What can and cannot be insulated with sawdust?
To ensure the most comfortable living conditions in the building, it is necessary to take care of the insulation of the following structures:
- floor on the ground in buildings with a warm basement or basement;
- ceiling over a cold basement or underground;
- exterior walls;
- covering the upper floor when designing a cold attic or technical floor;
- covering in the absence of an attic;
- pitched roofs when arranging an attic.
Since sawdust is a bulk material, it is almost impossible to use it to insulate walls or pitched roofs. They are best suited for increasing the heat-insulating characteristics of the attic floor and the floor above the cold underground .
Nowadays, although there is a large assortment of thermal insulation materials on the construction market, sawdust is not widely used. Most often, they are chosen by those owners who prefer to use completely natural and environmentally friendly materials in construction.
Main types of floors
All floors can be divided according to the base material:
- concrete;
- wooden;
- iron.
Concrete floors are used in brick, stone, block and monolithic houses. Their advantage is their high strength and the fact that they, to some extent, act as a reinforcing belt that tightens the walls and prevents them from being squeezed out under load.
Wooden floors are used where it is necessary to reduce the weight of the building as much as possible . They are less durable than concrete structures, but much easier to install and also noticeably cheaper.
Iron floors are used only in metal frame houses, so they are not widely used.
In addition, floors can be divided according to the shape and material of the subfloor :
- concrete screed;
- plywood or board;
- wooden logs covered with plywood or boards.
When choosing a method of insulation, it is important to take into account both the design features of the load-bearing structure of the floor and the movement of air in the underground space.
Otherwise, combating floor heat loss will not only be ineffective, but will also lead to water settling on the supporting structure, which will cause the latter to begin to collapse.
Why is insulation necessary?
The thickness of the wooden floor in a house does not always meet the requirements of heating engineering.
Making it thicker is not economically profitable, so they resort to various heat-insulating materials. The future owner of the house is faced with a choice: whether to take into account the requirements for thermal protection or take into account only the strength of the structures. Timely measures taken to insulate the floor allow you to avoid the following troubles in a wooden house:
- excessive heating costs;
- cold floors;
- condensation from the warm air, resulting in wood rotting and the appearance of fungus and mold.
Carrying out additional measures during construction will avoid high operating costs and the need for frequent repairs.
Pros and cons of sawdust as a material for insulation
Despite the regular skepticism towards the use of sawdust, they have several undoubted positive qualities over other heat insulators. And some of their disadvantages are eliminated by using them in combination with additives.
- Low thermal conductivity. Wood itself is a good insulator, and the dense layer of sawdust also contains air, which improves its resistance to heat transfer. According to this indicator, the purest sawdust is only 2-3 times inferior to such materials as foamed polymer and mineral wool. But by increasing the thickness of the thermal insulation layer, a comparable result can be achieved.
- Original cost. You can buy wood waste inexpensively, and some sawmills generally give it away for free. So the key costs are solely on delivery.
- Environmentally friendly. Natural material that does not contain or emit any harmful substances.
- Passability of steam. This is the ability of a material to absorb moisture and then evaporate it in a real way. In terms of this indicator, only acoustic heat insulators are comparable to sawdust. Most other materials are practically impervious to steam.
- Long service life with good installation. The age of individual houses in which the floors are insulated with sawdust can reach 100 years or more.
- Fire hazard. Floor insulation with sawdust, and even more so with shavings, is dangerous due to the danger of rapid fire when exposed to an open flame. However, even the purest sawdust, finished with modern fire retardants, is already quite difficult to ignite.
- Drying out. Over a certain time, the layer of any sawdust certainly decreases in volume. It is necessary to backfill or initially fill a layer of greater thickness.
- Prone to rotting. If exposed to high humidity and poor ventilation for a long time, they may rot or develop mold. Due to this, it is considered mandatory to treat the material itself and all structural components of the floor with an antiseptic.
- The specifics of this type of insulation do not imply its use under a concrete screed. The sawdust thermal insulation layer is unable to withstand the weight of concrete.
- Attractive to insects and rodents. Floor insulation with sawdust and lime practically eliminates this disadvantage.
- All these shortcomings ultimately lead to the fact that sawdust insulation needs to be looked after, sometimes checking its quality and eliminating noticed problems.
Advantages and disadvantages of sawdust as insulation
A sufficient number of positive characteristics allowed sawdust to become famous:
- low thermal conductivity and high degree of protection of the structure from freezing;
- availability of the material and its low cost (at some sawmills they are willing to give away sawdust for free);
- environmental safety and naturalness;
- the ability to carry out insulation work with your own hands.
