Foamed polyethylene for insulation, how to use, features
A relatively new insulating material is foamed polyethylene.
Ordinary polyethylene can be found everywhere - bags, handles, pipelines, containers, forms... The high consumer qualities of this material, first of all, resistance to impacts, environmental friendliness are inherited by foamed polyethylene. It is available in different densities, can be in the form of a film or in a certain form. Read more about the characteristics of foamed polyethylene and its application below.
Types, characteristics of foamed polyethylene
Foamed polyethylene is divided into cross-linked and non-cross-linked.
Non-crosslinked is obtained by mixing polyethylene with a gas mixture - propane-butane. This material differs from cross-linked material in its lower density - 20 - 25 kg/m3. We find it as a substrate for laminate or packaging.
Cross-linked polyethylene foam can be formed in two ways:
- chemical, with complex chemical transformations of the source material;
- physical (radiation) using energy beams to create foam.
The result is polyethylene foam with a higher density of 25-200 kg/m3, but also with greater water absorption - 1% versus 0.2% for non-crosslinked foam. Denser foamed polyethylene is used in various industries, incl. and in the automotive industry, we can find it as tubular insulation for pipelines.

Other characteristics of foamed polyethylene:
- Thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.038 - 0.045 W/mS depending on the density. Heat-saving properties at the level of modern insulation materials.
- Vapor permeability coefficient – 0.01 mg (m*h*Pa). We have a vapor barrier in front of us.
- Permissible operating temperatures – – 40 – +70 degrees. C. Cannot be near hot piping.
Where is it used?
Good sound-absorbing properties, especially with regard to low-frequency impact sound, combined with a low price, almost gave the material a second name - laminate substrate.
In this capacity, it is used with a thickness of 3 - 10 mm and a density of up to 30 kg/m3. It acts primarily as a sound absorber and compensator for minor irregularities, and increased thermal insulation in some cases is only an additional bonus, but not the main reason for choosing this material.

Packaging anything and everything. When transporting, it is important that many useful things, from a plate to an expensive appliance, are not damaged or subjected to critical loads from vibration or accidental impact.
And everywhere, the vibration absorber and packer, along with foam plastic, is foamed polyethylene. Opening the box with a newly purchased food processor, we throw away the packaging without looking, and it was...
For example, in cars you can also find foamed polyethylene both as a sound absorber and as a material that stabilizes the temperature inside the cabin. Pipelines are insulated with a dense shell. We will consider the issues of insulation with foamed polyethylene in more detail.

How is thermal insulation performed?
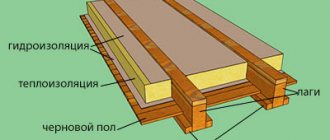
For insulation, foamed polyethylene is used as a vapor barrier layer with an additional insulating effect. It is not uncommon when, according to calculations, a thickness of insulation is required that is slightly greater than what is usually produced by the industry.
Instead of applying an additional layer, the designer introduces a layer of foamed polyethylene instead of a vapor barrier membrane, and underneath it also an air layer 1-2 cm thick, which is also a heat-insulating layer.

As a result, the thickness of the main insulation is reduced, for example from 19 to 15 cm, according to the thermal calculation, due to additional polyethylene foam with a reflective foil layer and an air gap above it.
Reflection of beam energy
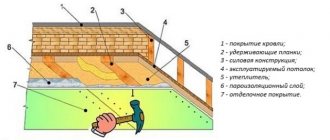
Foamed polyethylene covered with a metallized film (foil) is used mainly with a system of electric heated floors, as a vapor-proof layer, additional insulation to the main insulation layer, and as a reflector of radiation energy.
For electric heated floors, most of the energy produced is in the form of infrared radiation.
Certain types of electric emitters (infrared heated floors) generate an overwhelming amount of energy in the form of infrared radiation, without heating to a high temperature, but heating all dense objects in the room with radiation.
It is clear that without effective reflection from below, a significant part of the energy will be wasted.

