A well-functioning heating system is the key to comfortable living in a house, regardless of weather conditions. Along with traditional radiator technology, heating circuit devices are actively using a warm water floor system. Its installation is labor-intensive and financially expensive, but this heating option fully pays for itself in 5 years.
In order to somehow save money, many install a warm water floor in a private home on their own. Agree, the idea of obtaining efficient heating with minimal investment is very attractive, isn’t it? However, its implementation requires certain knowledge and skills from the performer.
We offer for consideration detailed material on the installation of water heated floors. The article outlines the design rules, provides advice on choosing system components, and also describes the step-by-step progress of the installation, connection and startup of the water circuit.
Types of heating equipment
On the modern market you can find many floor-standing units equipped with 2 types of burners: atmospheric (characterized by quiet operation, simple design and affordable cost) and forced or turbo (have higher efficiency, but are noticeably more expensive).
Gas floor-standing boilers are also single-circuit and double-circuit, and can often operate without electricity.
Non-volatile units
Non-volatile boilers can be chosen for use in areas where power outages occur regularly. In order for such a floor-standing gas boiler to function normally, there is no need for access to electricity, but there must be a nearby gas main.
The coolant circulation here is based on a natural cycle, which excludes the use of a pump, which obliges the user to use pipes with a minimum slope.
The most modern models of floor-type gas heating units are equipped with a “smart” system for monitoring the functioning of the system, which includes a safety valve, pressure gauge and air vent.
Important! If there is a need not only for heating the room, but also for heating and circulating hot water, then it would be advisable to connect a boiler and pump to a non-volatile boiler. .
Advantages and disadvantages
If the boiler is volatile, if the electrics are turned off, the system will stop working.
The advantages of the system are its reliability, high speed of response to consumer actions (adjusting the degree of heating). Residents will be able to maintain optimal temperature in the house year-round. Using an installation with a double-circuit boiler will allow you to have hot water in the house.
The disadvantages are related to the operating features of the units and the requirements for their installation. If the power or gas supply is interrupted, the system may stop operating. To prevent this from happening, the user needs to pay for resources on time, as well as purchase an uninterruptible power supply if power is often cut off in the area. In addition, installation of the boiler requires a separate room, which is subject to a number of requirements, compliance with which is necessary to ensure safe operation of the system.
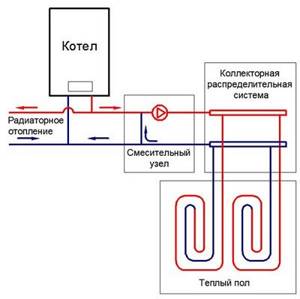
The design and principle of operation of heated floor heating
How to conduct heating in a private house with your own hands from a boiler
This floor is a structure made of small-diameter plastic pipes (cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic), which are characterized by high thermal conductivity, flexibility and low resistance. The length of pipelines ranges from 40 to 500 meters. They are manufactured as a single unit, which eliminates leakage at the joints.
To maintain the required temperature, warm water floors are equipped with a coolant mixing unit, consisting of a collector, a pump and a thermostatic mixer with adjustable temperature sensors.
Warm floor heating can operate from two sources:
- Central heating systems:
- individual gas boiler.
It must be remembered that connecting such a floor to the central heating system in apartment buildings is strictly prohibited due to the increased load on the system and the possibility of water hammer. This can be done after agreement with the heating supply organization only in houses of new series, where a separate riser is provided for pumping out hot water in the event of a breakdown in the heating system. In this case, heat consumption meters must be installed.
Using the second method is preferable, since the coolant parameters are set individually and do not depend on the central heating system.
The operating principle of heated floor heating is quite simple: through a collector, using a pump, hot water under low pressure moves along the entire length of a specially laid pipeline. The floor covering, which has good thermal conductivity, heats up and releases heat into the room. At the same time, the air temperature near the floor is higher than at human height, which is physiologically justified.
Then, through the return line, the cooled coolant flows through the collector into the riser of the central heating system or into the gas boiler for heating.
Collector devices
These systems can be separated into a separate category. What is the purpose of a manifold with a pump? Warm floors can be installed in one room or in several. When connected in series, there will be a significant difference in temperature during operation. This is based on the laws of physics. As the coolant moves through the pipes, it will release temperature and cool. To minimize such losses and achieve a similar microclimate in all rooms, a pump with a manifold is provided. It makes it possible to connect several circuits in parallel.

