From the entire arsenal, the following can be distinguished:
- Linen
- Adhesive sealant
- Silicone
- A thread
- FUM tape
The question “which pipe sealant is better and which is worse?” - incorrect. In order to understand this question, it needs to be posed somewhat differently: “What type of sealing of threaded connections should be used in specific conditions?”
Let's start with what sealant should not be used for threaded connections:
- Silicone (good for flange connections);
- Ship's red lead;
- Whitewash, various types of paints.
So, there are 4 types of material left:
- Linen;
- Thread;
- Adhesive sealant;
- FUM tape.
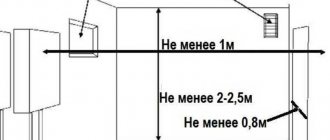
Threaded seals, antifreeze in the heating system
- font size change font size increase font size
- Druk
- Comment first!
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
An extremely important point for high-quality installation of a heating system is the correct choice of material for sealing threaded connections. This type of connection especially requires high-quality sealing. In recent years, when installing heating systems, modern sealants based on heat-resistant silicone or a special Teflon thread are often used for threaded connections.
Unskilled or unscrupulous workers sometimes use materials that are not intended for this at all to seal connections in heating systems. For such work, it is completely unsuitable to use cheap silicone for plastic windows, since this material cannot withstand high temperatures, and this always leads to a coolant leak.
The choice of the type of coolant also greatly influences the quality and operating features of the heating system. We suggest you understand these points, which are extremely important when installing heating systems.
Types of pipe seals
From the wide variety of materials intended for sealing threads, the following can be distinguished:
- linen;
- adhesive sealant;
- silicone;
- a thread;
- fum tape.
Linen
Many users use flax to seal threads in plumbing fixtures. This material is suitable for all metal parts: cast iron, steel, brass.
It is not recommended to use flax for plastic fittings and fittings made of metal and plastic. The thing is that sealing pipe connections with flax initially presupposes a high-quality seal. To do this, you need to apply force and tighten it well.
Plastic elements will be very difficult to tighten. It is more likely that you will be able to simply rip off the threads rather than create a tight connection with the flax gasket.
Plumbing flax
Plumbing thread
Plumbing thread is a good sealant that is of high quality and excellent strength. It can be used to seal pipe connections made of metal, plastic, metal-plastic.
Its only drawback is its high cost compared to other types of seals. Otherwise, it is a reliable sealant.
Plumbing thread Henkel Tangit Uni-lok
Adhesive sealant
The adhesive is suitable for almost any threaded connection. When working with this material, it is important to observe one condition - before applying it to the surfaces of parts, they must be thoroughly degreased.
As for products made of steel, this condition can become a serious obstacle to the use of sealant. This is due to the fact that thread cutting is usually performed directly at the installation site. To improve the performance of the tool, special lubricants are used. But it is very difficult to remove them from the surface of the metal in a working environment, and sometimes it is not possible to do this at all.
If you neglect this requirement and apply an anaerobic sealant to an oil-contaminated steel surface, you will get an unreliable connection that will deform very quickly.
Another limitation regarding the use of thread adhesive is how it is removed. The fact is that in the process of dismantling connections with sealant, it is necessary to heat the parts. This procedure is not dangerous for metal products, but products made of plastic or metal-plastic may be damaged.
It is worth saying that heating of parts during dismantling is provided only for certain types of sealant. Therefore, you need to carefully read the information provided on the product packaging.
Thus, the sealant can be used for any threaded connections, with the exception of steel products. When choosing a sealant, you need to take into account the fact that sooner or later the parts will have to be dismantled, so for plastic and metal-plastic products you should choose an adhesive whose application does not require pre-heating of the parts.
Anaerobic adhesive sealant Fixant encor
Fum tape
This sealing material began to be used relatively recently, compared to other sealants. Fum-tape builds - inexpensively, but it cannot boast of high strength, because... The material breaks with little effort.
According to manufacturers, fum tape is an excellent sealant, but as practice shows, the quality of connections leaves much to be desired.
When choosing a sealant for a threaded connection in an apartment or house, it is better to abandon the idea of using fum tape and give preference to more reliable sealants. For example, at a summer cottage or in a vegetable garden, fum tape can be used. There are no such stringent requirements in terms of reliability and durability.

