Good day, dear reader! I don’t know for what reason, but our five-story house is heated so well that even in the cold it was too hot. The windows in my apartment were constantly open for ventilation, and I had to pay huge sums for heating. Something had to be done about this.
So I decided to install a separate heat meter and thermostatic valve into the system. Now my apartment is quite warm, and the amounts on my bills have dropped by almost half.
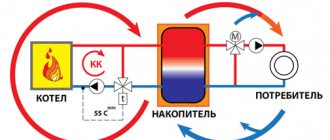
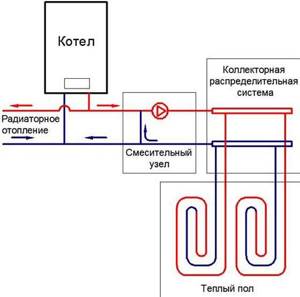
Rice. 3. Independent connection diagram of IHP with a pressure maintenance device
This scheme is somewhat more expensive than the dependent one, but at the same time it protects in-house heating devices from low-quality coolant coming from the central network. If it is necessary, in addition to heating, to provide centralized hot water supply, then additionally install one or more heat exchangers. Depending on the ratio of heating and hot water loads, single-stage and two-stage water heater connection schemes are used.
Examples and ROI
In Ukraine, modern automated heating stations with an independent connection scheme are offered by the Austrian company Herz.
IHP from Herz operate at the temperature of network water in the primary circuit (central heating supply) – 110–140°C / 65–80°C. At the same time, the temperature in the indoor heating system is ensured at 90–55°C / 70–45°C. The nominal pressure in the primary circuit is up to 16 bar. Operating pressure in the secondary circuit is from 2 to 10 bar. To maintain pressure in the system, a membrane expansion tank or, in the case of systems with a power of more than 300 kW, a pressure maintenance unit is used. Coolant circulation is carried out by highly efficient frequency-controlled pumps.
The ITP configuration includes circuits based on a two-way valve or a combi-valve - a flow regulator with an electric drive, and a plate or brazed heat exchanger. Weather-dependent regulation of coolant temperature and temperature settings are carried out by the controller. At the same time, it is possible to organize remote access and control of equipment via a GPRS modem. To account for heat consumption, an ultrasonic flow meter with a computer is used.
In addition to IHP, residential heating units are also used for multi-storey buildings. They allow the consumer to individually regulate the operation of the heating and hot water system and provide convenient accounting of energy consumption. For example, the Herz DeLuxe heating unit is designed for a maximum operating temperature of 90°C, a maximum operating pressure of 10 bar and provides a hot water flow of up to 15 l/min. Such heating points are installed directly on each consumer (apartment). There are options for open or hidden installation in the wall, as well as with a mixing unit for low-temperature panel radiant heating, for example: warm walls, warm floors (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Compact apartment heating substation Herz Bregenz
The payback time for investments in ITP when modernizing buildings ranges from 1 to 5 years and depends on the equipment used, the size of the building and the type of system. It is worth remembering that the installation of individual heating points is an important and necessary step, but not the only one on the path to energy efficiency in the heating system of a residential building. The greatest effect is achieved in conjunction with balancing the heating system and installing thermostatic valves on heating devices.
Views: 5,337
Valves and taps
Such fittings are a heat exchanger of a shut-off device. This means that the radiator is adjusted by turning the tap/valve in the desired direction. If you turn the fittings 90° all the way, the flow of water into the battery will no longer flow. To change the heating level of the heating device, the locking mechanism is set to the half position. However, not every fitting has this opportunity. Some faucets may leak after a short period of use in this position.
Installing shut-off valves allows you to manually regulate the heating system. The valve is inexpensive. This is the main advantage of such fittings. In addition, it is easy to operate, and changing the microclimate does not require special knowledge. However, there are also disadvantages to locking mechanisms, for example, they are characterized by a low level of efficiency. The battery cooling rate is slow.
Stopcocks
A ball design is used. First of all, it is customary to install them on a heating radiator in order to protect housing from coolant leakage. This type of valve has only two positions: open and closed. Its main task is to turn off the battery if such a need arises, for example, if there is a risk of flooding of the apartment. For this reason, shut-off valves are cut into the pipe in front of the radiator.
If the valve is in the open position, the coolant circulates freely throughout the heating system and inside the battery. Such taps are used if the room is hot. The batteries can be turned off periodically, which will reduce the air temperature in the room.
However, ball locking mechanisms must not be installed in the half position. With prolonged use, the risk of leakage in the area where the ball valve is located increases. This is due to gradual damage to the locking element in the form of a ball, which is located inside the mechanism.
Manual valves
This group includes two types of fittings:
- Needle valve. Its advantage is the possibility of half installation. Such fittings can be located in any convenient position: completely opens/closes the access of coolant to the radiator, significantly or slightly reduces the volume of water in heating devices. However, there is a drawback to needle valves. Thus, they are characterized by reduced throughput. This means that after installing such fittings, even in a fully open position, the amount of coolant in the pipe at the battery inlet will be significantly reduced.
- Control valves. They are designed specifically to change the heating temperature of batteries. The advantages include the ability to change position at the user’s discretion. In addition, such fittings are reliable. There is no need to frequently repair the valve if the structural elements are made of durable metal. There is a shut-off cone inside the valve. When you turn the handle in different directions, it rises or falls, which helps to increase/decrease the flow area.
Types and their structure
In a thermostatic distribution valve installed on a heated floor, the heated water is mixed with cooled water from the return pipe. This process is continuous as long as the heating is on.
There are two-way and three-way mixing valves for underfloor heating. They also differ in the method of mixing and the direction of flow.
Two-way
The two-way thermostatic valve is an improved manual type model. It can be hydraulic, pneumatic or electrically driven.
The design is simple, but capable of effectively regulating the temperature level of the coolant in automatic mode. The device is mounted in the heating system, instead of a manual valve.
Main advantages:
- Automatic reduction of liquid temperature level;
- Simplicity of design and low price;
- Easy installation.
Disadvantages - the possibility of installing it on pipelines with a small size. If you use this faucet when installing heating in a room with a large area, the thermostat will function intermittently. A two-way valve is more often used if heated floors act as additional heating.
The device is equipped with a thermostatic head with a scale. The head position can be changed manually or automatically. Manual models are simple and inexpensive. More modern devices work automatically.
The two-way valve operates according to the following principle - the coolant from the return line is again supplied to the floor pipes, but before this, a device is activated that opens the supply of heated water. The two flows are mixed inside the housing to the desired degree, then the temperature sensor is triggered and the shutter automatically closes the hole with the hot coolant.
The valve consists of a plunger and a seat. The plunger has a disc, needle and rod shape. It is located perpendicular to the movement of the fluid.
Three-way valve
The valve is designed for heating systems that are installed in large rooms. They have the same advantages as two-way valves. Particularly worth noting is the ease of adjusting the water temperature for heated floors.
But this thermostatic valve also has a minus - if the thermostat is triggered, the valve opens completely, thereby allowing hot coolant to enter the circuits. And this can cause overheating of the heating system, and even rupture of pipes. In addition, it has a lower flow capacity than a two-way valve.
Three-way thermostatic mixing valves are available in brass and bronze. They are equipped with a thermal head or thermostat, and can have an electric drive or a servo drive. The design is a faucet with two inlets and an outlet. Inside the case there is a mixing chamber, on which there is a thermostat with a regulator on which there is a digital panel. A thermal valve is connected in front of the manifold.
Operating principle of three-way thermostatic valve:
- heated water moves through the right and front pipes - if its heating degree meets the required parameters;
- if the temperature of the liquid increases or decreases, the thermostat comes into operation, it sets the rod in motion, as a result, cooled water is mixed with hot water;
- after reaching the set temperature, the front hole opens completely.
It should be said that when the device is turned on, the water flow voltage does not change. This leads to a uniform change in the temperature of the liquid supplied to the line.
By mixing method
Mixing taps for heated floors, depending on the mixing method, are:
With a thermostat function - with it it is possible to achieve and maintain the desired degree of heating of the coolant, since the device is able to regulate both flows (heated and cooled). The thermostat in the mixer, reacting to the level of heating of the liquid, opens or closes the hole through which heated or cooled coolant is supplied. In addition, the mechanism is designed in such a way that in the absence of cold water, the automation shuts off the flow of hot water.
Thermostatic - the device is equipped with a sensitive thermal head that has an external temperature sensor, it is located in each line. The operation of the valve is to determine the water temperature and send a command to the actuator.
Place and role of mixing valves in the heating system "warm floors"
The main task that consumers have to face when deciding to install heated floors in their home is to achieve the required coolant temperature. For radiators, water at a temperature of 750C is quite acceptable, which cannot be said about pipes that are laid in the thickness of a concrete screed.
Important! Excessive heating of the concrete screed leads to a deterioration in the temperature balance inside the heated room. At high temperatures, flooring (in most cases wood-based) quickly loses its aesthetic and technological qualities, becoming unusable.
In accordance with sanitary standards, the normal heating temperature of heated floors should not exceed 260C. Then the middle layers of the air mass inside the room warm up to comfortable values of 20-220C. In order to obtain such temperature parameters, the water entering the loops of the water circuit must be heated to 500C. Slightly less than 50% of the thermal energy of the heated water is spent on heating the layered cake of the heated floor. Taking into account the thickness of the concrete layer, material and type of floor covering, the temperature on the floor surface decreases.
A mixing unit, which is a set of interconnected instruments and devices, helps to achieve a significant reduction in the temperature of the boiler water at the entrance to the heating water circuits. One of the main roles in the operation of the mixer is played by the thermomixing valve, which mixes water for the heated floor. Thanks to this small device, two streams of water are mixed, cold and hot, so that the output is water at the required temperature. Valves installed in mixing units are of two types, three-way and two-way. Each type of crane performs its own tasks and functions determined by the technological process. Which device is best to use for your heated floors? What is behind the choice of the type of mixing and control device?
Thermostatic valve and control valve - differences
The use of thermal valves on a single-pipe heating system is especially important, but only if it is not flow-through. That is, if there are jumpers at the junction of the radiators - bypasses. It happens that there are no bypasses. As a result, the coolant sequentially passes through all radiators, one after another. Installing a thermostatic valve on such a system can only cause harm. Because the thermostatic valve will turn off all radiators located after it. Therefore, if for some reason it is very necessary for a flow-through system, it is better to install a control radiator valve. And don't cover it completely.
The difference between a control valve and a thermostatic valve is the ability to adjust the gap for the passage of coolant - more or less. The thermostatic valve, on the contrary, can only be in two positions. Firstly, it is open to a certain, previously adjusted level. Secondly, it is completely closed. Therefore, there is no need to install a thermal valve on a flow-through heating system without bypasses. Since, when the valve is closed, the circulation of coolant throughout the system will stop. This will create cooling and unbalance the heating system. It will also have a negative impact on the heating boiler. The situation can be aggravated by the absence or poor functioning of the safety valve. That is, a breakthrough may occur in one of the weak points of the system.
What materials are they made from?
Corrosion-resistant metals are used to make the thermostatic valve body:
- Brass.
- Bronze.
- Stainless steel.
Additionally, the surfaces of brass products are nickel-plated, and the bronze body is either also nickel-plated or coated with a layer of chrome.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of installing thermostatic valves in the heating system include the following factors:
- Energy independence of the device.
- Compactness.
- High precision temperature control.
- Easy to operate and highly reliable.
- Aesthetic appearance.
- The optimal combination of price and functionality.
The disadvantages of using thermostatic valves are:
- Difficulty setting up.
- There is a danger of the thermal head malfunctioning under the influence of a draft or a nearby stove.

