Everyone knows that the operation of a heating system, so to speak, by definition is associated with high temperatures of water or other coolant liquid. It is enough to have elementary concepts in thermodynamics to imagine that heating a liquid in some closed volume will cause a significant increase in pressure. This turns out to be a rather unsafe system, for the operation of which it is necessary to provide some kind of protective devices.
Safety valve in the heating system
The safety valve in the heating system is precisely such a device that ensures the safe operation of boiler equipment. You will not find it in apartments connected to the central system - in fact, it is not needed there, since the temperature and water pressure are adjusted at the elevator units of the general heating points. But for owners of houses or even apartments with an autonomous system, there is no way without this valve.
Therefore, let's take a closer look at this small but very important component of the heating system.
Features and principle of operation
A spring-type safety valve is a direct-acting valve that operates from the medium. Where can excess pressure come from in the system? As a rule, the reason lies in external and internal factors:
- incorrectly assembled thermomechanical circuit;
- heat transfer from sources;
- equipment is not functioning properly.
The spring-loaded safety clutch valve is installed wherever there is a risk of excessive maximum pressure. As a rule, these are household or industrial storage vessels operating under pressure.
The great popularity of this fitting is ensured by its simple design, easy settings, and product range. After all, such variety and possibilities allow you to choose the optimal model for specific conditions.
The safety throttle is installed vertically. The design of a spring flanged safety valve involves the use of a butterfly valve as a locking element, which, when locked, is placed between the seats.
The downforce is set using a special device and a spring for the safety valves.
When the pressure is very high, the specified clamping force is not enough to contain the media, so the excess is removed until the pressure is equalized to the operating level.
The passport for the spring safety valve allows you to learn about the design of the product. The main components are the setter and the shut-off element. The latter consists of a saddle and a bolt.
Using the adjuster, it is adjusted so that the spool is properly pressed against the seat to prevent the passage of medium. The adjustment is made using a screw.
The valve closing pressure, as a rule, is taken to be 10 percent lower than the operating pressure.
Product classification
Let's look at what types of safety products exist.
According to the nature of the elevation of the closing organ:
- two-position action;
- proportional action.
According to the height of the organ:
- full lift;
- mid-lift;
- low-lift.
By type of load on the spool:
- cargo;
- magnetic spring;
- lever-spring;
- spring-.
Based on the operating principle:
- direct – traditional safety products;
- indirect action – pulse devices.
One of the modifications widely used in industry is the angular safety spring choke.
Another classification principle is based on nominal diameter. For example, if a DN15 spring check valve is used, this means that the nominal diameter is 15 mm, and a DN50 spring clutch check valve is 50 mm.
Installation nuances
A spring-type safety valve is installed at any point in the system that is subject to increased pressure and is at risk of mechanical damage. The device does not require a lot of free space, which is a significant advantage compared to other types of safety devices.
To avoid operational problems, do not install any shut-off valves in front of the safety valve. To discharge the gaseous medium, special devices are installed or the discharge occurs directly into the atmosphere. To alert personnel, a special whistle is mounted along with the spring valves, which is placed on the discharge pipe. When the valve is activated, a whistle will sound, indicating that the pressure in the system has increased and the valve has opened to release the medium.
Product characteristics
Capacity calculation is carried out according to GOST 12.2.085. The devices can be used in petroleum, chemical, gaseous and liquid environments. Tightness is determined according to GOST 9789-75.
The closing pressure of the valve is more than 0.8 pH, where pH is the setting pressure, and is the highest at the inlet to the valve, at which it remains closed, while maintaining proper tightness.
Springs for them are most often made of 50HFA steel. Spring check valve type 402 is made of cast iron.
To check the serviceability of the device in working condition, the spring safety valve SPPK has a solution for manual opening, purging, therefore, products without SPPK do not have the ability to manually open.
The dimensions of the sealing surfaces of the flanges are determined according to GOST 12815-80.
As an example of one of the modifications of the device, we will give a 17s28nzh fuse, corresponding to TU3742-017-00218118-2002.
The device has the following characteristics:
- working pressure – 1.6 MPa;
- working environment – non-aggressive, gas, steam, water;
- case material – steel;
- sealing material – stainless steel;
- connection – flange;
- temperature - from minus 40 to plus 250 degrees;
- weight and length depend on the nominal diameter.