Fum tape
Sealing with FUM tape or plumbing thread
Due to their ease of use, these materials have gained high popularity. To seal most threaded connections in an apartment, it is enough to wrap the number of turns of tape indicated in the instructions around the pipe and tighten it with a wrench. In this case, special care is not required when laying; on the contrary, many manufacturers recommend winding it slightly obliquely. The connection with such a seal can be easily disassembled if necessary.
At the same time, fum tape does not tolerate vibrations, does not cling well to small threads, and can be damaged by rough cutting. It is not recommended to seal pipes of significant diameter with it.

Types of sealing compounds, their characteristics and methods of application
Based on the place of use, sealants for heating systems are divided into compositions:
- for external use - applied to the site of damage to the pipeline from the outside and, after curing, restores the tightness of the system;
- for internal use (liquid, volumetric action) – they are introduced into the circuit and seal damage from the inside;
- sealing - applied to gaskets and threads to improve the tightness of connections.
The choice of sealant type depends on the degree of damage and accessibility of the repair site. In addition, the choice of sealing composition determines the method of preparing the heating system for the upcoming repair.
Let's consider sealants in relation to common types of damage and connections of heating system elements.
Sealing compounds for external use
These sealants are produced as one or two component sealants.
Considering that the coolant in the pipes of the heating system is not only hot, but also under pressure, damage to the pipeline should be sealed with particular care. First of all, the sealant must be designed for operation at high temperatures, which is indicated on its packaging in the form of the “heat resistant” marking and the operating temperature range.
Important! Acrylic-based sealant (acrylic) is used only for sealing cold water pipelines. Acrylic glue is not suitable for repairing pipes of heating and hot water systems, since after curing it is not plastic and therefore collapses due to thermal deformations of the base.
Among the one-component compositions for repairing water heating systems, silicone-based sealing adhesives are common.
Heat-resistant silicone-based sealants
*
To restore the tightness of heating systems from the outside, the most common use of sealants based on various types of silicone, including rubber.
To repair steel pipes, it is necessary to use neutral types of silicone (a mark with this parameter is available on the packaging), because “acidic” silicone adhesives that are also produced, which form acetic acid during curing, react with the metal.
If the material meets the required temperature requirements, it is necessary to enhance the effectiveness and reliability of its application with additional means to ensure success. As a rule, the manufacturer recommends such sealants for use as a filler for cracks or holes. If the material indicates another application, but its characteristics and potential are high, the adhesive is quite suitable for use. For example, a composition recommended for sealing components on an engine can easily cope with the same task in a home heating system.

And yet, taking into account the responsibility of the application, it is necessary to apply silicone sealants to the pipes of the heating system in combination with a reinforcing mesh, for which striped fiberglass tape “serpyanka” is successfully used.

Sealing method
A layer of sealant is applied to the prepared surface of the pipe (drying, cleaning, degreasing), on top of which coils of serpyanka are laid end-to-end, then sealant again, after which the tape is wound in turns with an overlap of 1 cm. The number of layers of serpyanka with glue between them should be 4-5 , it is necessary to prevent the formation of air bubbles or loose areas between them. The last 2-3 turns of the serpyanka are made on a section of the pipe without glue and are tightly attached to it with a nylon clamp, which, after the silicone has cured, will be removed along with the excess turns of the tape. The top repair layer is made of sealant and smoothed out.
Work should be carried out at a temperature not lower than +5 °C, silicone should be at room temperature (20-25 degrees). Curing of the composition, which occurs due to contact of silicone with moisture, occurs depending on the type of silicone and amounts to several millimeters per day.
Products that have proven themselves abroad and in Russia are silicone sealants MakroFlex, Masterteks, Titan, MasterSil.

Two-component compositions for repairing heating and hot water systems are various types of adhesives based on epoxy resins and polyurethane.
These compositions are less common for pipeline repairs, since they require certain skills in maintaining proportions when preparing the mixture, have a short “survival” time of the solution after mixing the components, and have a high cost relative to other adhesives.

*
There are also one-component polyurethane sealants that cure upon contact with air. The quality of these mixtures is also high, curing takes a little longer than two-component compositions, and they are also much more expensive in price than silicone materials. The main disadvantage of polyurethane sealants is toxicity during work - there must be good ventilation in the room, and work must be done in protective clothing and gloves to avoid getting glue on exposed skin.

