I greet my dear reader!
In this article I will talk about what a HDPE pipe is - dimensions, characteristics, range, scope of application.
The most common plastic in our lives is polyethylene. Look in the refrigerator: it is full of bags of different sizes made of transparent plastic film, in the pantry - containers and buckets made of familiar plastic material, in the bathroom - cream, shampoos are packaged in tubes and bottles made of polyethylene, in the underground - the water supply from the main line is laid using a black pipe with a blue stripe, a blue water container in the garden - also made of familiar plastic.
We bring products from the store in polyethylene bags, “Korean” salads and popcorn are sold in polyethylene buckets, paints and putties are packaged, sheaths for wires are made from PE, new furniture and clothes are packaged.
Polyethylene was first accidentally produced in 1899 by the German Hans von Pechmann. The discovery did not interest him, and they began to study it again in 1933 in England, at the company ICI (Imperial Chemical Industries). Industrial production of PE began in 1939.
The very first use of polyethylene was the sheathing of radio frequency wires, then telephone cables. Widespread use was limited by the fact that polyethylene was first synthesized at high pressure. This method was relatively expensive and complicated.
In 1952, a group of German scientists led by K.V. Ziegler developed a method for producing polyethylene at low pressure in the presence of organometallic catalysts. From that moment on, humanity was literally overwhelmed by an ocean of plastic objects.
Almost all popular polyethylene products are made from low-density polyethylene, and this article is about it.
What is HDPE pipe
Inexpensive, technologically advanced and non-corrosive plastic is ideal for creating pipelines. HDPE has greater strength than LDPE, sufficient rigidity, ductility, chemical resistance and corrosion resistance.
Pipes made of low-pressure polyethylene are a current and technologically advanced type of pipe. Lightweight, strong, durable pipes can be used for a wide variety of systems. The dimensions of the pipes make it possible to replace even large-diameter pipelines with polyethylene structures. By design, HDPE pipes are single- and double-layer, corrugated and smooth-walled, socket-shaped, with perforation - for storm drains and drainage systems.
The current trend in the installation of utilities is to replace steel pipelines with plastic ones. Polyethylene pipes occupy more than half of the total volume of produced plastic pipes.
To what temperature can HDPE pipe be soldered?
One-piece pipe connections suitable for durable and reliable use are obtained by welding products. There are two popular methods:
- Butt welding.
- Electrofusion welding.
Modern welding devices are equipped with temperature sensors that control the heating process of the ends, not allowing values above 130-137°C. When this value is reached, the master is notified with an audible signal and/or the unit is automatically turned off. HDPE is a rigid material that can withstand increased loads, therefore its melting point is quite high when compared with LDPE.
To find out more, call our specialists now.
Areas of application
Pipelines made of low-density polyethylene are used in all areas of our lives:
- infrastructure of cities and towns;
- construction;
- technological industrial communications;
- agricultural engineering communications;
- oil and gas complex;
- communications of railways, airfields.
HDPE pipes of various sizes are used for water and gas pipelines, sewer systems, drainage, storm drains, laying electrical power, telephone, and information networks.
The spread of polyethylene pipelines is limited only by its instability to ultraviolet radiation, elevated temperatures and lower strength compared to steel: plastic still does not reach the strength of metals.
Performance characteristics
Low pressure polyethylene pipes are used for water, gas, and wastewater. They are included in renovation programs for existing sewers and are highly rated in terms of reducing maintenance costs and increasing the stability of urban and strategic utility networks.
Their advantages are:
- lack of corrosion, resistance to alkalis and acids, viscous and abrasive substances;
- immunity to stray currents, no need for cathodic protection;
- bacteriological resistance, no rotting;
- light weight even for large diameter products, which reduces the need for heavy equipment during installation;
- tightness of finished seams, fairly simple installation with a large selection of fittings for constructing networks of different geometries;
- greater elasticity and flexibility, which makes it possible to bypass areas without the use of adapters;
- stable pressure, no overgrowing of the internal diameter until the end of its service life;
- environmental safety, do not affect the environment;
- preservation of the properties and characteristics of the transported medium: do not change color, taste, smell, composition due to the inertness of polymers;
- frost resistance - the possibility of installation in winter, the absence of bursts after freezing with liquid inside;
- durability – service life of at least 50 years.
