What are the requirements for a room to house a gas boiler?
Installation work on installing gas equipment is not the time for experiments.
You need to act only in strict accordance with the norms and rules established in construction. Before starting work, you need to familiarize yourself with several SNiPs for gas supply - they are freely available on the Internet, and be sure to study the instructions supplied with the boiler by the manufacturer. It is also important to choose the right place for its installation
So, for example, a gas stove and a low-power boiler running on natural gas can be placed in a kitchen or hallway with a ceiling height of at least 2.2 m, an area of 15 m² or more, if it has a window with a window. If, however, a floor-standing gas boiler is to be installed, the power of which exceeds 30 kW and the combustion products are discharged into the chimney, then a separate room (boiler room) is required. To equip such a boiler room, according to SP 62.13330.2011 (Updated edition of SNiP 42-01-2002), you can use:
- separate building;
- extension to the main building;
- attic space;
- ground floor;
- basement room.
Moreover, it is allowed to use the basement and ground floor for arranging a gas boiler room only if they have window openings that provide natural light. A free-standing boiler room must have its own supporting structure, which is not connected to the foundation of the main building.
In addition, this room must meet a number of requirements, namely:
- area - at least 4 m² per heating device;
- volume - not less than 13.5 m³;
- ceiling height - from 2.2 m;
- separate entrance with opening width from 80 cm;
- an air intake opening with a cross-sectional area of at least 25 cm² at the bottom of the door leaf or wall or a small gap between the end of the door and the floor covering;
- windows with opening sashes. The standard glazing area for 1 m³ of explosive premises is at least 0.05 m²;
- plastered wall surface. Decorating with wallpaper or flammable panels is not allowed;
- flat floor made of non-combustible building materials.
The gas unit must be accessible from all sides. The oxygen-saturated air masses necessary for the fuel combustion process enter the furnace through the ventilation duct. It is installed in the upper part of the walls or in the ceiling. And to make this air duct more convenient to clean, a special hatch is equipped 300 mm below it, which is a small hole closed with a plug or flap.
Who inspects chimneys and ventilation ducts
So who carries out maintenance of ventilation and smoke ducts? By law, only those organizations that meet certain requirements are granted this right. First of all, they must have a special license - inspection organizations involved in monitoring ventilation ducts and chimneys must have such permission. Without it, not a single entrepreneur is worthy of trust, because putting the check in the hands of a non-professional is more expensive for yourself.
It is worth talking in more detail about the licenses required for specialists. The first of them is a permit for installation, maintenance and repair of smoke removal and smoke ventilation systems. It gives the right to inspect ventilation ducts and chimneys. In order to also clean smoke exhaust ducts, a second license is required - “Installation, repair, cladding, thermal insulation and cleaning of stoves, fireplaces, other heat-producing installations and chimneys.” It would be a good idea to make sure your employees have such permissions before entrusting them with your channels.

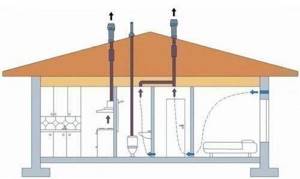
Ventilation from plastic sewer pipes in a private house
Fine. Let’s say that the performing company has already been selected, and the customer is completely confident in the quality of the services it provides. When is it worth calling its specialists for periodic inspection? Of course, problems arise in smoke and ventilation ducts, but calling people over trifles (and paying ridiculous money for it) is not worth it. The timing of the test must be chosen wisely.
As a rule, inspections of ventilation ducts are carried out on certain dates, for example, before the start of the heating season. After each repair or reconstruction, it is also necessary to check chimneys and ventilation ducts.
Further terms depend on the material from which the channel is made. Brick products require inspection at least once every three months. Other materials allow you to forget about checking for a much longer period - systems are examined at least once a year.
Do not forget that winter cold imposes additional requirements on inspection: the problem is that during severe frosts a dangerous amount of ice can accumulate on the heads of the outlet channels. To avoid such troubles during severe cold weather, you should check the condition of the hatches more frequently up to once a month.