To guarantee success when using two-component compositions, it is also necessary to carefully prepare the section of pipe being repaired and use reinforcing tape – serpyanka – in combination with glue.
Liquid sealants
Such sealants are used in situations where, in order to detect a leak, a large amount of dismantling of the decorative and insulating shells of the heating system (for example, a “warm floor” system) must be done, or the intensity of the leak is insignificant - no coolant leak is observed, but its volume decreases, and the pressure in the system is reduced when the circulation pump is running.
Important! If there is a visual absence of a leak and there is low pressure in the heating system, before adding liquid sealant to the circuit, it is necessary to check the functionality of the expansion tank - a drop in coolant pressure may also be due to the destruction of its membrane.
Liquid sealant, unlike adhesives for external use, affects damage to the pipeline or radiator from the inside. The sealing compound is introduced into the coolant of the circuit cut off from the main heating system. When the sealant is added to water, no reaction occurs, but in places of leakage where the coolant comes into contact with air, polymerization of the glue begins and sealing of the damage.
Many types of liquid sealants are produced, focused on use in certain heating systems, differing in the type of coolant, fuel of the heating unit, material of the pipeline, radiators, etc.

If the leakage of the system is not significant, and the sealing compound is selected and used correctly, then the likelihood of success in eliminating the damage from the inside is high.
Important! In heating systems with pipes and radiators made of steel or aluminum, if sealing is necessary, it is permissible to use a means to repair the car’s cooling system, but not the powder type, which settles in the lower part of the pipeline and its elements, but the liquid one.

*
Mode of application
This means of combating leaks in heating systems is relatively new, and there is no universal technology for its use, although the operating principle of all liquid compositions is common.
The sealant is purchased in accordance with the characteristics of the heating system installed in the home. In addition, when purchasing the composition, you need to know how much coolant the heating circuit holds in order to purchase the sealant in the required quantity - the glue instructions indicate the concentration in which it should be present in the system.
The use of each type of such sealant has its own nuances: the permissibility of the presence of filters in the circuit, the method of introducing the composition into the coolant, the duration of action, the size of the damage, the possibility of the presence of glue in the system after achieving the effect, etc. The algorithm for performing sealing with a liquid composition is described in detail in the instructions for its use, but often to independently perform this operation it is necessary to have a special tool or equipment, such as a compact electric pump for the initial introduction of the sealant into the circuit and its complete dissolution and uniform distribution throughout the entire volume of the coolant. Therefore, without having practical skills in this matter, it is better to contact specialists who will perform this procedure without possible negative consequences such as clogging the system or failure of its components.
Sealing sealants
To ensure the sealing of threaded joints, many years ago flax tow was used, strands of which were wound onto the external thread and covered with lead lead on natural drying oil (GOST), after which the joint was assembled along the thread. With the advent of modern artificial coolants in heating systems, tow partially lost its effectiveness due to the high degree of permeability of antifreeze and gave way to FUM tape, although it is used in combination with a special Unipak paste, which also contains flax fibers, when assembling cast iron pipelines of large diameters or simply due to the lack of fluoroplastic.

FUM tape is a synthetic fluoroplastic material of a matte, less often transparent color, which, due to its fluorine content, can withstand mechanical and temperature impacts without compromising its qualities.
Depending on the conditions of use, fluoroplastic tape is produced in several varieties:
- industrial, containing 20% petroleum jelly;
- household;
- for acidic environments;
- for systems with special requirements for environmental cleanliness.
Important! Fum tape is used for sealing connections in systems with cold and hot water at a maximum pressure value of 9.5 MPa.
Rules of application:
- the tape is wound tightly, with slight tension, in the direction of the thread;
- the end of the tape should not be located at the end of the joint.
FUM tape is wound onto the thread in a number of layers depending on the diameter of the thread:
- Ø 16-25 mm – 3 layers;
- Ø 25-42 mm – 4 layers.
The number of layers is very arbitrary, since low-quality material will require twice as much consumption.

