The stove or fireplace is called the “heart of the home” for a reason. But taming fire inside a residential building requires a whole series of actions and a long set of rules. After all, any mistakes in the design of a chimney are too expensive, starting from suffocating smoke inside the room and ending with a fire. And most often it all starts with a violation of draft and destruction of the walls of the chimney, and then adjacent building structures catch fire.
Today, chimney height calculations are often carried out through special programs, although experienced specialists always check the obtained values manually, using formulas that it makes sense to get acquainted with for peace of mind.
They are not complicated; to understand them, it is enough to have a school knowledge of geometry and the ability to substitute values in the right place. And we, in turn, will try to explain to you why each indicator is so important for determining the height of the chimney pipe, and how exactly it affects it.
Chimney location and wind direction: how to prevent turbulence
According to all building codes and regulations, the chimney must rise above the roof at a certain distance. This is necessary so that the air on the protruding parts of the roof does not cause reverse draft due to turbulence.
Backdraft can be seen firsthand in the form of smoke that pours from the fireplace directly into the room. But the extra height of the chimney is also not needed, otherwise the draft will become too strong and you won’t get any heat from such a fireplace: the wood will burn to ashes like a match, without having time to give off heat.
This is why it is so important to calculate the height of the chimney as accurately as possible, especially taking into account the direction of the winds in the area:
If the pipe is located too close to dense trees or a high wall, it must be extended with asbestos-cement or steel pipe.
In this video you will also find valuable tips on installing a chimney and solving problems with its height:
Materials for the construction of boiler pipes
Smoke exhaust systems are built from different materials - brick, steel, ceramics, polymer. A brick chimney, built over brick stoves and fireplaces, is characterized by good mechanical strength, excellent heat capacity, and a fairly high degree of fire safety.
These structures also have many disadvantages, which is why in modern construction completely brick chimneys are becoming less and less common. Regulatory documents limit the height of brick pipes to 30-70 m and the diameter to 0.6-8 m.
On the walls of a brick pipe with many protrusions and depressions inside, a lot of condensate and soot containing sulfur oxides always settle. The latter, reacting with water, forms acids that actively destroy bricks.
Surface unevenness and narrowing of the passage as a result of a gradual increase in the soot layer cause a decrease in the speed of smoke passage and overturning of the draft in the smoke exhaust channel.
Ceramic chimneys are more resistant to condensation and external factors; they have high fire resistance. But this system has a lot of weight, because Inside there are metal rods that give it additional strength. This entails the requirement for the mandatory installation of a separate foundation and supports, which increases the complexity and cost of installation.
Polymer chimney pipes are appropriate in boiler rooms with a maximum temperature of 250 degrees C, when installing geysers. They are lightweight, flexible and durable, but are only relevant for gas equipment.
A device for removing smoke from stainless steel is an assembly consisting of individual chimney elements connected to each other using shaped parts: tees, pipes, deflectors, tees, bends. Gas boilers are mainly equipped with steel chimneys.
Installation of such a chimney can be carried out after the construction of the building in a short time. There is a wide range of connecting parts, so the pipe can be given any configuration.
A modular chimney can be easily dismantled and moved to another location. The advantage of the design is its low weight, which allows you to do without a foundation, resistance to moisture, slight deposition of soot on the internal walls, and high speed of passage of flue gases.
Sanitary standards allow the use of steel pipes for the construction of chimneys with a height of more than 30 m; an exception is possible only if less than 5 tons of polyash fuel are consumed per day. The reason is that the service life of such structures is 10 years, and if high-sulfur fuel is used, it is significantly reduced.
Varieties whose body is made of steel alloy include coaxial chimneys, the design specifics and operating features of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
Traction force: how to achieve ideal fuel combustion
The traction force itself is influenced by several important factors:
- chimney material;
- foundation height above sea level;
- flue gas temperature at the furnace outlet;
- cross-sectional shape of the chimney pipe;
- smoothness or roughness of the inner surface;
- violation of the internal tightness of the chimney;
- temperature and humidity of outside air;
- ventilation of a room with a boiler or stove;
- completeness of fuel combustion;
- degree of contamination of the boiler (or stove) and chimney;
- type of burner used (modulating or discrete).
First of all, you need to determine the value of the static draft of the chimney, which is measured in the value ∆p [Pa]. Here is the formula for calculation:
h[m]=(∆p·Tp·Tн)/(3459·(Tp-1.1·Тн))
Tp is the average temperature in the pipe, and Tn is the outside temperature. It is measured by default in degrees on the Kelvin scale, but you can also specify it in Celsius by adding +273.
Calculating the average temperature is not difficult. This is usually reported in the technical data for the boiler, but it is also important to take cooling into account. This is 1 degree per meter of brick pipe, 2 degrees per meter of insulated steel pipe and 5 degrees for uninsulated one.
In this case, it is advisable to take the value of the outside temperature that is typical for summer as the most problematic time for traction:
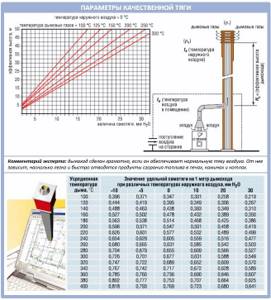
Make an aerodynamic calculation and find out the exact required height and diameter of the chimney. The amount of draft itself means the difference in the densities of air and flue gas, multiplied by the height of the house. It is 5 meters of the chimney that provide vacuum and draft for smoke .
But what to do if the height of the pipe cannot be set higher, and the draft for certain reasons is still insufficient? This often happens when flue gases cool down too quickly, especially in the cold season. Then, to restore traction, the required section of the pipe is simply insulated.
Also remember that real thrust is always less than static due to the resistance to the movement of gases inside the pipe walls. The narrower the flow section of the chimney, and the more bends, horizontal sections, etc. there are in it, the worse the draft will be, because the draft is affected by the loss of pressure along the entire length of the pipe.
Another problem with chimney height is cold air from the fireplace. So, when it is not working, cold air from the street is released from it. This happens when the chimney head is below the end of the ventilation hood, or when the attic is too large and poorly insulated.
Operating principles of stove chimneys and domestic boilers
For the normal functioning of heating devices that generate heat by burning fuel, a chimney is required.