Do-it-yourself manufacturing and installation of a gas duct
The rules for installing a boiler room oblige performers to begin it with the installation of chimneys and exhaust ventilation. The placement and connection of the gas boiler with engineering systems is carried out secondarily. In this case, boilers are not connected to polypropylene pipes.
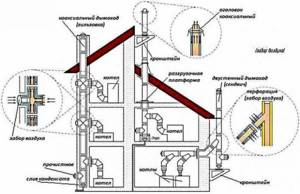
First, determine the diameter of the chimney for the gas boiler and the installation method. The first parameter is usually indicated in the boiler passport and in the design documentation for the installation of the boiler installation.
As for the installation method, it will depend on the structural characteristics of the house and the furnace room, but in the case of installing a boiler with a closed firebox, it is recommended to install the most innovative chimney system - a sandwich chimney with the same or larger cross-section than that of the boiler pipe.
Stabilizing the combustion process
Next, using the existing gas outlet installation diagram, a list of parts for installation is compiled:
- tee with a pipe outlet 89 degrees, for connecting a horizontal element to a vertical one;
- tee, with installed hatch;
- a block with a condensate drain to collect condensate in the chimney of a gas boiler;
- section with a coupling for connection to the boiler outlet pipe;
- flexible chimney transition section - sandwich;
- straight sections - with the number and length according to the chimney diagram;
- 2 elbows with an outlet angle of 30 degrees are required to bypass the roof;
- upper protective cap of the structure from exposure to precipitation;
- wall clamps with brackets;
- condensate collector for the chimney;
- support platform for the chimney of a gas boiler;
- insulation or thermal insulation.
For the internal location of the smoke exhaust system, adapters through the structural elements of the building and structural insulation at the points of contact will be required.
Size calculation
The choice of a gas duct must be made only after purchasing a boiler unit, otherwise it is very difficult to select the necessary parameters: length, angle of rotation, location of condensate traps. Separate modules of the smoke exhaust system can be purchased at a retail chain.
For professional installation of a flue, it is advisable to first calculate the cross-section of the inlet using the formula: F = (K x N) / (4.2 x √ N), where:
- K is the design coefficient of the unit’s smoke exhaust system, assumed to be 0.03;
- N is the power of the boiler unit, indicated in the technical documentation for the heating boiler;
- H is the minimum height of the gas duct, established by calculation by the manufacturer for a specific brand of boiler unit.
After obtaining the cross-sectional area, it is compared with the data of devices available in the retail network and, if necessary, the nearest larger option is selected. When using an asbestos pipe, the cross-section of the smoke exhaust duct is taken to be no less than 100 mm.
Installation of flues
- A passage element designed to pass through the wall is connected to the boiler flue outlet pipe.
- Markings are made on the surface of the wall according to the data of the pass-through component and an opening is made in the wall.
- Remove the chimney from the room.
- Insulation of the chimney from a gas boiler is carried out.
- Attach a tee to the chimney.
- The chimney is extended and new elements are added to the estimated length.
- Install a protective cap from precipitation.
- To secure the structure to the wall, brackets are used in increments of 2.0 m.
- Secure all butt joints with clamps.
The importance of kitchen ductwork
The existing general ventilation does not remove combustion products and evaporation specifically from the stove; it serves to replace air throughout the entire volume of the room.
Modern housewives are not happy with this situation. We want high-quality and durable repairs in the kitchen; a working woman does not have time to regularly wash the walls, ceiling and furniture. Demand creates supply - local ventilation units have appeared above kitchen stoves - hoods. But polluted air must be removed outside the room, and air ducts perform this function.

Advantages and disadvantages
There is only one advantage of the air duct: it is impossible to remove carbon dioxide, water and soot without it.
- They take up space.
- They spoil the kitchen interior.
- Poor installation results in increased fan noise.
- They require regular washing on the outside and periodic cleaning on the inside.
Is it always possible to install a hood?
There may be situations when installing a hood is prohibited by the operating rules for gas appliances.
If there is a gas water heater (boiler) or a gas heating boiler with an open combustion chamber in the same room as the hood, a hood with air removal (circulation) cannot be installed. Removal of combustion products from the boiler occurs without force; when the exhaust fan is turned on, the draft may overturn and toxic combustion products may be thrown into the room.
It is allowed to install a flow-through exhaust device only if a boiler with a closed firebox is installed (with a coaxial chimney and combustion air intake from the street).
You can install circulation-type devices with filters that clean the air from grease and soot.
Functions, types, selection of exhaust device
The importance of a hood in a food preparation area is obvious, because its main tasks are:
- removal from the working area of air contaminated with combustion products, smoke, fumes, odors;
- reduction of humidity and air temperature near the stove for more comfortable work;
- providing conditions that prevent the appearance and proliferation of unwanted microorganisms;
- increasing the durability of kitchen furniture, household appliances and interior items, on which soot, grease and dirt will not settle;
- ensuring an influx of clean air instead of exhaust air containing pollutants;
- creating comfortable conditions for working in professional kitchens and favorable living conditions in private properties near the kitchen premises.
The hood, connecting the air duct pipes to the ventilation shaft, helps remove contaminated air to the outside.
The following types of hoods are installed in kitchens: flat, inclined, built-in, T-shaped, island, corner, dome, telescopic.

Functionality of chimney draft stabilizer
To remove the entire volume of contaminated air, the dimensions of the hood must be the same or larger than those of the hob. The minimum productivity (m3/hour) of exhaust equipment should be at least 10 times the volume of the kitchen space.
Recommended hood installation height:
- above the gas stove – 0.75-0.85 m;
- above an induction or electric stove – 0.65-0.75 m.
Inspection of chimney systems and ventilation ducts
You can check ventilation ducts and chimneys using the traditional, classic method - using a brush, a short rope and a weight. Although today, more modern methods are almost always used to inspect ventilation and chimney systems. For example, they use digital photography and filming with a video camera with spotlights. There are also devices that make it possible to very quickly, effortlessly and accurately assess the draft in a ventilation or chimney.

