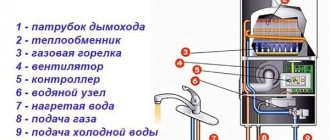
To avoid heat losses and prevent the network from freezing, it is recommended to use pipe insulation made of foamed polyethylene.
Experts recommend this material for a reason. This environmentally friendly product has a finely porous gray structure. This insulation is of high quality, moisture does not pass through it and it retains heat well. One of the main advantages of this product is its high elasticity and flexibility.
Areas of use
Foamed polyethylene shells are used for pipe insulation:
- Heat supply.
- Hot and cold water supply.
- Sewage systems.
- Air conditioning installations.
- Ventilation ducts.
- Refrigeration equipment.
Sheet insulation based on foamed polyethylene insulates:
- External and internal surfaces of building walls.
- Basements, foundation structures.
- Attic spaces.
- Roofs.
- Steam rooms, saunas, baths.
The following are sealed with foamed polyethylene strands:
- Interpanel seams.
- Gaps in window and door fillings.
Safety of polyethylene foam
Polyethylene is one of the most stable compounds on the planet. Polyethylene granules, which are used to make thermal insulation, are used to make water cans and bottles, food packaging, and water pipes.
At the household level, if used within the operating temperature range, polyethylene foam is harmless. PPE is dangerous when heated above 110-120 0C.
When burned, it releases acetic acid, formaldehyde, and carbon monoxide.
The decay period of the material is about 200 years. This, on the one hand, makes it one of the most durable materials (which is good). But on the other hand, polyethylene, like plastic, is a real disaster for the earth’s ecology, since a large amount of foamed polyethylene waste accumulates.
Manufacturing technology
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) granules are poured into a hopper, where they melt and mix evenly. Next, the resulting mass is foamed with gas or special reagents. At this stage, pigments and modifying additives are introduced into the melt. Then the heated mass is pressed through an extruder to give the insulation the required shape.

Advantages and disadvantages
Thermal insulation for pipes made of foamed polyethylene is endowed with numerous advantages:
- High thermal insulation properties. Its use makes it possible to reduce heat loss by up to 75% and ensure that liquids remain at the same temperature during transportation.
- Low hygroscopicity. Insulated pipes are less susceptible to corrosion, as they are protected from moisture from the environment penetrating their outer surfaces.
- Good vapor barrier effect. Condensation does not form on surfaces insulated with foamed polyethylene; additional waterproofing is not required when insulating pipes.
- Ability to withstand temperature changes in the range from -80 to +95 ºС. Thanks to this property, the insulation can be used in difficult conditions.
- Soundproofing qualities. Foamed polyethylene absorbs sounds from circulating fluid in communications and partially dampens the level of structural noise.
- Light weight. Insulation with lightweight polyethylene foam tubes will not lead to a significant increase in the load on utility networks.
- Easy to install - no special equipment required.
- The ability to quickly restore its original shape after compression.
- Biological stability. Foamed polyethylene is resistant to the formation of fungal deposits and mold.
- Inertness towards chemical elements. Polyethylene insulation does not lose its qualities from contact with various building solutions, alkaline and acidic environments, so they can be used to insulate pipes running through concrete structures or buried in the ground.
- Ecological cleanliness. Foamed polyethylene does not emit toxic substances; such insulation can be used for thermal insulation of pipes in educational institutions, medical centers, process pipelines of food production, etc.
- Affordable price. For a relatively small amount, pipelines can be insulated along their entire length.
- Long service life - at least 30 years.
However, this insulation also has three main disadvantages:
- Low fire resistance. Foamed polyethylene quickly begins to melt under the influence of open fire and can spread combustion to structures located near it.
- Increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. Foamed polyethylene becomes brittle when exposed to direct sunlight, crumbles and cracks. To compensate for this drawback, the insulation on the outside is covered with foil.
- Low mechanical strength. The insulation is easily damaged by a sharp object, and the rupture can spread further along the length of the insulation. Therefore, damage must be immediately sealed with reinforcing tape.
Basic requirements for thermal insulation materials for pipes
Products for pipe thermal insulation must have:
- Low thermal conductivity coefficient. The thickness of the foam polyethylene insulation depends on this indicator. Communications in apartments lie in cramped conditions; their insulation requires not only effective, but also small-volume materials. The use of thin-walled shells as insulation for pipes will save more usable space in these rooms.
- Hydrophobic properties. Moisture reduces the thermal insulation properties of any insulation, and when it accumulates in large quantities, it can form so-called cold bridges.
- Resistant to mechanical loads and environmental conditions, since pipes have to be insulated in open areas or under a layer of soil.
- Heat resistance. Insulation used to insulate pipes of hot water supply and heating mains must meet this requirement.