The smoke exhaust design provides an influx of oxygen, without which neither gas nor solid or liquid fuel burns. In addition, smoke containing combustion products is removed through the chimney, which is the key to the safety of the heating system - after all, smoke in rooms is deadly to humans. This gas exchange is called draft.
Internal combustion boilers are equipped with coaxial chimneys, which create forced draft, exhausting smoke through one pipe and sucking in fresh air through another. Wood stoves and most household boilers operate on natural draft, which is formed due to the difference in temperature and pressure in the heating device and at the chimney outlet.
The principle of operation of the chimney is simple:
- the gases released during fuel combustion have a high temperature, low density and high pressure and become cramped inside the heating device;
- the smoke is directed to where there are no obstacles for it, that is, it moves in the direction where the pressure is lower, trying to fill a relatively free space; in addition, due to the low density, the gases tend upward;
- if the chimney is constructed correctly, then at the outlet of the pipe the cold air has low pressure and is not an obstacle to the exit of hot smoke;
- since the low pressure area is located above the boiler, the smoke goes along the most convenient path - up the chimney to the street.
Chimney design depending on heating configuration
Go ahead. What chimneys are installed most often today? These are brick, ceramic and insulated and non-insulated steel.
And first of all, when designing a chimney, its minimum throughput indicators are calculated. If mistakes are made here, flue gases will begin to accumulate inside the pipe and cause a lot of problems.
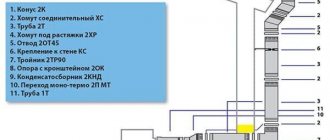
The general layout of the chimney looks like this:

If the temperature of the exhaust gases is low, as in modern low-temperature boilers, then so-called electric smoke exhausters are installed in the upper part of the chimney.
They are a small fan with blades. Such a device forcibly removes combustion products from the pipe, thereby increasing the traction force. And then the traction force no longer directly affects the height of the chimney, because it is achieved in a different way, and not by “catching the wind.”
If there is no additional device, then you will still have to catch the wind. And in this case, you need to build on the available power of the boiler, stove or fireplace, which can be found in the technical documentation. It is expressed in the amount of fuel that is burned in one hour of work.
If the amount of fuel volume is known, then the volume of gases is calculated using the following formula:
Vg = B∙V∙(1+t/273)/3600
The result will be in m3/s. This is the speed of gas movement in the pipe. We calculate the cross-section of the pipe using the following formula:
F = π∙d²/4
And the resulting value is determined in m2. This is the cross-sectional area of the chimney, and the diameter is calculated using the formula:
dt = √4∙B∙V∙(1+t/273)/π∙ω∙3600
The remaining characteristics are almost the same for most heating devices. Thus, the exit speed of gases in the chimney is usually no less than 2 meters per second, and the temperature of the gases at the entrance to the pipes is from 150 to 200 degrees.
Also, the standard gas pressure per 1 meter is no less than 0.4 mm H2O, or 4 Pa:
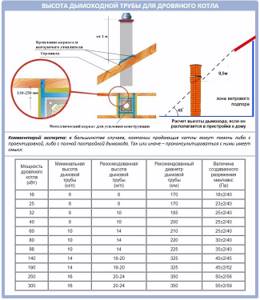
Therefore, according to SNiP, the height of the chimney from the grate must be at least 5 meters.
Why are calculations needed?
Natural air exchange, in which combustion products are removed into the atmosphere, occurs only if the smoke exhaust structure has the correct shape and size.
If there are obstacles - turns, corners, sections of the smoke channel with low throughput - the smoke can go in a different direction, where nothing will interfere with its spread. If the chimney height is low, the temperature difference will be insufficient to generate draft, or wind pressure will appear, which will prevent the smoke from leaving the chimney, practically driving it back.
Note! Defects in the chimney design will lead to the fact that the draft will either be insufficient for the normal operation of the heating device, or a reverse draft will appear and fuel combustion products will flow into the premises, which can cause poisoning or a fire.
However, about the size of the chimney it cannot be said that the larger the better. A chimney that is too long or wide will increase the cost of chimney construction. A stove or boiler with such a chimney will wear out under conditions of excess draft, burning fuel faster than necessary to warm the premises. The heat obtained during combustion will partially fly away into the chimney, causing heating costs to increase.
We recommend that you read: How to permanently get rid of condensation in a ventilation pipe?
Therefore, in order for the heating unit to work efficiently and not break down, it is important to accurately calculate the main parameters of the chimney, which will ensure the optimal level of draft.
Dependence of the chimney height on other roof elements
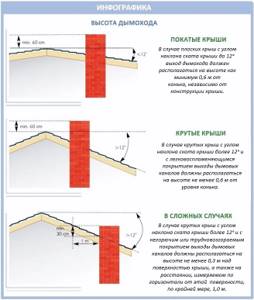
Of great importance is also how close the chimney itself is located to the ridge of the roof, parapet or its other elements:
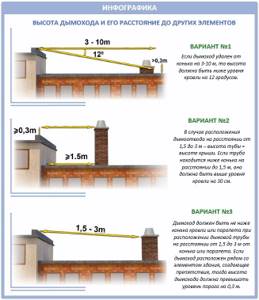
So, regarding the elevation of chimneys above the roof, there are the following rules:
- No less than 1.2 meters above a flat roof.
- No less than 50 cm above the roof ridge, if the pipe is located up to 1.5 meters from the ridge.
- Not lower than the ridge level if the pipe is located from 1.5 to 3 m from the ridge.
- Not lower than the line that can be drawn from the ridge down to the horizon at an angle of 10 degrees, if the pipe is located more than 3 meters from the ridge.
In this case, the smoke duct must be located at a certain distance from other elements of the building, minimum:
- 150 mm for pipes with insulation;
- 500 mm for pipes without insulation.
The minimum permitted pipe height is 50 cm. But these are too low pipes, which are only allowed to be installed on flat roofs without any protrusions. If the roof has a more complex configuration, you will have to tinker and take into account all the protruding parts.
So, if all these parts are located at a distance of 1.5 meters from the pipe itself, then the pipe only needs to be higher than all these elements. If they are closer than 1.5 meters, then the chimney must exceed their height by at least 59 cm:
Design of a structure: rules and approaches
All design work is based on the functional requirements for boiler room chimneys:
- operating modes must comply with environmental standards;
- ensuring good permeability of gases and emissions with their subsequent dispersion in the atmosphere;
- creating natural traction.