Launch and operation
How to install a mixing unit for a heated floor with your own hands
After connecting all the elements, the level and tightness of the system is checked: the heating equipment is turned on and hot coolant flows inside, under a pressure higher than the working one (up to 0.6 MPa). The initial verification process lasts about half an hour, without reducing parameters. Then, within 2 hours, the pressure increases to 1 MPa under the same conditions of temperature and pressure stability.
If the system has held up, then you can start pouring the cement screed, and it should dry naturally. When a water heated floor is put into operation, complete heating occurs within a few days.
Tips and tricks
When wiring passes through a wall or other building structure, protection from mechanical damage is provided; for this purpose, a corrugated pedestal is used. In general, flexible pipes require care when connecting them to a “warm floor” heating system, especially polyethylene
They are carefully laid out according to the diagram, checking for damage: cracks, deformed (whitened) creases, deflections. Flexible heating lines are not removed from the coil in coils, but are sequentially unwound
When laying bends, adhere to a loop radius of 5 pipe diameters, and when installing fasteners, do not tighten the loops tightly.
An additional way to save money is to assemble a circuit without a pump, with the installation of a three-way valve-regulator (it independently mixes two different flows into one common one). If the water floor is connected not to the boiler, but to centralized heating, then the coolant cannot be used directly due to high pressure (8–12 times more than the installation instructions require). This is due to the risk of a break in the flexible line. The maximum effect from the operation of the boiler is achieved by simultaneous operation of both the heated floor and radiators (their connection does not differ from the usual one).
The recommended thickness of the top screed is at least 30–60 mm. Otherwise, the risk of damage to the pipes in the water floor increases. The practice of adding plasticizers to the solution has proven to work well. If tiles are used as a floor covering, then a top layer of cement of medium thickness (up to 50 mm) is poured, and the step in the wiring diagram is reduced to 10 cm. It is undesirable to put a substrate under the laminate, this will worsen the heat transfer performance.
Common mistakes when installing and connecting underfloor heating:
- Filling dry expanded clay over the pipeline (increases the risk of damage to flexible heating sections).
- Lack of a flat base, lower thermal insulation, or its layer is too thin. This leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the entire heating system.
- Use of ordinary metal pipes. Even in flat distribution areas, there is no point in laying material that is susceptible to corrosion in the floor.
- Deviation from the diagram, connection of a heating circuit with an area of more than 20 m2 or violation of the pitch. Leads to the appearance of “cold zones” on the floor and unreasonable energy consumption.
- Early start-up of the system, hasty filling of the coolant under pressure higher than the operating pressure, drying under heating conditions (contribute to the violation of the integrity of the floor and thermal deformation).
- Unreliable fastening of the edge tape (heat losses are possible).
TVP Installation Guide
Before laying the heated floor structure, you should carry out preparatory work: purchase components, mark the installation location of the cabinet, drill holes in the walls for communications. Then you can proceed to the first stage.
Step #1 - subfloor installation
If you plan to install a heated floor directly on the ground, it is recommended to choose one of two options:
- make a “rough” screed from cement pouring;
- instead of screed, pour, compact and level a layer of sand.
A layer of sand will be required in any case, since it also serves as the basis for the screed. A layer of waterproofing is placed on it, the most basic option is a thick polyethylene film.