Nuances of choice
To choose the optimal product, you need to take into account the requirements that apply to them:
- timely and trouble-free installation of a safety valve at a specified increase in the level of operating pressure in the system;
- in the open position, the necessary throughput must be ensured;
- timely closing of the valve with the required level of tightness;
- ensuring stable operation.
Cost is of no small importance when choosing. For example, let’s look at how much you can buy a 17s28nzh spring safety valve: the price for a return clutch spring throttle starts from $300.
Of course, a lot depends on the manufacturer. Thus, a similar Danfoss spring check valve will cost more – from $400.
Features of the product (video)
Installation nuances
Before installing the spring safety valve, follow these simple steps:
- check the labeling;
- inspect the body for external damage;
- remove the protective cap;
- there should be no foreign objects inside;
- It should be remembered that during installation the components of the product will heat up.
The installation process is carried out in accordance with current safety rules and regulatory and technical standards. The choice of location, design and number of valves, as well as the direction of discharge of the medium, is determined by the project.
The location must be selected so that there is easy access for maintenance and repair. Installation is carried out in a vertical position at the top point of the vessel. The installation can also be carried out near a vessel or pipeline, but there should not be a shut-off device between the products.
The size of the fitting cannot be less than the diameter of the valve inlet pipe.
A check spring poppet valve with a large number of discs can provoke an increase in their resistance, which can change the pressure difference in the upper and bottom parts of the product. Therefore, it should be installed in the latter area.
Self-installation of such devices is a complex procedure that requires experience and certain skills. Therefore, it is necessary to turn to professionals.
Problems and repairs
Leakage of the medium through the valve occurs when the pressure is lower than the set pressure.
- delay of foreign objects on the sealing elements - it is necessary to purge the throttle;
- damage to the sealing elements - grooving or grinding is performed, followed by a leak test; if the depth of damage is more than 0.1 mm, mechanical treatment must be performed;
- spring deformation - it is replaced;
- misalignment of elements due to heavy load - the load is removed, the flow and inlet lines are checked, it is necessary to re-tighten the studs;
- reduced opening pressure - adjustment, deformation of the spring - it is being replaced;
- poor-quality assembly after repair - eliminate all assembly defects.
Repair of safety spring chokes must be left to professionals. The cost of the procedure will cost from $50.
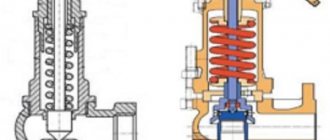
Spring safety valve (PPV)
– a type of pipeline fittings designed to automatically protect equipment and pipelines from excess pressure above a predetermined value by releasing excess working fluid and ensuring that the discharge stops when the closing pressure is restored and the operating pressure is restored.
Main valve assemblies and parts:
1 - body, 2 - seat, 3 - spool, 4 - cover, 5 - rod, 6 - nut, 7 - pin, 8 - spring, 9 - bellows (installed in bellows valves), 10 - locking screw, 11 - adjusting bushing, 12 - guide bushing, 13 - partition, 14 - adjusting screw, 15 - cap, 16 - threaded flange.
Principle of operation.
At normal operating pressure, the force of the compressed spring presses the spool against the seat (the passage for relieving the working medium is closed). When the pressure increases above the set value, an oppositely directed force begins to act on the spool, which compresses the spring, and the spool rises, opening a passage for discharging the working medium. After the pressure in front of the valve decreases to the closing pressure, the spool under the action of the spring is again pressed against the seat, stopping the discharge of the medium.
Installation position – vertical, cap up.
Shutter tightness
– class “B” GOST R 54808. At the customer’s request, it is possible to manufacture with other classes of tightness.
Possible valve designs:
- A sealed cap with a forced opening unit, and without one.
- Balancing bellows.
- Thermal barrier.
- "Open" lid.
- A locking element that prevents the valve from operating.
Pipeline connection:
- flanged;
- for lens gasket (flange according to GOST 9399);
- fitting;
- tsapkovoe.
Valves with bellows.
The bellows is a mechanism that compensates for the effect of back pressure at the outlet of the valve. The bellows is designed to protect the valve spring from the harmful effects of an aggressive working environment under conditions of high or low temperatures. Bellows valves are made of steel grades 12Х18Н9ТЛ and 12Х18Н12МЗТЛ and are intended for working environments with temperatures from minus 60 °С and below. Designation of bellows valves: KPP4S, KPPS.
The design of the sealing surfaces and the connecting dimensions of the valve flanges are in accordance with GOST 12815-80, row 2, face-to-face lengths are in accordance with GOST 16587-71.