Foiled polyethylene foam should be used only for its intended purpose, like any foil. Covering a room with it on all sides disrupts the normal distribution of electromagnetic fields, which is harmful to any living organism.
Properties of insulation based on PPP
Foamed polypropylene has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient in its class. The gas-filled polymer has a density of 40 kg/m3; its closed pores provide moisture resistance and high strength. The elastic material does not deform during operation. It is a low-flammability product and does not emit dangerous toxic gases during combustion.
Synthetic insulation is environmentally friendly and safe for health; contact of polypropylene with food is allowed.
The cellular structure helps absorb sound and vibration; the use of PPP is recommended for soundproofing buildings. To enhance the properties of the insulation, it is laminated with foil or lavsan threads. Composite products can be coated with non-foamed polypropylene. The most famous material with lavsan and foil coating is EPP. It is produced in the form of rolls of 15, 25 m, thickness of the canvas from 2 to 10 mm. The size of the sheets is 1×1, 2×2 m, thickness - up to 20 mm. The insulation is easy to cut and easy to install.

Technical characteristics of polypropylene foam
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.034 W/m*K;
- thermal shrinkage - 3%;
- water absorption - 0.74%;
- density - 40 kg/m3;
- compressive strength - 0.183 MPa;
- operating temperature - from −40º C to +150º C;
- service life - 20 years.
Installation features
When starting to install foil insulation, you need to prepare some tools that will be useful in your work:
- small nails, the heads of which can be quite large (preferably);
- construction stapler;
- hammer and nail puller;
- foil construction tape;
- the foil insulation itself.
The most important mistake that builders often make is laying insulating material with foil with the reflective side facing outward. Since foil is a reflector, it is designed to return thermal radiation inside the room, reflecting it. But if you put this insulation on the other side, the expected insulation effect will not be achieved.
Installing a reflector under the battery
When installing, you need to leave about 2 cm of space between the trim and the foil insulation to make the room even warmer. The air will also serve as a kind of additional insulator, and the entire structure will work on the principle of a thermos.
When laying the material, it is advisable to enclose it in a wooden sheathing.

Sheets, sections from a roll or slab of insulator are never laid overlapping each other! They need to be laid end-to-end in one plane, secured with a construction stapler or nails.

A foil insulator equipped with an adhesive coating does not need to be additionally fixed by mechanical means, but to ensure the durability of such insulation, it is better not to forget about nails. If the material does not have an adhesive coating, acrylic or rubber glue is suitable for attaching it, which only needs to be applied pointwise!
When all the sheets of material are laid in place and fixed, the joints between them must be carefully taped with special foil tape. Installation is complete!

If the foil material will be mounted on a vertical plane (for example, a wall) on which there is wallpaper, mold or other unnecessary phenomena, this surface must be cleaned before gluing the thermal insulation, otherwise the fixation will be mediocre, and the material may fall off over time. In addition, it is advisable to treat the surface with antiseptics.

Convenient to use, such thermal insulation with foil will save money and keep your home warm and cozy!

Foam materials are widely used for thermal insulation. They have good thermal insulation properties, are multifunctional, and are ideal for insulating roofs and walls. Let's talk about the pros and cons of one of the foamed polymers - polypropylene.
Foamed polypropylene differs from other thermal insulation materials in its combination of insulating properties and low specific gravity. The closed cell structure determined the increased strength of PPP among materials of its class.
To enhance waterproofing, as well as to increase the ability to absorb noise and vibration, manufacturers laminate sheets of foamed polypropylene.
The process of creating porous polypropylene takes place in several stages: – combining polyPP with various additives (fire retardant, plasticizer, antistatic, etc.); – high-temperature treatment (about 240°C) with the participation of a foaming agent – p-toluenesulfonylsemicarbazide. The result is individual small balls; – treatment of the resulting substance with hot steam under high pressure. In the process, the balls are fused together; – extrusion of the resulting mass of polypropylene (extrusion through a slotted head); – hardening period for 2 days.
“Solid” (polystyrene based)
First of all, it is polystyrene foam, which has pronounced advantages and disadvantages. Here are its strengths:

Foam insulation
- Low thermal conductivity (0.043 W/mK). Competitive indicator.
- Almost zero water absorption . Water is not absorbed and does not damage the material itself or the wall.
- Not friendly with fungus and bacteria . There is no unpleasant odor or hazardous fumes.
- Ease of processing . Sheets can be easily cut to size using a construction knife or a fine-tooth hacksaw.
- Ease. The panels do not put pressure on the walls and foundation, the load is insignificant even for non-permanent buildings.
- Durability. The myth that the material will crumble in ten years is unfounded. The actual service life is 40-80 years.
These properties are different from standard EPS (expanded polystyrene foam ). By paying an additional 20-30%, you can buy EPS (extruded polystyrene foam) . The modified version of the insulating building material is stronger and has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.028-0.030.

Insulation extruded polystyrene foam
And here are the promised disadvantages:
- Compatibility only with stone and brickwork . Installing foam plastic under the siding of a wooden building is a bad idea. The sheet material has zero vapor permeability, so the walls behind it stop “breathing.” This leads to the wood beginning to rot (due to moisture condensing on the surfaces). Often the problem becomes unsolvable even with a forced ventilation system.
- Toxic fumes . When heated, a whole range of dangerous compounds are released, so it is highly not recommended to install the sheets inside residential premises. Cheap sheets begin to produce styrene after a few years even at normal temperatures. For outdoor installation this is not so critical.
- Fire hazard . The “self-extinguishing” mark on the label often does not guarantee anything. Let the foam not burn on its own, but an open fire nearby can support its combustion.
- Vulnerability to rodents . Mice and rats make their own passages and destroy the integrity of the structure. The quality of thermal insulation decreases. The effectiveness of rodent control is limited, and it is often simply impossible to cover all vulnerable areas with solid shields.
Advantages and disadvantages of insulating walls from inside the house
The advantages of such insulation are associated with the impossibility of facade insulation. Such insulation is often resorted to out of dire necessity. However, the internal insulation of the house:
- does not require complex scaffolding for installation of thermal insulation;
- allows you to carry out work regardless of the time of year and weather conditions;
- sequence of work;
- no time limit.
Much more shortcomings are presented by users of construction sites and experts about insulating walls from the inside of a house, some of which we noted above.
- A serious disadvantage of indoor insulation is its insulation. The use of continuous insulation technology with polyurethane foam or polypropylene foam leads to the fact that the room stops “breathing”. Living in a plastic bag does not find many supporters;
- Any method of indoor insulation does not provide a complete guarantee against the appearance of dew point in the walls or in the insulation of the house, these are the laws of physics;
- The living space is reduced due to the use of polypropylene foam insulation, not to mention mineral wool insulation;
- The cost of this method of insulating the walls of a house exceeds the cost of insulating external walls, and the quality is usually higher with external insulation;
- The process of internal insulation takes longer compared to façade wall insulation.
Properties of heat insulators based on PPP
Foamed polypropylene has the lowest thermal conductivity in its class. The gas-filled polymer material has a density of 40 kg/m3; its closed pores provide moisture resistance and greater strength. The elastic material does not change its initial shape during operation. It is a product with low flammability and does not emit dangerous toxic gases during combustion.
Artificial insulator
environmentally friendly and less hazardous to health, contact of polypropylene with food is allowed.
The cellular structure helps absorb sound and vibration; the use of PPP is recommended for soundproofing buildings. To improve the properties of the heat insulator, it is laminated with foil or lavsan threads. Composite products can be coated with non-foamed polypropylene. The most famous material with lavsan and foil coating
EPP.
It is produced in the form of rolls of 15, 25 m, thickness of the canvas from 2 to 10 mm. The sheet sizes are 1?1, 2?2 m, thickness - up to 20 mm. The heat insulator
is easy to cut and easy to assemble.