Compaction and leveling of the sand layer is very important. Small depressions up to 5 cm deep are allowed, but for pipe installation it is better if it is perfectly smooth
When making calculations, it should be remembered that heat loss when installing the system on the ground is higher, therefore, the temperature of the coolant in the pipes should be higher than usual.
Step #2 - laying a heat-insulating layer
The insulation is laid on a clean, level floor. Before starting work, a strip is cut on the walls - the level of the clean floor; small depressions, if they were formed during the construction work, are filled with clean, dry sand.
Installation instructions:
- Spread the waterproofing - lay sheets of film with a density of 150-200 microns with an overlap of at least 10 cm and wrap them on the walls.
- Lay the slabs of extruded polystyrene foam with the markings facing up, joining the grooves together. It's better to start from the far corner.
- If necessary, cut out fragments with a construction knife.
- Secure the slabs with disc dowels at the corners, along the middle of the joints and in the center of the slabs.
- Seal the seams with construction tape.
If laying a second layer is required, then it is better to change the direction of the upper slabs, that is, lay them perpendicular to the lower ones.

When laying, avoid large gaps and cracks. If they do form, the voids can be blown out with foam or covered with scraps of polystyrene foam
To move on the slabs during installation, it is recommended to use thin boards or pieces of plywood - the structure of the slabs, despite their density, can be deformed.
Step #3 - marking and placing pipes
Markings are applied to the surface of the slabs using a marker or paint cord. If profile mats are used instead of EPS, markings will not be required.

There is a risk of bending and twisting of the pipe when unwinding, so it is better to use a special device for unwinding the coil. It will take longer to unwind manually
Before starting pipe installation, it is also recommended to install collectors and prepare places for connections.
Installation instructions:
- Unwind 15-20 m from the pipe, put a heat-insulating sleeve and a fitting on the end for connection.
- Connect to the collector.
- Carefully lay the pipe according to the markings.
- Secure the outline with harpoon staples.
- Bring the pipe to the manifold and connect the other end.
The length of each loop must be recorded, and not just remembered, but written down near the fitting on the wall.

A damper tape or some substitute is placed along the edges - for example, pieces of foam plastic 1.5-2 cm thick. They hold up well on liquid nails
Transit pipes passing through walls or transition zones are insulated as much as possible with sleeves. Instead of expensive imported products, you can use ordinary insulation - foamed polyethylene.
Step #4 - installation of reinforcing mesh
Properly laid fittings should be located above the pipes, not under them or between them. An acceptable option is a metal mesh with a 10*10 cm cell made of 3 mm wire.

It is also incorrect to fix the contours to a metal mesh; in this case, it will serve as a stand, not reinforcement. Proper installation - when the mesh is above the pipes
Nowadays, many people use plastic mesh instead of wire mesh. This option is also suitable, since the polymer creates the necessary rigidity.
Step #5 - system testing
Until hydraulic tests have been carried out to check the tightness of the system, the screed cannot be poured. Usually the circuits are checked one by one.
First, a main line and a pump are connected to the pipe, and water is supplied. For drainage, use a hose connected to the drain pipe of the manifold.

A pressure test pump is the best tool for testing the system. It can be rented. You can also hire a specialist for testing, who usually has the necessary tools
During inspection, staples may fly off as the pipe tends to straighten under pressure. The harpoons that fly off are attached 5 cm from their original place; after pouring the screed, they will no longer fly off.
Step #6 - laying cement screed
The pipes are left under a pressure of 5 bar and the screed is laid. Usually the traditional beacon method is used. You can use a metal profile for drywall as beacons.

A regular screed solution is not suitable; plasticizers and fiber must be added to the cement, since the load will be not only mechanical, but also temperature
Laying is done in parts, starting from the far corner. Immediately after pouring, each fragment must be leveled, dips and sagging must be eliminated.
After 2 days, the surface is cleaned, the damper tape is cut, the screed is sprayed with water and covered with film (the last two steps are repeated for 10 days).
Kinds
Do-it-yourself installation of infrared heated floors under laminate
Home heating is divided into several types. This depends on a number of factors. For example, based on location, a warm water floor is divided into an option for a home and an apartment.

In fact, a warm water floor is often installed in a private house built from aerated concrete. Due to it, the house is heated evenly. In your home you do not depend on central heating; you have the opportunity to install a chimney and ventilation. This flooring is suitable for unpredictable climatic conditions in Russia, so it is common among summer residents who spend a lot of time in their country house. With such a floor, you can come there at any time of the year, rather than wait for a warm period, when the house can warm up on its own due to the air temperature around it.