*
Disadvantages of FUM tape:
- when assembling rough threaded connections, the tape breaks and is squeezed out;
- does not have adhesion to the surface of materials;
- does not provide sealing of threads with a diameter of more than 25 mm, therefore cannot be used when assembling heating radiators.
To seal threaded connections, liquid and paste-like compounds are also used, which can dry out or remain elastic throughout their service life.
An example is the same non-hardening paste “Unipak” with flax fibers in the composition, which is used as an independent material that ensures not only the tightness of threaded connections, but also their protection from corrosion, as well as ease of disassembly
Drying pastes are solvent-based sealants, a modern material that is plastic when assembled and hardens after a certain time. For more effective use, they can be used in combination with flax strands, which slow down the assembly process and, after drying, provide a strong connection without shrinkage during use.
The disadvantage is the impossibility of tightening the threaded connection without breaking the tightness of the joint.
Anaerobic sealants are ready-to-use mixtures that differ in properties depending on the conditions of use (pressure, temperature, vibration), thread diameter, assembly density, etc.
Advantages:
- ease of use;
- low labor intensity of the process due to lubricating properties;
- seals the threaded connection even with low assembly force;
- wide range of operating pressures of the medium in the pipeline;
- easy removal of excess mixture upon completion of work;
- the presence of species with varying degrees of fixation;
- optimal price-quality ratio.
Anaerobic sealants are applied to both threaded surfaces being connected (internal and external), previously cleaned and degreased. The instructions for use, as a rule, indicate the air temperature permissible for the work - usually it is about 15 degrees Celsius (if no curing accelerators are used in the process).
An example of an anaerobic glue is the universal heat-resistant sealant for heating pipes PERMATEX 59214, which has proven itself well on the Russian market.
Medium strength, heat and vibration resistant sealing and sealing compound allows threaded connections to be adjusted within 24 hours of completion of assembly. Maximum operating pressure – 700 atm., maximum temperature + 200°C.
Sealing with plumbing thread
A prerequisite for applying thread is a thread with notches. If the thread is smooth, then a wrench should be used to apply notches. The thread is wound starting from the third turn. Despite the fact that it is written on the thread that you can wind it any way you like, it is best to wind it carefully, so that there are no free spaces.
p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 —>
After this, the thread should have free first two turns, just like in the case of flax, and a seal on the last two turns. If the procedure is performed correctly, with strict adherence to technology, the sealing of threaded connections will be reliable and will last a long time.
p, blockquote 21,0,0,0,0 —>
How to hermetically connect pipes with flax?
When starting to seal threaded connections, it is important to be very careful. Accuracy is the key to ensuring that there are no leaks. To work, you need to acquire a special paste, which is applied to the thread or to the already wound flax.
This paste has one obvious disadvantage: it gets dirty, and it’s quite difficult to wipe your hands off of it. In this regard, installers have the following rule: initially flax is wound on the thread, after that the quality of the winding is checked (it is important that there are no unevennesses) and after that the paste is applied. The connection must be free of protruding hairs, the first two turns remain free so that you can safely screw the coupling onto the external thread. And towards the end of the thread a certain ridge or thickening is formed.
Inch threads have a conical shape. And the entire compaction process is carried out on the last two threads. They are not completely cut through, and are smaller in size than the other turns. They are sealed, sealing material is glued between the two parts. And after that the paste is applied.
Application area
Thread sealing thread (or sealing thread) is a new generation universal polymer sealant used for both metal and plastic pipes for various purposes. It is made of two types of material: polyamide or fluoroplastic.

"SantekhNit", length 50 m.
Polyamide is a low-wrinkle synthetic fiber with an upper temperature limit of 130°C. Thread made from this material has increased wear resistance (10 times more than cotton) and resistance to many aggressive environments. When wound onto a thread, it can withstand a water pressure of 16 bar and a gas pressure of 8 bar.
Plumbing flax