When using sawdust, you should remember their negative qualities and features:
- any wood dries out over time, and the percentage of volume reduction in sawdust is quite high;
- susceptibility to rotting;
- the occurrence of mold;
- sawdust is an excellent habitat for various microorganisms, insects and rats.
These shortcomings are not inevitable. They can be eliminated by using sawdust in tandem with other materials. as protective additives to sawdust:
- clay;
- lime;
- cement;
- boric acid (antiseptic).
In this case, the mixture will not be susceptible to the appearance of fungus and the appearance of various living creatures.
How to use sawdust
Sawdust is never used in its pure form. To protect the material from adverse factors, eliminate shortcomings and increase service life, a solution is made, which, in addition to sawdust and water, includes one of the following components:
- clay;
- lime;
- cement;
- gypsum.
Clay based solution
Environmentally friendly clay, which has been used for hundreds of years to insulate wooden huts, is the best material for preparing insulating mortar or clay briquettes.
To prevent thermal insulation from cracking and turning into dust in the future, you need to know a few rules:
- Only fatty clay is suitable for insulation; skinny varieties will crack after a while.
- It is very important to soak the material correctly. The aqueous clay solution should have the consistency of thick sour cream. This can be achieved by mixing the components in a 1:1 ratio and then leaving the mixture for at least a day. After thorough mixing, if the composition turns out to be liquid, clay is added; if it is very thick, it is diluted with water.
- To lay out the floor under a screed or create briquettes, the clay solution is mixed with dry sawdust in the same proportion (1:1). In the bathhouse and in wet rooms, the clay castle also performs the function of waterproofing.
Thermal insulation with cement and gypsum base
For thermal insulation of log house floors, a cement-wood mixture is most often used.
This is explained by the fact that it is much easier and faster to insulate a floor with sawdust and cement than with a clay-based composition. The solution is made within a few minutes and does not shrink when hardened. Typically, wood waste and cement are mixed in a ratio of 10:1.5. Experts recommend adding lime to the mixture, in which case the ratio of the parts will be: 10:1:1.
The gypsum composition is made in the same proportions as the cement-based mortar. But when making the mixture, you need to take into account that alabaster dries very quickly and after mixing the solution you have no more than half an hour to work. Therefore, many people prefer to use cement, which dries much slower.
It is advisable to use gypsum for the manufacture of piece blocks. A gypsum mat will dry completely within 2-3 days, while a cement mat will take at least a week to dry.
Lime-sawdust insulation
A mixture of lime and sawdust is used exclusively for dry backfilling. To prepare the composition, dry, settled wood chip waste and lime powder are taken in a ratio of 10:1. Lime here acts as an antiseptic.
The mixture shrinks very much, and it is periodically fluffed and topped up. This method is usually used to insulate the attic, where access is much easier than underground.
Floor pie during insulation
Insulation is not the only component of proper thermal protection of a structure. Sawdust requires preventing water and steam from getting on it, so waterproofing and vapor barrier will become additional layers. It is very important not to confuse their location, otherwise all insulation work will be pointless.
Insulating an attic with sawdust will require laying the components in the following order from bottom to top:
- floor design;
- vapor barrier;
- sawdust;
- waterproofing;
- attic floor.
Scheme for insulating an attic floor
When insulating the floor above a cold underground, the layers are arranged in a different order:
- floor design;
- waterproofing;
- sawdust;
- vapor barrier;
- first floor floor.
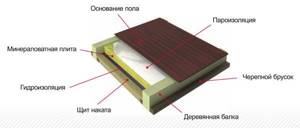
Scheme of floor insulation above a cold underground
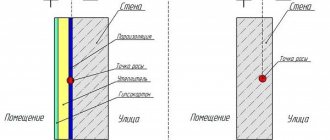
Sometimes it is said that it does not make much difference which side the vapor barrier is laid on, but this is not true. Steam can penetrate into the insulation only from the side of warm air, so it is logical to install protection against it inside the heated room. Waterproofing, on the contrary, protects against condensation that falls from the cold air onto a warmer surface. Failure to comply with these rules will lead to disastrous consequences for the insulation and it will cease to perform its functions.
How does heat loss occur?
To determine the best way to insulate a floor, you need to understand how heat escapes through it.
The operation of heating systems heats the air, which rises to the ceiling and partially escapes through it into the atmosphere.
Proper insulation of the ceiling reduces heat loss, but allows a small part of the air to escape, because this is necessary to maintain optimal humidity .
Read more about proper ceiling insulation here.
The air escaping into the atmosphere creates a vacuum in the rooms, due to which fresh air penetrates inside both through windows and doors, and through various cracks and loose connections. The air entering from the street has a lower temperature than the air in the room, so when mixed, the overall temperature decreases.