Valves DN 25 PN 100 kgf/cm2 can be manufactured with union ends for connection to a pipeline in accordance with GOST 2822-78, as well as with a flange connection in accordance with GOST 12815-80, row 2.
Safety valves with nominal pressure PN 250 kgf/cm2 and PN 320 kgf/cm2, like other models, are designed to protect equipment from unacceptable excess pressure by automatically releasing excess working fluid. Used on equipment with liquid and gaseous working media that do not cause corrosion of body parts greater than 0.1 mm.
Safety valves with a stamped-welded body can be manufactured with individual face-to-face length (L and L1), height (H) and flange mounting dimensions, which allows them to be used as substitutes for imported valves without changing already installed equipment and pipelines.
Calculation of valve capacity - according to GOST 12.2.085-2002.
Setting pressure, pH
– the highest excess pressure at the inlet to the safety valve, at which the valve is closed and the specified tightness of the valve is ensured.
Opening start pressure, Рн.о.
(starting pressure; set pressure) – excess pressure at the inlet to the safety valve, at which the force tending to open the valve is balanced by the forces holding the locking element on the seat. When the opening pressure begins, the specified tightness in the valve shutter is broken and the locking element begins to rise.
Full opening pressure, Рп.о.
– excess pressure at the inlet to the safety valve, at which the valve moves and maximum throughput is achieved.
Closing pressure, Рз
(reseating pressure) – excess pressure at the inlet to the safety valve, at which, after the working medium is discharged, the locking element is seated on the seat, ensuring the specified tightness of the valve. Valve closing pressure, Рз – not less than 0.8 Рн.
Back pressure
– excess pressure at the outlet of the fittings (in particular, from the safety valve).
Back pressure is the sum of the static pressure in the exhaust system (in the case of a closed system) and the pressure arising from its resistance when the working fluid flows.
Mandatory minimum order information.
When ordering valves, you must fill out a questionnaire (Appendix B):
- product type, designation, type designation (according to the table of figures);
- nominal diameter of the inlet pipe, DN, mm;
- nominal pressure, PN, kgf/cm2;
- setting pressure (Рн, kgf/cm2) or spring number (when only the spring number is specified, the valve is adjusted to the minimum value from the range of the specified spring);
- body material;
- the presence of a manual detonation unit in the valve design;
- the presence of a bellows in the valve design.
Example of designation when ordering a spring safety valve:
An example of designation when ordering a spring safety valve DN 50 PN 16 kgf/cm2 made of steel 12Х18Н9ТЛ with a manual detonation unit, setting pressure – Рн=16 kgf/cm2, model KPP4R according to TU 3742-005-64164940-2013:
Safety valve KPP4R 50-16 DN 50 PN 16 kgf/cm2, pH=16 kgf/cm2, 17nzh17nzh. When placing an order, the need to complete the valves with matching parts (matching flanges, gaskets, studs, nuts; for valves DN 25 PN 100 - nipples with union nuts and gaskets) is specifically stated.
A safety valve is a pipeline fitting that protects high-pressure equipment and pipelines from mechanical damage and various types of destruction as a result of emergency situations. This is achieved by releasing an excess amount of liquid, gas or steam from the system, as well as the vessel in which excessive pressure is formed. In addition, this valve prevents the release of the working fluid when the nominal pressure is restored.
A safety valve is a mechanism that operates in direct contact with the working environment together with other structures that perform the function of protective fittings, including pressure regulators.
Which valve to choose?
The variety of models presented for sale, despite the similarity in design, is very large. Therefore, it is difficult to give any specific recommendations. We can only list some criteria that are worth paying special attention to.
- As already mentioned, the valve must have an inlet connection size (DN) that is the same as the pipe on which it will be installed. No transitions to more or less!

The nominal diameter is indicated on the valve body.
- The second most important parameter is the valve activation pressure. As already noted, for most autonomous systems the optimal threshold is a level of three atmospheres. However, there are exceptions - it is better to discuss this with specialists when designing heating.
By the way, some companies practice color marking of their valves - according to the color of the plastic release handle. For example, red – 3.0 bar, black – 1.5 bar, yellow – 6.0 bar.

Valves of different response ratings - the manufacturer has highlighted them in different colors
However, you cannot completely rely on such signs - this is not some generally accepted standard. It is quite possible to see valves with a blue head, and with ratings of six, eight, and ten bar. So always check what exactly is indicated on the device.
- It has already been said above that preference should be given to devices in brass cases.