Plumbing flax is a product of processing flax and hemp. It is a purified and combed fiber that looks like hair. It is a natural sealant.
Application of sanitary flax
It is used for sealing threads of hot and cold water supply heating and systems . Equally effective for connections made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. It is used to seal not only threaded connections, but also, for example, to seal connections of sewer pipes , seal cracks in bathhouses, and log houses. Even for sound insulation , sanitary linen is very effective.
Characteristics of sanitary flax
Plumbing flax is divided into two grades.
Combed sanitary flax.
These are long, thin and strong fibers, purified from plant stem residues. Used to seal water pipes and gas pipelines.
Frayed sanitary linen.
This is the raw material for the production of combed sanitary flax. It has a more torn and heterogeneous structure due to the presence of a large number of chips and plant remains. It is for this reason that it is not suitable for gas pipes, but is suitable for sealing all other connections.
Advantages of sanitary flax
- Durability.
- Low cost.
- Can be used for any diameter . Greatest efficiency on large diameters.
- No preliminary thread preparation .
- Possibility to adjust the position without breaking the seal.
- Possibility of use in heating systems .
- It has the ability to expand as it absorbs moisture.
Disadvantages of sanitary flax
- Not effective without special plumbing paste .
- Due to the use of paste, your hands and the area around the thread get dirty.
- Requires precise adherence to turns.
- To work with tow, experience is required .
- Due to its biological origin, it does not very long service life , about 5 years.
How to wind plumbing flax

First you need to lightly coat the thread with plumbing paste, then you need to separate strand of flax tow from the general bundle straighten the fibers across the width. Winding should be clockwise for right-hand threads . Upon completion of winding, the excess should be cut off, and the laid seal should be coated well with paste.
How much flax to wind on the thread
You should wind so much that the material completely covers the entire thread for at least 2 - 3 turns . It all depends on the thickness of the chosen strand, and may differ from one time to another.
Manufacturers of sanitary flax
- Russia PREMIUM . Quite a popular manufacturer of sanitary linen.
- Europe VALTEC . One of the best manufacturers of thread seals.
- China Chinese sanitary linen for some reason without a name.
Basic requirements for compositions
The sealant can be used for polypropylene, bimetallic, and other heating system pipes. But before purchasing, it is important to clarify that its characteristics correspond to a particular pipe material, because compositions for plastic are not suitable for metal networks. You can get acquainted with such information on the packaging, where exact data on the composition and properties are always indicated.
In addition, the sealant must meet the following requirements:
- Resistance to adverse factors. The water in the pipes is under pressure, and it is also hot. Therefore, the product must be moisture resistant and not responsive to temperature changes or aggressive chemical environments. If the sealant is used in steam systems, it must be high temperature (heat resistant).
- Long service life. The operating time of the entire CO depends on this factor. If the sealant is reliable, the system will work for at least 5-10 years. The cost of such funds is usually quite high.
- Elasticity. Sealants against leaks after hardening must remain plastic. This way they will easily, without destruction or detachment, tolerate the expansion and contraction of the base material that inevitably occurs with temperature changes.

How to seal connections in heating and water supply pipelines
On sale you can find many different materials that are designed to seal pipeline joints.
The question arises: which material should be used in which cases? And also, how to properly use this or that seal? It is often possible to use two or more thread sealants at once; then clarification is required as to which to prefer. The recommendations given should help to understand these issues and find a solution that will ensure sufficient reliability of the connection of pipes and threaded fittings for the entire period of operation.
Linen winding
Flax is a cheap material for threaded joints that creates a very high-quality seal. The only thing is that it cannot be used in all cases.
It is intended for connecting metal parts, as it creates significant density. It is very durable; the force applied by the keys to the two parts being connected is required to be significant.
Therefore, flax is not compacted:
- plastic parts - the tightening torque exceeds the strength of the material, the parts will be crushed and destroyed, at least the threads.
- parts in which a metal coupling with a thread is embedded in a plastic (polypropylene) shell, due to the danger of rotation (disconnection).
For all metal products, flax is the No. 1 material for winding threaded joints.
Next, let's look at how to apply it correctly.

Flax cannot be used “dry”; it must be lubricated with a special plumbing paste. It is applied either directly to the thread or to wound flax.
People's experience also suggests that sunflower oil can be used instead of paste, but the quality of the joint does not decrease, at least there is no such information.
A strand is separated from the flax and wound along a thread along each stream. Winding is done tightly and neatly. There should be no protruding hairs. The first two turns are not filled, but a shoulder is made at the end of the thread.