What is examined during the inspection? During the examination it is established:
- the length of channels, narrowings and bends, places of connections, marks of cracks and congestions found in the system;
- materials from which the channels were made, their cross-section;
- density and isolation of channels;
- condition of hatches prepared for cleaning, heads, fire-prevention cuts;
- tightness of pipes;
- the presence of traction, an area of wind support (or its absence), horizontal sections;
- general position of the system.
Also, during the inspection of ventilation ducts, the condition of the ducts, air intake grilles and exhaust shafts is checked.
Based on the results obtained during the inspection, a report is drawn up.
Requirements for chimneys for gas boilers
All requirements for smoke ducts are specified in regulatory documents - SNiP 2.04.05-91 and DBN V.2.5-20-2001. Their implementation is mandatory. To summarize, everything can be reduced to several points:
- The cross-section (diameter) of the chimney cannot be smaller than the outlet pipe on the boiler. That is, if the output of a gas boiler is 150 mm, then the chimney must have an internal cross-section of at least 150 mm. More is possible, less is not. In extreme cases, they can turn a blind eye to a difference of a few millimeters.
- The chimney must go vertically upward. It is advisable to develop the structure so that there are no inclined sections. In extreme cases, a slope of 30° is allowed. The length of the inclined section is no more than the height of the room.
- Throughout the entire length of the chimney, it should not have any bends or narrowings.
- The chimney must be made of gas-tight materials.
- The joints must be carefully insulated - they must be airtight (they must not allow gaseous substances to pass through and must not allow moisture to pass through).
- Since the flue gases at the outlet of modern gas boilers have a low temperature, there is a high probability of condensation forming. Therefore, when installing a chimney, it is necessary to provide a condensate collector in its lower part. This is a removable glass made from chemical resistant materials. The best option is a stainless steel condensate collector; a cheaper option is a plastic one. Galvanized steel is a cheaper option but degrades quickly.
- The chimney for a gas boiler in a private house must have a height that will provide good draft. To do this, it must rise 50 cm above the ridge of the roof if it is installed in close proximity to it.
- It is advisable to install a protective canopy at the top of the pipe - an umbrella. It protects the pipe from clogging and precipitation.
These are the basic requirements. They must be followed. They provide the required degree of security. After all, the fact that the exhaust of a gas boiler is colorless does not mean that it is harmless. Therefore, maximum attention must be paid to all aspects of ensuring safety.
Standardization of ventilation during operation of gas boilers
It should be noted that gas equipment is a source of increased danger. Therefore, the procedure for designing and operating boiler houses is standardized by the state, and compliance with these requirements is strictly controlled by it.
To streamline all requirements, “Building Norms and Rules 2.04.05” have been developed and applied. II-35", and II-35–76. The basic requirements for premises for gas boilers are set out above.
This document also regulates:
- procedure for developing technical documentation;
- sizes and capacities of ventilation systems for different types of buildings;
- their types and order of arrangement.
Chimneys and ventilation ducts
It is permitted to erect and place a chimney and ventilation in a private house only if there is a design and compliance with all norms, rules and requirements for construction work. In this case, all rules and requirements for fire safety, ease of installation and repair work, as well as maintenance and operation must be taken into account and observed.
A ventilation system with natural draft ensures the removal of air from the room where the fireplace is located, and the chimney system is responsible for removing combustion products from the hearth. By the way, the channels for ventilation and chimney must be made vertically, a slight slope is allowed, but without ledges. The internal surface of the chimney must be smooth and of the same cross-section. If you correctly design and install chimneys and ventilation, then thanks to this there will always be optimal air exchange in the room and the possibility of reverse draft in the ventilation ducts will be eliminated. Also, there will be no smoke and carbon monoxide in the living room with a fireplace. It is allowed to place a single block in ventilation and chimney ducts, separating them in height with partitions (hermetically sealed). It is recommended to place the ventilation pipe close to the chimney. There are no strict requirements here.
The ventilation duct is capable of passing a limited amount of air, which depends on the cross-section of the pipe and the speed at which the air flow moves. The quality of natural draft may deteriorate due to the narrowed cross-section of the channel, clogging inside, unevenness of the inner surface of the pipe and the complex shape of the channels - these are the main factors that affect draft. And one more thing: air flows that pass through the channel create noise. Strong draft (ventilation through the chimney) is always accompanied by a hum in the chimney. In order to reduce the noise in the chimney, it is necessary to select the optimal channel cross-section and thereby maintain a low air flow rate.
Inspection of ventilation and chimneys must be carried out at strictly defined times, guided by established standards and common sense, + clean them if necessary. As a rule, chimneys are checked quarterly before the start of the heating season, and it is enough to check ventilation ducts once a year.
Hearth and air exchange
In houses where the ventilation system has a natural draft and in houses where an automatic supply and exhaust system, air exchange and natural draft are different. The fireplace in action increases ventilation in the room and requires regular supply of fresh air.
Often, the main mistake of fireplace owners is that they do not take it into account in the overall ventilation system of the house. The air exchange system of the room is interconnected, and based on this, the following should be taken into account: how air will be removed through the ventilation ducts, how fresh air will enter the room, and how much air will be burned. Therefore, the design of the chimney and ventilation should always be taken into account at the construction stage of the facility.
Calculation of the ventilation system
According to building standards, the entire air space of the boiler room must be replaced with new one every 20 minutes. To ensure the appropriate air circulation, you will have to arm yourself with a calculator and formulas.
If the ceilings are located at a height of 6 meters, then without special devices the air in the room is renewed three times per hour. Six-meter ceilings are a luxury for a private home. The reduction in ceilings is compensated for in calculations in the following proportion - for each meter lower, air exchange increases by 25%.
Suppose there is a boiler room with dimensions: length - 3 m, width - 4 m, height - 3.5 m. To solve this problem, you need to perform a number of actions.
Step 1. Find out the volume of air space. We use the formula v = b * l * h, where b is the width, l is the length, h is the height of the ceiling. In our example, the volume will be 3 m * 4 m * 3.5 m = 42 m3.
Step 2. Let's make an adjustment for the low ceiling using the formula: k = (6 - h) * 0.25 + 3, where h is the height of the room. In our boiler room the correction turned out to be: (6 m – 3.5 m) * 0.25 + 3 ≈ 3.6.
