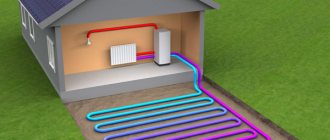
Types of heating systems
To organize space heating, you can use several heat sources at once. Heating installation in a wooden house can be done using the following heat generators:
- bake;
- fireplace (classic or modernized);
- gas convector;
- electric convector;
- heat gun.
When choosing a suitable option, it is worth considering how light and easy it will be to operate. The cost of equipment maintenance becomes an important factor; sometimes incorrect calculations lead to unnecessary costs. The same applies to reducing heat losses to a minimum. An important role when creating heating in a wooden house with your own hands is played by the aesthetic appearance of the units and their compliance with the chosen interior.
Distinctive features of pumping systems
The movement of the coolant at a suitable speed is ensured by a special pump. This helps to avoid temperature loss and also leads to faster heating of the premises.
A common system is a system with natural water circulation. Due to the difference in pressure, the liquid returns to the boiler after cooling. The warming up process is carried out more slowly, but the cost of installing a system of this type is more affordable for a wide range of buyers.
High efficiency can be achieved by installing a circulation pump. The use of such a system makes it possible to use pipes of smaller diameter. With natural circulation, the volume of heated space is limited; when operating a circulation pump, there are no space restrictions. Additional equipment requires money to be spent at the purchase stage, but the efficiency of its use will reduce fuel consumption, so it will bring tangible benefits.
Heating boiler diagram
Water heating in a wooden house cannot be imagined without a boiler that provides heating of the coolant. The boiler is a device operating in automatic mode. There are several types of equipment that use different types of fuel.
Heating boiler diagram
The heating system in a wooden house can be installed using the following types of boilers:
- gas;
- electrical;
- diesel;
- working on solid fuel.
It is worth considering separately the features and types of infrared heating. This model of heating system uses electricity to operate, and at the same time has economical consumption compared to electric boilers. The disadvantage of this option is the inability to heat large rooms; often infrared equipment plays a supporting role.
Pipe installation
In order for the heating complex to operate smoothly and efficiently, it is important to choose the right layout of communications from the boiler to the radiators. There are two main types of it
- Single-pipe. Assumes the presence of one line closed to the heat generator. Devices sequentially crash into it. This heating layout is ideal in a small wooden house, as it is easy to implement and effective for 3-5 radiators in the system. As their number increases, a drawback of the scheme appears: uneven heat distribution in the rooms. The appliances farthest from the boiler receive already cooled water, so the room where they are installed remains cold.
- Two-pipe. The wiring is more complex in execution, in which two highways are laid. The heated coolant moves along the supply line, while branches are made for each radiator separately. As a result, all devices receive water at the same temperature. The second line, the reverse one, collects the spent working fluid. Two-pipe wiring is equally effective for both simple and large-scale branched systems.
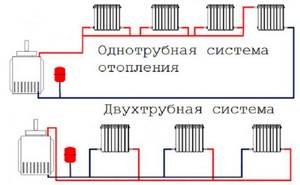
When answering the question of how to properly lay heating pipes in a wooden house, it is worth taking into account the increased flammability of this material. Therefore, it is better to install communications in an open way. If they are intended to be installed in walls or under the floor, it is important to ensure thorough insulation. The best materials for the pipeline are polymeric: polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene, metal-plastic. They are light in weight, so they do not create excessive load on the floors, which is important for log buildings.
Gas boilers
If it is possible to connect to a gas pipeline, a gas boiler in a wooden house will be a good option. There are three types of boilers:
- atmospheric (a distinctive feature is a constant combustion mode, but when heated to a certain level, the gas supply automatically stops);
- turbine (in many ways similar to atmospheric, the difference is the presence of an air mass control system);
- condensation (has a more complex structure, in it the condensate located on the surface of the combustion chamber is first heated, which subsequently heats the coolant).

Condensing boilers from Germany are characterized by high energy efficiency; they have decent efficiency. The only reason to refuse such equipment is the need to install heating in a wooden house without gas.