- Of course, you should not dig for safety valves of completely unknown origin. Even if the price seems very tempting. Never forget that in this case we are also talking about your personal safety.
The stores have plenty of high-quality products from well-known brands - Valtex, BAXI, Ariston, Beretta, Danfoss, Ferroli, Vaillant, Watts and others. It would be useful to read information about the products in advance on the official websites of the companies.
Of course, the purchase should be made in a specialized store. Do not hesitate to request documents that can confirm the originality of the selected product.
- Many argue that from the point of view of both convenience and overall cost, it is much more profitable to purchase a ready-made “security group”.

In conclusion, we attach a video in which the author shares his experience in identifying and eliminating problems with the safety valve.
Main types of valves and their purpose
All safety products may differ from each other in a number of parameters, depending on the design features, namely:
- By type of closing valve:
- proportional;
- two-position.
- According to the lifting height of the closing organ:
- low-lift;
- mid-lift;
- full lift.
- Depending on the type of load on the spool:
- spring;
- lever;
- lever-spring;
- magnetic-spring.
Also, safety valves can differ in the nature of their operation and can be direct or indirect acting devices. The former are considered classic safety mechanisms, while the latter belong to the class of impulse devices. The most commonly used modification in industry is the spring-type corner safety choke.
High pressure (or rather its excess) can occur in the system for various reasons, caused by physical internal processes or other external factors, such as:
- equipment malfunctions;
- unwanted heat input from outside;
- errors when assembling the thermomechanical circuit. A safety valve is often installed in areas where such complications are likely to occur. These devices are compatible with almost any equipment, but they are most in demand when used with household or industrial tanks operating under high pressure conditions.
Nominal diameter
Determination of the nominal diameter of this safety device is carried out using special methods that were developed by the State Technical Supervision Authority. For these purposes, it is advisable to invite qualified specialists.
If this is not possible, it is recommended to use the following principle: the diameter of the valve must be no less than the outlet pipe of the boiler unit. In this case, a significant margin is obtained, which will ensure the safety of the system.
The safety valve of the heating system is adjusted so that the critical pressure is approximately 10-15% higher than the operating pressure. The functionality of the device can be checked by forcing it to open. The safety valve of the heating system must be adjusted annually before the start of the heating season.
Spring type safety valve
Spring-loaded safety valves protect equipment and thereby prevent its destruction as a result of pressure exceeding the norm. They are used on boilers, various tanks, containers, pipelines and perform the function of relieving the working environment. Excess can be simply released into the atmosphere or into a special discharge pipeline system. After the pressure returns to normal, the valve closes. The main characteristics of a spring safety valve are its flow capacity, as well as its response pressure. The latter is configured on special equipment in the factory, and to test the operation of the device, or to remove dirt that accumulates during operation, the valves have a device that allows you to manually open the device, although some modifications can be done without it. For efficient and reliable operation of the valve in a gaseous environment, its design may include a forced blowing device. In spring-loaded valves, the pressure of the medium on the valve is opposed by the degree of compression of the spring. It is this that determines the actuation force, and the range of adjustments depends on the elasticity of the spring used. This fitting has gained wide popularity due to its simple design, easy settings and wide range of these products. All this allows you to select the most suitable model for use in specific conditions. The safety choke is mounted vertically. The locking element in the spring valve device is a butterfly valve. A special device, along with a spring, sets the clamping force and in the event of excess pressure, the declared clamping force is not enough to hold the medium. As a result, the process of removing its excess from the system occurs until the pressure level is normalized to the original level. You can learn more about the design and design features of a particular spring valve by studying its passport. Its main components are a locking body, consisting of a bolt and a seat, as well as a setter. The setpoint allows you to adjust the valve. It is very important that the spool fits tightly to the seat and prevents leaks. Such adjustments are made using a screw. The valve, as a rule, closes when a pressure appears that is 10% less than the operating pressure.
Safety relief valve: protecting the gas pipeline from high pressure
Safety relief valves (SVR) are devices that are used in various gas pipeline structures and perform the function of releasing excess gas into the atmosphere or an auxiliary pipeline.
Relieving gas is necessary in order to get rid of excess pressure in communications.
PSKs are also used in other types of pipeline structures (heating, water supply), however, everywhere they perform the same function.

Excessive pressure in any system is extremely dangerous, which is why relief valves are installed on almost all types of pipelines
Why are PSCs needed?
Relief valves are necessary to equalize the pressure in the system during a short-term increase.