Why might a valve leak?
The pressure relief valve in the heating system can leak for various reasons. In some situations, this is an acceptable natural process; in other cases, a leak indicates a malfunction of the device.
Leakage of the protection valve can be caused by the following reasons:
- Damage to the sealed rubber cup or disc as a result of repeated use. If during repairs a replacement part cannot be found on sale or is not included in the package, you will have to replace the device completely.
- In spring types, the opening of the side drain pipe occurs gradually; at borderline pressure values or short-term surges, the valve may partially operate and drip, which does not indicate its malfunction.
- Leakage can be caused by incorrect settings or malfunctions of the expansion tank - damage to its membrane, air escaping through a depressurized housing or a damaged nipple. In this case, sharp pressure surges are possible as a result of water hammer, causing periodic short-term leakage of coolant through the safety valve.
- The cause of leakage in some adjustable valves is fluid seeping down the stem through the top during actuation.
- If a back pressure is created at the outlet pipe above the device's response threshold, a leak will also occur.

The safety valve of steam boilers is designed to protect them from excess pressure in the system caused by various factors, and is a mandatory element when operating this type of equipment. There is a wide range of safety devices on sale from Chinese, domestic and European manufacturers, which are characterized by a relatively low cost. When purchasing, it is rational to choose a protective group from several devices, which additionally includes a pressure gauge and an air release valve.
Purpose of the device
It happens that in rooms, in addition to radiators, there are other heat sources - household appliances, gas or electric stoves, and so on. On sunny days, the temperature rises and the house becomes warmer than usual.
Important! The task of the thermostatic valve installed on the radiator is automatic temperature control, during which it takes into account temperature fluctuations in the room at a height of up to 2 meters.
Thermostatic valve for radiators ensures the reliability of heating equipment. By including it in the heating system, a comfortable and optimal temperature in the room is achieved and, at the same time, money spent on energy consumption is saved. The valve stabilizes the operation of the heating system if the pressure in it drops or disappears.
Tips for choosing
An ignorant homeowner who decides to look through the catalog of any well-known company in search of a three-way valve may be confused by the number and variety of products offered. To help you choose the right valve from a wide range, we will give some recommendations and start with a list of brands whose catalogs are generally worth opening. Here is a list of well-known companies whose products are trustworthy:
- Danfoss (Denmark);
- Herz Armaturen (Austria);
- Honeywell (USA);
- Icma (Italy);
- Esbe (Sweden);
- Caleffi (Italy).
The 3-way thermal valve was not invented yesterday. The photo shows an ESBE product from 1935
Now the main block of recommendations:
- To protect a solid fuel boiler from condensation, you can choose 2 types of three-way valves - with a fixed setting and a thermal head with a remote sensor. The second option will cost 20-30% more and is not always justified, since changing the return temperature is unnecessary. Buy a regulator with an internal thermostat set to 50 or 55 °C.
- To control the heating of individual branches and underfloor heating circuits, you definitely need a 3-way valve with a remote sensor and a thermostatic head. The sensor bulb is installed on the collector or pipeline whose temperature needs to be monitored.
- Ball (also known as rotary) regulators operate in tandem with an electric drive or are set manually. If you do not want to complicate the circuit and depend on electricity, choose a product that is suitable for its characteristics among seat valves powered by thermal heads.
- The most popular case material is brass or bronze. Stainless steel elements are more expensive, but cast iron is resistant to temperature shock and has a decent mass.
- In the schemes, both mixing and separating three-way taps are used with equal success. But if you are not a heating specialist and are assembling the system with your own hands, then it is better to take a mixer valve. It’s easier to understand and install correctly, which the expert will talk about in detail in his video:
Automatic adjustment
The advantage of this method is that there is no need to constantly change the position of the valve/faucet. The desired temperature will be maintained automatically. Adjusting the heating in this way makes it possible to set the desired parameters once. In the future, the heating level of the battery will be maintained by an automation unit or other device installed at the input of the heating device.
If necessary, individual parameters can be set multiple times, which is influenced by the personal preferences of the residents. The disadvantages of this method include the significant cost of components. The more functional the devices are for controlling the amount of coolant in heating radiators, the higher their price.
Electronic thermostats
These devices superficially resemble a control valve, but there is a significant difference - a display is built into the design. It displays the room temperature that needs to be obtained. Such devices work in conjunction with a remote temperature sensor. It transmits information to the electronic thermostat. To normalize the microclimate in the room, you just need to set the desired temperature value on the device, and the adjustment will be performed automatically. Electronic thermostats are located at the battery input.
Criterias of choice
The technical characteristics of a three-way device have a significant impact on the quality of underfloor heating. Therefore, when selecting a valve, it is worth considering the following indicators:
- The volume of the heated room. Heating large areas requires the installation of a three-way valve with automatic regulation, which independently controls the temperature of the coolant entering the pipeline of the floor heating system. For small rooms there is no need to buy expensive mixing devices with a complex design. A simple valve is suitable for heating balcony rooms, bathrooms and small corridors.
- Throughput indicator. The maximum level of liquid pumped by the mixing valve is determined at the beginning of the design of the floor heating system. The three-way valve must meet the established flow rate, otherwise the device will not withstand the pressure load.
- Cross section diameter. This parameter is necessary to connect the mixing device to the heating system. If necessary, special adapter devices are used that allow precise connection of devices.
- Material of manufacture. The valve must be made of metal that has a low expansion coefficient and does not change its original characteristics when interacting with a hot coolant. Three-way valves made of bronze and brass have these properties.
It is recommended to purchase mixing devices from trusted manufacturers. The product must be accompanied by warranty documentation, instructions with the specified technical characteristics and a quality certificate.