Electric boilers
Electric heating in a wooden house involves the use of two boilers, one of which performs only an auxiliary function. The main boiler is a model in which the heating element function is performed by a heating element (tubular electric heater). In some cases, an electric boiler with electrodes is used; its operation is carried out using the ionization of water molecules.

Electric boilers
Before choosing electric heating in a wooden house, it is worth considering the subsequent costs. The equipment itself is inexpensive, but the price of electricity may scare off potential buyers. This method has advantages:
- small size of the unit;
- complete safety of use;
- possibility of autonomous operation (without human intervention);
- Efficiency is close to 100%.
Solid fuel boilers
If the cost of electrical energy is unaffordable and there is no possibility of connecting to gas, the best choice would be a solid fuel boiler in a wooden house. There are various models of equipment with different firebox heights. One load of fuel allows the unit to operate autonomously for up to 12 hours. The most popular types of fuel are coal and wood. This type of boiler is the most profitable in terms of operating cost.
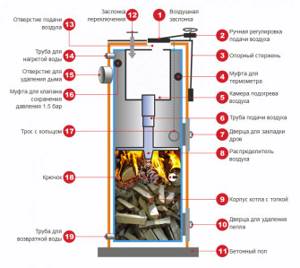
Solid fuel boilers
The disadvantage of heating in a private house using solid fuel boilers is the dependence of the efficiency on the level of humidity. You should not choose too cheap models, otherwise you will have to deal with such troubles as the formation of soot and soot. Most inexpensive boilers require frequent cleaning, which takes a lot of time.
Diesel boilers
One of the common options for heating a wooden house is purchasing a diesel boiler. The advantage of such systems is their ease of installation and subsequent operation. When installing most models, you do not have to worry about the need to create a complex chimney system.

Diesel boilers
When using water heating, such equipment will have a number of disadvantages:
- high fuel consumption (15 liters per day) and corresponding maintenance costs;
- low efficiency rate (from 75 to 85%);
- the need for constant monitoring (if bad fuel is used, work may simply stop).
Among all the options, this one has the lowest efficiency and the need for constant monitoring, however, quick heating of the room and the ability to regulate the temperature make the installation of a heating system of this type popular. You can also choose a diesel boiler if fuel costs do not become a serious problem for you.
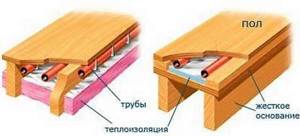
Warm floor
Modern homes often use underfloor heating to create a more comfortable environment. If the power is correctly calculated, such a system can be used as a method of heating rooms if there is no severe frost outside. When using a water system, pipes are laid under the final coating, thereby heating the surface.

Warm floor
If you use an electric heating connection in a wooden building, you should definitely install heated floors. This will increase consumption slightly, but the increase in comfort will be clearly felt.
Underfloor heating is rarely used separately as heating; most often it is part of a combined system. When installing, take into account the need for additional thermal insulation to comply with fire safety regulations. Before installation, it is worth taking care of the possibility of temperature control in order to control the condition of the system.
Electric heating

If in your case schemes using gas boilers are not available, then you can use electricity as a coolant. There are a large number of options for creating heating. For example, you can make a heated floor, which is purchased with ready-made mats and installed during the floor installation process.
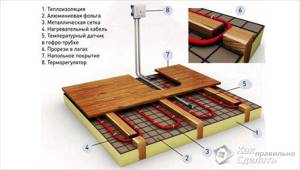
Electric heated floor
You can also use an electric water boiler. Metal-plastic pipes Ø16 or Ø20 cm are laid from it. They are mounted on a heat-insulating layer. As for the scheme itself, here you can choose a combined or spiral one.
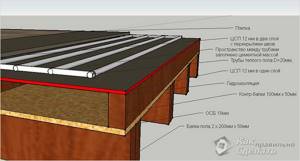
Water heated floor
From the collector pipe, a contour should be drawn from the wall at a distance of ten centimeters. The next contour should be located at a distance of forty centimeters from the first. This gap is necessary in order to mount the return line. Thus, the pitch between the supply and return pipes will be twenty centimeters.