Technical properties of polypropylene foam
- thermal conductivity index - 0.034 W/m*K;
- thermal shrinkage - 3%;
- water absorption - 0.74%;
- density - 40 kg/m3;
- compressive reliability - 0.183 MPa;
- operating temperature - from ?40? C to +150? C;
- service life - 20 years.
The use of foil thermal insulation materials
The use of insulation with foil always depends on two indicators: the properties of the place in which they will be used, and the properties of a particular insulation. In general, foil materials insulate the floor, increase heat transfer from radiators, and insulate pipelines and air ducts for various purposes. Insulation of entrance doors, entryways, balconies and verandas also has a significant effect.

Production of porous polypropylene
The process of producing foamed polypropylene from ordinary polypropylene consists of several stages:
- granulated polypropylene is mixed with plasticizers, antistatic substances, fire retardants and other agents, depending on what special properties the final product should have;
- one of the added agents is toluenesulfonyl semicarbazide, which ensures the process of foaming the material when heated to 240 degrees Celsius;
- as a result of heat treatment, many small balls are formed, which are then fused into a single mass under the influence of hot steam;
- The material takes its final shape during extrusion through special slotted heads;
- the sheets of the resulting polypropylene foam gain strength and hardness within two days.

Polypropylene (PP) - physical properties and characteristics
PP is an elastic polymer material that is resistant to aggressive chemical-based substances, flexible and has low vapor permeability.

Polypropylene products are made in 5 main ways:
- injection molding;
- extrusion;
- rotational molding;
- blowing;
- foaming
The material, obtained by foaming granules of a polymeric material, has found great use in heat, steam and sound insulation of building structures and pipelines. To give it special qualities, low molecular weight organic substances, fire retardants, antistatic and other substances are added to PP granules. Porous or polypropylene foam (PPF) is formed through the extrusion process.
Standard sizes, varieties and colors
Polypropylene foam sheets in their pure form are extremely rare on sale. Composite EPP is the most popular - in this case, EPP is supplemented with a layer of foil or Mylar threads, or is located between sheets of ordinary polypropylene (i.e. lightweight PP).
Each EPP manufacturer has established its own standard sizes. For example, OOO Penotherm, which was the first in Russia to foam PP, sells polypropylene foam in rolls with a standard width of 1.2 m. The length varies depending on the thickness of the material: 2, 3, 4, 5mm - 25 linear meters, 8, 10mm - 15 linear meters.
Standard sizes of lightweight PPP sheets from various manufacturers (thickness 10 - 20mm): 1×1, 2, 3, 4, 5m; 2x2, 3, 4, 5 m, 1.5x3 m, 1.5x4m.
The color of foamed polypropylene without adding dyes is milky. The following colors are also available - green, gray, blue. Color selection is possible upon individual order.
Technology of wall insulation with polystyrene from the outside
Before you begin insulating the wall with polystyrene foam, you should dismantle the gutters, decorative elements, clean and prime the wall. Next, insulate the sills and window slopes.
Now let's talk about the thickness of polystyrene foam.
You can also use thinner sheets 30-40 mm thick if they are laid in two layers.
Let's start installing insulation on the walls with our own hands:
- a profile is installed at the bottom of the wall to hold polystyrene foam;
- the adhesive mixture is applied to the wall over the entire area in spots and onto the insulation sheet (amply on the center and edges of the sheet);
- tightly attach the sheet for gluing to the wall;
- Use dowels to secure the panel so that the dowel penetrates the wall at least 50 mm. The dowels are placed in the center of the panel and at the joints. It is recommended to use plastic nails;
- if gaps form (up to 2 cm), then they are sealed with polyurethane foam , if the gaps are larger, then they are first sealed with pieces of insulation, and then foamed. Excess foam is cut off;
- The heads of plastic nails are cleaned and puttied.
What is foamed polyethylene, types of material, production technologies
Foamed polyethylene is a polymer material obtained by introducing a hydrocarbon gas mixture into the polyethylene structure, resulting in a porous, plastic and durable polymer with a cellular structure. It is produced in the form of sheets, strands and rolls.
All foamed polyethylene produced today is divided into three types:
- Unstitched (NPE). The cheapest of the line of foamed polyethylene. Europe launched its production at the end of the last century. The polymer mass melted in the extruder is saturated with gas, usually butane. When poured into a mold, polyethylene enters a zone of atmospheric pressure, gas bubbles try to escape to the surface, and, when solidified, form a cellular structure. Non-crosslinked polyethylene foam is a good heat insulator, but due to its low density and loose, large-porous structure, products made from it are rarely used in construction. The material is mainly used to make packaging.
- Chemically cross-linked (CCPE). The equipment for the production of foamed polyethylene CPPE is used the same as for non-crosslinked polyethylene, but additional processing with hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the technology. This eliminates all the disadvantages inherent in non-crosslinked polyethylene - the material becomes denser, the cells are smaller, the polymer can restore its original shape after deformation.
- Cross-linked by physical or radiation method (FPPE). The most expensive of foamed polyethylenes. The cross-linking of polymer molecules occurs due to the flow of electrons emitted by the emitter. Irradiation forms cross-links that strengthen the molecular network of polyethylene foam. The output is an elastic soft fabric with a smooth surface that can withstand pressure up to 0.035 MPa. Physically and chemically cross-linked PE have similar characteristics, but FPPE recovers its shape faster after loading and adheres better to compacted forms. The floor underlay is made of polyethylene foam produced by radiation.
Useful advice from professionals
For high-quality insulation, it is recommended to listen to the advice of builders. The main ones:
- Insulation from the inside is carried out along the entire perimeter of the housing, and not just those walls that border the street.
- To prevent the formation of condensation and further problems with the insulation, care should be taken to ensure reliable ventilation. Air ducts are installed in the walls during the construction of a building or in the ceiling structure.
- To secure polystyrene foam boards, it is recommended to use mushroom dowels with plastic rods.
- According to reviews from builders, double-layer insulation with thin slabs of polyurethane foam on the outside is preferable to single thick insulation.
Simple tips will help you avoid making mistakes when insulating your home.
It is up to the owner to decide which polystyrene foam is best for insulating a house made of timber or brick. Each type has a number of advantages, for which professionals value it. The material is durable, lightweight, provides high-quality insulation and is affordable. With proper installation, the results will last for decades.
How to properly insulate with polyurethane foam?
The technology of insulation using polyurethane foam has some features, and the technology for performing the work must be strictly followed - otherwise it will be impossible to achieve the desired result.
It should be borne in mind that it is naturally more convenient and best to carry out work at the stage of construction and/or renovation of a house. But it is quite acceptable to carry them out in a building in use, especially when it comes to exterior work.
But it should be taken into account that when insulating walls indoors, you will still have to do cosmetic repairs, since a decorative cladding will be required for the applied layer of thermal insulation.
But another factor must be taken into account: internal insulation always loses to external insulation, and primarily due to a possible shift in the dew point, which may appear either inside the wall, contributing to its gradual destruction, or on the inner surface - in this case, problems associated with the fight against mold and mildew , can't be avoided.
Before insulation is carried out, its future thickness should be correctly calculated, which is directly determined by the climate characteristics of a particular region, as well as the thermal conductivity of the material from which the walls of the building are constructed.
First you need to clean the surface to be treated from old coating and paint, from remnants of thermal insulation and other types of finishing. Particular attention should be paid to areas with oily stains, which can reduce the adhesion of the insulation and the surface - they are removed mechanically.
In addition, weak areas of the surface also deserve attention - they also need to be removed, and if necessary and large-scale such damage will need to be repaired using repair compounds or, for example, cement-sand mortar.