The correct choice of the type of pipe, calculation of its diameter, height, aerodynamics fundamentally affects the fulfillment of the above requirements. A competent design process involves carrying out calculations to determine the stability and strength of all structural components, taking into account both the foundation and fastening mechanisms.
The sequence of design stages for chimney boiler pipes is as follows:
1. Determination of the type of structure. The criteria are the following factors:
- expected location of the pipe;
- is there a need for additional fastening;
- technical characteristics of boiler equipment.
2. Calculation of the aerodynamics of the structure. Such parameters as the type of traction (it can be artificially forced or natural) and wind load are taken into account.
3. Calculation of the height of the chimney and its diameter. The initial data for this is the type and volume of fuel burned.
4. Calculation of stability and strength, determination of the type and method of fastening.
5. Drawing up drawings, technical documentation and determining cost estimates.
For private construction, it is possible to carry out independent calculations of the chimney, but obtaining a passport, as well as technical documentation, such an approach to solving the issue will not allow.
Location of the chimney exit from the house
There are also rules for installing a chimney through the roof and wall. Here is an example of installing a pipe directly through the roof:
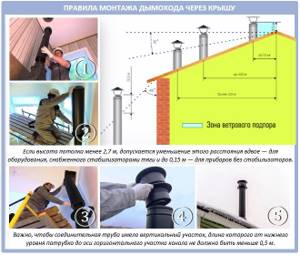
Maintaining a chimney height of 5 meters from the firebox grate to the top cut of the pipe is not difficult if a one- or two-story house was built. But problems arise if the fireplace was installed on the upper attic floor - the height of the ceiling and attic is insufficient.
The installation of a chimney through the wall of a house or bathhouse occurs a little differently:
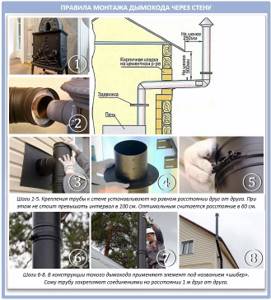
Please note that stoves should be connected to chimneys using chimney pipes no longer than 0.4 m.
What to do if the chimney cross-section is square?
Cylindrical chimneys, especially after the advent of sandwich pipes, are the most common types of devices. But when building a brick kiln, you have to lay out a square or rectangular shape.

In such chimneys, turbulence is formed, which prevents the normal passage of exhaust gases and reduces draft. But for wood stoves or fireplaces, rectangular pipes remain the most popular shape. Such devices do not require an increased level of exhaust gas extraction.
The calculation of a chimney for a wood-burning stove with a square or rectangular cross-section is made taking into account the ratio of the dimensions of the pipe to the size of the blower hole on the stove. This proportion is 1/1.5, where 1 is the internal cross-section of the pipeline, and 1.5 is the dimensions of the blower or ash pan.
Environmental considerations for industrial buildings
In a word, the throughput of the chimney pipe must ensure the unhindered passage of smoke and its release into the atmosphere. Moreover, the environmental aspect is also important here, namely, whether the products of fuel combustion are properly dispersed in the atmosphere.
Thus, during the construction of commercial and factory enterprises, certain sanitary standards are taken into account. And they depend on the weather conditions of the area, the typical speed of air flow, the topography of the landscape and many other factors.
So, what value did you get and is it exactly equal to 5 meters?
Types of chimneys
Chimneys are designed to remove smoke and combustion products harmful to humans from a stove or other heating device outside the room. In any chimney, the draft of the chimney formed during the process of filling the latter with gases must be produced naturally, that is, without the use of additional devices.
Currently, chimneys are manufactured:
- made of brick. For such a chimney, a solid foundation is additionally constructed. It is advisable to add lime to the composition of the connecting mixture used for bricklaying. This will avoid excessive accumulation of condensate, which can destroy the walls of the product;

Brick chimney is very popular
- made of sandwich pipes made from two layers of metal, between which insulation is laid. In most cases, stainless steel is used to make sandwich pipes, and basalt is used as insulation;

Sandwich pipes have a layer of insulation inside
- from ceramics. Such chimneys are highly durable, but also very expensive. Therefore, they are used for arranging industrial chimneys. Due to its heavy weight, a ceramic chimney, like a brick chimney, requires the manufacture of an additional foundation;

Ceramic chimneys are quite expensive
- made of polymer. Such a chimney cannot be exposed to too high temperatures, so it can be used to remove harmful substances from geysers and small boiler rooms. A polymer chimney is highly durable, low cost and easy to install.

A polymer product is easier to install
In some cases, materials for the manufacture of chimneys can be combined. For example, a polymer chimney is lined with bricks.