When choosing a three-way valve, consider the flow rate
Before installing a three-way valve in a heated floor system, you should check the device for functionality. To do this, set the control ring to the lowest temperature value, and then pass a hot stream of water through the valve. A properly functioning device should immediately close the hole.
Types of mixing valves
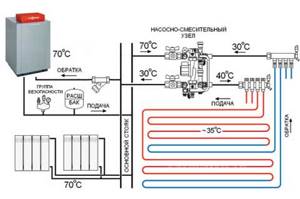
The main element by which the units are distinguished is the control valve. Basically, two types are used - two and three-way. The differences in their internal design determine the different operating principles. And which one to choose primarily depends on the surface area of the heated floor.
Two-way
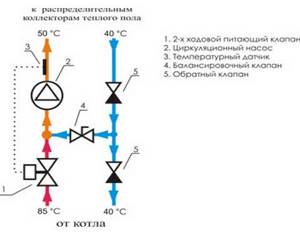
This is the most popular type of such device. It works on the following principle - the valve periodically recharges the line with hot coolant from the heating system. As a rule, the required heating value is indicated on the device body. It can be changed using the built-in or remote sensor. The latter is mounted in the inlet comb.
The coolant, after leaving the return comb, circulates through the pipelines. Enough for the liquid to cool below the specified level, the valve is activated and the addition of hot coolant begins. The rod closes only after the temperature rises to the optimum value.
This principle is more suitable for medium-sized ones, less than 200 square meters. m. In the case of a larger quadrature, the frequency of operation of the two-way valve increases. This can easily be explained by constant signals about a decrease in coolant temperature coming from the thermostat. If we take into account how long the pipeline may be in this case, it becomes obvious that it is characterized by large temperature differences. In other words, the liquid cools down greatly as it moves along the line, so it has to be constantly replenished with hot coolant from the heating system.
Attention
A large volume of hot water can negatively affect the integrity of the pipes and the operation of the entire heated floor. There is a high probability of exceeding the value of 50°C, which is unacceptable. Therefore, it is necessary to use a control valve of a different design as a control device.
Three-way
The two-way model has only the following operating modes - the damper is open or closed. To constantly mix coolant with different temperatures, a three-way valve for underfloor heating is required.
The flow volume is regulated by a special damper by changing the mixing proportion, and we can say that both cooled and hot liquid are constantly present in the line. The position of the damper is adjusted using a thermostat with a smooth servo mechanism.
The main problems that arise during the operation of a three-way device are a large volume of hot liquid entering the system, therefore a small failure of the mechanism for regulating the position of the damper or temperature sensor can cause a sharp increase in floor heating and, accordingly, damage the line.
On a note
In low-heating systems operating in 70 to 50 or 65 to 50 modes, the installation of a mixing unit is not necessary at all.
Collector connection diagram
The order of work is as follows:
- The collector box is mounted in a place that is convenient for access and at the same time so that it does not interfere. Pipes supplying heated water and return are connected to the cabinet. But before this, shut-off valves should be installed on the collector.
- In order to control the temperature and pressure in the system, a thermometer and a pressure gauge are placed in close proximity to the valves.
- To connect pipes connected to the manifold, compression fittings are used using a threaded connection.
- If it is necessary to combine pipes with different diameters, adapters or universal fittings are used, taking into account the connection diagram for the heated floor.
A complete heating scheme with heated floors has the following additional elements:
- circular pump;
- three-way mixer or pump-mixing unit;
- tap to drain water;
- air vent.
What types of valves are there?
Design features are not the only way modern thermostatic valves differ. These elements are made of different materials, have different diameters and connection methods. Let's get acquainted with the main types.
Material of manufacture
The main condition is that the material from which the valve is made must be resistant to mechanical stress and corrosion. This is explained by the fact that the element is in constant contact with the coolant liquid.
The operational and technical characteristics of the product depend on the material from which the valve is made. It is recommended that the valve be made of copper, brass or cast iron. Copper options are expensive, but last a long time. Brass samples also have a long service life and do not cause difficulties during operation. In general, in order to make the right choice, it is better to seek advice from the company’s specialists who will set up the heating system.

Valve
Control method
*
Based on this parameter, there are 2 types of devices:
- electrical;
- manual.
Often a manual version is installed, visually similar to an ordinary ball valve. More modern models with electric filling are popular in private homes - they are controlled automatically, distributing heat throughout the room. Adjusting the thermostatic valve is simple - the user sets the desired heating temperature for each room and the device supplies working fluid to the heating device. If desired, such a system can be combined with a “warm floor”, but you need to consider a way to create a protective coating for pipes.
Connection diagram
Having figured out what the valve consists of and on what principle it operates, let’s consider various schemes for connecting it. It all depends on the purpose for which the thermostatic balancing valve is installed.
Why do you need a valve:
- Protects the solid fuel boiler from the effects of condensation and temperature shock, which happens as a result of a sudden power outage.
- So that the coolant circulating in the “warm floor” system does not warm up above +45 degrees Celsius.
- Maintains the required temperature of the coolant in the heating system, and therefore the pressure in the pipeline.
To protect a heating unit operating on solid fuel, it is not allowed for cooled water from the heating system to enter its circuit. To do this, the boiler is connected according to a special circuit, which includes not only a mixing valve, but also a bypass. The operation of the circuit is as follows: the coolant will circulate in a small circle through the bypass until the heat generator warms up. When the temperature reaches +50-55 degrees Celsius, the valve will begin to open, adding cold water from the system. When the boiler reaches operating temperature, the bypass closes and the entire flow begins to flow through the radiators.
Similar functions are available when connected to a “warm floor” system. The pump circulates the coolant in the circuit until it cools down. As soon as this happens, the sensor and valve are activated and hot water from the boiler will begin to be added to the system.
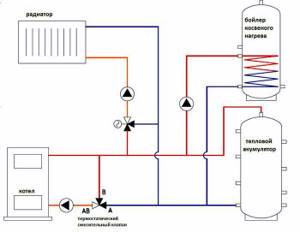
This important part is also used when piping a solid fuel boiler and a buffer tank, which plays the role of a heat accumulator. To warm it up effectively, the coolant temperature must reach +70-85 degrees Celsius, which is higher than the norm for radiators. The thermostatic valve is used to lower the temperature. To do this, it is installed behind the container, paired with pumping equipment.
Note! When installing a mixing valve, the pump should be located on the side where the tap pipe is always open.
*
Often, thermostatic switching valves are installed in large cottages with a complex heating system, with a water gun and a distribution manifold. Each circuit in such a situation requires a certain temperature. The boiler needs the highest level of heat, so no temperature control is supplied to it. But for other consumers, a coolant that is not so hot is supplied, so they are connected via thermostatic valves.