During operation, such devices are in a closed position, so they are classified as closed pipe fittings.
Such devices are mounted at the communication point, which is located behind the regulator, and are triggered in the event of an increase in pressure in the gas line. After releasing excess gas, the valve returns to its original state.
In the absence of a PSC, various emergency situations are possible, among which the most common is considered to be mechanical destruction of the gas pipeline. Excess pressure arising in the system is removed automatically by the PSK.
Note! PSKs remove excess gas into the environment or into a branch of the main pipeline with a low pressure indicator.
PSK is an indispensable device that is responsible for the safety of pipeline structures, as well as pumps and fittings. Let's consider the main factors that precede the occurrence of excess pressure in the system:
- various problems that arise in the equipment during its operation;
- increase in temperature in communication;
- various physical processes that occur within the network;
- errors in the thermomechanical circuit.

An increase in pressure can occur for various reasons and an accident can only be prevented by relieving it
Main advantages of PSK
Shut-off safety valves can have different designs, however, they all have common advantages that we recommend paying attention to. Let's consider the advantages of these devices:
- in addition to providing automatic monitoring of pressure indicators in the system, these safety devices provide sealing in the pipeline;
- one of the main advantages of PSCs is that they have a simple design;
- PSKs are easy to install;
- the versatility of these products allows them to be used in any type of communications;
- equipped with sealing elements and are wear-resistant;
- have an optimal building height;
- resistant to temperature changes;
- resistant to corrosive influences. PSC can be used even in pipelines transporting aggressive chemicals;
- capable of carrying heavy loads.
Lever type safety valves
A lever valve is a device in which the shut-off element is sealed using a spring or weight. The purpose of such valves is unchanged - to discharge excess volume of the working medium in case of excessive pressure increase. Adjust the lever valve so that at normal pressure levels, the shutter position always remains closed. The valve spool feels pressure from two forces at once - this can be a load or a spring, as well as the working substance itself. The weight is fixed on the lever arm and its weight is transferred to the valve stem. With predetermined pressure parameters, the force of pressing the valve against the seat must be higher than the pressure force of the working medium and, accordingly, the valve is held in the closed position. As the pressure increases, at a certain moment the downforce becomes equal to it and it is at this moment that the valve opens. During the period when the valve is open, excess working fluid is taken in, resulting in a decrease in pressure in the system. After this, the shutter is again pressed against the seat and the valve closes. The vast majority of lever valves are designed as an angular body (the angle of the fittings is 90 degrees). But there are also designs in which the fittings are located on the same axis. This building is called a pass-through. The main purpose of lever valves is to protect against all kinds of emergency situations. In this regard, this type of reinforcement is considered a particularly important critical unit. Like any other product, lever valves must meet certain requirements: when overpressure occurs, operation must be carried out quickly and without any complications, and when its indicators decrease to normal, the valve must return to the closed position;
Safety valves
- a type of pipeline fittings designed to protect the heating system from excess pressure. The safety valve is a direct acting valve, i.e. fittings operating directly under the control of the working medium itself (as well as direct-acting pressure regulators).
| Photo Designation | Name | Du, mm | Working pressure (kgf/cm2) | Housing material | Working environment | Connection type | Price, rub | ||
| 20 | 16 | bronze | water, steam | coupling-pin | 3800 | ||||
| Spring safety valve | 25 | 16 | bronze | water, steam, gas | union-fitting | 12000 | |||
| Low-lift spring safety valve | 15-25 | 16 | steel | ammonia, freon | pin-type | 1200-2000 | |||
| Steel safety valve | 50 | 16 | steel | liquid or gaseous non-aggressive medium, ammonia | flanged | 6660-10800 | |||
| 50-80 | 25 | steel | flanged | 6000 | |||||
| double lever safety valve | 80-125 | 25 | steel | Water, air, steam, ammonia, natural gas, petroleum products | flanged | 9000-19000 | |||
| Full-lift spring safety valve | 25 | 40 | steel | water, air, steam, ammonia, oil, liquid petroleum products | flanged | 20000 | |||
| Angle safety valve | 50-80 | 16 | steel | water, steam, air | flanged | 12500-16000 | |||
| Single lever safety valve | 25-100 | 16 | cast iron | water, steam, gas | flanged | 1500-7000 | |||
| Double lever safety valve | 80-150 | 16 | cast iron | water, steam, gas | flanged | 6000-30000 | |||
| Spring safety valve | 15-25 | 25 | steel | freon, ammonia | union-fitting | 5000-7000 | |||