An important advantage is the ease of use for the rehabilitation of existing collector networks, as well as the relatively affordable cost. In relation to cast iron and concrete, which are cheaper in commercial form, low-pressure HDPE pipes are ultimately more profitable, since they require less installation costs, do not require maintenance and last 5-8 times longer.
Technical characteristics and properties
Polyethylene is made from petroleum. Density – 0.931–0.97 g/cm2. The rigidity is greater than that of high-density polyethylene. Melting point - 120...135 °C, brittleness temperature - -60...-150 °C, frost resistance - -70 °C. Tensile strength is 100–170 kgf/cm². Brinell hardness – 1.4–2.5 kgf/mm². Elongation at break – 500-600%.
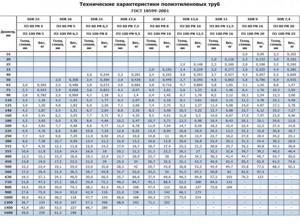
Pipes are characterized primarily by physical dimensions and ring stiffness (depending on wall thickness).
Composition of materials
Polyethylene is a chain of ethylene units. This organic compound has long, flexible chains of carbon with hydrogen atoms attached (formula CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—, or (C2H4)n). Low-density polyethylene has a small degree of chain branching, so its density is higher than LDPE.
Depending on the brand, dyes, antioxidants, heat and light stabilizers are added to HDPE.
Life time
The service life of HDPE under optimal conditions reaches 50 years or more. Optimal conditions are the absence of sunlight, overheating, and cyclic mechanical bending loads on the pipe.
Bandwidth table
When designing home water systems, the owner must decide what size pipe to use. Ideally, a hydraulic calculation of the system is performed - this determines the minimum permissible cross-section of the pipeline, ensuring the normal operation of all plumbing fixtures.
But the calculation is quite complicated; for a private house you can use an approximate figure. First, according to Appendix 1 of SNiP 2.04.01-85, the estimated water flow at each water collection point (mixer for sink and shower, faucet, etc.) is determined. Then the costs are added up and the maximum (peak) water consumption in the building (flow) is obtained.
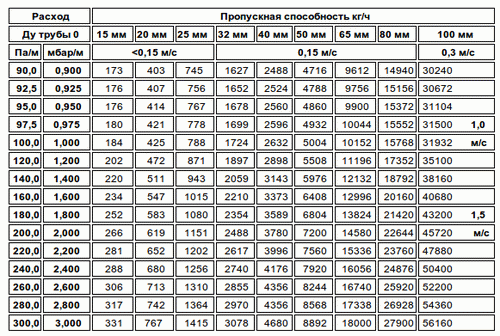
Then open Shepelev’s tables or an online calculator based on these tables. The tables are too large to include in this article. On the left side of the table you need to find the estimated flow rate in l/s. In the next column, find the speed of water flow. At the top of the column, find the minimum size in mm (internal). The speed for private houses is 0.7–1.5 m/s. It should be borne in mind that the tables were calculated for steel, and for plastic pipes with smooth walls without rust, the size can be slightly reduced.
What pressure can they withstand?
The maximum pressure for HDPE is 12.5 MPa. Nominal operating pressure – no more than 10 MPa, or 100 atmospheres. These data are for particularly durable PE 100 structures used for gas pipelines. For conventional plumbing systems, the pressure is 2.5 MPa and 1.6 MPa, respectively.
Composition of materials
HDPE pipes are made of polyethylene - plastic obtained by polymerization of lower hydrocarbons under low pressure conditions. This produces a dense substance with a linear structure, consisting of enlarged molecules with many side branches.
Depending on the conditions of the reaction, the intermolecular bonds formed can be weaker or stronger, therefore polyethylene for the production of pipes differs into several subtypes, marked with different indices (a larger index indicates a “stronger” material). Of these, the following two types are most applicable for pipes:
- PE-80, which is characterized by weaker internal bonds. It has a lower density and melting point, is slightly less tensile strength (tensile strength - 700 hours), but is more plastic, and therefore pipes made from it are more flexible and can more easily withstand small deformations.
- PE-100 has a larger number of internal bonds, therefore it is more dense, rigid and tensile strength (tensile strength - 1000 hours). At the same time, it loses some of its plasticity properties and becomes brittle at higher temperatures than for PE-80.