The pipes are secured to a special mesh using fasteners. Once the entire system is ready and all pipes have been laid, it should be checked. This can be done in two ways. For example, you can pour water under pressure. If a leak is detected, then it should be repaired immediately. Another option is simpler; for this, air is pumped into the system. At the location of the leak, the air will make noise as it exits, and you will notice a leak.
It is necessary to produce high-quality thermal insulation of the floor.
Options for choosing the right system
It is impossible to talk about a clear advantage of one system over all others; in a particular case, your own option is optimal. The following factors should be taken into account:
- cost of equipment;
- cost of radiators and other consumables;
- operating and maintenance costs;
- efficiency;
- exercising control;
- frequency of residence in the house (all year round or only in warm weather);
- types of thermal media used.
Each factor must be taken into account to make an informed decision. Do not forget about the aesthetic component of the question of how to hide and conceal heating pipes. All potential problems should be considered at the stage of choosing the type of system. Do-it-yourself heating schemes for a wooden house allow everyone to carry out installation independently without the involvement of third parties.
The relevance of the issue of heating wooden houses
Heating of houses made of logs, beams or carriages
Problem No. 1: Ventilation of the log house
The main feature of houses using log technology, a particular and most famous example of which are houses made of logs, is the crown construction of the wall, between the crowns of which there is actually a through gap. According to the technology, this gap is laid with various insulating materials in order to prevent the penetration of cold air into the house, as well as to reduce heat loss.
In winter, the air temperature outside is lower than in the house, but the air pressure, on the contrary, is higher. As a result, if there is any connection between the external and internal volumes of air, then a baric flow of air is formed from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. But it should be noted that air cannot flow inside the house endlessly. A house is not a balloon; it cannot inflate.
Warm air in the room rises. As a result, there is “excess” air at the top of the room. It needs to go somewhere: part of it, cooling down, falls, and part is pushed through the cracks back into the street.
It is this law of nature that is explained in school through an experiment with a candle at the doorway.
Thus, it becomes clear that in log technology this process is inevitable. But it must be kept to a minimum. How to do it? It is necessary to use materials and techniques that will maximally prevent the penetration of air into the room.
This is used for the inter-crown groove of insulation materials, which not only have low thermal conductivity, but also have poor air permeability. For example, periodic caulking of a log house is necessary to eliminate the presence of voids in the groove and reduce the ventilation of the log house.
Another method or technology is sealing, primarily external, of inter-crown grooves. The most well-known is the “warm seam” technology, when, in addition to inter-crown insulation with good porosity and low thermal conductivity, insulation with low vapor permeability and airflow is used along the outer perimeter, and then it is additionally sealed with a special wood sealant. This sealant has high elasticity, which allows it to compensate for wood movements.
Problem No. 2: Required thermal resistance of a wooden house
Another pressing issue in heating a wooden house is the thermal resistance of external walls and the heat-storing properties of wood.
Thermal resistance depends on the thermal conductivity of the wood and the thickness of the wall. If the thermal conductivity of the wood species used in construction differs insignificantly, but there are still differences, then the thickness of the wall very noticeably affects the thermal resistance, and therefore heat loss. hence the need to heat more.
It turns out to be a very strange situation. If we are talking about a stone house, then everyone understands that the thicker the wall, the better. In relation to a wooden house, on the contrary, there is often an illusion that it will be warm in the plank house. The pattern for stone and wood is the same!
If the norm for comfortable living in central Russia is the thickness of a wooden wall or the diameter of a log of 37 cm, then you need to understand that smaller sizes will not correspond to comfortable conditions, but will only suit acceptable or insufficient operating conditions.
How do you know what diameter of log or thickness of wooden wall to choose? The most primitive recommendation: “Focus on the average January temperature of the area. Think of it as the radius of the log. Accordingly, to obtain the diameter of a log or the thickness of a beam, it is necessary to multiply by 2. For example, if the average January temperature is 16 ° C, then the diameter of the log should be at least 32 centimeters, and preferably larger. This way you will only save on heating your home.”
Problem No. 3: Low thermal storage capacity of wood
This is not a problem, but a myth, but when it comes to heating a wooden house, it cannot be avoided. The fact is that issues of heat accumulation in the heating issue are often used to lobby for this or that material. But this property, in fact, does not have a direct relationship between “good or bad.”
A simple example. A brick stove accumulates heat well, but a metal stove does not. But it is precisely thanks to poor heat accumulation, but good heat transfer, that a metal stove will heat the room faster. I think the idea is clear.
The situation in wall materials is also ambiguous. Firstly, not every “stone” material has good heat accumulation. For example, a gas silicate block does not really shine with this ability. Secondly, having good heat accumulation, such a material quickly absorbs heat, including from the air. Accordingly, the heating of such a room will be slower.
Do not bake wall material. It should most likely be inert, retain heat in the room, and not take it away.
Heating of frame wooden houses
According to their general concept, such houses are not “monolithic”, since an absolutely tight fit of wood materials to each other is impossible. For this reason, there may also be a problem with the walls being blown through.
It must be added that the issue of ventilation is relevant for any construction. Since microcracks always occur, including in stone houses. On the other hand, it is the micro-slits that provide the flow of fresh air into the house.
Modern technologies are aimed at controlling this process. Therefore, the first task is to stop the flow of air into the house as much as possible, making it as airtight as possible, and then organize a special ventilation system for the flow of fresh air. Control of air flow, as a necessary condition for living in a house, is beneficial both for manufacturers of building materials and for their sellers and construction companies. Everyone profits from this.
In order to solve the problem of uncontrolled air flow in wooden frame houses, special films or membranes are used. An air-protective film is installed on the outside, the purpose of which is to prevent any air from entering the house through the walls. It is for this reason that it must be glued. Otherwise, its purpose will not be realized.
At the same time, a vapor-tight membrane is placed inside, the purpose of which is to maximally prevent air, and especially water vapor, from escaping from the house through the walls.
Insulation materials are placed inside the frame of the camp, which are significantly superior to wood in their thermal resistance. As a result, the cost of heating a frame house is lower, but only if all the technology conditions are met, the films perform their function.
To say that a frame house is cheaper is not entirely correct, since only the use of high-quality materials, including films that are capable of fulfilling their purpose for a long time, can solve problems with ventilation.
The technology of frame house construction itself was invented and used in two specific cases:
- it is necessary to quickly build temporary housing, so frame houses in the USSR were made during the construction of the Baikal-Amur Mainline and in a number of other construction projects
- construction of more permanent housing is inappropriate due to natural conditions
- In earthquake zones, for example in Japan, frame houses were traditionally built
- in the USA, in the tornado zone, they prefer to build frame houses, since they are quite easy to restore (the concept of the American frame house: “a house breaks easily, but is also quickly restored”)
Types of thermal media
Thermal energy can be transferred in various ways; the following options can be considered:
- air heating of a wooden house;
- using water (the most popular option);
- stove heating in a wooden house;
- underfloor heating systems.
We have already discussed the underfloor heating system above; it will not be able to fully provide the house with heat in the winter. This option is used as part of a system with different coolants or when living in a cottage only in the summer.
Water is most often used as a coolant for many reasons. This is the easiest way to provide room heating; the system will have high performance and efficiency.
Stoves for heating a wooden house are a traditional option for heating rooms. This method has been tested by time; in our time, it remains in high demand. Stove heating in a wooden house is sometimes not capable of heating distant rooms, which becomes a serious drawback. However, when combined with other options, the stove demonstrates good efficiency indicators.
The use of air as a coolant is also often used. It is relatively safe; the downside is often significant heat loss during long-distance transmission. If you plan to heat houses with a large area, you will have to think about a way to avoid a drop in temperature when moving.
Separately, it is worth noting quartz heating, which is more economical compared to classic electric heating systems. Quartz equipment consumes several times less electricity, while being able to heat rooms in a short time.
Types of heating of wooden houses
To keep a log house cool in summer and warm and cozy in winter, it is important to choose the right heating options based on modern heating systems
Electric heating
Heating a wooden house using electric heating guarantees residents ease of control of appliances and the absence of harmful emissions. In addition, there is no need to build a separate boiler room and chimney.
The electrical system has virtually no shortcomings, but it can be affected by external factors in the form of constantly increasing resource costs and imperfect operation of electrical networks with frequent voltage drops. To protect yourself from such problems, you can stock up on a generator, but in this case the issue of saving becomes moot.
If electric water heating is used, the risk lies in the coolant, which can leak or freeze if the equipment is not used correctly.
Electric heating is provided by:
- heaters (mounted, floor, built-in - such as underfloor heating);
- radiators equipped with individual heating elements;
- radiator heating circuit, the “heart” of which is considered to be a heating electric boiler.
Gas heating
Gas heating in a wooden house is an easy-to-maintain and fairly effective method that provides high efficiency, but at the same time requires increased attention to safety precautions. This is especially true for wooden structures in which it is planned to install a gas boiler.
In addition, not all suburban settlements are supplied with gas, which is also a problem that can be solved by installing a special container on the site for storing imported gas - a gas holder or purchasing cylinders, but this will significantly increase costs.
Solid fuel
Solid fuel equipment is considered the best option for heating those houses that do not have access to a gas pipeline and where there is questionable operation of electrical networks.
Such heating is effective and less expensive than an electric unit, and is also attractive due to the low price of the equipment and the ability to install all the elements yourself. Modern models of solid fuel boilers include components and parts that improve their efficiency: for example, an automatic machine for dosed supply of coal into the boiler.
For normal operation of the unit, it must be installed on the ground floor or in a specially built boiler room.
The raw materials for heating this type of boiler are coal, peat, firewood, sawdust or pellets. The device becomes very hot during operation, which increases the risk of fire.
To ensure safety, it is important that the boiler room is lined with non-combustible material. In addition, it is necessary to take care of the premises intended for storing raw materials
Pechnoe
Stove heating in a wooden house provides warmth and comfort. The most commonly used stoves are the Swedish type, which combine not only heat transfer functions, but are also equipped with a hob and oven. If desired, such a stove is complemented with a fireplace and sleeping places are arranged against its wall.
The disadvantage of stove heating is the likelihood of poisoning by combustion or ignition products. In addition, the stove can heat a house with an area of no more than 100 square meters using wood or coal. m.
Liquid fuel
Oil boilers are also particularly popular in areas where other heating options are not possible.
Diesel fuel (diesel fuel) is used as the main raw material. The advantage of this type of heating is considered to be the low cost of raw materials, and the main disadvantage is the possibility of carbon monoxide poisoning, the occurrence of fires if safety precautions are not followed, and the need to equip special premises.
Infrared
Considering the difficulties with popular heating systems, an innovative and efficient heating scheme based on infrared radiation was developed.
The principle of operation of this equipment is the operation of heating elements that radiate thermal energy on the surface of a wooden house (furniture, walls, ceilings, floors), which, when heated, release heat into the air. At the same time, warm air rises and mixes with cold air, which avoids overheating and saves up to 70% of energy.
Sometimes combined types of heating are used, when several types are used simultaneously. This can be heating with an electric boiler, the functions of which, in the event of a power outage, begin to be performed by a solid fuel unit.
What can you save on?
When purchasing equipment and installing a heating system, the issue of saving invariably arises. Correct calculations of power will allow you to spend less money, while in terms of comfort you will not lose anything. For example, there are several options for installing a gas boiler in a wooden house. The heat exchange pattern and overall efficiency depend on its location.
The efficiency of the system depends on how good the heating radiators are, which ones are best to use in a particular situation, calculations will show. These elements may have different designs. A massive element will not be highly efficient if you need to heat a small room. Radiators according to the type of material used are divided into the following types:
- aluminum (they can be cast or obtained as a result of processing a workpiece);
- panel steel (ease of installation, efficiency of use);
- cast iron products (they take a long time to heat up, but can be used for more than half a century);
- tubular steel;
- modern bimetallic structures.
If gasification is present, you should first consider options using gas for heating. Options may vary in cost; you can always choose the best option for a particular case. It is possible to install a stove under a gas boiler, which will make your life more comfortable.
Features of installing heated floors (water and electric) in a wooden house
The technology for laying water-heated floors in a wooden house depends on the type of floor. If the first floor and basement are covered with reinforced concrete panels, then the heating system is made according to the “classical” scheme:
- leveling mortar screed;
- insulation (extruded polystyrene foam, perlite concrete);
- heating cable or plastic pipes;
- leveling screed covering the heated floor;
- finishing coating (tiles, parquet, laminate).
It is more difficult to make a warm floor when wooden beams are used to cover the basement and first floor. In this case, there is no solid base, so the structure is assembled according to one of two options:
Option #1
- a board is placed underneath the beams to support the insulation (mineral wool, polystyrene foam, ecowool, perlite);
- Having laid the thermal insulation, plastic pipes are attached to the side faces of the beams;
- cutouts are made in the beams to allow pipes to pass through;
- lay a finished wooden floor from tongue-and-groove boards or a rough floor for laying parquet or laminate flooring.
Option No. 2
- Thick plywood or OSB board (15-20 mm) is laid over the beams;
- wooden blocks with a cross section of 50x50mm are attached to the coating;
- insulation is laid between the bars;
- lay a material that reflects heat (aluminum foil);
- pipes are placed on top of the thermal insulation, fixing them to the bars;
- install a subfloor from boards, gypsum fiber sheets (gypsum fiber sheets), particle boards or plywood;
- lay the finishing coating (ceramic tiles, parquet, laminate).
In advanced systems mounted on wooden floors, heat-distributing metal plates are used. They perform two functions: they form channels for pipes and reflect heat.

To simplify installation, you can use ready-made factory chipboards with milled recesses for pipes. In addition, on the market you can find panels made of dense foam plastic with stamped channels (foam shield). In them, the pipework is fixed quickly and easily.

If foam is used, there is no need to attach a board to the beams to support the insulation. In this case, rigid insulation is attached directly to the surface of the subfloor. After this, a substrate under the laminate is spread on it or an adhesive solution is applied, then a reinforcing mesh is applied and the tiles are laid.

The main disadvantage of ready-made structures (foam panels and milled chipboard) is their high cost. Therefore, some home craftsmen use a cheaper method of forming channels. They stuff wooden strips onto the base, leaving gaps between them for laying pipes.
Heating system installation
Self-installation forces you to take into account the following operating features:
- installation of special compensators;
- selection of material for pipelines and radiators;
- correct connection of all elements so that there are no leaks;
- wiring on all floors, reducing the number of risers to a minimum.

It is worth deciding where the boiler room will be located in a wooden house.
For its arrangement, basements or a separate extension can be used. There are always different options for how to attach a boiler room to a wooden house, differing in the cost of installation, the complexity of the work and the ease of subsequent operation.
How to make heated floors in a wooden house: design and installation options
Warm floors are an invention of the 20th century. Our great-grandfathers did not have electric heating cables or gas boilers. However, they came up with their own heating method. To do this they used the walls of buildings. When making masonry, they left channels in them for the movement of hot furnace gases.
Today there is no need to resort to such tricks. You can make heated floors in a wooden house with minimal effort and money.
Choosing a heating heating system is very simple:
- Electrical cable or mats with flat current-carrying conductors;
- Warm floor based on plastic pipes with liquid coolant.
Both heating options have earned positive reviews. They are equivalent in comfort and heat transfer, but not the same in energy cost. Electricity is significantly more expensive than gas, so heating cables for heated floors are best used in small spaces: bathrooms, kitchens and hallways. A liquid system made of pipes, a gas or solid fuel boiler is optimal for bedrooms and living rooms.
A lot has been written and said about the fact that heated floors are better than radiators.
We will only note its most important advantages:
- Optimal heat distribution. The comfortable temperature zone coincides with the living space (from the floor surface to a height of 1.7 meters). When the batteries are running, the air near the ceiling warms up the most.
- A radiator heating system activates dust movement to a greater extent than a warm floor.
- From the point of view of interior aesthetics, heated floors are superior to radiators.
Single pipe system
The heating system can have a different number of circuits; the single-pipe version is most common. A single-pipe system ensures that hot water rises due to the difference in mass and density with the colder part of the coolant.
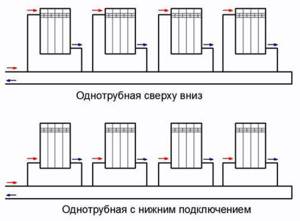
Single pipe system
This option is best used for small houses, since with natural circulation the difference in temperature on different floors will be felt. A good way to get rid of this drawback is to use a circulation pump. It is worth calculating all the expenses to understand whether this option will have truly suitable efficiency.
Installation of a "warm floor" system
We use heating mats
Stage 1: it is most convenient to use electric heating mats, although they will cost 20-25% more than cable. A groove is made in the wall and floor where the cable in a corrugated tube will go, connecting the heating mats to the energy source, and the temperature sensor. Then all debris and dust are removed from the floor surface. Heating mats can be placed directly on old tiles. The mat mesh is easy to cut, and if the mat is rotated, a cut can be made, but the heating cable must not be touched.
Stage 2: the mat is attached to the floor using a heat gun or tape. Sometimes an adhesive layer on the mesh is already applied to the surface of the mat, and the mat itself sticks well.
Stage 3: a layer of tile adhesive is applied on top of the mat. You need to let it dry completely for 5-7 days.
Stage 4: all connections must be made and the thermostat connected. The functionality and serviceability of the heating system is checked.
Stage 5: You can lay the floor covering on the completely dried adhesive base.
We use a cable
main source of heating
Stage 1: the floor is cleared of old tiles or other material before laying the heat insulator. All debris is swept out and dust is removed.
Stage 2: sheets of heat insulation are laid out on the cleaned surface. The joints between the sheets are taped.
Stage 3: a reinforcing mesh is laid on top of the thermal insulator and an intermediate screed no thicker than 3 cm is poured. Wait 3-5 days until it dries completely.
Stage 4: after the screed has completely dried, mounting tape is applied to it.
Stage 5: a detailed cable laying diagram is drawn up. You need to start laying from the bridge connecting the wiring to the thermostat. It is necessary to take into account the cable manufacturer's recommendations regarding the minimum bending radius of the cable and the minimum distance between the cable threads. Do not run the cable under areas where plumbing fixtures and furniture will subsequently be installed.
Stage 6: the thermostat is installed inside the corrugated tube. All components of the electrical system are connected.
Stage 7: after checking the operation of the heating system, a second screed 3-10 cm high is laid. You must wait a month until it dries completely.
Stage 8: Now you can lay any flooring.
Two-pipe system
If there are two circuits, the hot coolant enters the radiators through a separate line. This ensures faster heating of the rooms, as well as the same temperature in opposite parts of the building. In large houses, uniform heating is important, so this option is optimal there.
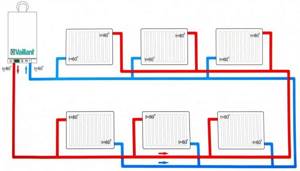
Two-pipe system
Sometimes there is a need to expand the house and make new extensions. When using a double-circuit heating system, this will not be a problem; such a system is considered scalable, that is, you can always extend any line. When building houses with a large area of premises, opt for a two-pipe system.