Main brands on the modern market
Manufacturers of domestic foamed polyethylene: Tepofol, Vilaterm, Izolon, Energoflex (ROLS ISOMARKET), Thermaflex, Polyfom, Penofol, Porilex.
European and American manufacturers of polyethylene foam: DOW, Sealed Air, Pactiv, TROCELLEN, EPE Corporation Group, Alveo.
Every year, up to 185 thousand tons of foamed polyethylene foam are produced around the world. This is a lot. Despite the fact that this market is considered relatively young, the pace of PPE production has already outpaced the production of film, the largest segment of LDPE polyethylene. It is expected that the growth in consumption of this thermal insulator will continue to grow due to the displacement of more expensive substitutes and the use of foamed polyethylene in areas where it was not previously used - in electrical engineering, travel equipment, etc.
Classification types and dimensions
Thermal insulation materials made of polyethylene foam are divided into types according to several criteria:
- By structure - stitched and unstitched.
- By type of surface finish - uncoated, aluminum foiled on one or both sides, with a protective polymer coating.
Rolls have a width from 60 to 120 cm, a length from 2 to 30 meters, the thickness of the sheet is no more than 5 cm. Tubes are produced in lengths from 1 to 10 meters with a wall thickness of 6–32 mm, and a diameter from 6 to 160 mm.
Stitched
Cross-linked is polyethylene foam whose structure is modified at the molecular level under the influence of external factors. The result is a material consisting of very small closed cells and is more resistant to stress.

There are two types of cross-linked polyethylene foam:
- Chemically cross-linked (CS PPE). The molten polymer is mixed with foaming agents and treated with chemicals.
- Cross-linked by radiation method (FS PES). The foamed polymer mass is exposed to a pulsed beam accelerator, which orders the molecular structure of the material with a flow of electrons.
Cross-linked polyethylene pipe insulation is more durable, elastic and dense. It has a shape memory effect for insulated structures.
Unstitched
Non-crosslinked polyethylene foam is designated by the letters NPE. It is formed during the processing of polyethylene with gaseous reagents (a mixture of propane-butane or freon). This type of insulation has a structure with larger gas-filled cells.

Split
Tubes made of foamed polyethylene, which have a technical slot along their entire length, are easily put on already installed lines. To install them, you do not need to dismantle sections of pipes. The edges of the halves are joined end-to-end and sealed with metallized tape.

One-piece
The thermal insulation material has the shape of hollow cylinders with a solid surface. Installed on the pipe during pipeline assembly.

Foil
The material is covered on one or both sides with a thin layer of aluminum foil or metallized film. Maximum adhesion of layers is achieved by thermal welding. To increase the heat-reflecting effect, the foil is polished. Foiled polyethylene foam insulation has:
- Higher thermal insulation coefficient.
- Shock-absorbing qualities.
- Fire resistance.
- UV resistant.

Review of manufacturing companies
I have heard a lot of positive reviews about the insulation materials Vilaterm, Isolon, Penolin, Merilon, Energoflex and Thermaflex.
- Vilaterm
Vilaterm is produced by a Moscow company. The material has a fine-cell structure with closed pores, is hygroscopic, absorbs shock and noise, and is environmentally friendly. Due to the high air content it has high thermal insulation properties.
The range consists of bundles and cylinders. Insulation in a cylindrical form is suitable for insulating pipes both at new, installed facilities, and for existing, operating pipelines.

- Izolon, foam
OJSC Izhevsk Plastics Plant produces two types of sheet insulation with a thickness of 1 to 5 cm under the Izolon brand:
- NPE - from unstitched.
- PPE, PPE-L, PPE - NR, PPE-NH - made of cross-linked foamed polyethylene.
Izolon has a very low thermal conductivity coefficient. It reliably protects the room from steam and moisture.

Thermal insulation mats and pipe insulation Penolin are produced by ZAO Information Technology Plant LIT. It comes in various thicknesses and colors, the width of the canvas is 110 and 125mm. It is possible to cover the insulation with aluminum foil, metallized plastic film and other materials.
- Merilon
Pipe insulation MERILON (Czech Republic) is available with an internal diameter from 15 to 110 mm and a wall thickness from 6 to 18 mm, which provides varying degrees of insulation. Foamed polyethylene Merilon has an extremely porous structure.
It is waterproof and does not rot. The structure with many air cells provides it with good thermal insulation properties.

- Energoflex
Energoflex is an environmentally friendly insulation made of polyethylene foam that meets all European quality standards. Freon is used for its manufacture, so the material better resists the diffusion of water vapor.
It is used to protect various pipes, containers and fittings from heat loss. Thermal insulation is produced in the form of sheets, rolls and sleeves of various diameters.

- Thermaflex
(Netherlands) produces a wide range of pipe and sheet insulation for engineering systems operating in the temperature range from -80 to +110 °C. Thermoflex has low thermal conductivity and high resistance to water vapor diffusion, retains good elasticity at sub-zero temperatures, does not absorb moisture and does not decompose.

Choice of insulation
The choice of thermal insulation material must be made taking into account certain factors
The choice of thermal insulation material should be made taking into account the following factors:
- Diameter of pipes used;
- Operating conditions of the system;
- Coolant heating temperature.
Depending on the diameter of the heating pipes, the heat insulator can be soft mats in rolls or hard molded cylinders and half-cylinders, which are used to insulate small-diameter pipes. Rigid insulation materials, moreover, due to their strict geometric shape, provide additional protection from mechanical damage.
There are many materials used for these purposes; let’s look at the most popular ones.
Mineral wool
- High temperature resistance. Values up to 650°C do not cause changes in thermal and mechanical characteristics.
- Fire resistance;
- Chemical resistance to solvents and other chemically aggressive substances.
- Environmentally friendly.
The best types of mineral wool include stone wool, produced from melts of basalt rocks. Another type of material is glass wool, obtained from glass fiber, obtained, in turn, from quartz sand. It is not so heat-resistant and does not have such high other performance characteristics.
Expanded polystyrene
There are many materials used to insulate heating pipes.
It is a new type of foam made using improved technology. It has higher strength and elasticity, good heat resistance and a low degree of moisture absorption. Has good ability to retain heat. Used in the form of convenient shells for pipes, they consist of two halves fastened with a lock, the internal diameter of which is equal to the diameter of the pipe.
Foamed polyethylene
Quite a popular and frequently used material. It is moisture-resistant, resistant to temperature fluctuations, and easy to install and transport. It has good heat and sound insulation qualities. Easily takes a given shape and is environmentally friendly. Compatible well with all types of building materials.
For thermal insulation of pipes, it is produced in the form of covers of a certain diameter with a cut on the side for putting on.
Penofol
It is a slightly improved version of foamed polyethylene, in which a layer of this material is supplemented with a layer of foil. This two-layer design retains heat better due to the combination of the reflective properties of aluminum and the insulating properties of polyethylene foam. It has a unique ability to retain heat along all possible paths of its distribution. The thickness of penofol is about 14 mm. This is a light, thin, flexible and easy-to-use material. The disadvantage is the frequent occurrence of corrosion in the foil layer.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is chemically and biologically stable, not afraid of mold or chemically aggressive environments.
To insulate heating pipes, this heat-insulating material can be used in the form of a hard shell placed on the pipes, or it can be used by a more progressive method - the spraying method. You can read more about pipe insulation here - /kak-uteplit-truboprovod-svoimi-rukami-instruktsiya-sovety-domashnih-masterov/
The material is a record holder among insulation materials for the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient among them. It is also distinguished by low water absorption and high vapor and sound insulation properties.
Polyurethane foam is chemically and biologically stable, not afraid of mold or chemically aggressive environments. It has high strength to mechanical stress, is resistant to temperature changes, and is durable.
Application of the material by spraying allows you to obtain a homogeneous, absolutely seamless coating with no joints. Such high tightness, combined with unique thermal properties, allows for the best possible heat retention.
An analysis of all the features and performance qualities of the material allows us to conclude that this is the best insulation for heating pipes today.
The remarkable properties of polyurethane foam are fully manifested only with proper application. Specialists provide professional spraying services in compliance with all existing norms and standards, including international ones.
How to choose
When choosing polyethylene foam insulation, consider the following factors:
- Size and location of the insulated structure. You can insulate the floor using rolled materials, heating and sewer pipes using shells. Harnesses are suitable for sealing cracks in doors and windows.
- Density of the material. The higher the density of the insulation, the greater external loads it can withstand while maintaining its shape and properties.
- Convenience of installation work.
- The maximum heating level of the coolant and the lowest temperature in the environment. This criterion influences the choice of insulation wall thickness.
- Manufacturer's reputation.
approximate price
Average prices from different manufacturers are:
- Vilaterm: sealing harness with a cross-section of 6 mm - from 3.5 rub./l.m.
- Merilon: with foil coating (3 mm, length 30 m) - 1450 rub./roll, thickness 10 mm, length 15 m - 2100 rub./roll.
- Energoflex: pipe insulation: 16 RUR/roll (22×9 mm); 150 RUR/roll (110/13 mm).
- Penolin: with a thickness of 2 mm, the cost is 450 rubles; with a thickness of 5 mm - 1030 rubles.
- Thermoflex: 750 RUR/roll (25 m length, 2 mm thickness).