| Low lift safety valve VALTEC | 15-50 | 16 | brass | water, water vapor, air | coupling | 860-10600 | |||
| safety valve | 34-52 | 0,7 | steel | water, steam | flanged | 15000 | |||
| Spring safety valve | 50-150 | 16 | steel | flanged | 20200-53800 | ||||
| Spring safety valve | 50-150 | 40 | steel | water, air, steam, ammonia, natural gas, oil, petroleum products | flanged | 20000-53800 | |||
| Spring safety valve | 50-150 | 16 | steel | water, air, steam, ammonia, natural gas, oil, petroleum products | flanged | 20200-53800 | |||
| Angle spring safety valve. | 50 | 100 | steel | gas, water, steam, condensate | flanged | 37900 | |||
| 80 | 100 | steel | gas, water, steam, condensate | flanged | 39450 | ||||
| Spring safety valve with angular damper | 50 | 64 | steel | steam | flanged | 37300 | |||
| Spring safety valve with angular damper. | 80 | 64 | steel | gas, water, steam, condensate | flanged | 46500 | |||
Classification of safety valves:
According to the nature of the elevation of the closing organ:
- proportional action valves (used on incompressible media);
- on/off valves;
According to the height of the lift of the closing organ:
- low-lift (the lifting height of the locking element (spool, plate) does not exceed 1/20 of the seat diameter);
- medium-lift (plate lifting height from 1/20 to ¼ of the saddle diameter);
- full lift (lift height is 1/4 of the saddle diameter or more);
By type of load on the spool:
- spring
- cargo or lever-load
- lever-spring
- magnetic spring
In low-lift and medium-lift valves, the lift of the spool above the seat depends on the pressure of the medium, which is why they are also called proportional-acting
.
Such valves are mainly used for liquids when large throughput is not required. In full-lift valves, the opening occurs simultaneously, which is why they are also called on-off
.
Such valves are high-performance and are used for both liquid and gaseous media.
Check valve installation rules
When deciding where to install a check valve for heating, you need to be guided, first of all, by the requirements of the project. If the wiring diagram requires a check valve, it must be installed in the right place and taking into account all requirements and standards. As a rule, such fittings are installed at the time of piping the heating boiler.
Please note that for proper installation of a check valve, you need to correctly select its type in accordance with the operating pressure and temperature of the coolant
In addition, it is important to install the product in the manner specified by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet for the fittings. As a rule, the location of check valves is determined at the design stage of the heating system. As a rule, the location of check valves is determined at the design stage of the heating system
As a rule, the location of check valves is determined at the design stage of the heating system.
Installing check valves on a heating system allows you to cope with several tasks at once. First of all, such devices allow you to prevent negative consequences for the heating system in the event of emergency situations. In addition, this is a kind of insurance against unnecessary repair costs in the future. Another important point is the consistency of the operation of various devices looped into one system. This is achieved precisely through the installation of shut-off valves.
Thus, if you are concerned about the durability and reliability of your heating and do not want to incur additional costs in the future, then you should definitely consider having a check valve in your heating circuit.
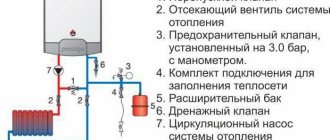
When equipping a heating system, it is important not only to think through the parameters of its main functional parts (pipes, heating boiler, etc.), but also to pay attention to its small components and mechanisms, the quality of installation of which will largely determine the heat supply. The element responsible for safe operation is the safety valve in the heating system, the main function of which is to protect against potential hazards associated with system overload, as well as to control the circulation of the coolant. Despite the relatively limited range of tasks it performs, a check valve for heating is installed at different points in the system and is an important part of it.
Despite the relatively limited range of tasks it performs, a check valve for heating is installed at different points in the system and is an important part of it.
Despite the relatively limited range of tasks it performs, a check valve for heating is installed at different points in the system and is an important part of it.
The element responsible for safe operation is the safety valve in the heating system, the main function of which is to protect against potential hazards associated with system overload, as well as to control the circulation of the coolant
Despite the relatively limited range of tasks it performs, a check valve for heating is installed at different points in the system and is an important part of it.
What a relief valve for heating can be like, as well as the features of its design and connection will be discussed further.