In an apartment, problems may arise with the installation of water heated floors. Old houses are not suitable for this - the floor is uneven, the heating system is old, the management company is even more unlikely to take risks and will not agree to install the floor. In a new building, the situation may be different. Plus, you need written consent from the company servicing the house that the installation of such a floor is indeed permitted. Otherwise, you may receive a fine.

Basics of equipment selection
In order to correctly select a suitable device, one rule must be followed - the technical characteristics of the system must coincide with the technical properties of the pump. That is, the choice is influenced by the following factors:
- Performance. Indicated in cubic meters/hour. This indicator gives an understanding of how much coolant is pumped per hour of operation. For normal operation, the entire volume must be pumped three times during this period of time. To perform a high-quality calculation, you will need to take into account a number of factors: the length and complexity of the highway; the material from which the pipeline is made; pipe diameter; volume of liquid in the system.
- Pressure. For small circuits this value is not as important as for long pipelines with a significant number of bends. Having determined the performance of the device, you should also clarify the operating pressure - whether it will correspond to the technical specifications.
- Energy consumption. It is better to choose a model with a power shutdown and control module. This will significantly reduce the cost of this item during operation.
- Additional characteristics. It is important to pay attention to the operational features of the device. This will help you avoid unnecessary repair costs in the future.
As a result, you can make high-quality and inexpensive “warm floor” heating.

A pump can significantly increase the efficiency of such a device. But for this it is important to calculate and select the right equipment. It's better to trust the professionals. Or use a calculator on the Internet.
Collector diagram
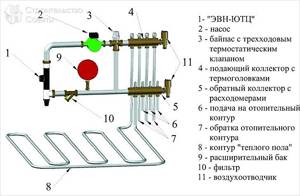
The cabinet must be located in a room whose space provides free access for supply and return pipes. The side outlets of the manifold are connected to the ends of these elements to supply and receive heating fluid. Before performing the last step, it would be useful to install protective shut-off valves and temperature regulators in the system.
To simplify this entire procedure, many manufacturers began to produce ready-made valves that include not only the elements described above, but also shut-off valves for all outlets of underfloor heating pipes and radiators, which provide for disconnecting some circuits of the system when the main part of it remains turned on.
Valves, pipe ends and the manifold are connected using compression adapters - fittings that have completely different inlet and outlet sizes depending on consumer preferences. Often, the outlet pipes of a heated floor are connected to the collector using connectors that include a support sleeve, a ring with a clamp and a brass nut. The simplest connection consists of simple clamps with locking valves. The supply and return pipes are connected to the manifold, and it, in turn, is attached to the floor coolant outlets.
The named scheme is the simplest and will not be able to fully ensure proper control over the entire heating system, since it completely depends on the type of boiler (the only thing is that the shut-off valve can be closed a little to slightly reduce the supply of heating mass).
Connection methods and installation features
Having considered what types of boilers there are, we can come to the conclusion that gas options are most suitable for connecting a warm water floor. Basically, the heating system is connected to a wall-mounted gas boiler.
If you want to connect the heating system with your own hands, then you will need:
- roulette;
- level;
- keys;
- screwdrivers;
- perforator;
- pipe cutter and other tools that will help in the work process.

When installing a warm water floor, the most important thing is laying the pipeline. Before this, you need to level the base using ties that protect the hot water pipe from various damages. The composition includes a sand-cement mortar, after hardening which forms a hard crust that protects the pipe. The pipe also acts as a battery with a large dispersion area. Expanded clay is best suited for insulation. You need to put a waterproofing film on top, as well as a reflector

The reflective material cuts off the heating circuit from the floor slab and the space underneath it. It must be of high quality so that the heat goes to the floor and heats the air in the room, and not vice versa. The pipes are laid in spirals directly on the reflector. The connection, in this case, comes from an already existing network, which is served by one boiler.

There are two options for attaching pipes:
- The first is using reinforcing mesh, to which the pipes are attached with wire.
- The second is with the help of fastening tapes and special clips, which can be purchased in specialized stores.

The length of the pipeline should not exceed 80-90 cm. A pipeline longer than one meter is not suitable for installation of such a structure. If this is not enough, you will have to add a new contour, taking into account that they must be the same.

The next stage is securing the pipeline to the supply manifold. Immediately after this, you can lay the contour. It must be laid in one piece to avoid leakage. The technology for installing heated floors includes checking the entire system. This stage consists in the fact that hot water, under pressure, is supplied to the pipeline. The test lasts approximately two hours. If everything is in order, you can lay the screed. Next, the boiler is installed. To do this, you need permission from the gas and fire departments.

Then you can connect all the pipes to the pipes with nuts or couplings. The boiler piping is done only with metal pipes. Afterwards, an expansion tank is installed to regulate the pressure in the circuit. Then comes the installation of the manifold - two pipe elements that are located one below the other. The number of pipes must match the number of circuits. The connection of the lower and upper sections of pipes is made using a bypass. A pressure gauge and an air vent are installed on the upper section of the pipe, and a tap is installed on the lower section to drain water from the pipeline.
The pump for underfloor heating can be installed anywhere, and the thermostat can be installed at a point that is not subject to drafts. After checking again whether the automation is connected correctly, you can make the first connection of the water floor. To do this, all circuits are filled with water and air is released. You need to check how the taps and valves work, and whether the connections are tight. To do this, several pressure control checks are done at intervals of one to two hours. During this time, it is allowed to reduce the pressure by only 20 kilopascals. If everything is in order, then you have coped with such labor-intensive work yourself.
Marking
When choosing a circulation pump for a heated floor, you should pay attention to the characteristics displayed on its body. In the “Type” line you can see both letters and numbers:
- UPS – determines the control or the number of speeds (UP – single-speed, UPS – three-speed, UPE – electronic control).
- The first number indicates the diameter of the inlet/outlet pipes in mm.
- The second number indicates the height of the coolant rise. It can be 40, 60, 80, i.e. at 4, 6, 8 m or 0.4; 0.6; 0.8 atmospheres.
- A – presence of an air vent or housing material. A – there is an air vent, B – the body is made of bronze, N – the body material is stainless steel.
- The third number indicates the installation length.
Data on power consumption and other information are additionally included in the labeling. It all depends on the manufacturer. To select equipment, the main line is “Type” with symbols.
Choosing the right boiler
The further microclimate in the rooms will depend on the gas boiler in the house. Often, such systems are chosen based on the cost benefits (outcomes) of one of the energy carriers. This approach, surprisingly, is the most correct one. When choosing a coolant, you should be guided by the following factors:

Boiler and heated floor
- The degree of complexity of the necessary installation work, which is aimed at installing complex equipment.
- Further degree of ease of use. The cost of its subsequent maintenance plays an important role.
- It is also worth considering the possibility of power outages and its complete shutdown in a particular region.
- Maximum and minimum system power.
- What is the most profitable energy source from an economic point of view?
The fact is that there is no company that produces heating boilers designed for heated floors. You can find models whose instructions contain information regarding its operation with heated water floor systems, but nothing more. The main distinguishing feature of floor circuits from radiator systems is the temperature of the main coolant. When using radiator systems, the coolant temperature can reach 80°C. The water floor pipes are only 55°C.

Boiler characteristics specification
In order to achieve an optimal indoor microclimate, the system must heat up to 40°C. The cooled coolant will have a temperature of 30°C. If radiators and heated floors are used for heating, which are supplied with heated coolant from the same boiler, then choosing a heat generator should not cause difficulties. Not every heat source can work to maintain the optimal temperature. To do this, you can additionally tie the unit.
Difficulties in connections may depend on the choice of one of the types of boiler and heated floor used:
- coal and automatic pellet;
- floor or wall gas;
- solid fuel;
- electric.
Boiler classification scheme
Accessories for work
Main components:
- a gas boiler;
- collector installation;
- automatic system for adjusting modes;
- pumping system;
- shut-off valves;
- fitting;
- Mini piping floor system for installation on subfloors;
- the main pipeline for creating the distribution of the coolant throughout all living rooms.
How to choose a gas boiler for heated floors
Gas boilers are divided into groups.
According to the installation method, there are:
- Wall-mounted boilers are hung on the wall, and the wall must be strong enough and strong, since the weight of the boiler is rather large. They are mainly used for the heating system of houses with a small area, from 230 to 360 m2.
- Floor-mounted - the advantage of this system is that it is installed on the floor surface, eliminating additional load on the wall. Suitable for use in frame houses where the walls are not particularly strong. They are suitable for heating a house with a large area due to their large dimensions.
By number of circuits:
- Single-circuit - used to work with one line of the heating system.
- Double-circuit - serve as a power source for the heating system and as a source of heating hot water, which is used for domestic purposes. Please note that working in two modes at the same time is impossible. When the water gets hot, the heating turns off.
According to heat transfer material:

Boiler heat exchanger
- Steel is a budget material. It does not have a long service life, because under the influence of temperatures it quickly wears out and cracks. Also, the material rusts within a short time, despite applying various anti-corrosion agents to it.
- Stainless steel is one of the expensive materials that is rarely found on sale. The characteristics of the material are good, because combines the best performance of devices made of cast iron and steel.
- Cast iron is highly resistant to corrosion processes, the advantages are strength and long service life. When installing such a device, control of heating uniformity is required, because Different temperatures in different areas can cause cracks to appear. The disadvantage is the high fragility of the material.
- Copper is more often used when installing a boiler on a wall surface; it is resistant to corrosion processes and is light in weight. With this material, the boiler has low inertia, and this allows you to quickly adjust its operating mode.
By type of firebox or combustion chamber:
- Open type - combustion processes are carried out using air, which enters through channels designed for this purpose. When installing such a system, you need free access to air and a room that will be specially designed for this. The cost of this type of boiler is low.
- The closed type or turbine type is much more expensive than the open type, and is more often used in houses with a small area, such as frame houses, since it does not require a separate room for installation.
Vertical chimneys are used to eliminate smoke. If you use a horizontal one, you need an additional fan that will supply fresh air, with the help of which the combustion process is carried out. Turbocharging or supplying air flow to increase the intensity of the combustion process is a function that is present in almost all new generation gas boilers. When choosing a boiler, familiarizing yourself with its technical characteristics will help you find out all the advantages, capabilities and disadvantages.
First of all, when choosing, you should pay attention to the boiler power, types of combustion chambers, number of circuits, fuel volume. You also need to take into account the amount of water consumed and the possibility of heating it (the average is 2.5-15 l/min.). The efficiency should be approximately 90-95%.
Then you should choose a water heater for your floor heating system. When calculating power, you need to focus on the average value, which is approximately 1 kW per 10-12 m2 of the entire occupied area. It is advisable to prefer a type where it is possible to regulate the operating mode of the boiler. It is preferable to opt for a system with continuously variable adjustment. The number of circuits and type of installation should best suit the requirements of the room.
Pipes

The pipes are made of copper, metal-plastic, REHAO. Copper - have a long service life, strength, and good heat transfer. Disadvantages: the price category is quite high, not everyone can buy them. Metal-plastic pipes are not as durable as copper pipes, but are more affordable financially. REHAO pipes are more than affordable, but not as convenient as the 2 previous options. When working with them, polyethylene quickly straightens when heated, so creating the desired pipe shape is not so easy. The advantage is that if they break down they can be easily repaired.
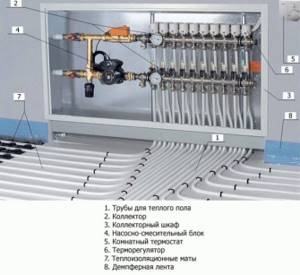
Water floor connection, mixing unit
When connecting a water floor to a boiler, a problem arises: different temperature conditions. If the coolant heats a regular boiler, and not a low-temperature one, then its output temperature is 70 o C-85 o C. Sometimes higher, sometimes lower, depending on the situation and boiler settings, but, in any case, the temperatures for a heated floor are unacceptable. Even taking into account the thermal inertia of the cement screed, it is impossible to apply more than 50 o C: this will threaten overheating. The most optimal option at the entrance to the water floor pipes is 40-45 o C.
How to connect a water floor to a boiler
The heated floor must be connected to the boiler in such a way that coolant at a lower temperature is supplied to the circuit. In a closed system, which is a heated floor, the temperature can only be lowered by mixing the cooled coolant from the “return” with the heated coolant. This is what the mixing unit or mixing unit does.
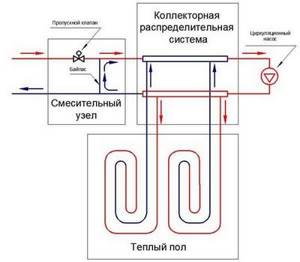
A schematic diagram for connecting a warm water floor can be depicted as follows:
If there are several underfloor heating circuits, a collector unit is installed (or assembled) after the mixing unit. This is a comb with several inputs and outputs (from 2 to 20), to which the heated floor circuits are connected. In the simplest version, this is a unit for parallel connection of underfloor heating loops.
In more “advanced” collector models, various devices are installed at each input. There are often bleed valves on the manifold to remove trapped air from the system. An air lock can block the movement of the coolant along the circuit, therefore the use of air vents is advisable.
In collector groups there are shut-off valves on each circuit. They can be controlled manually or using servomotors. Servomotors receive commands from automation, but such devices are already called collector groups or devices. They can also contain a mixing group and a circulation pump, and are then called collector stations. Naturally, the more complex and functional the device, the higher its cost.
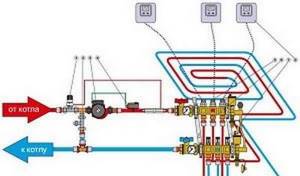
This is what a connection diagram with a two-way valve might look like
You can save money if you wish. Assemble the mixing unit yourself and install a pump in the system. You can also make a collector group yourself, or you can buy a ready-made, but not very expensive, collector.
Mixing unit
Connection diagram for a water floor with a 2-way valve
The operation and capacity of the two-way valve is adjusted depending on the readings of the remote sensor. High-temperature coolant from the boiler is supplied through it. Cooled water flows from the return pipeline through the balancing valve. At the junction point the two streams mix. Coolant with a reduced temperature is pumped through a circulation pump and supplied to the collector. The temperature of the mixed flow is controlled by a sensor, adjusting the gap (and hot water supply) on the two-way valve.
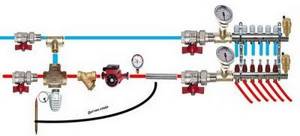
Detailed wiring diagram for a heated floor boiler (with a two-way valve)
To prevent backflow, you need to install two check valves on the “return”. As mentioned earlier, this scheme is good because the adjustment is smooth (due to the low throughput of the valve). In addition, in this scheme the addition of cold water is constant. And therefore the possibility of supplying only hot water from the boiler is excluded.
Water floor diagram with 3-way valve
The operation of the three-way valve can be controlled by a servomotor or an external temperature sensor (depending on the configuration you choose). The difference here is that the flows are mixed inside the valve, and the accuracy of maintaining the temperature depends on its operation. And this device has a large throughput, so that minor measurements in the position of the valves lead to quite sharp temperature changes. But when using weather-compensated automation and with large water floor contours, such a system is the only option.
Two options for mixing unit or mixing unit (click to enlarge size)
Connections of a water floor to a low-temperature boiler
If the temperature of the coolant at the boiler outlet can be set at your discretion (in systems without radiators), then the collector unit is connected directly to the boiler. This is the simplest option for connecting a water heated floor, but, unfortunately, not always possible.
Malfunctions and repairs
In a heating system, especially in areas with hard water, salts accumulate and can settle on pump parts. The rotor may jam. And if after a summer holiday the pump stops working, then you should carefully disassemble the device and push the impeller with a screwdriver. I gave in and spun it several times - you can install the system back. This breakdown is typical for systems with a wet rotor. This should be done especially carefully with pumps that have ceramic bearings. The material is fragile, and in the event of a breakdown, you will have to look for a suitable spare part and carry out major repairs.

The pump for the “warm floor with a dry rotor” system must undergo maintenance, lubricate parts, and replace gaskets. With proper care, such devices have a long service life.