ATTENTION! Differences in HDPE types become significant only at the extreme points of the permissible ranges, for which stronger or more ductile materials are chosen. Under standard “average” pipe operating conditions, these differences are insignificant.
How are they produced?
HDPE is produced in devices with a pressure below 0.1–2 MPa; temperature 120–150 °C; in the presence of metal halide catalysts (most often a mixture of TiCl4 and R3). Petroleum products are used for the reaction. The degree of crystallization of HDPE is 75–80%.
HDPE products, regardless of size, are made by extrusion, squeezing molten polyethylene through an extruder.
Production technology
First, polymer granules are poured into an extruder and melted while mixing. Then the PE is extruded through the outlet of the extruder, calibrated, and slowly cooled. The finished products are cut and packaged.
Advantages
HDPE pipe has the following advantages over standard metal pipes:
- Much less weight. Weight affects transportation, weight affects the installation process. Less weight makes all these procedures easier;
- Do not rust or oxidize. This, in turn, eliminates such procedures as insulation, especially when it comes to laying products in the ground;
- Simple and quick assembly. The fastest installation is carried out using compression fittings;

Low pressure plastic pipes
- Does not enter into chemical reactions with water, so the water is always clean and has no foreign taste or odor;
- Normally tolerates the process of freezing and thawing, even with water inside. If metal materials can simply crack, then a HDPE pipe can increase its diameter without loss of strength;
- Long service life. Drainage systems, water supply systems, and electrical wiring protection systems can last for decades;
- Relatively low cost.
So, it becomes clear that the technical characteristics that all such products possess are an order of magnitude higher than those of similar materials made of iron.
However, in many respects they are inferior to them. But due to the fact that HDPE pipes are manufactured specifically for drainage and sewer systems, as well as for water supply systems with low pressure, technical characteristics such as strength or rigidity do not matter at all, and it is precisely for these reasons that iron is ahead of plastic.
Regulations
HDPE itself is produced in accordance with GOST 16338-85 “Low pressure polyethylene”. The standard specifies the composition of dozens of grades of polyethylene known only to specialists. Typically, the term “polyethylene brand” refers to the names PE 80; PE 100 (PE-80, PE-100). PE-63 is being discontinued. The numbers 80 and 100 correspond to operating pressure in MPa of 8.0 and 10.0.
Standards and GOSTs
PE pipe standards:
- GOST R 54475-2011 “Polymer pipes with a structured wall and fittings for them for external sewerage systems”;
- GOST 22689-2014 “Pipes and fittings made of polyethylene for internal sewerage systems”;
- GOST R 50838-2009 “Polyethylene pipes for gas pipelines”;
- GOST 18599-2001 “Polyethylene pressure pipes”.
What temperature can HDPE pipe withstand?
Production standards and building codes establish that pipe products must be used to move drinking and industrial water, liquids and gases at temperatures from 0 to +40°C. The maximum temperature value considered critical is +70°C. At this indicator and above, prolonged use of products is prohibited, as they lose their properties.
Practical use of pipe products at sub-zero temperatures has shown that even when water freezes in the internal cavity and is exposed to temperatures down to -30°C, the line does not rupture - only expands by 3%.
Types, range, sizes and sections
HDPE pipe design:
- Smooth-walled for pressure systems and electrical networks. Such HDPE structures are produced with an outer size of 10–2000 mm.
- Smooth-walled gas ones are available with Ø up to 630 mm.
- Corrugated single-layer and corrugated double-layer are available in sizes up to 2400 mm.
- Bell-shaped elements for non-pressure systems - with diameters from 32 to 315 for internal installation, up to 2400 mm - for external installation (corrugation).

Products up to 180 mm in size are supplied in coils and sections, larger than 180 mm - in sections of 6 and 12 m. Corrugations are sometimes produced upon request with a length of 9 m, bell-shaped elements - from 0.5 to 6 m.
The range is given in the standards for each type of pipe - see above.
Wall thickness and weight
The wall thickness of smooth-walled HDPE pressure pipes is from 2 to 95.5 mm. Corrugations (structures with structured walls) – 19–170 mm.
Mass l.m. – this is a calculated data, it is found from tables in the relevant GOSTs. Weight depends on wall thickness.