Special plumbing thread
A special thread for seals, of high strength (cannot be torn by hand), wound on spools, is sold in stores. Its main drawback is its high price, but otherwise it has solid advantages.
- It can be used on any parts, the tightening torque is less compared to flax, so you can also wrap plastic.
- It seals very well and can be used even on torn threads.
If it were not for the cost of this material, then only such plumbing thread would be used for joints.
Winding is carried out in exactly the same way as with flax - the first two turns of the thread are left empty so that the parts can be joined, and then winding is carried out along each thread of the thread, at the end of the winding - a double layer, i.e. shoulder

Fum tape is not suitable for creating reliable connections on pipelines. The material is not very durable; there is no sufficient density in the threaded connections of metal products with it. But for plastic connections that will be dismantled, for example, a summer pipeline for irrigation, fum tape is the most suitable sealant.
With fum tape, the parts to be joined can be wrapped by hand. In this case, a small density of the joint along the thread occurs, so that leaks do not occur for some time. A slight tightening force does not provide sufficient tightness and does not guarantee that the joint will not leak. For fixed connections, especially if they will be inaccessible during operation, it is recommended to use other materials.

Heating in the house can be done independently - the main installation issues
If the connection to the fum tape, which is already in operation, is turned, a leak will most likely occur. This is a serious drawback, considering that rotation does not require much effort.
At the household level, fum tape can be used (and is popular due to its low cost, ease of use, and low effort) for connections that are in plain sight - when connecting showers, taps, etc. Which heating scheme is best to use in a private house?
Plumbing adhesive sealant for threaded connections
The material is special, not exactly cheap, seals well, no cases of leakage have been recorded after its correct use. But only after the wrong...

The obvious disadvantage of sealant adhesive is that the quality of the joint will depend on the “human factor” more than with windings. The fact is that glue does not work well on oily surfaces.
Where do greasy surfaces come from? It could simply be carelessness - they dropped oil on the thread or rubbed the part in oil with their hands. Parts can be stored in a lubricated state (primarily steel ones). But the main thing is that a lubricant is used when cutting threads. After such an operation on steel parts, glue and sealant are completely unsuitable.
Please note that there are glue samples with which undocking the pipes requires heating of more than 100 degrees. Such heating is often difficult, not safe, plastic can be damaged, etc. Therefore, the adhesive-sealant is still selected according to the circumstances.
The glue is easy to apply. It is applied only immediately before joining, squeezed out of the tube onto the thread and smeared with your finger over the entire thread without skipping.

In what cases should you choose glue?
- When connecting plastic parts to metal ones, glue will be preferable. But such a connection does not occur often.
- The second case is when access to the docking site will be difficult. It is better to place such a connection with glue, and lubrication is carried out generously, without saving, on both parts being joined.
Winding Features
Winding on threads requires great care. The thread must be filled in an even layer without gaps, and there must be sealing material in each groove. It is laid to the end of the thread, where a shoulder is formed from it.