Step 3. Calculate the air exchange provided by natural ventilation. Formula: V = k * v, where v is the volume of air in the room, k is the correction for lowering the ceiling height. We got a volume equal to 151.2 m3 (3.6 * 42 m3 = 151.2 m3).
Step 4. It remains to obtain the cross-sectional area of the exhaust pipe: S = V / (w * t), where V is the air exchange calculated above, w is the air flow speed (in these calculations taken as 1 m/s) and t is the time in seconds. We get: 151.2 m3 / (1 m/s * 3600 s) = 0.042 m2 = 4.2 cm2.
The dimensions of the channel also depend on the area of the internal surface of the boiler. This number is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical documentation of the device. If this number is not indicated, calculate it yourself based on the volume of the device. Then compare the area with the radius of the section according to the inequality:
2πR*L > S, where
R – internal radius of the chimney pipe section,
L – its length,
S is the area of the internal surface of the boiler.
If for some reason such a calculation is difficult, you can use the table.
| Boiler power, kW | Chimney pipe diameter, mm |
| 24 | 120 |
| 30 | 130 |
| 40 | 170 |
| 60 | 190 |
| 80 | 220 |
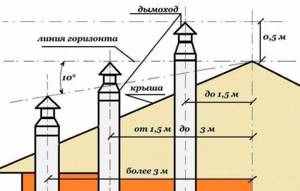
The last stage of the calculation is the height of the weather vane relative to the roof ridge. The need for this is due to the creation of additional draft by the wind, which increases the efficiency of the entire exhaust structure. At this stage, we are guided by the following principles:
- the height of the weather vane above a flat roof, or at a distance of up to 1.5 meters from its ridge, must be at least 0.5 meters;
- at a distance from 1.5 to 3 meters - not lower than the ridge of the roof;
- at a distance of more than 3 meters - not lower than a conventional line drawn from the roof ridge at an angle of 10˚;
- the weather vane should be 0.5 meters higher than the building, which is attached to the heated room;
- if the roof is made of flammable materials, the chimney must be raised 1-1.5 meters above the roof ridge.
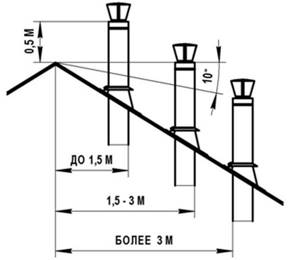
Calculation of the height of the chimney relative to the roof
Calculation of ventilation cross-section
To correctly calculate the cross-section of the boiler room ventilation system pipeline, you will need the following data:
- The cubic capacity of the boiler room, depending on the height of the room. According to SNiP requirements, its height should not be less than 6 meters. Obviously, in the conditions of a village house such a requirement is impossible to fulfill. When calculating, it must be taken into account that when this indicator decreases by 1 meter, the amount of air required for fuel combustion must be increased by 25%;
- Air mass flow velocity (at least 1 m/s).
- Air exchange rate. The value depends on the height of the boiler room.
The result of the calculation will be the air requirement, on the basis of which, using special tables, the cross-section of the ventilation system pipeline can be determined.
The calculation is made using the relationship V = L x SX (6 - H) x 1.25 xn, where:
- V is the volume of air for fuel combustion;
- L is the length of the room;
- S is the width of the room;
- H is the height of the room;
- n is the frequency of air change in the boiler room, equal to 3.
Thus, when determining the air requirement, the actual size of the room and the increase in air turnover are taken into account. Having received the desired value, the diameter of the air duct can be selected from the table.
Table: dependence of the duct diameter on the required air flow
| Sediments | Natural deposits on the walls of chimneys and ventilation ducts in the form of soot, dust and grease. The first ones need to be cleared of soot immediately after such signs appear. |
| Humidity | A blockage can appear very quickly after burning poorly dried firewood and household waste, as well as with a large amount of tar. In such cases, cleaning the ventilation and smoke exhaust systems is mandatory. |
| Other reasons | The instructions also say that traction may weaken due to: |
| Air duct diameter, mm | Air flow in m 3 /hour at speed in m/s | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 100 | 28,3 | 56,5 | 84,8 | 113 | 141 | 170 | 198 | 226 |
| 125 | 44,2 | 88,3 | 132 | 177 | 221 | 265 | 309 | 353 |
| 140 | 55,4 | 111 | 166 | 222 | 277 | 332 | 388 | 443 |
| 160 | 72,3 | 45 | 217 | 289 | 362 | 434 | 506 | 579 |
| 180 | 91,6 | 183 | 275 | 366 | 458 | 549 | 641 | 732 |
| 200 | 113 | 226 | 339 | 452 | 565 | 678 | 791 | 904 |
| 225 | 143 | 286 | 429 | 572 | 715 | 858 | 1001 | 1145 |
| 250 | 177 | 353 | 530 | 707 | 883 | 1060 | 1236 | 1413 |
To ventilate rooms with gas appliances, it is advisable to install a duplicate ventilation system so that one of them works under any circumstances.
When there is a power outage, ventilation of the premises will be carried out through natural circulation channels.
Video: calculation of air exchange in a boiler room
How to do it yourself?
Schemes and calculations
Natural ventilation scheme:
- The air supply is located opposite the hood.
- The air is exhausted through an exhaust pipe, the beginning of which is on the ceiling, and the end is above the roof ridge. If the ventilation system is located on the wall, then this should be done as close to the ceiling as possible.
Mechanical ventilation scheme:
- The pipe with the fan must be discharged either through the roof to the street or through the wall outside the house.
- The air duct exits into the existing ventilation shaft with a fan.
During the heating season, it is recommended not to turn off the exhaust fan, leaving it to run on a regular basis.
Calculation of ventilation for a boiler room with a gas boiler is carried out taking into account the area of the room, the frequency of air exchange, and the number of family members regularly living in the house. Using these parameters, you can calculate the required hood cross-section for a gas boiler.
Attention Formula for calculating the amount of air exchange:
L (boiler power, kW/h) = N (air renewal rate) × S (room parameters) × H (boiler room ceiling height, m).
Attention Formula for calculating the number of family members:
L (boiler power, kW/h) = N (number of family members) × Lн (minimum air consumption per person, m³/h).
Generally accepted minimum air consumption standards per person:
- sleep – 20 m³/h;
- rest – 40 m³/h;
- vigorous activity – 60 m³/h.
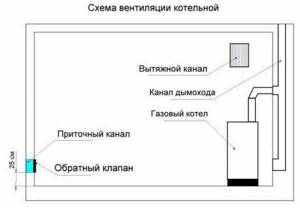
Boiler room ventilation diagram:
Materials and tools
Basic materials and tools:
- Hammer or drill with a crown attachment.
- Saw for processing pipes.
- Tools for marking - ruler, pencil.
- Air ducts and adapters for them.
- Protective grilles.
- Adapter with check valve.
- Protective sleeves for slabs.
- Self-tapping screws, dowels, mounting clamps.
- Sealant or polyurethane foam.
- Hacksaw.
- Protective equipment: gloves, glasses.
Installation
Installation of natural ventilation:
- The installation location is outlined. The necessary calculations are made, a diagram or drawing is created.
- A pipe is applied to the wall, its dimensions are noted.
- A perforator is used to make a through hole with a slope of 60 degrees outward to drain the condensate (with exhaust ventilation, the slope is not made, the pipe is installed evenly).
- A pipe with insulation and a grille on the outside is inserted into the finished through hole.
- A housing with a check valve is attached to a part of the pipe inside the house and the wall with dowels (how to make a check valve for ventilation with your own hands?).
Installation of forced ventilation:
- A through hole is made in the wall with a slope towards the street. It is recommended to use a hammer drill or a drill with a diamond bit.
- A pipe is installed in the hole.
- The gaps between the wall and the pipe are filled with sealant or foamed.
- A duct fan is installed.
- Electrical wiring is laid and connected.