Type of valve
The nuances of installing a three-way valve in a heating system
In order to correctly install a three-way mixer, it is important to know some of the nuances on which the uninterrupted and efficient operation of the heating system will depend. Each product comes with instructions; strict adherence to them is necessary to avoid troubles:
Each product comes with instructions; strict adherence to them is necessary to avoid troubles:
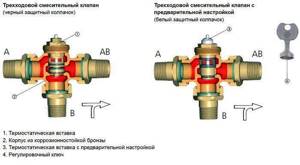
Follow the instructions on the body to set the valve to the correct position.
The symbols on the body mean:
- A – straight forward.
- B – perpendicular or bypass stroke.
- AB – input and output are combined.
It is important to determine the faucet model. This determines where the coolant will come from to the tap;
- In a symmetrical (T-shaped) scheme, the liquid enters the holes from the end and exits after mixing through the center;
- in an asymmetrical (L-shaped) scheme, the warm flow enters through the end hole, and the cooled flow enters from below. After mixing, the coolant exits through the second end hole.
It is important! The drive or thermostat should not be located at the bottom. After this, you need to prepare the heating system
First, turn off the water, then check for sediment in the line, which can damage the mixer. For installation you need to choose a convenient place with open access
After this, it is necessary to prepare the heating system. First, turn off the water, then check for sediment in the line, which can damage the mixer. For installation, you need to choose a convenient place with open access.
Connection diagram for distribution and mixing valve
Three-way and thermostatic mixing valves
Mixing valves are plumbing fittings that provide a certain degree of heating of the liquid by mixing flows with different temperatures. The resulting temperature is controlled by changing the flow ratio.
Three- and four-way mixing valves are available. The former allow you to lower the temperature of the coolant, the latter - to obtain separate adjustable circuits (an example of application is the protection of a heating boiler from low-temperature corrosion). In a number of schemes, three-way valves work to separate flows.
During operation, the temperature control of the mixing valve is carried out by a drive; there are several types:
- The thermostatic actuator presses on the rod due to the expansion of the liquid medium placed in it, which is sensitive to temperature changes. Typically, household three-way thermostatic mixing valves of small diameters are initially equipped with this type of actuator; it can be easily removed to install another type of device.
- Instead of a standard drive, the mixing valve can be controlled by a thermostatic head, which has its own sensitive element that responds to the ambient temperature, or to adjust the water temperature, the thermal head must be equipped with an external temperature sensor, which must be placed in the pipeline with the coolant. Such regulation is more precise.
- An electric drive controlled by a controller (room thermostat, overhead thermostat, etc.) can also influence the rod. Electrical sensors, called temperature transducers, continuously measure the coolant parameters and signal their exceedance to the controller, on which the operation of the electric mixing valve depends. The most common and most accurate method of regulation.
- A simplified version of the previous type of product is a three-way mixing valve with a servo drive. The difference is that there is no controller; the actuator controls the valve directly, receiving signals from the temperature sensor. Most often used in conjunction with three-way valves with a ball or sector distribution element.
vote
Article Rating
Selection of heating pipes
The process of selecting pipes is quite complex. When choosing pipes, you should decide:
- with pipe diameter;
- material;
- quantity.
The choice of pipes is made depending on what heating system will be used.
Steel pipes need to apply welding
Propylene pipes are very economical and profitable. They heat the room and prevent heat loss. The use of this type of pipe is possible only when the coolant temperature does not exceed 60 -70 degrees.
Metal-plastic is another modern material that is very convenient to use for heating systems. The disadvantage of installing this type of pipe is the need for additional equipment. Metal-plastic is afraid of sunlight, high temperatures, and shocks.
For private houses it is best to choose polypropylene pipes, and for apartments - metal-plastic. For a summer house or a compact private house, it is best to choose steel pipes.
If the batteries are too hot
In this case, the question arises of how to adjust the heating radiators in the apartment. The user cannot change the network temperature; all that remains is to reduce the fluid flow rate in the heating devices. For this purpose, special manual or automatic devices are used.
A manually operated valve is the simplest and long-known method. By reducing the available cross-section of the pipe using a rod, we reduce the flow of heated liquid into the radiator and thereby reduce its heat transfer. In this case, you should check whether such “heat adjustment” will not be an unprofitable enterprise: when all batteries are connected in parallel, a decrease in the flow in the first one automatically causes cooling of the others. Thus, if the first radiator in the chain is located in the bedroom and it is too hot, you can reduce its heating. But then the last radiator - for example, in the kitchen - will turn out to be almost cold and the heating in the room will be insufficient.
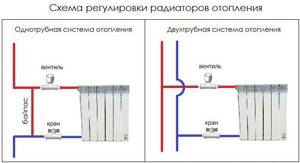
To regulate heating radiators, install either a valve and a ball valve on the inlet and outlet pipes, respectively, or a thermostat on the heating radiator.

To manually adjust the heating system in an apartment, special control valves with direct or angular connections are used.
The choice of the desired position of the rod in this case depends on the outside temperature, the heating of the water supplied to the heating system and the wishes of the users. How to regulate radiators with a regulator? Carefully monitor the temperature in the apartment (house) and “tighten” the valve to the desired result. Interestingly, manual valves have a built-in thermal valve and you can relatively easily turn a device for manual adjustment into an automatic one by purchasing and attaching a thermal head to it.
Automatic regulators
Automatic devices consist of a thermal valve and a thermal head.

The valve allows you to change the cross-section in the supply pipe; the thermal head, based on remote or built-in temperature sensors, as well as additional controllers, gives a command to change the position of the rod in the valve.
The simplest (and cheapest) version of the device contains a capsule of gas or liquid, which expands and contracts under the influence of temperature changes. The rod piston located next to this capsule moves towards decreasing or increasing the flow area of the pipe. More complex devices are powered by a battery or accumulator and transmit force to the rod using electric current. Some options connect to the home electrical network, for example, thermostats built into the overall smart home system.
The question of how to regulate the temperature of a heating battery using a thermostat - in a fully automated mode or with the control of the homeowner - is decided depending on the general scheme of the smart home system and the features of its operation.

The quality of operation of remote temperature sensors is also affected by:
- thick curtains covering it;
- the distance between the window sill and the sensor is too small;
- installation of a heating device in a niche.
Job
Without going into technical details, we can answer this way: to extend the life of the heating boiler and make it more economical.
A three-way valve mixes heated water with cooled water after passing through the heating devices and directs it back to the boiler for heating. Everyone can answer the question of which water to heat faster and easier - cold or hot.
Simultaneously with mixing, the valve also separates the flows. There is a natural desire to automate the management process itself. For this purpose, the valve is equipped with a temperature sensor with a thermostat. In this case, an electric drive works best here. The quality of functioning of the entire heating system depends on the drive device.
Please note: an automatic three-way valve installed in the heating system allows you to achieve up to 50% fuel savings.
Recommendations for installing devices
To be able to regulate the temperature of the battery in the apartment, consider any type of valve: they can be straight or angular. The installation principle of such a device is simple; the main thing is to correctly determine its position. Thus, the direction of coolant flow is indicated on the valve body. It must correspond to the direction of water movement inside the battery.
Place valves/thermostats at the inlet of the heating device; if necessary, install a tap at the outlet as well. This is done so that in the future it will be possible to independently drain the coolant. Regulating devices are installed on heating radiators, provided that the user knows exactly which pipe is the supply pipe, since a tap is made into it. In this case, the direction of movement of hot water in the riser is taken into account: from top to bottom or from bottom to top.
Compression fittings are more reliable, which is why they are used more often. The connection to the pipes is threaded. Thermostats can be equipped with a union nut. To seal the threaded connection, use FUM tape or flax.
Sometimes it becomes necessary to adjust the temperature in each specific room. This can be done by installing a thermostat for the heating radiator. This is a small device that regulates the heat transfer of a heating battery. Can be used with all types of radiators, except cast iron. One important point is that the device can lower the initial temperature, but if there is not enough heating power, it cannot increase it.
Kinds
Valves can be roughly divided into:
- with manual control;
- with thermal head;
- with electric drive;
- hydraulic;
- pneumatic.
In a private home, an electric valve would be most acceptable. Sensors installed inside issue a command through the controller to the drive if the controlled water parameters change. As a result, it becomes warmer, or vice versa, cooler.
Thermal mixing effect occurs automatically
It does not matter which boiler is installed in the system - gas or solid fuel
Expert tip: It is not recommended to choose a manually operated valve. In this case, it will be difficult to control the heating of the house.
If it is not possible to install an adjustable valve in the heating system, then the best solution in this case would be a valve with a thermal head.
Why do you need to make adjustments?
The main factors explaining the need to change the heating level of batteries using locking mechanisms and electronics:
- Free movement of hot water through pipes and inside radiators. Air pockets may form in the heating system. For this reason, the coolant stops heating the batteries, as it gradually cools. As a result, the indoor microclimate becomes less comfortable, and over time the room cools down. To maintain heat in the pipes, shut-off mechanisms installed on radiators are used.
- Adjusting the temperature of the batteries makes it possible to reduce the cost of heating your home. If the rooms are too hot, by changing the position of the valves on the radiators you can reduce costs by 25%. Moreover, reducing the heating temperature of the batteries by 1°C provides savings of 6%.
- In cases where radiators heat up the air in the apartment very much, you have to open the windows often. It is not advisable to do this in winter, because you can catch a cold. To avoid having to constantly open windows in order to normalize the microclimate in the room, regulators should be installed on the batteries.
- It becomes possible to change the heating temperature of radiators at your discretion, and individual parameters are set in each room.
Three way hydraulic valve
This hydraulic valve has three passages. Of these, two serve to supply water flows, the third conducts the boiler into the water circuit structure. To prevent metal corrosion, the block body is made of stainless metal. During operation, the thermal floor reacts perfectly to the environment, changing the position of the axle boxes and controlling the degree of heating of the liquid at the outlet. The thermal head is equipped with a meter that transmits signals to the actuator (close or open the valve).
Features of Three Way Valve:
- it is easy to install;
- it allows mechanical and automatic adjustment;
- it is durable;
- it has an average price;
- it contains chemical and water protection.

Thermostatic heads
There are three types of thermostatic elements for heating thermostats - manual, mechanical and electronic. They all perform the same functions, but in different ways, provide different levels of comfort, and have different capabilities.
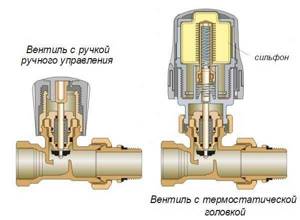
Manual
Manual thermostatic heads work like a regular faucet - you turn the regulator in one direction or another, allowing more or less coolant to flow through. The cheapest and most reliable, but not the most convenient devices. To change the heat transfer, you must manually turn the valve.

Manual thermal head - the simplest and most reliable option
These devices are quite inexpensive, they can be installed at the inlet and outlet of a heating radiator instead of ball valves. Any of them can be adjusted.
Characteristics of two way valve
The two-way valve is an upgrade to the valve. Built into the collector, it operates automatically and maintains the set temperature level. Unlike a traditional valve, this model is focused on passing liquid flow in one direction. If you install it back, the entire process of functioning of the heated floor will be disrupted. To extend the service life, a filter is installed in front of the valve to retain mechanical impurities.
Thermal mixing unit for heated floors
This thermo-mixing tap is made from brass, steel, and cast iron. Includes a thermostatic head with a liquid sensor, the purpose of which is to control the temperature of the coolant. During its operation, cool water coming from the “return” is constantly supplied, while hot coolant is supplied only when necessary.
Two way valve diagram
Thanks to this scheme, the heated floor does not overheat, therefore, its service life is extended. Since the throughput of a two-way valve is relatively low, temperature control is smooth, without jumps. Experts recommend using this device when installing heated floors over a large area exceeding 200 m2.
Advantages and disadvantages
Sewage pump: types and methods of application
Advantages of thermostatic valves:
- does not require special maintenance;
- compact dimensions;
- aesthetic appearance;
- automatic adjustment of water temperature in the pipeline;
- ensuring a comfortable microclimate in the home;
- the ability to set the desired temperature in each individual room.
Flaws:
- complexity of setting up the device;
- Thermostat failure can occur under the influence of a draft or a nearby stove;
- dependence on hot and cold water supply.
Thermal heads for heated floors
Chinese automatic equipment for warm water floors! Test!
Heating in a private house has already been done. But we decided to add a warm floor in the washing room. Room area
Correct connection of the heated floor to the boiler.
Warm floor (working principle)
Anyone who has been following my work for a long time knows that I am not a stranger to any simple methods of adjusting the floor.
Automatic water heated floor. After watching the video, you will learn: - how to choose a room regulator, - which ones.
How to make a heated floor? Connecting a heated floor to a heating system without a collector
How to make a heated floor with your own hands? In the house I made 3 circuits with heated floors: in the kitchen, bathroom.
How to assemble a three-way mixing unit for a heated floor yourself. Pressure testing of your own underfloor heating.
Main functions and features of the device
Based on the principle of operation of the element, you can guess the origin of its name - a three-way valve performs the main function - it passes water from different sources through 2 channels:
- High-temperature coolant from a supply pipe connected to the central heating riser or boiler-heater;
- Cool water that has cooled during circulation through the water circuit.
The flows mix with each other inside the valve and leave it through the third valve at a temperature set by the owner. The device operates continuously, since mixing is carried out during each operating mode of the heating circuit in the floor screed.
The operating cycle has the following sequence: heating - heat release - mixing of cooled water - heat release - mixing. The proportion in which streams of different temperatures are mixed must be controlled automatically and continuously.
Otherwise, the performance of heat exchange between the floors and the air in the room will not be directly related to possible changes in temperature degrees. In this case, the owner will have to set the water heating parameters manually.
Heating systems
The presence of a heat-sensitive head allows mixing hot water into the mixer without the participation of the owner. It is she who is responsible for the throughput capabilities of the valve based on the temperature of the mixed water streams, ensuring the specified parameters at the outlet.
Three-way valves can be used in different conditions and have different purposes, so there are several types of them.
Home heating systems with batteries connected to an autonomous boiler require the simplest device. A three-way valve is relatively inexpensive and is simple in design, so you can install them yourself. In this case, the flow mixing volumes are manually regulated by the owner himself.
DHW systems
In the hot water supply, a three-way valve is needed to ensure a safe water temperature - a person should not get burned. The devices have a simple and understandable design and differ from heating analogues in a special protective block, the purpose of which is to shut off hot water if there is no cold water in the pipes.
Water heated floor
The three-way valve as part of the water circuit has a complicated design, since it is needed to maintain the coolant in the specified temperature range depending on the ambient temperature.
The mixer uses a three-way valve to adjust the heating intensity of the home automatically, without the intervention of the owner. The faucet has a handle for adjustment, as well as a printed measuring scale on which you can make manual adjustments.
How to choose
Three-way valves for heating points and central boiler houses are installed in accordance with design solutions. Therefore, the models specified in the project or their analogues are selected.
For a private home, a 3-way device is selected according to the cross-section of the pipelines on which it will be installed. The method of controlling the three-way valve must be taken into account. If it is installed in a boiler room, then with an electric drive and a control unit, from a temperature sensor located in the living room. The permissible cable length to the sensor must be taken into account.
If the device is selected for installation in front of a radiator, then the best option is with a thermostatic head. You should know that there are thermostats with a remote capillary thermostat, which can be installed at a distance of up to 2 meters from the regulator. This option is worth considering if it is impossible to avoid heating the thermal head from the radiator. For example, when it is located very close to a wall with a riser and the device has to be installed close to the battery.
Design and principle of operation
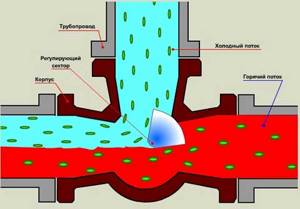
To understand what the thermo-mixing three-way valve of the most common saddle type consists of and how it works, you should study the diagram below. Inside the brass body with three nozzles, 3 chambers are arranged using the casting method, the passages between which are blocked by poppet valves. They are fixed on one axis - a rod coming out of the body on the fourth side.
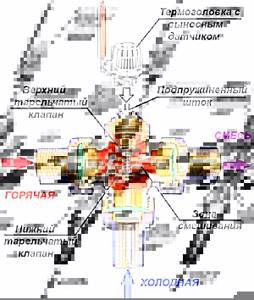
In a 3-way mixing tap, the outlet pipe (from where the mixed water comes) is always open, the remaining 2 fittings are alternately closed with a thermal head
The operating principle is as follows: when you press the rod, the passage for one flow will begin to open and gradually close for another, resulting in water of the required temperature in the mixing chamber of the valve. It leaves the brass body of the element through the third pipe. The force of pressing on the rod is adjusted by a thermal head with an external temperature sensor installed in accordance with.
The whole process is worth explaining in more detail:
- Imagine that an insufficiently heated coolant comes from the hot water side. Then the mechanism passes it further, and the third pipe is closed. The remote sensor is filled with a heat-sensitive liquid and is connected through a capillary tube to a reservoir (bellows) inside the thermal head.
- When the sensor heats up, this liquid expands, its volume in the tube and bellows increases, as a result of which the latter begins to press on the three-way valve rod. The moment of pressing is determined by the adjustment on the scale of the thermostatic head, set to the required temperature.
- After this, cold water from the third pipe is mixed into the flow of heated water and the temperature of the water at the outlet of the thermal valve remains unchanged, although heating of the coolant at the inlet continues.
- If the incoming water continues to heat up above normal, then to maintain the set outlet temperature, the thermostatic valve can completely close the inlet and open the side flow. In this case, the rod lowers to its lowest position.
- As soon as the sensor detects cooling of the coolant, the head slightly releases the stem, the valve seat on the hot side opens and the addition of heated water begins.
If we are talking about a dividing valve, the principle of its operation is almost the same, only when you press the rod, one flow begins to divide into two. But in the switching element, the direction of movement is changed by the electric drive, which is described in detail in the video:

Watch this video on YouTube
Installation and connection: how to install it?
Devices with any type of drive are installed in the same way. The main difficulty is not connecting the tap to the system, but drawing up the correct heating circuit, determining the location of the valve in it and choosing equipment. To accurately calculate the system, you need to have special knowledge, so it is better to entrust the installation to qualified specialists.
Installation instructions

Thermostatic elements usually have a factory-fixed setting. Servo drives are configured using controllers, following the included instructions.
- Prepare the three-way valve and installation tools.
- If the heating circuits have been used previously, drain the water.
- Position the valve along the flow direction according to the arrows on the body.
- Check the openings of the product; residual welding particles, debris, and dust should not get into them.
- Place the axis of the thermostatic head perpendicular to the axis of the pipeline. Any mounting position is permitted, except when the actuator is located under the valve.
- Make the assembly easily removable for possible replacement. To do this, mount the valve using special connectors with internal or external threads and seals or “American” ones.
Types of thermostats
The choice of thermostat for a particular system is determined by the following factors:
- equipment power;
- method of regulation;
- functions performed;
- type of installation.
Power
For most equipment, 3 kW is sufficient. If there are a large number of heating circuits, several thermostats are used, or a magnetic starter is installed. The larger the area of the room, the longer it takes to warm it up from one thermostat.
What types of sensors are there?
Different systems are responsible for comfortable floor temperature and air heating. Accordingly, different sensors are used. In the first case, a floor sensor is used. It is placed in a screed between the circuit pipes, at a distance of more than 50 cm from the wall. A pipe or corrugated hose is attached to the floor, into which a cable with a sensor at the end is inserted. The pipe is filled with solution, but its end comes out. If necessary, the failed sensor is pulled out by the wires and replaced with a working one.
An external sensor located in the room is responsible for heating the air. It is usually installed inside the thermostat housing. However, it should not be in a draft, heated by the sun's rays or located close to devices that generate heat.
A groove is made under the sensor in the wall, going to the floor level. A hose is placed in the groove, which is then brought out at one end to the measurement site, and at the other end it is inserted into the installation box with a thermostat fixed in it. The hose is isolated from the solution with a plug. A floor temperature sensor with wires is inserted into it.
You should first check its serviceability by measuring the resistance and then comparing it with the passport data. If a large difference appears, the sensor should be replaced. Then the necessary connections are made. A test run of the system is carried out before pouring the screed.
The indoor microclimate significantly depends on the weather outside. In this regard, a climate control mode has been developed using an external sensor and controller (climate compensator). The program includes a number of dependencies between the temperature of the coolant and the outside air. By selecting one of them based on the outside air temperature, the controller calculates how much the coolant should be heated.
If the calculated coolant temperature is less than the actual temperature, a signal is sent to shut off the supply of hot water to the heating circuit. All measurements and adjustments to coolant flow continue in the direction of reducing data mismatch. The controller can also control the performance of the mixing pump or switch to another mode.
Types of thermostats and their functions
A mechanical regulator is the simplest and relatively cheapest device. The temperature is set by turning the wheel to the desired level. Then the system maintains the temperature using it. When the weather changes, you must manually change the temperature setting.
The electronic device is also a simple, but much more convenient device (diagram in the figure below). Different temperatures can be set for several periods of time, which saves energy and provides more comfortable indoor conditions. Affordable prices and necessary functionality make the devices the most popular.
Control diagram for a double-circuit heated floor using an electronic thermostat
For large or medium-sized underfloor heating systems, it is advisable to use programmable thermostats. A correctly selected program for the mode of use of the premises makes it possible to save heat and quickly recoup the cost of the device.
A remote controller works in the same way as a programmable controller, but with remote control. You can even program the device via the remote control. It uses a control system from two sensors: in the room and on the floor, which allows you to optimize the thermal regime and manage energy consumption more economically.
Thermostat with remote control
Situations often arise when the floor surface is warm but the room is cool. Here it is advisable to use an additional sensor that measures the air temperature, after which it is compared with the set one. The temperature of both the floor and the air will not rise above the installation. A two-level thermostat provides greater comfort if equipped with suitable accessories. It should be borne in mind that monitoring the temperature of the floor surface is more accurate, since the sensor readings are not affected by drafts and sunlight.
Related Posts
- Optimal temperature for heated floors
- Mixing unit for heating
- We make a water heated floor from a gas boiler
- Installation of an electric heated floor: types, diagrams, do-it-yourself installation
- Electric heated floor in a private country house: installation features in a wooden and frame house
- At what temperature of the coolant is the heating system turned off and turned on in an apartment building according to GOST
- Sewage check valve
- Calculation and selection of a pump for a water floor
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Installation of a warm water floor
- Calculation of underfloor heating power
- Safety relief valve: operating principle, applications and installation
- Choosing a manifold for heated floors: types, equipment
- A supply of hot water that is always at hand: how does an electric water heater for heating work?
- How to choose and install an air valve for heating
- How to make a heated floor from a stove in a bathhouse
- Toilet flush cistern
- Balancing valve for heating system
- Connection diagrams for water heated floors
- Overview of the model range and types of temperature relays
- Heated floor consumption, how much electricity is needed
- Electric heated floor under linoleum
- Radiator design: three-way valve for heating with thermostat, operation diagram, main types and nuances of installation
- Categories and groups of classification of water supply systems
- Manufacturing and connecting a sauna stove with a water heat exchanger
Read with this
- Optimal temperature for heated floors
- Mixing unit for heating
- We make a water heated floor from a gas boiler
- Installation of an electric heated floor: types, diagrams, do-it-yourself installation
- Electric heated floor in a private country house: installation features in a wooden and frame house
- At what temperature of the coolant is the heating system turned off and turned on in an apartment building according to GOST
- Sewage check valve
- Calculation and selection of a pump for a water floor
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Installation of a warm water floor
Type #1 - non-adjustable bypass pipe
An uncontrolled bypass in a heating system is a regular bypass pipe without any additional equipment.
The lumen of the pipe is constantly open and the movement of liquid through it occurs in an uncontrolled mode. The main application of such bypasses is when connecting radiators.
When designing a heating system, it should be taken into account that the liquid will pass along the path with the least hydraulic resistance.
Therefore, the diameter of the flow area of an unregulated bypass installed vertically must be smaller than the diameter of the flow area of the main line. Otherwise, under the influence of gravity, the coolant will flow into a nearby bypass.

In horizontal wiring, different laws apply. A hot medium tends to rise upward because it has a lower specific gravity. Therefore, the bypass of the lower wiring is usually made equal to the main line, and the pipe going to the radiator is smaller.
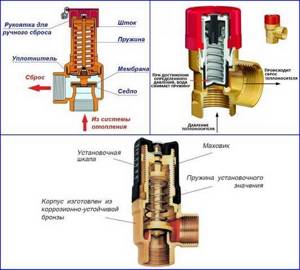
Mechanical thermostat: operating principle
If the air space in the room is heated to the required level, the working sphere in the bellows expands under the influence of heat, which causes the hydraulic cylinder to straighten. The rod, combined with the bellows, rushes forward, exerting pressure on the hydraulic valve, pressing it closely against the through hole. In this case, the supply of coolant to the battery (heating) stops.
After the remaining media in the heating battery has cooled, the mixture (or gas) in the thermoelement is compressed, causing its walls to shrink, which leads to the opening of the valve. The heated coolant enters the system, then the course of action begins all over again.
Varieties
Existing types of valves are capable of working with boiler equipment from leading foreign (Vaillant, Baxi, Ariston, Navien, Viessmann) and domestic (Nevalux) manufacturers using gas, liquid and solid fuels in situations where automatic control of the system operation due to the type of fuel is difficult or broken when the automation fails. Depending on their design and operating principle, safety valves are divided into the following groups:
- According to the purpose of the equipment in which they are installed:
- For heating boilers that have the above design, they are often supplied on fittings in the form of a tee, into which a pressure gauge is additionally installed to check the pressure and a venting valve.
- For hot water boilers, the design includes a flag for draining water.
- Tanks and pressure vessels.
- Pressure pipelines.
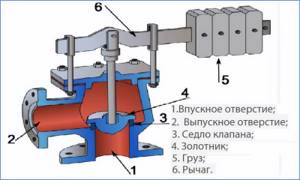
- According to the operating principle of the clamping mechanism:
- From a spring, the clamping force of which is regulated by an external or internal nut (its operation is discussed above).
- Lever-load type, used in industrial heating systems designed to discharge large volumes of water; their response threshold can be adjusted by hanging weights. They are suspended on a handle connected to the shut-off valve using a lever principle.
- Locking mechanism speeds:
- Proportional (low-lift spring) - the sealed lock rises in proportion to the pressure and is linearly related to its increase, while the drain hole gradually opens and closes in the same way with a decrease in the volume of coolant. The advantage of the design is the absence of water hammer under various modes of movement of the shut-off valve.
- Two-position (full-lift lever-load) - operate in open-closed positions. When the pressure exceeds the response threshold, the outlet hole opens completely and the excess coolant volume is released. After the pressure in the system is normalized, the outlet is completely blocked; the main drawback of the design is the presence of water hammer.
- By adjustment:
- Non-adjustable (with caps of different colors).
- Adjustable screw parts.
- According to the design of the spring compression adjusting elements:
- An internal washer, the operating principle of which was discussed above.
- External screw, nut, models are used in domestic and communal heating systems with large volumes of coolant.
- Using a handle, a similar adjustment system is used in flanged industrial valves; when the handle is fully raised, it is possible to perform a one-time release of water.
Water floor servos
Automatic control of the temperature of a warm water floor is impossible without the presence of servos. These are small electro-thermal devices that open/close the coolant supply. They are also called servomotors, and the official name is “electrothermal servodrive”. In principle, the same devices can be installed on radiators, but this is not done often.

This is how the servos look “live” on the commutator
How do servos work? The main working element is the bellows. This is a small sealed and elastic cylinder, which is filled with a substance, the volume of which strongly depends on temperature. There is an electric heating element around the bellows. When a command is received from the thermostat, power appears on the heating element. It starts working, the substance inside the bellows heats up and begins to expand. The enlarged cylinder presses on the rod located below. And it, in turn, blocks the flow of coolant. As you can see, no motors or gears, only electricity and thermal energy. That is why they are called thermoelectric.
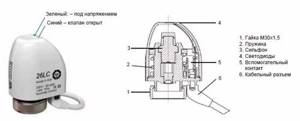
Servo drive - appearance and internal structure
A little about the varieties. There are servos that are normally closed and normally open. These names show what position the valve is in when there is no power: the first is open in the normal position, and closes when a signal appears; the second, accordingly, is closed in the normal state, and opens when a signal is present.
Which one is better to use? For our country, it is better to give preference to normally open servos. And here's why: if it fails, the coolant will continue to circulate and the floor will not freeze (although long and low temperatures are needed for the pipes in the screed to freeze).
There are also devices that operate on 220 V AC or 24 V DC. To supply 24 V voltage, you will need to install an inverter.
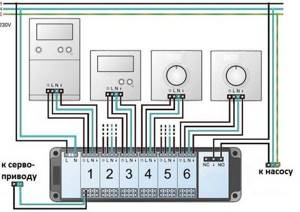
How to connect servos
The connection diagram may be different and depends primarily on the type of thermostat. If thermostats control one circuit of a heated floor, then they are directly connected to the corresponding servos by wires. If the thermostat is multi-zone, then the wires are connected to the corresponding terminals.

One of the switching units for water heated floors
Heated floor switches are used to organize wires. In addition to the standard function of connecting and connecting different devices, they also perform a protective role. When all circuits of the water floor are closed, a signal is sent to turn off the circulation pump. This is convenient if automated heating boilers are installed (the pump will not run idle without flow, and the system will not fail due to excess pressure).
How to connect devices through a water floor switching unit
But in systems with conventional solid fuel boilers, the pumps cannot be turned off: the boiler will not go out and turning off the pump threatens to rupture the system. In this case, install a bypass and a bypass valve (see connection diagram). The bypass valve is set to a pressure slightly lower than the maximum pressure of the pump (if it has a maximum of 5 meters, set it to 3-4 meters). When this value is reached in the system (this happens if a small number of underfloor heating circuits remain open), the bypass valve begins to turn part of the coolant flow into the “return” and feed it back to the boiler.
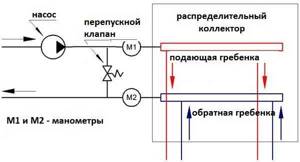
Switching circuit with a bypass valve to prevent the system from running dry
This scheme will work with any type of boiler, not only solid fuel. But for them, it is practically the only inexpensive way to protect the system from overheating.
Checking water heated floors when using cross-linked polyethylene pipes
For these pipes, the test mode for water heated floors is different.
The system must be loaded with pressure twice the operating pressure, but not less than 6 bar. After such a load, the pressure begins to drop. After 30 minutes, restore test pressure. This must be done 3 (Three) times. After increasing the pressure three times, bring the pressure to test pressure (twice the working pressure) and leave the system for 24 hours. After 24 hours, check: If the pressure in the system has dropped by less than 1.5 Bar and there are no leaks, then the test (pressure testing) of the water heated floor system was successful. Date: September 25, 2021
Thermostatic valve: principle of operation, types, adjustment
A standard heating system cannot be called flexible. To adjust the operating parameters of batteries, various devices have been invented.
One such device is a thermostatic valve for heating radiators. It is used to regulate the heat transfer of the system depending on weather conditions. In this article, we will analyze the design and operating principle of a thermal valve, and get acquainted with the existing varieties and main manufacturers.
We will also provide installation recommendations, providing the material with visual photos and video reviews on the installation and response speed of devices of various brands.
The content of the article:
Why is a thermostatic valve needed?
The valve solves two problems: maintains the room temperature at a comfortable level and saves energy.
But in order for it to really cope with such functions, you need to understand in what cases the device is appropriate and how to install it correctly.
If in the middle of winter there is a need to open the windows so that the temperature in the room drops to an acceptable level, a thermostat is definitely needed. But it won’t help when the radiators are barely warm—it will probably make it even colder.
In the second case, it is better to try to regulate the temperature in the room differently: change the volume of coolant in each radiator, adjust the operation of the boiler (for a large area), select the optimal circulation pump or adjust the operation of the existing one.

The price of a thermostat ranges from several hundred rubles (200-600), so re-equipment of the heating system will not be expensive. But there are also expensive models
As a temporary measure, control valves can be used. But it is not recommended to use ball valves for these purposes.
Design and operating features of the device
Let's look at how a thermostatic valve works and on what principle it works.
How does a thermal valve work?
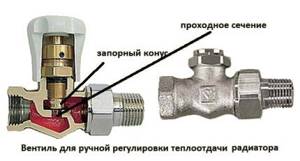
The device consists of two main working elements - a valve and a thermostatic head. The first is most often made of brass, sometimes nickel-plated, its lower part blocks the pipe, and its upper part continues the pressure rod and spring.
Valves are also available in bronze (nickel-plated or chrome-plated), as well as stainless steel. The latter are rare and expensive.
What happens inside the valve? The head device contains a sensitive element. It is located in a cavity with gas or liquid (bellows).
Heating provokes expansion in this environment, the element is pushed forward, pressing on the rod, spring, and later on the valve. The force of pressure determines the degree of overlap.

The figure shows a device with liquid in a bellows. Gas thermostats react faster to temperature changes (5-10 minutes), but are also more expensive. There is no significant difference from this during operation
An additional part of the thermostat is a plug or handle with a scale. Some devices have electronic controls.
Operating principle of the device
Let's take a closer look at the working principle of battery thermostatic valves. The mechanics of their action looks schematically like this: when the temperature of the coolant or the environment changes, the gas or liquid in the head reacts to these fluctuations.
The sensing element acts on the pressure rod, and it goes up or down. When the rod moves down, the valve blocks the flow of coolant, which stops the flow of heat and slows down the circulation rate. No heat enters the battery, so the room temperature does not rise.
And here it is important to distinguish a thermostatic valve from a control valve. The latter can reduce the valve capacity and thus regulate the temperature of the batteries.
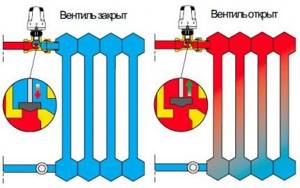
When turning the knob or entering a digital value on the panel, the user sets the initial pressure value in the thermal head, to which it “adjusts” during operation
The control valve does not have a thermal head. The thermostat is open or closed, it is controlled by a thermal head, it does not change the volume of coolant, but only turns its supply on and off
Let's look at the operating principle of a thermal valve using an example. So, set the device to the recommended temperature of 20 degrees. This is usually a three or the largest point on the regulator scale.
What happens inside the device? If the surrounding air heats the head to 21 degrees, i.e. increases the set temperature by 1 degree, it presses the rod, the flow of coolant into the battery is completely blocked by the valve.
The radiator does not heat up and the room temperature begins to drop. When the ambient temperature drops to 19 degrees, the thermal valve will open and the battery will begin to heat up.
We understand the types of devices
According to the method of adjustment, valves are divided into mechanical and automatic . The first require manual rotation of the mechanism for narrowing the flow in the pipes.