The main tightening of threaded connections occurs on the last two threads. On parts, more often than not, the last two turns of the thread are not cut to the full depth. Therefore, in this place the material is wedged between the two parts very tightly.
It would be nice if, when carrying out work, you organize additional (cross-cut) quality control of the flax winding. This is especially true when several dozen similar connections are performed at once.
- For those who are constantly engaged in installation, it is recommended to always have flax, plumbing thread and adhesive sealant with you in order to quickly and efficiently complete any connection. It is recommended to apply all this in accordance with the tips given above.
- When doing work at home with your own hands, when doing something simple and in plain sight, you can use cheap fum tape, but you need to wrap more. When installing entire systems with your own hands, it is better to use flax (with vegetable oil) on metal, and for small volumes of work it is even better to use thread. Maximum attention should be paid to the quality of winding on the thread.
What should never be used to seal threaded connections:
- There is no need to use simple silicone; it is designed for flange connections.
- There is no need to use paints, whitewash, or red lead, which are of little use, but make the connections semi-dismountable - this is long outdated.
Types of sealants
In today's everyday life, a large number of products with sealing properties are used.
Based on their chemical composition, sealants are divided into the following main types:
- acrylic - unstable, do not tolerate temperature changes;
- polyurethane - elastic, have high adhesion to metals, resistant to corrosion and temperature;
- silicone - the most common type of universal sealants, retain elasticity and moisture resistance over a wide temperature range, and are durable.
When sealing leaks in metal elements of a heating system with silicone sealant, it is permissible to use only its neutral variety, but not the acidic one, since the acetic acid contained in the acidic sealant will cause active corrosion of the metal.
Heat-resistant sealant for heating pipes is used for metal and polymer materials. This product properly fulfills its purpose - to prevent the penetration of moisture from damaged elements of the heating system. The sealing substance, which is a viscous mass, hardens quite quickly at the site of application and subsequently withstands high temperatures.
To seal threaded connections in modern heating networks, anaerobic adhesive sealant is used instead of flax tow and FUM tape. The environmental friendliness of such a sealant allows it to be used not only in heating systems, but also in plumbing systems.
Sealant for heating boilers is used to eliminate gaps in places where heat resistance of the material up to 1500°C is required.
Using this product, it is possible to seal cracks in heat exchangers and chimneys of boilers and furnaces. After hardening in the seams between surfaces of different materials (metal, brick, concrete), the substance retains its tightness.
Why is additional sealing of threaded connections necessary?
So, before moving on to choosing the optimal option for sealing threaded connections, it is worth carefully studying all the options where this installation method can be used. In the heating system of an apartment or house with a gas double-circuit heating boiler, the threaded connection units will be used:
- On cold water supply taps from the water supply system;
- On the gas supply valves to the boiler there is a gas valve from the gas pipeline, a gas filter and the inlet itself into the boiler;
- On the hot water supply pipe to consumers;
- On the supply line of hot coolant to the heating system;
- On the pipe for the return supply of cooled coolant to the boiler;
- At connection points for heating devices - at the inlet and outlet of the radiator;
- On the heated towel rail (if there is one);
- There is a heated floor at the line distribution node in the system.
This number of points where a threaded connection is used is far from complete, since it describes only the minimum version of the heating system for an ordinary apartment. But even in it, each node has its own characteristics. So, for gas equipment, and a gas heating boiler refers specifically to this type of equipment, the connection of the gas pipeline must be done in strict compliance with the rules. Here it is necessary to make a reliable seal to prevent the leakage of natural gas.
At the connection point for the direct and reverse coolant supply, it is necessary to make a seal, taking into account the fact that when the coolant heats up and cools down, the metal parts will expand and contract. This means that the hermetic seal must withstand not only the maximum expansion of parts, but also ensure integrity during uneven expansion or contraction of the connection when the temperature drops.
The joints of heating radiators will also experience such mechanical stress, because when hot coolant is supplied, the metal, especially in cast iron batteries, expands more slowly than in shut-off valves made of brass or aluminum alloy.
And of course, in addition to the temperature factor, the seal must also take into account the chemical factor, because with repeated heating and cooling, the chemical composition of the water changes. Not to mention that in some systems, instead of the usual prepared water, antifreeze is poured or chemicals are added to prevent the water from freezing in the event of a breakdown.
Now that you can see how many problems can arise when operating a heating system with a minimum number of threaded connections, the importance of installing seals during installation becomes obvious.
Packaging for hardening and anaerobic sealants
As with winding, careful cleaning and degreasing of both sides of the threads will be required. In addition, it is recommended to wear disposable gloves, as most sealants are quite sticky and difficult to wipe off the skin.
Using sealing pastes is extremely simple, the only problem is that there are quite a lot of varieties of such products. They should be selected according to the thread diameter, the type of liquid and its temperature, and the set fixation time. All conditions under which a particular sealant can be used are indicated in the instructions.