- The rest of the equipment is installed - filters, sensors, sound absorber.
- Grates are attached to both sides of the pipe.
separate article
Installation of natural ventilation
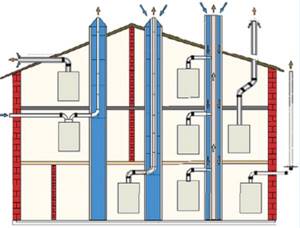
Ventilation system placement options
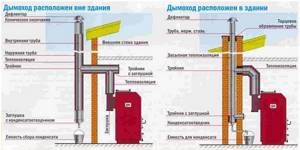
Chimney design depending on location
Natural ventilation in the boiler room is ensured by installing supply and exhaust ducts.
To install the supply channel you need:
- Select a piece of plastic pipe, a suitable size grille and a check valve. The diameter of the first is selected taking into account the power of the boiler. If the power is less than 30 kW, 15 cm is enough. Higher power means larger diameter.
- To allow air to pass directly into the firebox, a through hole to the street is punched next to the heating device and not higher than its working area. Then a pipe is placed in the hole, the gaps inside are filled with mortar or foam.
- From the outside, the hole is covered with a fine grille to protect it from dirt and animals. It is necessary to install a check valve from the inside to prevent backdraft to the street.
The exhaust duct is ducted outside through an opening above the boiler at the top of the room. Usually it is also equipped with a check valve that prevents air from entering from the street. The chimney can also be equipped with a protective rain canopy or weather vane, condensate drains and inspection windows for cleaning.
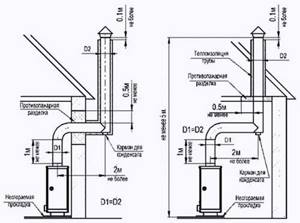
Ventilation system design diagram
How to ventilate
In houses built from aerated concrete, ventilation can be made of plastic, galvanized steel or asbestos-cement pipes. They can also be used to install aircraft in a house made of gas silicate. In a large house, as a rule, the air duct is extended into each room. To make it easier to install the hood, you can connect the outlet from the bathroom and kitchen into one branch. The work is carried out at the attic level, where all pipes are insulated with insulating material.
For natural ventilation, pipes with a cross-section of 15 cm are suitable; for forced ventilation, it is better to take slightly smaller pipes. A hole of the required size is cut out in the blocks. A 12.5 cm pipe is inserted there and secured with a solution. It is necessary to install an outlet in the first block, to which the ventilation duct is subsequently attached.
If the wall is thin, the channel is made of slate, pre-cut into narrow strips. These sections are mounted in a pre-prepared opening and then plastered over it. You can make ventilation pipes yourself from available material, for example, from corrugated slate. To do this, you need to saw off two half-waves and connect them together with thin wire. The homemade pipe is also mounted on a brick base and plastered inside.
A separate shaft is always equipped for this; this is a fairly convenient way of ventilation in a finished house.
Rotary turbines for forced draft
These are mechanical devices installed on the chimney and use wind energy to produce rotation.
Produced by industry under the name Turbovent, Turbomax and others. The direction of rotation does not depend on the direction of the wind. Thanks to the design - a ball formed by a system of petals, the turbine rotor reliably protects the chimney outlet from contamination by debris and leaves, as well as from nesting birds during breaks in the heating season. The disadvantage of rotary turbines is that they do not operate in calm weather and continue to rotate when there is no need for this - during the non-heating period. Often used for ventilation devices.
Smoke exhausters or smoke fans
These devices are heat-resistant fans installed in the chimney duct to forcefully increase draft.
A smoke exhaust fan should not be confused with fireplace fans, which are designed to increase draft in a fireplace or hearth and are installed in a room to supply air to the firebox. Fireplace units are designed to distribute heated air evenly in a room. The smoke fan is a 220-volt electric motor with an impeller. It is designed to create additional draft forcibly inside smoke channels from a fireplace with a reduced cross-section.
Smoke pipes (channels) for fireplaces
The main difference between a fireplace and a stove is the much larger cross-section for air access to the firebox, which is why large masses of air are sucked into the fireplace, which causes a decrease in the temperature in the flue (compared to stoves). Therefore, the traction force in a fireplace per 1 linear meter of flue height is less than in a stove.
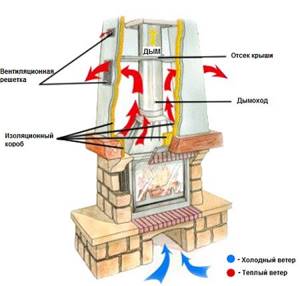
To create normal draft, the height of the fireplace chimney must be correspondingly greater than that of the stove. To ensure sufficient draft during operation, it is IMPORTANT that the flue gases are cooled minimally as they move through the chimney. The cornice formed in the narrow section of the chimney (the so-called smoke tooth) plays an important role and has a dual purpose
During the combustion process, it retains the cooled gases descending along the rear (colder) wall, preventing them from passing into the combustion space, because this can lead to the traction capsizing
The cornice (the so-called smoke tooth) formed in the narrow section of the chimney plays an important role and has a dual purpose. During the combustion process, it retains the cooled gases descending along the rear (colder) wall, preventing them from passing into the combustion space, because this may cause the rod to tip over.
Cold gases retained by the eaves are picked up by a stream of hotter gas flowing from the narrow section of the chimney that forms the front wall of the fireplace and the edge of the “tooth”, and are carried into the overlying chimney.
The second purpose of the cornice is to collect falling soot deposits. A cleaning door is installed in the immediate vicinity of the ledge on the inside, through which the chimney is periodically cleaned. A damper is installed in the neck at the level of the chimney cornice to regulate the draft and disconnect the fireplace from the chimney. To reduce heat loss, the walls of the fireplace chimney must be of sufficient thickness.
The most harmful effect on draft is caused by atmospheric air leaks into the chimney through leaks in the masonry, as well as non-working stoves connected to a common chimney, i.e. The chimney for the fireplace must be separate from all other ducts. All leaks must be identified and eliminated.
The next condition for maintaining normal draft (without describing the hydraulic properties of draft) is the construction of a chimney with a circular cross-section, then square and finally rectangular. This is explained by the fact that in right angles the movement of gases is difficult and, moreover, soot is often deposited in them.
Therefore, it is best to use asbestos-cement or ceramic pipes for installing chimneys. Due to the difficulty of fitting to the fireplace chimney, chimneys are most often laid out square.
Types: materials and characteristics
For the installation of small home ventilation systems, the industry produces a wide range of pipes and components.
Air ducts for domestic ventilation are divided into:
- By material - plastic, aluminum or galvanized steel.
- Shape: square, rectangular, round.
- According to the degree of flexibility - flexible or rigid. Flexible boxes are made of corrugated aluminum or galvanized steel. Rigid air ducts made of metal are not used due to the complex installation and complexity of manufacturing galvanized pipes of small sizes (from 100 to 150 mm in diameter or section side length). Aluminum pipes of suitable sizes are expensive, there are no special advantages in their installation, so they are also not used for kitchen hoods.
Plastic
Plastic air ducts are round, square and rectangular with a smooth surface. They come in white and painted in different colors - it’s easy to choose a shade that matches your furniture set or wallpaper.

