply system. That is, you don’t have to worry that in certain parts of the contour it will be sloped or narrowed. Moreover, if there is no circulation at all, then you can’t do without a pump.
- Increased efficiency value. If a pump is used, the efficiency of the entire system will increase.
- Reliability. And the reliability of the pumps, as well as ease of operation, means that there can be no doubt about the reliability of the heating system.
- The system accelerates faster. Thanks to the device, the system will accelerate in just a couple of minutes, and this allows you to heat the room many times faster. Natural circulation does not demonstrate such success, since heating in it occurs many times slower.
Disadvantages of a system with a pump.
- Electricity costs are rising. The pump requires current to operate, which is just an additional expense. And the size of these costs will directly depend on the power of the pump.
- Additional installation costs. Of course, the installation procedure costs money, but you can install it yourself – we’ll talk about this below.
- You will need to purchase additional equipment. These are various filters and taps, bypass. All this significantly affects the cost.
- You will be dependent on electricity. This is a significant disadvantage, but it can be minimized. You can buy a diesel generator that will run your heating system. There is another way - to make some sections of the highway at a slope, so that it can work for some time even without electricity. In other words, again natural circulation.
Read about how to calculate heating costs in this article.