Standard sizes and markings
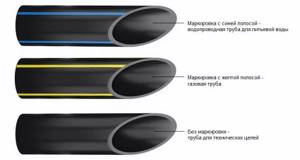
Painting HDPE pipes in different colors helps to quickly determine the purpose of communications; the bright color helps to find structures in the ground and not damage them during excavation work. HDPE pipes come in the following colors:
- For drinking water supply pipes, bright blue or black with a blue stripe is used.
- Yellow or black with a yellow stripe pipes are used for gas pipelines.
- Pure black/black-gray color is used for technical purposes.
- The drains are painted green.
- External sewer pipelines are painted orange or red.
- Red color is used to paint casings for laying electrical wires.
The marking is applied to the surface of the pipes at a distance of no more than 1 m between the inscriptions. The text for marking HDPE pipes includes the following elements:
- name of the standard in accordance with which the pipes are manufactured;
- international designation of the HDPE brand (PE100, PE80);
- outer diameter and wall thickness in mm;
- rated working pressure;
- date of manufacture;
- batch number.
Polyethylene grades
Polyethylene in accordance with GOST 16338-85 is produced in dozens of grades (compositions) with slightly different characteristics. This marking is known only to narrow specialists. Much more often they use markings based on maximum pressure - PE-100, PE-80, P-63, PE-32. The higher the strength of HDPE, the higher the density and weight of 1 meter.
SDR coefficient of polymer pipes
GOST 18599-2001 provides for certain standard ratios of the outer diameter of pipes to the wall thickness. This ratio is called the SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio). SDR is a standard value, taken from tabular data. The thickness of the pipeline wall and, accordingly, the ring rigidity and strength of the pipes depend on SDR.
SDR6; SDR7.4; SDR9; SDR11; SDR13; SDR13.6; SDR17; SDR17.6; SDR21; SDR26; SDR33 and SDR41 – a range of SDR sizes.
Diameter of polymer pipes
Smooth-walled HDPE pipes have sizes from 10 to 2000 mm. Corrugated and bell-shaped – up to 2400 mm.
Pn – nominal pipe pressure
The nominal pipe pressure is the nominal operating pressure Pn. For systems in multi-storey buildings, Pn should not be lower than 1.6 MPa (16 atm). For private houses two floors high, the nominal pressure is usually within 0.3 MPa.
Characteristics of HDPE pipes that determine their choice
There are three main parameters for HDPE pipes:
- brand of polyethylene;
- SDR indicator;
- diameter.
There are 3 brands of polyethylene: PE-63, PE-80 and PE-100. PE-80 products are distinguished by their ability to withstand significant internal pressure. They are well suited for water pipes with a cross-section of up to 9 cm. PE-100 water pipes are used for laying cold water supply systems in the country and are made on the basis of PE-80.
Such products can provide the required throughput with a smaller diameter. Pipes made of PE-100 are characterized by a maximum tensile strength at internal tensile strength of 1 thousand hours and resistance to mechanical stress. The SDR indicator is determined by the ratio of the pipe diameter to the wall thickness. For HDPE products for plumbing, a lower SDR value means higher strength of the products.
Helpful advice! For private use in the country, the diameters of HDPE water pipes for cold water supply of 25 or 20 mm are sufficient. If the daily water consumption is large (for example, for watering a garden), then you can take pipes 3.2 cm in diameter.

To install a water supply system in a country house, HDPE pipes of small diameter are sufficient.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of low pressure polyethylene pipes:
- Durability. In the absence of sunlight, HDPE can last 40-50 years.
- High strength.
- Sufficient ring rigidity.
- Resistance to water hammer.
- Non-fragility.
- Frost resistance up to -70 °C.
- Non-toxic.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Chemical inertness. HDPE is resistant to acidic and alkaline aggressive environments and organic solvents.
- Environmentally friendly. HDPE is disposed of harmlessly.
- Plastic.
- Polyethylene restores its original shape after deformation (freezing).
- Low adhesion. The lumen is not blocked by calcium and magnesium salts.
- Light weight.
- Easy installation.
Disadvantages of HDPE:
- Photodestruction under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. HDPE should not be used in the open sun.
- High coefficient of thermal expansion. Long sections may bend when heated.
- Low resistance to elevated temperatures.
- Unaesthetic for installation in the residential area of the house.