Plastic boxes are very smooth - they are easy to clean, and less grease and soot accumulate inside. Smooth walls provide the least air resistance - therefore, such pipes vibrate and make less noise. Plastic boxes are the quietest compared to corrugated boxes.
The service life is at least 10 years.
Made from flexible corrugated aluminum pipe
A very practical option for an air duct is a corrugated aluminum pipe of round cross-section. The flexible pipe is easy to install; it does not require rotating elements - it can simply be bent. An aluminum pipe is durable, but it is very difficult to clean it from grease and soot deposited on the walls. The corrugated inner surface creates great resistance to air flow; the pipes make more noise when the hood is operating.

Metal
The corrugated pipe can be made of galvanized steel. This pipe is a little stiffer and stronger, but otherwise its installation is as simple as for aluminum corrugation.
Places with a damaged zinc layer rust, the rigidity of the pipe complicates its installation, so steel corrugation is rarely used for internal household ventilation systems.

By degree of flexibility
Aluminum corrugation is more ductile than steel, it is easier to bend, stretch and compress.
Plastic air ducts are used only for rigid ones; corrugated plastic pipes are not suitable for transporting hot air.
Manual
Ventilation-type installations require certain care during operation to promptly resolve various types of problems, and also require periodic inspection.
If we talk about the process of testing fans in industrial systems, we should look at the following points:
- are there any restrictions on rotating parts;
- are all locknuts in place?
- how quiet and smooth the work can be called;
- how well the installation is attached to the base;

- Are the bearings and electric motor well lubricated?
- what is their temperature;
- Are there drive belts, are they well tensioned?
- what is the condition of the vibration bases, protective coating, and so on;
- if grounding?

It is also necessary to periodically inspect the condition of the air outlets in smoke installations and bleed air from them. The same applies to irrigation chambers.
Their maintenance should be carried out as follows:
- checking and thoroughly cleaning the injectors;
- cleaning the surface of the water filter mesh from the inside, chambers, as well as droplet eliminator plates;
- checking the device that is responsible for ensuring that the water level in the pan is at a certain level;
- checking how tightly the doors are closed.

When checking ventilation pipes and other elements of air exhaust systems from the room, it is necessary to inspect them for the absence of mechanical damage. For example, if the insulation is damaged in some place, the pipes may stop performing certain functions efficiently. It is also necessary to check the reliability of the fastenings. The throttling devices of such systems must be positioned as correctly as possible, and the opening degree indicators must be in place
Particular attention must be paid to the condition of the filters. If they are too worn, it is better not to try to clean them, but to replace them