Lever (lever-weight) safety valves, operating principle:
| Load to 17s18nzh, 17h18br |
The principle of operation of a lever-load safety valve is to counteract the force on the spool from the pressure of the working medium - the force from the load transmitted through the lever to the valve stem. The basis of the mechanism of this type of valve is a lever and a load suspended on it. The operation of the device depends on the weight of the load and its location on the lever. The greater the weight and the further it is on the lever, the higher the pressure the valve operates. Lever valves are adjusted to the opening pressure by moving a weight along the lever (the weight of the load may change). Levers are also used to manually purge the valve. Lever valves are prohibited for use on mobile heating devices.
Internal structure of lever safety valve:
1.Inlet; 2. Outlet; 3. Valve seat; 4. Spool; 5. Cargo; 6. Lever.
Sealing of large diameter seats requires heavy weights on long arms, which can cause severe vibration of the device. In these circumstances, valves are used, inside of which the medium discharge cross-section is formed by two seats, which are closed by two spools using two levers with weights (see for example:,). The use of these two-lever valves with two gates, which reduces the weight of the load and the length of the levers, ensuring normal operation of the system.
Adjustment of the lever-weight valve, as noted above, is carried out by moving the weight along the lever. After the required pressure has been adjusted, the load is secured with bolts, covered with a protective casing and locked. This is done to prevent unauthorized changes to the settings. Flanges are often used as weights.
Features of lever-weight valves:
Lever valves are pipeline fittings that were developed before the 40s of the last century. This is an obsolete valve, purchased only to maintain boiler points and similar facilities from the Soviet public utilities era.
A special feature of the valve is the need to grind in the working surfaces (spool and seat - pressed bronze sealing ring) directly at the valve installation site. Lapping means treating the bronze seat with abrasive materials to achieve tighter contact between the spool and the seat. The spool in the valve body is not secured and during transportation and loading its working surfaces are easily damaged. A valve without lapping will not be sealed.
Advantages of lever safety valves:
- Simplicity of design;
- Maintainability;
- Manual adjustment of valve actuation;
Disadvantages of lever safety valves:
- The need to grind in working surfaces;
- Short valve life;
- Bulky design;
Exploitation
The longevity of the protective mechanisms depends on compliance with all technical operating conditions. During operation of the protective unit, the following defects may occur due to wear of the main parts:
- Seat leak. The defect may occur as a result of metal shavings and scratches on the seat. The defect can be eliminated by grinding in the seat or replacing it with a similar fitting.
- Low opening pressure of the device due to the valve spring losing its elastic properties or misadjustment of the setting. To eliminate the failure, you need to replace the spring or the fitting itself, adjust the pressure, check the operation and put a seal.
- If it is necessary to replace the unit for repair, then a plug or valve cannot be temporarily installed in its place. It is necessary, for the safety of the facility, to first select a valve with exactly the same characteristics, and only install it instead of the removed one.
- If pulsation occurs during operation, rapid opening and closing of the device valve, then such a defect can cause unwanted vibration of the pipelines, which can lead to their deformation. The reason may be a mismatch between the cross-sectional sizes of the main pipeline and the pipeline connected to the unit. To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to install pipes of the same cross-section during installation.
Spring safety valves, operating principle:
| safety valve |
The principle of operation of a spring safety valve is to counteract the spring force - the force on the spool from the pressure of the working medium (coolant). The coolant exerts pressure on the spring, which compresses. When the set pressure is exceeded, the spool rises and the coolant is discharged through the outlet pipe. After the pressure in the system has dropped to the set pressure, the valve closes and the coolant drainage stops.
Internal structure of spring safety valve:
1 - body; 2 - nozzles; 3 — lower adjusting sleeve; 4, 5 — locking screw; 6, 19, 25, 29 — gasket; 7 - upper adjusting sleeve; 8 - pillow; 9 — spool; 10 — guide sleeve; 11 - special nut; 12 - partition; 13 - cover; 14 - rod; 15 - spring; 16 — support washer; 17 — adjusting screw; 18 — lock nut; 20 - cap; 21 - cam; 22 — guide sleeve; 23 - nut; 24 - plug; 25 - cam shaft; 27 - key; 28 — lever; 30 - ball.
The response pressure of the spring safety valve is set by equipping the valve with various springs. Many valves are manufactured with a special mechanism (lever, fungus, etc.) for manual detonation for control purging of the valve. This is done in order to check the functionality of the valve, since various problems may arise during operation, such as sticking or freezing of the spool to the seat. However, in industries using aggressive and toxic environments, high temperatures and pressures, control blowing can be very dangerous. Therefore, for spring valves used in such industries, the possibility of manual blowing is not provided and is even prohibited.