Distinctive properties of low-density polyethylene (HDPE)
Polyethylene, like any other isomer, is obtained as a result of a catalyzed polymerization reaction. In this case, the starting material is ethylene gas (C2H4).
As a result of creating the necessary conditions (pressure, temperature, introduction of a catalyst into the reaction medium), the double bond between the carbon atoms in the original molecules breaks down and a single polymer chain is formed. The resulting product has specific properties that allow it to be used in relevant areas of life.
Specifically, low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is produced in a pressure chamber at a pressure of about 20 atm. And the temperature is about 150°C. The resulting material has the following main advantages that affect the technical characteristics of HDPE pipes:
- ability to withstand high pressure (up to 5 MPa);
- low weight of the finished product, which is a consequence of the low density of the material (a cubic meter of low-density polyethylene weighs less than a ton).
Tips on how to choose
HDPE is the optimal choice for installation in the ground or basements without ultraviolet rays, sudden temperature changes and mechanical vibrations. When choosing the type and size of pipes, they are guided by the purpose and operating conditions. First, the purpose of the pipelines is determined - pressure and non-pressure, sealed or not. Power, telephone or Internet networks are laid in casings made of larger tubes; often these pipelines are not sealed.
The second important factor is the working pressure in the water supply or soil pressure on free-flow networks. The choice of pipe design (smooth-walled, corrugated, double-layer corrugated, bell-shaped) depends on these factors. In addition, the temperature regime is taken into account - overheating of the ground in summer, freezing in winter.
The choice of pipe parameters for sewerage depends on the weight of the overlying soil layer. If the depth is more than 5–6 m or the sewage system is located under a platform for cars, use corrugated two-layer pipes with high ring rigidity. Corrugation is also used for deep laying of water pipes and a large layer of screed over a heated floor system.
When choosing materials in a store, it is better to choose products from well-known brands. Corrugation is definitely better than imported ones. Smooth-walled pipes can also be selected from domestic manufacturers.
In any case, the pipes must be inspected when purchasing to see if there are any cracks, chips, sagging, if they are too soft and if the wall is thin. Receipts and certificates are required for purchase.
Approximate price and best manufacturers
The best domestic ones, “Kazanorgsintez”, “TekhStroyPolymer”, “PolyPlastik”, “BaltEnergosystems”. There are many imported manufacturers, but the quality of imported HDPE pipes is not much higher than domestic ones, but the price is significantly different. The availability and prices of pipes from foreign manufacturers must be determined separately for each region: the range and prices are very different!
Price of popular domestically produced products:
- 1 m of smooth-walled water pipe Ø 32 mm costs from 50 mm, Ø 40 mm - from 70 rubles;
- 1 m of single-layer corrugated pipe Ø 50 mm costs approximately 60 rubles; Ø 63 mm – 90 rubles; Ø 110 mm – 150 rubles;
- bell-shaped HDPE design with a running size of 110 mm and a length of 2 m costs about 300 rubles; corrugated - about 400 rubles.
Symbols and parameters
Detailed information about the pipes can be found in the text markings. It indicates the operating conditions (maximum pressure, permitted temperature of liquid/gaseous substances), dimensions (diameter) and information about the manufacturer. Also on the outside there is a color marking in the form of longitudinal lines:
- yellow ones indicate belonging to gas pipeline systems;
- blue ones confirm the possibility of contact with drinking water.
According to international standards, the stripes are located on a black background. If they are not there, then the product is intended for technical needs.

Important! Another indicator is SDR. It depends on the outer diameter of the inlet/outlet holes and the wall thickness. The first figure can reach 10...1.2 thousand mm, the second - 5...60 mm. The lower their ratio, the higher the permissible pressure in the network.
Methods for connecting pipes of different diameters
Pipes of different sizes are connected with all kinds of adapter couplings. The easiest way is with socket pipes - elements for them are produced for literally all variants of complex system configurations. Rubber couplings with clamps are sometimes used for sewerage.

The issue of connecting smooth-walled pipes is a little more complicated. Small pipes are connected using compression adapter couplings (collet couplings).
The reduction in diameter is combined with bell-shaped elements and the installation of shut-off valves.

For the installation of large pipelines, transition elements for welding or segment fittings are also available (see photo).

The transition is carried out after the transition from HDPE to metal - there are definitely many transition fittings for metal.