If the house is insulated correctly, then as it passes through the insulation, the street air gradually heats up, thereby reducing the temperature difference caused by its appearance.
Air coming through the floor first passes close to the foundation, then moves through the cold crawl space, making it much cooler than the temperature of air entering the room through other means.
Because of this, the influence of an uninsulated floor on the climate in the room is much higher than that of uninsulated walls, and this effect manifests itself even if the underground space is completely isolated from the street.
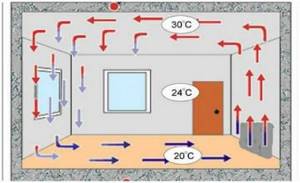
In this case, circulation begins.
The heated air rises to the ceiling and creates a local low-pressure zone that sucks cool air from the subfloor.
Then the cooled air sinks to the floor and is drawn into the underground by the rarefaction resulting from the movement of warm currents.
Insulation cannot prevent circulation, because it is caused by the difference in the masses of cold and warm air , however, the speed of movement of air from the underground through the insulation is sharply reduced, due to which it has time to heat up, which leads to a reduction in the temperature difference.
Which sawdust to choose
Going into the forest to cut down a tree and use it for sawdust is not the best option. There are many other ways that cause minimal harm to nature and are more intelligent. Sawdust obtained during carpentry is ideal for insulation. This material has good moisture content and is less susceptible to damage by mold, mildew and insects.
Sawdust is available in large quantities at sawmills. They are waste of wood that has not yet dried, so their characteristics are worse than those of the previous ones. But such material can also be used to insulate the floor in a wooden house.
It is best to choose small chips. They will be able to provide the most effective thermal insulation.
Recommendations for material selection and protection
Fresh wood waste cannot be used for insulation.
It is necessary to let them rest for at least three months, but it is better to leave them for a year, since wet sawdust contains specific substances that prevent adhesion to cement. If it is impossible to postpone insulation for a long period of time, liquid glass is added to the sawdust before use to increase adhesion. Round sawdust is wet and must be dried before use. It is advisable to do this in the summer; while drying, it is not recommended to cover the sawdust with polyethylene, otherwise they may smudge.
Insects may remain in the material obtained from bark processing, so such sawdust cannot be used for thermal insulation.
For thermal insulation of the floor, it is best to use sawdust obtained from cutting coniferous trees, as they contain resin that prevents the formation of mold and mildew. Fragments of hardwood, which are more resistant to moisture and dampness, are usually used in baths and saunas.
The material is protected from biological factors (mold, fungi, parasites) using antiseptic agents that are added to the main solution. You can buy ready-made antiseptics, which are available in large quantities on the market today; you can also use proven folk remedies - copper sulfate or boric acid.
A fire retardant should also be added to the insulation composition to protect against fire. For these purposes, you can use borax (no more than 7% of the total mass of dry insulation), or take a ready-made product.
Preparing to start work
Before laying the insulation, you need to determine its thickness. This value depends on the construction area. In a wooden house that is used all year round, the thickness of sawdust for the floor will be approximately 30 cm. After this, it is better to calculate the exact volume of necessary materials so as not to encounter difficulties during the construction process.
For insulation work you will need:
- sawdust;
- lime;
- cement or clay;
- wood antiseptic (for example, boric acid);
- container for diluting the mixture;
- kneading spatula;
- watering can for spraying the finished mixture with boric acid.
Types of sawdust

Sawdust is a product of wood processing, and its shape depends on the type of technological operation as a result of which it was formed:
- Small trash. It is formed when cutting wood. The parameters of the dust strongly depend on the characteristics of the saw.
- Chips (3-5 cm in size). It is obtained by drilling and planing.
Depending on the method of wood processing, the fractional composition of sawdust also changes. Fractions usually go on sale in the range of 5-30 mm. Being highly environmentally friendly, sawdust is very inexpensive. In addition, they are lightweight and have excellent sound and heat insulation properties. Sawdust of various species is further used:
- ate;
- pine trees;
- oak;
- ash
Work order
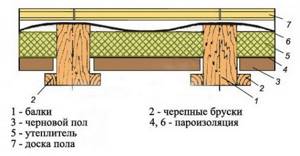
For ease of understanding, all the necessary steps are presented point by point:
- Installation of cranial bars [2] from the side surface of the joist. The cross section is recommended to be no more than 30 by 40 mm.
- Laying on cranial bars [3] made of third grade boards or plywood sheets. The material is not secured.
- Laying waterproofing material [4] , which can be an ordinary polyethylene film. It is secured to the joists using nails with wide heads.
- After this, sawdust [5] is poured or a sawdust-cement (sawdust-clay) mixture is laid. If you use clean sawdust, they must be lightly compacted. The cement-based mixture will require 4 weeks to dry completely, but you can proceed to the next stage after about 14 days.