Both devices perform the same function - they adjust the flow of coolant to the radiator in accordance with the parameters set by the user, but using automation is less troublesome
Automatic models do not require manual adjustment. When the temperature around the thermostat decreases, they independently detect this and adjust the coolant flow.
Manufacturers also offer different thermostat designs:
- Common for two-pipe systems - the simplest device. If you need hydraulic linking of radiators along one branch, it is recommended to add a shut-off and control valve to the supply (return) circuit.
- With hidden and open hydraulic superstructure - such devices have a coupling with an internal rod, so hydraulic adjustment is possible.
- For single-pipe, gravity systems - due to the increased passage, the throughput of these devices is increased to 5.1 m3/hour, so they can be installed in non-pressure systems.
- 3-way for circuits with bypass - they can regulate and distribute the coolant in conjunction with the bypass. When the set temperature reaches the valve, the coolant is sent to the bypass; when it drops, the bypass is partially closed.
The percentage of thermal valves for two pipes is much greater than for single pipes, and the latter in our country are about 80%.
This is due to the fact that the device was originally invented for the former, where the coolant is distributed among the devices forcibly under high pressure. Pre-setting by valves is designed to distribute pressure evenly throughout the system.
Only some manufacturers have valves for single pipes - Heiz, Danfoss, Heimeier, Oventrop.
In single-pipe schemes, you cannot use conventional “two-pipe” thermostats : they have a lower capacity, they can only operate with a large difference in pressure between the supply and return, so there will be a risk of redirecting the coolant to the bypass.
Externally, “one-pipe” valves are larger in size.

Three-way valves are appropriate in circuits with a solid fuel boiler, as well as for flow separation and bypass piping of radiators. The device can also be used in single-pipe installations
Thermostatic valves also differ in shape. They can be straight, angular or included in sets with jumpers for pipes. Direct ones are suitable for regular batteries. Angular ones are needed in schemes with lower pipe connections, when the CO is partially disguised under the floor.
A separate type of thermal valves is electronic. They have wider functionality than regular ones. With their help, you can set different room temperatures for each day of the week and even hourly.

Electronic thermal heads are more expensive and larger than usual: inside the case there is a compartment for two batteries. There are models with removable and built-in control units
Electronic thermostats provide significant savings in coolant consumption. If there is no one in the apartment or house from 8 am to 6 pm, the device will properly maintain the minimum temperature. And when the owners arrive, it will heat the premises to a comfortable level.
Valves with anti-vandal casing are also available for sale. They are reliably protected from unqualified intervention and are suitable for installation both in a home with small children, and in kindergartens and schools.
Features of installation and connection of the valve
The device itself is simple, but special attention must be paid to installing and calibrating the thermostatic valve on radiators. Correct installation will ensure the accuracy of the device.
What factors are considered during installation? A type of thermal valve is for one-pipe or two-pipe. Plus the direction of movement of the coolant - it comes from below or from above.

On the valve itself, the direction of movement of the coolant is indicated by an arrow. According to this marker, it is necessary to install thermostats on radiators, otherwise the device will not work correctly
Hot water supply pipes to the battery are supplied in different ways. It depends on the heating scheme. The placement of plugs and thermostats are also different. The general recommendation for most thermostat models is to place them within 40-60 cm from the floor level.
The installation algorithm is approximately as follows:
- Disconnect the radiator from the heating system and drain the water.
- We remove the section of the horizontal pipe and the tap too.
- The thermostat can also be mounted in the radiator cap if a shut-off valve is installed in front of it. Or make an insert into the horizontal part of the pipe in front of the battery.
- The tightness of the joints is important. We provide this by standard winding of FUM tape onto the threaded area.
The traditional connection diagram is as follows: bypass - ball valve - thermostat.
One more point: there are systems where the coolant moves in different directions in different rooms. This is especially true for U-shaped risers.
Installation nuances for one-pipe and two-pipe systems
In a single-pipe system, hot water circulates through one pipe with radiators connected in series. The coolant pipe goes into the top of the batteries. The latter runs through the installation, exits from below on the same side and is sent to the main highway.
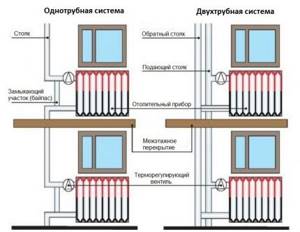
Single-pipe CO is considered ideal for private buildings and apartment buildings up to 5 floors. In other cases, it is recommended to install a two-pipe CO
In a one-pipe system, the thermostat is placed on an unregulated bypass. This jumper connects the direct pipe and the return pipe, so hot water moves freely after the pressure is blocked by the valve.
Such a jumper can be welded to the pipe yourself, for which a piece of pipe with a diameter of no more than 8 cm is suitable. In this case, you need to prepare holes in the appropriate places.
Standard and recommended thermostat installation diagrams for one-pipe and two-pipe CO systems. The figure shows how to connect a valve with a jumper (bypass) and a foot valve
In a two-pipe system, the coolant enters the radiator through one pipe and is discharged through the other. A bypass is not needed; the thermostatic valve must be installed on the water supply pipe.
Rules for adjusting the operation of the device
After installation, you need to adjust the operation of the device. To do this, we first close the windows and doors - we insulate the room to prevent heat leakage.
Then we proceed like this:
- We turn on the heating.
- We set the valve to the position of maximum heat transfer and measure the temperature.
- We are waiting for the room temperature to rise by 5 degrees and become constant.
- Close the valve and wait for a comfortable temperature.
- Then we open the thermostat a little bit until we hear the sound of passing water. The body of the device itself should become warmer.
- The last point needs to be remembered.
In a private home, air must be bleed from the batteries before adjustment. In this case, maximum care must be taken to avoid the release of hot steam.
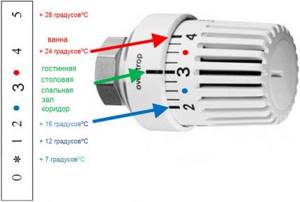
When more than three batteries are connected to the boiler, each thermostat must be opened to a different level so that the heat is distributed evenly throughout the rooms
The adjustment starts from the coldest room. It needs to be warmed up well before moving on to other rooms.
Frequent installation errors and possible problems
The first mistake is placing the thermal head vertically. The problem is the hot metal valve under the head: hot air flows upward from it.
This air heats the head, and it mistakenly turns off the radiator. As a result, the battery is almost always disconnected and the room does not warm up. The device must be installed horizontally (“head” into the room).

In the instructions for the thermostat, the diagrams show how and where to install it in different cases, but there is not a single diagram with a vertical arrangement. If it doesn’t work vertically, you need to use devices with remote sensors
The second mistake is the location of the thermostat where the temperature differs from the real one in the room. Example: in a niche with a battery. In this option, the head will always be “hot”.
A significant malfunction in its operation will also be present when placing curtains behind thick fabric, under window sills, or at the edges of window openings.
If it is impossible to position the thermostat otherwise, a model with a remote sensor will again help out. They differ from conventional devices by the presence of a capillary tube about 2 meters long with a temperature sensor at the end. You can attach such a device on the wall away from the window and radiator.

Models with a remote element determine the temperature more accurately than conventional devices due to their location at a distance from the radiator, but they also cost much more.
Heads with remote regulators are also available for sale, the installation of which can be done anywhere at a distance of up to 15 m from the battery and valve. There are also electronic heads that are controlled by thermal computers.
The thermostatic valve completely blocks the coolant flow. If in a radiant heating system all devices do this at the same time, there will be problems with the boiler. A possible solution is bypass valves on the circuits.
If there are 2-3 radiators in a room, does it make sense to install thermostats on each radiator? Will there be conflict between them? In this case, you need to do balancing using tuning valves (ball valves).
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What is a thermal head, what is it for and how does it work.
Analysis of a finished system with a thermostatic valve.
An experiment on the response speed of thermal heads from 4 manufacturers.
The use of thermal valves for radiators allows you to make the heating system as flexible as possible.
With their help, you can regulate the temperature of individual batteries so as to constantly maintain a comfortable microclimate in the room. But at the same time, it is important to take into account the appropriateness of installing such devices and correctly installing and configuring them.
Are you thinking about installing a thermal valve, but want to clarify a couple of installation points? Ask your questions under this article - our experts and site visitors who use such temperature control equipment will try to answer you in as much detail as possible.
If your heating system is equipped with thermostatic valves, please share your opinion with other users. Tell us, which manufacturer’s equipment did you prefer, is it convenient to use, are you satisfied with the result? Write your recommendations in the comments block, add unique photos of the thermal valve.