In general, as you can see, today there are a large number of ventilation pipes, which has led to the presence of a large number of ventilation systems that differ significantly from each other in purpose and other characteristics. If desired, you can select pipes yourself for a particular system. But for this you need to have good theoretical knowledge and understand how ventilation systems work as a whole.
To learn how to make ventilation in an apartment, see the following video.
How to install?
Installing a fan on a fireplace is quite simple and does not require any special theoretical knowledge. The first step is to calculate the direction of air flow. This information is available on the packaging with the device or in the instructions for it.
Installation is carried out from above at the mouth of the chimney pipe. Please note that it is easier to install the device on brick chimneys than on stainless steel chimneys. You should also think about the power supply system to the smoke exhauster and correctly position the wire with the switch and speed mode switch.
Click “Like” and receive only the best posts on Facebook ↓
Why make a ventilation duct if there is a stove, air is constantly removed through the pipe; when the stove is heated, a lot of air is removed along with flue gases. When the stove is heated, shut off the hot zone, and I recommend opening the damper into the room and not closing it, you can only adjust the amount of air removed through the gap. The greater the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air, the smaller the gap should be for air removal through the pipe.
During periods when there is no need to heat the stove, the removal of air through the pipe may come to naught; for these periods, I consider it advisable to install a fireplace or smoke fan that will always remove air. Install the fan on top of the pipe, instead of protecting it from rain. It is possible to use this fan when the stove is flooded, when the draft is still insufficient and some smoke can enter the room from the stove. When the fan is running, this phenomenon will not occur. The fan can be installed with a speed controller.
A beautiful, stylish kitchen-dining room is a necessity for every family, but it requires careful cleaning. The times when the kitchen was simply whitewashed and repainted every year are gone. The cooking process is always accompanied by the release of moisture and combustion products that settle on the walls, furniture, and ceiling. A hood helps get rid of this problem.
But another problem arises: the hood and exhaust pipe in the kitchen do not look very aesthetically pleasing, they try to disguise them and make them as compact as possible. We welcome our dear regular reader and offer an article on how to select and install an air duct from a range hood with your own hands.
Requirements for ventilation of a solid fuel boiler and room
The main conditions for ventilation in a boiler room in a private house are compliance with a certain area and volume. This is caused by the required frequency of air exchange per unit of time, fire safety and regular inspections of equipment. Therefore, for normal ventilation of the boiler room, the distance of the boiler from the walls and free access to it must be ensured depending on the performance of the unit:
- For a boiler with a capacity of up to 30 kW, at least 3.5 m2.
- For a thermal device from 30 to 60 kW – 5 m2.
- If the unit has a power of more than 60 kW, then the boiler room area is over 6 m2.
In addition, the height to the ceiling should be 2.2 m.
Use of ventilation pipes in everyday life
Residential buildings must have ventilation. In the process of breathing, a person emits carbon dioxide and moisture, cooking - moisture, soot, fat, carbon dioxide, sanitary appliances - a lot of moisture. Moisture settles on walls and furniture, which leads to the formation of mold. Carbon dioxide and combustion products, odors from cooking lead to rapid fatigue, irritation of the respiratory tract, deterioration of well-being, and decreased performance. Some of the substances formed during frying are carcinogens.
In old Soviet-built houses with small apartments and loose doors, ventilation in the kitchen and bathroom simultaneously removed some of the air from the living rooms. Ventilation ducts were built into the building structure. In private houses, ventilation was not provided at all - the situation with carbon dioxide was saved by a stove with a chimney: the air for firing the stove was taken from the house and removed, along with the products of fuel combustion, outside the living space. Fresh air entered houses and apartments through leaks in wooden windows and doors. The smoke and soot simply settled on the walls and ceiling - they had to be whitewashed every year.
In apartments there are ventilation ducts in kitchen hoods, additional ventilation in bathrooms and toilets.
In modern houses, in addition to the hood, additional ventilation systems are often installed - exhaust and supply and exhaust. In passive and energy-efficient houses, supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery is a mandatory component of the house design.
Installation of ventilation and chimneys of apartment buildings ↑
Ventilation ducts and chimneys in apartment buildings are varied in design, methods of execution and, ultimately, comfort and safety for residents.
The most common is the natural, supply and exhaust type of ventilation and chimneys. In this case, through satellite channels, air or combustion products from the premises enter a common channel (or a collector in the attic), and then into the atmosphere. Air is taken in through natural gaps and leaks in windows and doors.
A more advanced and effective solution is forced ventilation using exhaust and blower fans. There are hybrid projects combined with a supply and exhaust system, options with air recovery (a recuperator is a device that transfers heat from the exhaust air to the injected one).
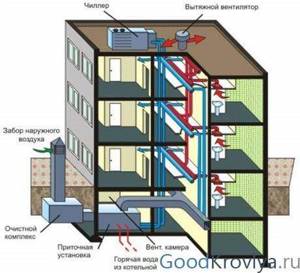
Modern ventilation of an apartment building
The most productive and stable design is the one in which the ventilation ducts from each apartment are removed separately. This increases the stability of the system and prevents the flow of odors and gases into other apartments (for example, when one of the residents installs a high-power exhaust fan).

Ventilation system design diagrams
Maintenance of smoke and ventilation ducts in apartment buildings is practically not required due to the well-thought-out systems and built-in characteristics. According to Soviet SNiPs, up to 80% of air exchange was carried out through window and door blocks. Therefore, the main problem for high-rise buildings of old construction is the replacement of such elements by residents with modern, practically sealed, metal-plastic and steel structures. At the same time, air exchange sharply deteriorates, dampness and fungus appear.
They are mounted under the window above heating devices to heat the air coming from the street. It is also recommended to leave gaps at the bottom of interior doors or equip them with breathable grilles.