- After the drying process is completed, the thermal insulation layer is checked for voids . If they are found, it is necessary to add sawdust.
- The installation of a vapor barrier layer [6] allows you to complete the process of protecting the insulation from moisture. The following can be used as a vapor-proof material:
- plastic film;
- polypropylene film;
- foil film;
- reinforced;
- laminated.
a gap for air circulation between the vapor barrier film and the flooring . If the height of the lags is not enough for this, thin counter-battens .
8. The last stage is the installation of flooring [7] .
Sawdust and clay

Clay can also be used as the main material for insulating floor structures. It is a reliable binder and meets safety criteria. This method provides additional waterproofing. A film up to 220 microns thick can serve as a protective element. This design feature does not allow the use of sawdust insulation for walls and ceilings, because they must “breathe” so that drops of condensation do not appear. To prevent the film from moving and allowing moisture to pass through, it is glued to the floor surface. The overlap is deliberately left wide.
The main stages of preparing the heat-insulating mixture:
- add water;
- mix the solution in the ratio: 70 kg of clay without taking into account the error per 100 liters of liquid;
- bring the solution to the consistency of rare sour cream, taking into account the fraction of wood chips.
It is impossible to bring large volumes of the mixture to the desired consistency without the help of special equipment. A construction mixer is suitable for this purpose. For the first portion, two buckets of bulk material will be enough. Liquid and wood are gradually added.
Laying is done in the following way:
- the first layer is poured, no more than 10 cm high;
- compaction of the layer is carried out with a solid flat object, for example, a shield;
The mixture hardens within two weeks. This period depends on the room temperature, as well as the fraction and humidity of the original bulk material. Most likely, grooves are formed in the hard layer. They are sealed with clay. Experts recommend covering the heat-insulating material with a special mastic that will protect it from moisture. The final stage involves laying the flooring.
Features of this type of insulation
When using sawdust for the floor in a wooden house, you need to prepare and take into account the following features of the material:
- All wooden elements, including sawdust, must be treated with antiseptic compounds to avoid damage by insects, mold and mold.
- This technology requires a temporary reserve, since the sawdust mixture must dry and gain strength.
- The sawdust must be allowed to dry before use. The normalized moisture content of wood for construction is 12%.
A competent and thorough approach to the issue of insulation will avoid a large number of problems with the operation of the building in the future. If the house has warm walls, but no attention has been paid to protecting the floor and ceiling, then the temperature and humidity conditions in the room will be disrupted. Insulating a frame house with sawdust will be an economical and effective solution.
Types of sawdust products
*
You can insulate the floor not just with sawdust, but with insulating materials created using them.
Sawdust granules
They are obtained by mixing sawdust with glue. Antiseptic additives must be included in the mixture. The granules retain the thermal insulation properties of ordinary sawdust, but have better resistance to rotting and are difficult to ignite.

Sawdust granules
Sawdust concrete
These are ready-made blocks of insulation obtained by mixing sawdust with sand and cement in different proportions. It is used for construction purposes, but for floor insulation it is better to take blocks with a high sawdust content. They are less durable, but their thermal conductivity is lower.

Sawdust concrete blocks
Arbolit
To make arbolite blocks, large wood chips are used, mixed with cement mortar without adding sand.

Arbolit
Sawdust for winter shelter of plants
Mulching or hilling garden plants with sawdust for the winter, as well as covering them with plastic bags with this material, will help them survive the cold without loss.
If you do not want the plant to be delayed in growth, do not forget to remove the sawdust cover with the arrival of spring. The soil under the sawdust warms up much more slowly. Even some root vegetables can overwinter in a bed of sawdust! These are frost-resistant crops: daikon, root parsley, carrots. When frost occurs, the tops of wintering root crops are cut to a height of 5 cm. Next, you need to loosen and hill up each plant, and mulch the bed with a thick layer of sawdust. The crop must be dug up in early spring before the leaves begin to grow.
In damp winters, sawdust can get wet and then completely turn into an ice ball, so additional covering with polyethylene is recommended.
The best materials for winter covering of plants 15 covering materials that will protect your plants from freezing, damping off, frost damage and sunburn.
How to insulate a floor in a wooden house with sawdust
For all types of low-rise wooden buildings - made of logs, timber, frame structures - the floor insulation procedure is carried out. The frame of their base or ceiling is also made of wood and is less durable than a concrete slab or metal frame. Therefore, insulation of such a lightweight design should be light and effective. Sawdust in bulk and in granules, mixtures based on them with various binders, ready-made dry blocks are an inexpensive and reliable option suitable for the designated purpose. It is possible to use other insulating materials. Comparative characteristics are presented below.