For example, regular white or gray paste is considered the most versatile option. These sealants are suitable for connecting pipes with a diameter of up to 2", but for threads larger than 3/4" additional winding of flax fiber may be required. Read the instructions carefully: the drying time for conventional sealants can be up to a day; before this, liquid must not be introduced into the system.
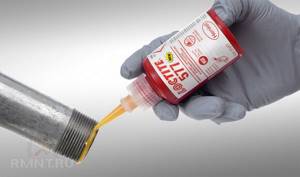
Anaerobic sealants are typically blue, green or red in color. There is no single dependence of properties on color, but in most cases there is a difference between cold and warm shades of sealant:
- Blue and green gels are standard anaerobic sealants. Their main property is the ability not to harden in air; polymerization occurs only in an airless space upon contact with metal.
- Red and orange anaerobic sealants are considered a means of quickly fixing high-strength joints. They harden in just a few minutes, which allows them to be used to quickly eliminate leaks and put the system into operation almost immediately after packaging. However, this may require preheating the threads.
Materials for sealing threaded connections
Today there are no highly specialized materials for sealing one or another type of threaded connection. The materials on the market are applicable to almost all installation points and materials, however, provided that the work is carried out by an experienced specialist. Therefore, it is important to know and understand all the strengths and weaknesses of sealing materials.
End gaskets
Installing a sealing end gasket between parts in modern heating systems has very limited use. At the same time, this option can well be used for end-tightened connections. For installation, paronite, fluoroplastic or rubber gaskets are used. The positive side of this method is the ease of installation and reliability of the connection. The clamped gasket between the two planes ensures both tightness and reliability of the connection. The disadvantage of this method is that when clamped, the gasket is deformed, and quite often it simply narrows the internal lumen. Such a narrowing negatively affects the fluid flow rate, which ultimately leads to a loss of temperature in the coolant and slow heating of heating devices.
Another disadvantage is the need to carefully prepare the joint surfaces so that during installation there is no misalignment of the gasket. For those who do not have experience installing such gaskets, it is recommended to have 1-2 gaskets in stock, since if installed incorrectly after disassembly, the gasket is not reused, but replaced with a new one. Another tip is that it is recommended to apply sealant to the gasket before installation to ensure that all voids are filled as tightly as possible.
It is recommended to purchase gaskets for installation for heating systems, although almost all gaskets made of rubber, paronite and fluoroplastic can withstand temperatures of +100-120 degrees, not all react equally to contact with water and antifreeze.
FUM tape

PTFE tape is actively used for installation of water intake fittings for hot and cold water supply systems. It is also used for heating systems. Compared to other types of materials, it is easy to use, perfectly seals the connection and does not lose its properties during operation. The latter is very important when carrying out repair work - such connections can be easily dismantled even after many years of active use.
FUM tape is available in several sizes, which allows you to choose the right option for the job. A positive point is that it does not react with water and antifreeze. It also easily withstands high temperatures and repeated heating-cooling cycles.
However, when working with it you need to consider:
- When sealing connections with very tight threads, it will tear and be squeezed out when screwing on the thread;
- If the connection is not tight, leaks are possible, since the tape is not able to adhere to the metal and expand in volume upon contact with water;
- When used, it is most effective on connections up to 25 mm, so when screwing a plug or nut into a cast iron battery, it is worth using another material for sealing.
Sealing thread

This is a relatively new material for filling cavities between joint parts. The thread is made of Teflon or fluoroplastic. Therefore, it has approximately the same properties as tape. But, given that it has a different cross-section and fills the cavity between the turns more tightly, its use for sealing becomes more attractive.
In addition, there are samples of plumbing thread that consist of several fibers; these types are recommended for use with liquid sealants.
Hemp or linen span

A material of plant origin traditionally used in sealing threaded connections. To seal threaded connections, it is used in conjunction with liquid or gel sealant.
Flax is used for installation in connections of large and small diameters. When used correctly, linen can last quite a long time. The truth has significant drawbacks:
- Not everyone can wind a flax span correctly and not the first time; the work requires experience and dexterity;
- As a material of plant origin, it has a limited service life;
- Reacts to changes in temperature and humidity, reacts to chemically active substances;
- During repairs, great effort is required to separate the joint, which was sealed with flax span.
Chemical sealants

The basis for the production of this group of materials is silicone. Among the advantages of silicone is its stability at high temperatures and neutral reaction with most chemically active substances.
During installation, silicone sealants provide lubrication of rubbing surfaces, making it easier to twist threads. After installation, the substance fills all cavities and ensures reliable connection.
There are drying and non-drying sealants. When sealants dry, after a certain time they become viscous or turn into a solid state. This group distinguishes between sealants that dry when exposed to air - the anaerobic type and substances that change their state upon contact with water.
The disadvantage of this group of sealants is that when they dry, they shrink, which means that over time, the coolant may start dripping in this place.
Non-hardening sealants remain liquid or gel-like for a long time, so such materials are easy to apply and, even after prolonged use, the joints are easy to dismantle. On the other hand, during installation and operation, there is a high probability that such sealant may be squeezed out of the thread.