Supply valve in the apartment
Inspecting, repairing and cleaning ventilation ducts and chimneys is a troublesome and responsible task. Therefore, it is better not to risk the health and lives of loved ones and neighbors. Leave such work to the professionals and simply enjoy life in a cozy, warm home filled with fresh air.
How to arrange ventilation of a gas boiler room in a private house
There are and are used several types of ventilation for rooms with gas boilers:
- supply;
- exhaust;
- supply and exhaust;
- natural.
None of the listed types is practically used in isolation. The most effective methods of ventilation are combinations of these methods in various combinations.
Natural supply ventilation
This is the most common and mandatory way of supplying fresh air to the boiler room.
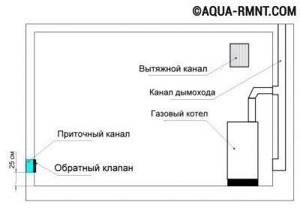
In the scheme of supply natural ventilation, air enters through the inlets at the bottom of the room and is removed through the upper exhaust ducts due to natural circulation
The manufacture of the ventilation duct is carried out as follows:
- Markings are made along the diameter of the pipe with a margin of approximately 10 mm. The diameter of the air duct pipe must be at least 15 cm.
- A hole is drilled. You can use a drill with carbide tips (for walls made of building stone) or a special crown.

The hole for the ventilation duct is made using a hammer drill and a crown or drilled with a drill along the contour

The part of the ventilation pipe facing the street is covered with a grille to protect it from debris and small animals.
When choosing a place to install the ventilation duct, you should take into account the fact that its outlet must be at least a meter away from the boiler, then the cold air from it will not affect the operation of the unit. Of course, modern automation can easily cope with this circumstance, but there is no need to overload it unnecessarily.
The influence of external conditions, including weather, on the operation of the ventilation duct of natural ventilation should be taken into account, but one of its advantages is undeniable - it will work independently of the power grid, providing a constant supply of air from outside.
Video: how to make a ventilation duct for a boiler room
Forced exhaust ventilation
Combined supply and exhaust systems with wide adjustment capabilities consist of fans, filters and air heaters. Essentially, these are climate systems. Considering that modern boilers are equipped with various regulators that automatically control its operation depending on the microclimate in the boiler room, the use of such ventilation devices ensures optimal operation of the heating unit and contributes to significant fuel savings.

Supply ventilation systems supply and extract air due to the operation of fans installed in laid channels
Duct and free ventilation systems
One of the characteristics for classifying ventilation systems is their design features and the method of air movement.
Indoor ventilation
Ventilation in a room depends on the overall air exchange in the entire house. The natural circulation of air and ventilation in the house is hampered by metal-plastic windows with sealed glass packages, interior doors with seals, and kitchen hoods with powerful fans. But, there are legislative standards for air exchange in apartments and houses. They say that all rooms must have the same air pressure, and air inflows must compensate for the exhaust.
When drawing up a house project, you should take into account all devices that require ventilation, namely: fireplaces with chimneys, gas boilers with chimneys, ventilation in the boiler room, in the kitchen, in bathrooms and bathrooms, as well as the supply duct in the fireplace room. In case of insufficient supply air, the operation of the ventilation duct is disrupted and reverse draft is formed
But it is not always possible to correct the situation by ventilation alone.
What models are there and how much do they cost?
The cost of a smoke exhauster depends on which model you are going to order and with what parameters (standard, heat-resistant). For clarity, you can demonstrate the cost of several popular models.
Approximate cost:
- model BAHCIVAN BRCF-M 315 (power 550 W, consumes 1800 m3 of air per hour) - cost 14,000 rubles;
- model Sputnik-555 (power up to 105 kW, productivity about 550 m3 per hour) - cost 12,000 rubles;
- Elicent Tirafumo model (productivity about 850 m3 per hour) – cost 30,000 rubles;
- model Vents KAM KFK 150 (productivity about 520 m3 per hour) – cost 19,000 rubles;
- model Vents KAM 140 (productivity about 480 m3 per hour) - cost 11,500 rubles.
Ventilation system testing
The quantitative characteristics of thrust are measured using a wind force measuring device. Its impeller must be placed inside the ventilation duct and this indicator must be determined on a scale. Knowing the size of the pipeline cross-section, it is easy to calculate the performance of the system, that is, its sufficiency to provide the required amount of air in the room for normal combustion in the boiler.
Closed combustion boilers with coaxial chimneys stand apart. In them, air is supplied to the firebox directly from the atmosphere through pipes of a special design, and the room air does not take part in combustion.
The ventilation duct of the boiler room should not be connected to the air lines of the general exhaust. This will prevent the gas from spreading throughout all areas of the house.
The main reasons for the deterioration of draft in the ventilation system
Among these it should be noted:
- difficulties encountered with the flow of outside air into the boiler room after replacing traditional window units with double-glazed windows. Their tightness significantly reduces the possibility of air penetration;
- the same consequences after replacing doors if the gap between the floor and the bottom edge is minimal or absent;
- decrease in natural draft in the hot season due to a decrease in temperature difference outside and inside the house;
- the appearance of stagnant zones or zones with low pressure during strong winds in the atmosphere, which also negatively affects the operation of ventilation systems, so in such conditions additional draft control is needed.
When using forced ventilation of a boiler room, you need to select fans with an impeller that does not spark from impacts. Products made of aluminum alloys, copper or plastic are suitable for this.
The inadequacy of the ventilation system of a gas boiler house is dangerous not only for health, but also for human life. In addition, it reduces the heating efficiency. Excessive ventilation leads to disruption of the thermal regime, worsening living conditions in the house. When starting to install ventilation yourself, try to get qualified advice from a specialist and take into account his comments.
Conclusion
The draft in the chimney and proper ventilation of the premises make it possible to create comfortable and safe living conditions in the apartment and house. We recommend that you do not ignore the proposed recommendations and try to follow them. Ultimately, your health and the health of those who live with you will depend on this.
The video in this article will help you find additional information on this topic.
A ventilation device is necessary to organize constant air renewal. This is especially important if there are gas-flame appliances in the house - heating boilers, water heaters and stoves. When starting to install ventilation devices, you need to carefully study the rules for their arrangement and strictly follow them during design and installation.