Excellent set of characteristics
This insulation has all of the listed properties due to its technical characteristics:
Technical characteristics of foamed polyethylene
| Characteristic | |
| Thermal conductivity | up to 0.4 W/m*K |
| Operating temperature range | from -65 to +100 C |
| Noise absorption | up to 18 dB |
| Water permeability | no more than 1.5% per day |
| Density | 25 - 80 kg/m 3 |
| Moisture absorption | no more than 2% |
| Lifetime | up to 80 years old |
In addition, this insulation can perfectly compensate for the volumetric and linear thermal expansion of the pipeline, which is especially in demand if the pipes are planned to be installed inside walls.

Related Posts
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Cross-linked polyethylene pipes for water supply: material features, areas of application, installation technology
- Polyethylene: properties and applications
- Foil insulation: types, properties and possibilities of use
- Foiled penofol: technical characteristics and material features
- Choosing non-flammable insulation for walls and ceilings: tips and tricks
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Isover thermal insulation overview
- The unique characteristics of thermaflex insulation for pipes
- How to insulate an outdoor water pipe
- Which rehau pipes are best for heating and water supply?
- Fum tape technical characteristics, how and how much to wind on the thread
- Energoflex insulation for pipes: characteristics
- Underfloor heating: selection rules, characteristics, best brands, installation tips
- Insulation of a veranda in a wooden house
- Thermal insulation for heating pipes, and what you need to know about it
- How not to spoil the efficiency of a heating battery with a decorative screen
- Rules for laying sewer pipes
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- Sound insulation of sewer riser
- Baswool insulation: characteristics and scope of application
- Dismantling of heating systems
- What are polyurethane foam pipes and where are they used?
- Insulation of a concrete floor in an apartment
Read with this
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Cross-linked polyethylene pipes for water supply: material features, areas of application, installation technology
- Polyethylene: properties and applications
- Foil insulation: types, properties and possibilities of use
- Foiled penofol: technical characteristics and material features
- Choosing non-flammable insulation for walls and ceilings: tips and tricks
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Isover thermal insulation overview
- The unique characteristics of thermaflex insulation for pipes
Instructions for use
There are several general rules that must be followed when installing polyethylene foam insulation:
- The surfaces of insulated objects are prepared in advance. They are cleaned and leveled, cracks and seams are sealed.
- All equipment should not operate during thermal insulation work.
- The joints are glued with glue, and the seams are fastened with self-adhesive tape.
- There should be a small space - an air gap - between the working surface and the insulating material.
- It is not recommended to install thermal insulators made of foamed polyethylene overlapping, but only end-to-end.
- Foil insulation is mounted with a shiny layer towards the room.
To thermally insulate the door leaf, it is enough to cut a blank from a sheet of polyethylene foam to measure and secure it on top with finishing material. On the surface of the enclosing structures from the inside of the house, foam thermal insulation can be laid under drywall, which will significantly reduce heat loss.
It is better to insulate a balcony or loggia with polyethylene foam with a protective film against ultraviolet radiation or with foil material. It will reliably protect these structures from moisture and street noise, while their area will be reduced slightly.
Insulation marking
Polyethylene-based insulation is divided into many types; markings are used to indicate the presence of certain features, namely:
- “A” - polyethylene, covered with a layer of foil on only one side, is practically not used as a separate insulation, but only as an auxiliary layer with other materials or a non-foil analogue - as a waterproofing and reflective structure;
- “B” – polyethylene, covered with a layer of foil on both sides, used as a separate insulation in interfloor ceilings and interior partitions;
- “C” – polyethylene, covered with foil on one side and a self-adhesive compound on the other;
- “ALP” – material covered with foil and laminated film on one side only;
- “M” and “R” are polyethylene, covered with foil on one side and having a corrugated surface on the other.
Features of pipe insulation work
The installation of pipe insulation is often carried out after the pipeline has been assembled. It is impossible to put solid cylinders on the assembled sections of the pipeline, so they use products with ready-made cuts or cut them during installation. After installation on the pipes, the edges of the cut sleeves are fixed with special tape.
Installation should begin with preparing the surface of the pipes:
- Thorough cleaning of dirt and dust.
- Any abrasive material can be used to remove rust. They need to scrub the pipe well, then wash with warm soapy water. The dried pipe can be painted or primed.
I usually glue external pipe insulation along the cuts and at the joints. If the pipes are located inside the building, then it is not necessary to glue the insulation along its entire length. You can simply secure it with one piece of tape.
See the video for details of installing thermal insulation in places where pipes branch.
How to calculate insulation for your home
If it is necessary to insulate the walls of the house from the inside, then you need to measure their width and height in all rooms. Then multiply these parameters to calculate the area of each wall separately, and sum the resulting values to determine the total insulation area. Next, from the resulting amount you need to subtract the area of window and door openings to determine the required amount of thermal insulation material.
Pipe insulation is calculated even more simply - based on the total length of the insulated pipelines.