Combined polymer and brick chimney
The choice of material for making a chimney depends on the intended heating device.
Things to know
The above calculations will only be correct if there are no very tall trees or large buildings located near the house. In this case, a chimney with a height of less than 10.5 m may fall into the zone of the so-called “wind backstop”.
To prevent this from happening, the outlet pipe of the boiler room of a private house located in such a place should be increased. In this case, to choose the optimal pipe height option, you should:
- find the highest point of a large building located nearby;
- draw a conventional line from it down at an angle of 45° to the ground.
Ultimately, the top edge of the assembled chimney should be located above the line thus found. In any case, a country building should be designed in such a way that the boiler room exhaust pipe is located no closer than two meters to tall trees and neighboring buildings.
The height of the chimney is usually increased even if the roof of the house is sheathed with flammable material. In such buildings, the outlet pipe is most often increased by another half meter.
Indicators for practical aerodynamic calculation of a chimney
Chimneys of boiler houses and private houses with solid fuel boilers (fireplaces) require careful calculations taking into account a number of indicators:
- climatic features of the area;
- the terrain and type of soil on which the building is being built;
- regional seismic activity;
- wind speeds and precipitation rates, as well as critical values;
- type of furnace masonry;
- dynamic vibrations of equipment;
- the material from which the chimney will be built and its thermal expansion;
- type of fuel, its heat transfer;
- technical characteristics specific to the boiler;
- outlet gas temperatures.
Using such data, you can calculate:
- height of the structure;
- optimal diameter;
- the permissible weight that the chimney being built may have and, therefore, select a material suitable for arranging the structure.

The calculation results will allow you to determine the diameter of the future chimney, its height and weight
Correctly calculated height and permeability, selection of shape and materials will contribute to natural traction, ensuring good heat transfer. Correct calculation is facilitated by the involvement of professional specialists. Negligence will result in design errors resulting in:
- internal surfaces will be subject to excessive settling of soot and ash;
- the internal cross-section will gradually decrease, which will lead to a weakening of draft and the penetration of carbon monoxide formations into the interior;
- the possibility of ignition of accumulated resins and pipe deformation caused by temperature changes will increase;
- fire hazard will increase.
Location of flues
A chimney as close as possible to the ridge ridge is the optimal solution for operation. The ridge barrier will not become an obstacle to the influence of air flows on the product. Positive result: financial savings when installing and operating the smoke duct. Fire safety requirements allow for any optimal location of the flue relative to the ridge. The owner of the premises, taking into account safety requirements, independently determines the distance. In practice, options are implemented for using boilers with chimneys almost in the center of the facility, at a considerable distance from the ridge. They are typical mainly when arranging premises with industrial furnaces. In industrial facilities equipped with boilers, a minimum distance of the chimney from the ridge fin is practiced.
Height above ridge
In order for the heating device to function without problems, the influence of wind pressure should be taken into account when installing the chimney pipe. What it is? Winds, the structure of the roof and its uneven heating cause turbulent air flows above the building. These air turbulences can “overturn” the thrust, or even cause counterdraft. To avoid this, you should make the height of the pipe no lower than 500 mm from the ridge.
In addition to the location of the ridge, it is also necessary to take into account tall structures on the roof or next to the building, and trees growing near the house.
If the distance from the pipe to the ridge is three meters, then it is permissible to make the height of the chimney level with the ridge. If the distance is more than three meters, the height can be determined using the diagram shown in the photo.
Avoid turns and horizontal sections. When designing the location of the chimney, you should make no more than three bends, and also avoid horizontal sections longer than one meter. If a horizontal section cannot be avoided, the channel should be laid with at least a slight slope.
Operation of chimneys
Proper design and proper installation of pipes - and the boiler room works like a clock. But choosing a chimney and installing it efficiently is only half the battle. Regardless of whether the chimney is brick, ceramic or made of steel modular elements, it is necessary to regularly clean it, removing soot that has settled on the walls.
If the device is used regularly, preventative cleaning should be performed at least twice a year - when the seasons change. Brick chimneys are more susceptible to soot accumulation due to the rough inner surface and rectangular cross-section of the duct. Cleaning hatches must be provided for cleaning and repair.
If the boiler room operates on liquid or gaseous fuel, the temperature of the exhaust gases may not be high enough and condensation will form. To remove it, a condensate collector should be installed in the smoke exhaust duct.
The installation of a chimney according to all the rules and proper operation contribute to warmth in the house and fire safety.
Elevated location
When the external outlet of the channel is located on a flat roof, the element must rise above the covering by at least 0.5 m. If the distance between the outlet and the ridge of a pitched roof is less than 1.5 m, the operation of gas ducts is carried out with the element protruding 0.5 m above the ridge. When the exit location exceeds the specified distance, a new rule takes effect. The height of the top point of the structure must correspond to the height of the top of the roof of the building. Pipe connections are made with crimp clamps using temperature sealants. External fastenings are provided with brackets on dowels or anchors with a distance of 2 m.