When working with aggressive chemical media, the spring is isolated from the working environment using a seal along the rod with a stuffing box, bellows or elastic membrane. Bellows seals are also used in cases where leakage of the medium into the atmosphere is not allowed, for example at nuclear power plants. The maximum operating temperature for safety spring valves is up to +450°C, pressure up to 100 bar.
The relief safety valve opens before the set pressure is reached. The valve opens completely when the pressure exceeds the set pressure by 10-15% (depending on the model). The device closes completely only when the pressure is 10-20% less than the set pressure, because the escaping coolant creates additional dynamic pressure.
If the heating system is functioning stably, without failures or overpressure, the relief safety valve remains without “working” for a long period of time and may become clogged. Therefore, it is recommended to clean it periodically.
Advantages of spring valves:
- simple equipment design;
- small size and weight with large flow sections;
- Possibility of installation in both vertical and horizontal positions;
- possibility of obtaining high throughput.
Disadvantages of spring valves:
- a sharp increase in the spring force when it is compressed during the process of lifting the spool;
- the possibility of receiving a water hammer when closing the valve;
Features of three-way safety valves
We should also talk about a device that is not so well known to consumers - a three-way valve with a manual or electric switch. It is used in heating systems with low temperature circuits.
The fuse design is equipped with three holes, one of which is input, two are output. The flow of the medium is controlled by a damper made in the form of a ball or rod. The moving fluid is redistributed by rotations.

Three-way fuses are appropriate for condensing boilers and in cases where several different systems operate from one heating equipment
Let's imagine a situation: the house has a heating scheme with a system of conventional radiators and heated floors. The technical requirements for the operation of the second option provide for not too high coolant temperatures.
The boiler heats water at the same temperature for all systems. In such conditions, there is a need for a redistributing device, the tasks of which are perfectly handled by a three-way valve.
It is responsible for the following functions:
- delimitation of areas;
- distribution of flux density by zones;
- facilitating the mixing of coolant from the main supply/return branches to send colder water into the underfloor heating pipeline than into the radiators.
In order not to constantly control the temperature of the medium yourself, you need to pay attention to valve models equipped with a servo drive.
This device operates from a sensor installed in the low-temperature circuit. When the temperature changes, a shut-off mechanism is activated, opening or closing the liquid supply from the return line.
We talked in more detail about the types of three-way valves for heating and the criteria for its selection in the next article.
Magnetic spring safety valves, operating principle:
Magnetic spring safety valves use an electromagnetic actuator. The electromagnet provides additional pressing of the spool to the seat. When the response pressure is reached, the electromagnet turns off and only the spring counteracts the pressure, and the valve begins to operate like a regular spring valve. Also, the electromagnet can create an opening force, that is, counteract the spring and force the valve to open. There are valves in which the electromagnetic drive provides both additional pressing and opening force; in this case, the spring serves as a safety net in case of power failure. Magnetic spring valves are typically used in complex impulse safety devices as control or impulse valves.
A safety valve is a safety device that prevents a substance from flowing back through a pipeline and releases excess into a low pressure area or atmosphere. This is an indispensable device, as it allows you to save pumps, equipment and the pipeline itself in case of emergency situations.
Possible causes of damage
Spring safety valves are devices that are reliable and durable, but can lose functionality for several reasons. Safety valves need to be repaired if a leak occurs, the locking element is not completely closed or opened, or if it fails to operate. Among the main causes of malfunctions are violations during the installation of safety valves, incorrect settings, misalignment of the valve and the entry of foreign objects.
To avoid emergency situations and ensure uninterrupted functions, it is necessary to carry out testing before putting water safety valves into operation. The tightness of flange connections and sealing surfaces is also checked periodically.
Why are valves on batteries needed?
Valves are also installed on radiators and circuit batteries, but their main function is to remove air from the system.
The installed valve for the heating radiator can be manual or automatic. The manual valve is opened and closed manually using a key and screwdriver.
The automatic valve on the heating radiator does not require human intervention. It removes air perfectly, but its main drawback is its sensitivity to blockages due to contamination of the coolant. To remove dissolved air from the coolant and clean it of dirt and sludge, it is recommended to install air separators.
- How to fill water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler made in Russia
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes for malfunctions
Recommended reading
Bypass in a heating system - what is it and why is it necessary? Expansion membrane tank for a heating system: structure and functions How to accurately choose an expansion tank for heating? Heating thermostat - operating principle of different types
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts