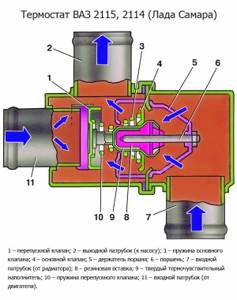
Why is the thermostat faulty?
The thermostat is a complex electronic device, and it is best to entrust its repair to a specialist.
Let's take a closer look at what problems can occur with the thermostat, and for what reason they appear:
- due to excessive loads, damage to the valve seat: constant flow of coolant through the radiator, the engine warms up longer than usual;
- complete destruction of the temperature-sensitive element of the thermostat due to excessive loads: water gets inside the working element, or wax comes out, which disrupts the correct response to temperature changes;
- opening the valve of the device earlier than usual: the coolant penetrates inside the thermoelement, due to which the volume of heat-sensitive wax increases, which is what the valve is triggered by opening;
- late opening of the thermostat valve: water flows out of the thermoelement body, due to which the working volume of the element decreases, which leads to an increase in temperature for the necessary compensation of the amount of wax;
- at high ambient temperatures, the engine overheats: when the device opens in time, the heated cooling liquid cannot enter the main radiator, but returns back to the engine through the bypass pipe;
- insufficient opening of the thermostat valve, due to which insufficient coolant volume enters the radiator;
- The thermostat valve does not close: there is coolant in the working element, which prevents the valve from completely closing;
- the thermostat is faulty (signs of its malfunction): possible change in the initial settings due to significant overheating of the cooling system;
- The rubber seal of the valve disc is broken: as a result of a malfunction, engine oil has entered the coolant, which dissolves the seal of the thermostat valve.
So, the thermostat in a car is a special valve that regulates the cooling and lubricating flow of the emulsion (coolant) in the car engine. During combustion of fuel, a sufficiently large amount of heat is generated that can cause engine damage. To prevent this, it supplies a mixture of antifreeze and water under the required pressure to the radiator to cool it. The thermostat remains closed until the emulsion reaches the optimal operating temperature, while circulating through the engine without passing through the radiator. And all this happens only in its normal, correct working condition.
To increase the service life of the thermostat, you should change the coolant on time, monitor the appearance of scale on its temperature-sensitive element and carry out preventive maintenance on time.
Varieties and location
The installation location of the thermostat depends on several factors: the model of the internal combustion engine, the location of the internal combustion engine in the engine compartment, the design features of the CO. Often the device is installed at the point where the coolant exits the cylinder block. It is also a priority to install it near the pump, at the entry point of the centrifugal pump.
There are several models of motors, the design of which requires the presence of two thermostats in the CO - the so-called dual-circuit systems. The first device monitors the temperature of the cylinder head and maintains a set value of 87 degrees. The other is located in the area of the cylinder block itself.
There are different variations of this device:
- 2-valve is the most common option in the domestic automotive industry for cars and trucks. The principle of its operation, as mentioned above, is the effect of the internal filler of the thermostat on the bayonet, which in turn opens and closes the path of coolant. Its location is between the upper radiator tank, the water jacket outlet and the pump. The opening of the large circle overlaps the small one, which is why the liquid passes only through the radiator.;
- A 1-valve device does not have a small circle hole. This type is most often found on models of the foreign car market. It is installed between the lower radiator tank and the pump located at the entrance to the water “jacket”. In this scheme, opening the large circle leaves the small one also open for fluid circulation.
- The circuit of some motors produces quite a lot of pressure that prevents opening. To solve this issue, a 1-valve thermostat with 2 stages was developed. Its design contains a main and a small plate. First, a small plate is opened, which contains a small amount of the cooling mixture. Then the main one opens and the remaining volume of liquid enters.
- Electronic differs from its predecessors in the ability to use not only coolant as a heating substance, but also an additional part. It is connected to an electronic unit that automatically controls all CO and the operation of the thermostat. The electronic control system allows you to keep the temperature at 90-110⁰C during standard engine operation and 80-90⁰C at maximum power. This type of device allows you to reduce fuel consumption and increase power at low speeds through more efficient cooling of the intake air.
Diagnosis at home
To check, place the thermostat in a container, then fill its body with boiling water. If the device is working properly, the valve should begin to open almost immediately. When the water temperature drops, the return spring will return the valve to its original position.
To most accurately test the thermostat, place a container with the thermostat immersed in water on the heater. Using a thermometer, check at what temperature the valve begins to open. The operating temperature range of the thermostat can be found in the repair and operating manual for your car. Manufacturers often indicate this information directly on the thermostat housing.
Resource
A mechanical thermostat is an extremely reliable car part with virtually nothing to wear out. It fails only due to natural wear and tear of the rubbing parts of the valve stem and guide. It is extremely difficult to predict the mileage of a car that will require replacement, but often this happens no earlier than 150-200 thousand km.
Electronically controlled thermostats fail much more often. In this case, the malfunction may be either in the heating element or in the control circuit from the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
Using low-quality coolant and driving on water significantly accelerates mechanical wear. Corrosion, deposits, and scale slow down the valve's performance and can cause jamming in the open/closed position.

Electronic thermostat
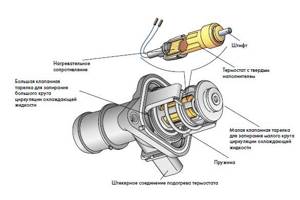
The design of the electronically controlled cooling system on Volkswagen, Skoda, and Audi vehicles requires the presence of a heater built into the thermostat valve sensing element. At certain engine operating conditions, the heater is used to accelerate the opening of the thermostat.
The self-diagnosis system is capable in many cases of determining the nature of the malfunction and displaying it in an error code. Using diagnostic equipment, you can check the functionality of the system without removing the thermostat from the car. By reading the fault code after the “Check Engine” appears on the dashboard, you can see:
- open circuit;
- short circuit to ground;
- Short circuit to +.
You can indirectly check the performance of the heating element by measuring its resistance. Usually this value is within 12-15 Ohms, but before checking it is better to clarify the normal resistance of a specific model of electronic thermostat.
If you know how to use a multimeter, you can test your heater at home. Infinite resistance will indicate a break in the heater. Also, in the resistance measurement mode, you can check the integrity of the control circuit wires. The ECU controls the heater using a PWM signal, so you won’t be able to check the signal at home without an oscilloscope.
Replacing the thermostat and checking it
by admin May 19, 2014
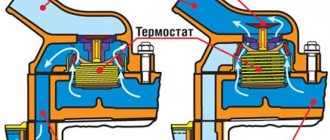
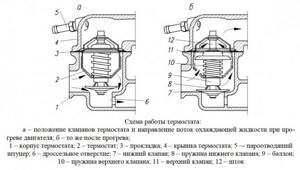
In a car with an internal combustion engine, the cooling system is configured to maintain a certain operating temperature of the engine. Usually it is 90? C. To prevent overheating and, at the same time, to allow the car to quickly warm up, there are two circles of coolant movement in the cooling system - a large and a small circle. When the car has not yet warmed up, the antifreeze moves in a small circle, bypassing the radiator, so that it does not cool down. When the liquid reaches a certain temperature, a valve is activated, which opens a large circle and the liquid passes through the cooling radiator. This valve is called a thermostat. Thermostats on different cars may differ in overall dimensions and response temperature, otherwise the principle of their operation is the same.
The thermostat consists of a housing, a diaphragm valve, a spring inside which has a cylinder with a drive mechanism, and a hole for bleeding air when filling the cooling system. When the car is cold the spring is released and the valve is closed. When a certain temperature is reached, the drive mechanism compresses the spring and the valve opens, allowing the liquid to flow in a large circle. The drive mechanism operates based on the thermal expansion of materials. Inside there is a substance with a high coefficient of thermal expansion. When heated, the substance expands, causing the spring to compress and the valve to open.
This seemingly simple device plays a very important role in the proper operation of the engine. Its malfunction leads to overheating of the engine, the car “boils”, and to underheating in the cold season.
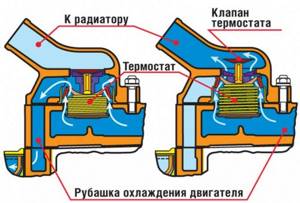
When the thermostat is stuck in the closed position, the antifreeze constantly circulates in a small circle without passing through the radiator and does not cool down - this leads to overheating of the engine. When the engine overheats, there is a high probability of mechanical damage to engine parts: the cylinder head is driven, cracks appear in the block or head, gaskets are squeezed out, etc. Operating the engine with such damage will inevitably lead to expensive repairs. Therefore, if you notice that the engine temperature is higher than expected, you need to pull over to the side of the road and let the car cool down. Check the coolant level in the radiator and expansion tank. If everything is in order with the level, the fans worked properly when overheating, most likely the thermostat has become unusable. You need to go to a garage or service to replace the thermostat. At the same time, be sure to closely monitor the engine temperature to prevent overheating; it is better to stop once again and let the car cool down than to repair the engine later.
When the thermostat gets stuck in the open position, the antifreeze circulates in a large circle and the engine either takes a very long time to warm up or does not warm up to normal operating temperature at all. Engine underheating is usually detected in the cold season, when the heater blows cold air. Cold air from the heater is not the only problem when the engine is underheated. In such a situation, fuel consumption increases significantly, engine response decreases, and wear of parts increases.
Therefore, the performance of the thermostat must be monitored carefully. If the situation described above occurs, it is imperative to check the functionality of the thermostat. It is better to change the thermostat at least once every two years; it is better to do this when it is time to replace the antifreeze.
The cause of thermostat failure may be corrosion of the metal parts of the device due to the use of low-quality coolant or a very long service life. Damage to the thermostat gasket may also warrant replacement. Yes, and no one canceled the marriage...
There are several ways to check that your thermostat is working correctly.
On the car without removing it. You need to start the car and let it warm up to operating temperature. Then turn off the engine, open the hood, find the pipes through which the coolant flows - usually these are thick tubes that go from the engine to the radiator in the upper and most delicate part of it. Next, you need to carefully touch both of these pipes. This should be done extremely carefully so as not to get burned. their temperature can be about 90 degrees. If the pipes are at the same temperature, your thermostat is working properly. If the upper pipe is significantly hotter than the lower one, there is a high probability of thermostat failure and it is better to replace it.
The second method will require direct work with the thermostat, so you need to remove the thermostat from the engine. To check, you will need a container of water. The water will need to be heated; everyone decides how to heat the water for themselves. You can even use a boiler; there are no electrical parts in the thermostat, so it won’t harm it. The thermostat must be placed in a container of water and heated until it begins to boil. Because you need to check the functionality of the device, and not at what temperature it operates, so you won’t need a thermometer. In heated water, the thermostat should open and close as it cools without any freezing. If everything went smoothly, your thermostat is working, but if opening or closing is accompanied by freezing or does not happen at all, replace the thermostat.
Replacing a thermostat is already a service work, so if you don’t know how or don’t like tinkering with your car, leave this task to service specialists. If you decide to do everything yourself, then you will need a thermostat itself that is suitable for your car, a couple of liters of coolant (antifreeze or antifreeze that is poured into the cooling system), a set of keys, screwdrivers, gloves, rags, etc... It is imperative to purchase a thermostat with a gasket , if it is provided for by the design, if not provided, a good sealant will be required.
Before replacing, you must let the engine cool down to avoid getting burned.

Open the radiator cap to relieve pressure in the system. Close the lid.

Find where the thermostat is located. Usually from the housing where the thermostat is located there is a thick pipe to the radiator. The thermostat can be located in a housing on the engine itself or in a remote separate housing, which varies on different machines. Remove the pipe from the housing. Coolant will flow. That's why we stocked up on it to top it up to the required level after replacement. It is best to combine replacing the thermostat with replacing the antifreeze so as not to spend money on topping up. Unscrew the bolts and remove the housing cover or disassemble the housing. After this, you will have access to the thermostat itself. Pull out the old thermostat.

Remove dirt and wipe the seat. Install the thermostat into the seat. When installing, be sure to make sure that the air bleed valve is on top, otherwise the thermostat was installed incorrectly. If you do not have a gasket, you need to lubricate the thermostat seating belt and the housing cover with sealant. Screw the cover back or assemble the entire body.
Thermostat operation
Schematic diagram of a thermostat.
When the car engine is initially started, the temperature of the thermostat coolant is the same as that of the environment, and in order to reduce the engine warm-up time, the thermostat is automatically limited to a small circulation circle (cylinder head, block cooling jacket and heater). As operating temperature rises, the thermostat valve regulates the correct flow of coolant from the main system radiator to the engine. And if the temperature drops, the valve responds to this by increasing the amount of coolant that bypasses the radiator.
This thermostat operation scheme allows you to maintain the required operating temperatures at the proper level, ensure fairly good temperature characteristics of the interior heater, and at the same time reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases while simultaneously increasing the service life of the engine.
The thermostat design has a sealed temperature-sensitive element filled with wax. Depending on the temperature, the volume of wax changes, which entails the opening and closing of the thermostatic operating valve strictly at certain temperature levels.
How can a motorist understand that these signs of car malfunction indicate the need to look for their causes primarily in the thermostat? Engine overheating or insufficient heating, uncomfortable interior temperature in the cold season, a noticeable decrease in vehicle dynamics, as well as increased fuel consumption are the first signs. But before you think about repairing or replacing the thermostat, you need to understand that the thermostat is just one of many elements of the cooling system, which may not be related to the given car malfunction.
To be completely sure that the cause of the cooling system failure lies in the thermostat, you need to check the coolant level, the coolant temperature sensor itself and its indicator (warning lamp) for serviceability.
What types of car thermostats are there?
Nowadays you can find several types of thermostats. They differ from each other in operating principles and have their own characteristics. Russian-made options are cheaper than German or Polish ones, but it is foreign options that are famous for their high quality and good wear resistance. Universal parts options remain in demand. They are valued for their ease of installation, ease of use, low cost and sufficient prevalence. Let's consider what types of devices exist.
Single valve
Popular type of device. It is still installed in foreign and domestic cars. Leading companies, on the contrary, believe that the model is morally outdated and cannot provide high-quality cooling for a powerful motor. The judgment is correct, but only partially. The capabilities of a single-valve thermostat are not enough only for racing cars.
The classic system works successfully in many cases, but the specific model and device should be determined depending on the equipment of the entire engine cooling system.
The single-valve automobile thermostat is characterized by its simple design. Surprisingly, this parameter is key. The device successfully performs the actions assigned to it and is considered reliable. Leading manufacturers of modern cars still choose this design to equip their own products.
Two-stage or two-valve
There were no fundamental differences in the device when compared with the single-valve version. The only difference is the expansion of capabilities to ensure an efficient cooling process.
The thermostat, as in the classic version, has two plates. One of them provides a shutter for a large circulation circle, and the second for a small one. The functioning of the systems is ensured synchronously. When one circle closes, the second one starts immediately - this is the advantage of a two-valve device. The work is synchronous, the locking of one valve provokes the opening of the other.
The design of the two-stage thermostat is different. They decided to revise the fundamental structure of physics and auto mechanics due to a certain imperfection of the previous version. The cooling system creates high antifreeze pressure and the car thermostat valve cannot overcome it.
The design change consisted of the introduction of two plates (small and large). The first one opens first, it is designed to reduce the force and reduce the pressure inside the system. It opens smoothly, triggers the interaction of a large chain. Because of this, initially the liquid does not pass into the large circle.
Electronically controlled
The electronic device is presented in the form of a classic single-valve thermostat that includes a heating resistance. The control function of the latter is provided by an electronic unit for controlling engine functions. The latter is capable of reaching temperatures of 95-100 degrees at partial load. At maximum power, the marks remain in the range of 85-95°C.
Another good article: Lambda probe: what is it, principle of operation, what is it for, where is it located, service life

Behr Thermot-tronik thermostat with electronic control
Equipment of this class will allow you to save fuel and use it rationally due to additional cooling of the air absorbed by the cylinders. An electronic thermostat increases engine efficiency.
Hulled and unhulled
In many cases, the thermostat is sold in auto stores without a housing. In this case, you can install it simply by removing the old one. But some manufacturers produce car thermostats already installed in a housing, which must be connected to the pipes of the car’s cooling system.
Most often, thermostats are sold with a special rubber gasket that can withstand the effects of coolant.
There is a separate version of thermostats - frameless. They are installed directly into the engine block.

Frameless thermostat GAZ-3302,2705 doors. GAZ-560 “Steir” LUZAR
When the wax ball is heated, it melts, becomes larger in size and pushes out the rod (about 2 cm). The valve on the stem rises and closes the pipe. The higher the antifreeze temperature, the more the rod is pushed out. And when the engine cools below 70 degrees, the wax ball shrinks and becomes hard, and the valve stem falls into place thanks to the spring.
Ways to check functionality
The engine cooling system uses a thermostat to quickly warm up and then maintain operating temperature. After a cold start, the thermostat valve shuts off coolant flow to the main radiator. The engine warms up much faster, since antifreeze circulates only in the “jacket” (small coolant circulation circle). A sensitive element is installed in the thermostat housing, which expands in volume during the heating process, forcing the main valve to move and open coolant access to the main radiator. Antifreeze begins to circulate in a large circle, thereby cooling the engine.
How to check the main signs of a thermostat malfunction?
- According to the degree of heating of the outlet pipe going to the radiator. Before the coolant reaches the opening temperature, which on most cars is between 80-90 degrees Celsius (at 95-105ºC the valve opens completely), the pipe must be cold. If it warms up almost immediately after starting the engine, the thermostat is stuck in the open position, and the coolant is constantly circulating in a large circle. When the thermostat is stuck closed, the hose will be relatively cold even when the engine is fully warmed up. The situation is extremely dangerous, as you risk losing a large sum while eliminating the consequences of engine overheating.
- Carry out a test by placing it in a heated liquid. Below we will describe in detail how to fairly accurately check the thermostat at home.
Is it worth checking without removing it from the car?
The advantage of diagnostics based on the degree of heating of the pipe is that you can check the thermostat without removing it from the car. But unlike the test at home, the method does not allow you to accurately estimate the opening temperature and response speed.
By controlling the degree of heating of the liquid, you can simulate changing the cooling and warming up modes of the engine several times in a row. The tricky thing about faults is that they can manifest themselves periodically. Therefore, if there are serious suspicions that the thermostat is not working properly, we recommend checking it only with a test at home.
Design and principle of operation of a car thermostat
What is this device made of? Car thermostats are made from non-ferrous metals. The most commonly used materials are brass or copper. The first option is considered more suitable. The principle of the device is simple, it includes the following elements:
- frame;
- small and large cooling circle valve;
- outlet pipe connected to the pump;
- wax ball;
- inlet pipe connected to the radiator;
- springs;
- piston.
All devices of a car thermostat are presented in the form of a cylinder, a return pin, a wax ball and a shut-off valve of a large and small circle. It is this simplicity that ensures the reliability of the design.
Attention! Despite the popularity of retrofits in the automotive industry, the design of automotive thermostats has remained the same for many years. The only thing is that manufacturers often switch to two-stage options. The principle of operation has not changed from this.
In certain brands of cars, the thermostat can be set to operate when the engine reaches certain temperatures. Usually there is a note about these capabilities in the instructions for the device. This is a kind of plus that allows you to reduce gasoline consumption when the engine warms up.
Circulation patterns
A regular mechanical thermostat does its job on its own. To understand how the operation is ensured, you need to consider the circuit diagram:
- When the engine has just started, but has not yet warmed up to the required temperature, the main shut-off valve blocks the flow of coolant to the radiator. The small circle remains open and allows antifreeze to pass through to prevent it from cooling and allow the engine to warm up completely.
- After the temperature rises, the wax inside the cylinder is heated. This component systematically expands, which ensures that the rod is pushed out. It rises and allows antifreeze access to the second circle. The height of the valve lift and the amount of cooling flow depend on the heating force of the liquid.
- If the antifreeze is hot, access to the small cooling circle is blocked and the entire flow goes to the radiator - to the large cooling circle.
- After the liquid cools, the substance cools and contracts. The rod is lowered by a spring, and the valve reduces the flow to the cooling radiator.
Therefore, the functionality of the system lies in monitoring and restoring normal engine temperature. If we consider the diagram in detail, we can conclude that the process is autonomous. Susceptibility to temperature fluctuations depends on the composition of the filler.
Video: car thermostat. How it works in 3D animation
In this visual video you will learn the structure and operating principle of a thermostat in 3D graphics.
Why do you need a thermostat?
The thermostat is an extremely important device that is found in every car whose engine is cooled using a special liquid. If it fails, the engine begins to overheat. {typography legend_blue}Experts recommend changing it every 2 years. But sometimes this may be required much earlier (we’ll talk about how to determine this a little later).{/typography}Why do you need a thermostat? Its main task is to prevent antifreeze from entering the radiator until the engine is completely warmed up. As long as the thermostat is closed, the coolant moves in a small circle, thereby gradually warming up the engine.

This allows you to reduce exhaust emissions and extend the life of the power unit. As soon as the internal combustion engine warms up to 95 degrees, the thermostat opens and hot liquid enters the radiator. Now you know why you need a thermostat in a car. There is no way to do without it. And at the first sign of a breakdown, it must be replaced immediately. How can you determine that the thermostat is faulty? For this, there are so-called “folk methods” of verification: {typography list_number_bullet_blue}1. When the engine is hot, you need to open the hood (the car must be turned off) and carefully, so as not to get burned, touch the upper and lower hoses that are attached to the radiator (these are black rubber hoses, approximately 5 cm in diameter, at the ends of which there are metal clamps). If they are hot, then everything is in order. If one of the hoses is hot and the other is cold, then most likely the thermostat is closed and therefore coolant does not flow into the radiator. In this case, it is necessary to urgently change this device.||2. Another sign of a faulty thermostat is when it takes too long to warm up the car. When in a traffic jam, the operating temperature is normal. But when the car drives at high speed, the engine overheats. {/typography} The cost of a thermostat depends on the brand of the car manufacturer. For domestic brands, the price of the device can be around 500 rubles, but for foreign cars the price ranges from 500 rubles to several thousand. We found out why a thermostat is needed and also got acquainted with methods for checking its performance. Now you know, in order to avoid costly repairs, it is better to change this device on time - either every 2 years, or at the first sign of breakdown. Why do you need a thermostat?
Types of thermostats
Several types of thermostats are used in car power plants:
- With 2 valves, which provides control of the refrigerant flows going to the radiator and through a small cooling circle (through the power unit jacket and the cabin heating unit).
- With 1 moving element that adjusts the flow of fluid to the radiator.
- With 1 valve and two-stage opening. When the engine warms up, a small diameter duct opens, then antifreeze is supplied to the heat exchanger through an opening with a larger cross-section.
- Electronic thermostat equipped with a sensor that measures the temperature of the antifreeze. The control unit fixes the position of the damper using a stepper motor. The regulator adjusts the supply of antifreeze to additional cooling circuits, which reduces fuel consumption.
Thermostat operation
Principle diagram of a thermostat.
When starting the car engine for the first time, the temperature at the center of the thermostat is the same as for the coolant, and in order to speed up the engine warm-up time, the thermostat is automatically circulated with a small amount of circulation (cylinder head, which cools the block and both grіvach). At the same operating temperature, the thermostat valve regulates the correct supply of coolant from the main system radiator to the engine. And as the temperature drops, the valve reacts with a greater amount of cooling water, which bypasses the radiator.
This scheme of thermostat operation makes it possible to maintain the required operating temperatures at the same level, ensure good temperature characteristics of the cabin heater, and thereby reduce the toxicity of processed gases with an immediate resource saving. lshennyam machine engine.
The design of the thermostat has a sealed thermo-sensitive element, filled with wax. Every time the temperature of the wax is changed, this will force the thermostatic operating valve to open and close strictly according to the current temperature readings.
How can a motorist understand that these signs of car malfunction indicate the need to look for their causes first in the thermostat? Overheating of the engine or insufficient heating, uncomfortable interior temperature in the cold season, markedly decreased display No car dynamics, as well as fuel movement are the first signs. Before you even think about repairing or replacing the thermostat, you must understand that the thermostat is just one of the many elements of the cooling system that may or may not have been worn out before the vehicle malfunctioned.
To be sure that the reason for the breakdown of the refrigeration system lies in the thermostat, it is necessary to check the temperature sensor of the refrigeration unit, the temperature sensor of the refrigeration unit itself and its indicator (signal lamp) for correctness.
Causes of thermostat failure
The most important sign of a thermostat failure is a lack of circulation in the engine cooling system, which leads to overheating.
There can be many reasons why a thermostat may malfunction, but the most common problem is corrosion eating away at the cylinder and locking pin, causing fluid flow to not completely stop in any valve position.
In such a situation, it will be much more difficult for the engine to warm up, and it will take much longer than in normal mode. If, on the contrary, the thermostat constantly remains closed, the engine quickly overheats, which leads to a complete inability to continue driving or more serious consequences, such as thermal deformation of the cylinder block and expensive engine overhauls.
When the coolant temperature indicator is on the verge of overheating, despite the fact that one hose is hot and the other is cold, we can most likely say that the thermostat valve is stuck closed and the liquid is not passing through the radiator.
How to check a car's thermostat
There are two main ways to check a car's thermostat. One of them is carried out without removing the part, but requires a pyrometer, and the second is simpler, but the element will need to be removed from the engine during the test.
As you know, the thermostat housing is connected to the upper radiator hose, which is included in a large circle of coolant circulation. Accordingly, with the thermostat working, after starting the engine, the upper radiator hose should remain cold (slightly warm) for some time until antifreeze is released through it.
To check the thermostat without removing it from the engine, get a pyrometer (temperature measuring device). You may come across the opinion that the check should be done without a device, measuring the temperature with your hands, but this is quite dangerous, given the large number of moving parts when the engine is running.
Point the pyrometer at the upper radiator hose and start the engine (cold start). For two or three minus periods, observe the device’s indicators. Next, draw a conclusion about the serviceability of the thermostat according to the following rules:
- The hose was cold for two or three minutes (or its temperature rose slightly), and then quickly warmed up. This indicates that the thermostat is working properly, and it switched the coolant circulation from a small circle to a large circle after the engine has sufficiently warmed up;
- The hose initially warmed up slowly. In this case, we can say that the thermostat is stuck in the open position and the antifreeze does not circulate in a small circle;
- The hose did not begin to warm up quickly after two or three minutes. That is, the thermostat is faulty and it does not switch the coolant circulation from a small circle to a large one.
Important: While checking the thermostat, monitor the engine temperature on the instrument panel. If the thermostat is stuck and does not switch the coolant to a large circle, the engine will begin to overheat, which can lead to the failure of expensive parts
A widespread and well-known way to test the thermostat yourself is using a saucepan. As you might guess, before diagnostics you will need to remove the thermostat from the car engine and bring it home. After this, do the following:
Take a pot and fill it with water; Inspect the thermostat housing and read the technical information on it, which indicates at what temperature it should switch; Hang the thermostat in the pan so that it is immersed in water, but does not touch the walls and bottom of the container, that is, it comes into contact only with water; Start heating the water and put a regular thermometer in it to measure the temperature of the liquid; When the water approaches the thermostat switching value from closed to open, make sure this happens. Also compare the thermometer reading, recording the temperature at which the coolant circuit switching valve opens with the ideal values indicated on the device body.
If the valve opens when heating water, track its behavior when cooling the liquid, checking at what temperature it returns to its original position. Based on the data obtained, draw a conclusion about the functionality of the thermostat.
How to choose a thermostat
In the event of a breakdown, it is better to choose an identical thermostat, or contact the manager of any auto parts store, also providing the VIN code of your car. He will select a spare part of the required size, and will also clarify the possibility of working in one thermal mode.
A slightly more interesting case: individual parts have already been changed, and adjacent ones have been added. It is difficult to do without the help of a car mechanic. He will analyze the following things: melting point thresholds, number of valves, overall dimensions, opening temperature, specifics of engine temperature indication. Accordingly, the best thermostat will be selected. Note that not all car enthusiasts know exactly what temperature display system is in their car, so they risk getting into trouble when choosing a thermostat on their own.
Thermostat operating principle
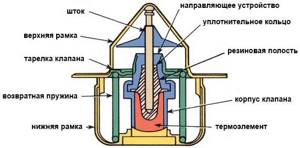
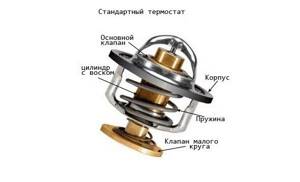
The main component of the thermostat is a mechanical valve: it is activated by a fairly simple and correct mechanism. The sealed housing contains a heat-sensitive unnatural wax, which when melted increases in quantity and compresses the rubber chamber, pushing out the chrome-plated iron rod, which causes the valves to act. This is the principle of operation of the thermostat.
This is how a thermostat works
If the integrity of this mechanism is compromised, wax leaks out due to the use of low-quality antifreeze (antifreeze) or corrosion and the friction force of the moving rod increases. The thermostat begins to function incorrectly, slowly and inexorably turning the driver’s life into hell.
Types of thermostats based on operating principle
If we consider the operating principle of the thermostat, all models can be divided into several subgroups:
Mechanical thermostats
Such devices are designed without any electrical components. They are most often used on kitchen stoves. Parts are often found in ovens where it is necessary to maintain the temperature at the same level. They are often combined with gas taps. After reaching a certain point, the thermostat activates the minimum operating mode to save resource consumption. When the indicators decrease, the fuel supply increases again.
The oven thermostat must ensure automatic maintenance of the set temperature in the range from 160-2700 C
Thermostat device
The thermostat is a valve
, placed in a housing from time to time, regulates the flow of coolant in
your car's
. In terms of design features, it is not uncommon for thermostats to be designed as either framed or open-framed.
Housing thermostat with two terminals
1. Housing thermostat
As can be seen in the figure, one of the types of thermostats is a device enclosed in a housing and, in most cases, having at least several terminals. The exception is thermostats with a housing device, which form complex 2-level circuits. Thermostat housings are made of plastic, brass or aluminum.
Two terminals located next to each other are in most cases called a “small circuit”. It prevents coolant from entering the radiator, allowing it to circulate into the radiator and heater motor. This makes it likely that the engine will rapidly warm up to the desired (operating) temperature - the point at which the thermostat opens completely. On domestically produced cars, the temperature at which the thermostat is fully opened is often 80-85 degrees.
In most cases, with case thermostats, manual adjustment of the opening and closing temperature is not feasible, but experienced auto repair shops will be able to provide such a service.
2. Frameless thermostat
Additional thermostat elements
In many modern cars, thermostats have a temperature sensor and a heater. Their adjustment occurs thanks to the ECU - an electronic control unit. How does this happen?
At medium engine speeds, the antifreeze temperature is maintained at a higher temperature. At maximum load on the internal combustion engine, heating immediately turns on, so the car thermostat works earlier. This in turn leads to a decrease in coolant temperature by 10 degrees, and also saves fuel.
Signs of a malfunctioning I4CAR thermostat

A thermostat is a valve that is highly sensitive to temperature changes. This valve also controls the flow of coolant into the radiator.
Malfunctions in the thermostat may be indicated by:
1. insufficient heating of the passenger compartment;
2. slow engine warm-up.
Both of these reasons can be caused by the thermostat not closing completely (or closing but not tightly). Otherwise, the engine may quickly overheat, while the radiator will remain cold to the touch. The reason for this is that the thermostat does not open. If you think the thermostat needs to be replaced as a matter of urgency, take your vehicle to a repair shop.
Tips: Tips for car beginners
The cylinder head gasket provides a tight connection between the cylinder head and the cylinder blocks, so that oil, combustion products, gases and coolant do not penetrate from underneath it to the outside.
Signs of a leak in the cylinder head gasket may include:
— bubbles in the coolant when the engine is running,
— smell of gasoline or exhaust gases in the coolant.
Such signs can also be the presence of oil in the coolant, which looks like a thick whitish sediment. Antifreeze accumulates in the expansion tank of the system, or, conversely, in the oil, which will also look like a whitish deposit on the oil filter cap or on the dipstick.
Signs of a bad thermostat
Other signs of a leaking cylinder head gasket include:
- water dripping from the exhaust pipe when the engine is hot,
- loss of power,
- whistling noises in the engine,
- engine overheating.
If you begin to suspect that the cylinder head gasket is broken, take the car to a repair shop as quickly as possible, where professionals can help you and fix the problem.
Repairing a stuck thermostat
Malfunctions in the operation of the thermostat may not be caused by a breakdown of its moving parts, but by debris getting under the valves, scale deposits, or failure of the o-ring. In this case, you can do without replacing the part by removing it from the car and treating it with a conventional means for removing deposits on household water heaters, similar to “anti-scaling”, boiling it for 15 minutes. If the device is working, this will be noticeable by the valve opening in boiling water. Before installing the “reanimated” thermostat, the internal sealing ring is replaced and the cooling system is flushed with special means intended for this purpose.
How to check the thermostat
Without removing the thermostat from the car, it is possible to check its operation approximately conditionally. Exceptions are cases when it is stuck in the fully open or closed position. In this case
Based on the temperature of the pipes, warm-up time and temperature sensor, it is possible to conclude that the thermostat is likely malfunctioning.
In warm water the thermostat should open
It is possible to check the thermostat yourself by removing it from the car. For this
it is either poured with boiling water, visually noticing the opening, or heated in a container of water on an electric stove, the temperature is monitored with a thermometer and the length of extension of the rod is measured. Both of these methods give a very inaccurate result, not allowing you to display the hysteresis loop of the thermostat and compare it with a standard one taken in the manufacturer’s laboratory.
It is possible to professionally check the thermostat only at special diagnostic points, since its incorrect operation is often associated with other engine problems, which must be distinguished. If you have no complaints about the operation of the engine, that the thermometer “keeps” the thermometer needle in normal territory in the winter, and does not overheat in the summer, then everything is in order with your thermostat. Correct diagnosis of the thermostat requires the participation of special equipment and an experienced specialist.
Video on how to check the thermostat yourself
When should you change the thermostat, how to do it, and how to check its performance?
Replacing the thermostat on any car or motorcycle may be necessary when the engine overheats, or vice versa, when the engine does not warm up to operating temperature. This article will describe in detail how to verify that the thermostat has indeed failed and how to replace it on most cars.
Of course, the procedure for replacing a thermostat on different cars may differ slightly, and it is unrealistic to describe the sequence of work on different cars in one article. But still, replacing the thermostat on most cars is not at all difficult, because the principle of its operation, and therefore its location on different cars, is almost the same.
First, you should drain the coolant from the cooling system of your car by unscrewing the drain bolt-plug from the bottom of the radiator, or simply remove the lower rubber pipe from the radiator if the drain bolt is soured from corrosion and it is difficult to unscrew it.
To find a thermostat on any engine for a beginner who has never done this, you should find the location of the thermostat specifically on your engine model in the manual for that engine, or simply read what is described below.
Any thermostat is needed so that when the coolant reaches a certain temperature, it opens and the heated liquid begins to circulate not in a small circle (see picture on the website), but in a large circle, that is, through the radiator, and thanks to this the engine will not overheat. I hope this is clear, and if so, then the thermostat on any engine is located between two rubber pipes - between the lower radiator pipe (see picture) and the pump that pumps coolant.
Well, there is one more pipe, indicated by the red arrow in the figure, after which the rubber hose-pipe bifurcates into two hoses (using a pipe angle), one of which goes to the upper radiator pipe, and the second goes to the engine head (more precisely, to the cooling jacket motor). On some cars of rare models, the thermostat may be located slightly differently, but not so that it would be difficult to find.
Now there is one more nuance: there are non-separable thermostats (for example, like on the VAZ classic), in which the body is rolled and the thermoelement cannot be removed. And although there are no non-separable parts for Russian Kulibins, why flare it when the new thermoelement is sold together with the body, and not separately.
But on most foreign cars, the thermostat housing is easily disassembled to remove the thermoelement, and a new thermoelement for such cars is sold separately (without the housing). And to remove and replace the thermocouple, just unscrew a couple of bolts and open the housing. On machines with a non-separable housing, simply disconnect the cooling system hoses from the thermostat housing pipes.
But before you run to the store for a new thermostat, the standard one should be checked for functionality. The possible cause of engine overheating (or vice versa, lack of operating temperature) is not in the thermostat, but in a malfunction of the cooling system pump - the pump. How to accurately check the thermostat (its opening at the desired temperature) directly on the engine or separately from the engine. Read more
Source: subscribe.ru
Indicators of thermostat malfunction
Clear indicators of a thermostat malfunction are:
- prolonged warming up of the engine to operating temperature, and its rapid overheating;
- the engine temperature arrow drops at speeds below normal and rises when the car stops;
- the lower pipe is warm after a few minutes of warming up the engine: this indicates that the thermostat is open all the time;
- The thermostat is stuck in the closed position, the engine is boiling, but the lower pipe remains cold, even when the engine is warm
Required reading:
- How to determine the real mileage of a car
- European protocol for road accidents in 2015
- How is a traffic police report on an administrative offense required to be drawn up and filled out?
- What to do if the Check Engine light comes on?
- What should you do when a traffic violation report is drawn up against you?
- Car antennas for TV
- Liquid rubber for a car: its pros, cons, use
conclusions
You can replace the thermostat yourself. At the same time, the faulty part should be replaced as soon as possible - this allows you to get rid of possible expenses for engine repairs. We also note that the thermostat should be checked on the eve of the onset of cold weather. A properly functioning part will not only reduce engine resource consumption, but improve heating of the car interior and normalize fuel consumption.
There are quite a lot of thermostats in different price categories on the market. We consider the above brands to be priority, their quality has been tested by time. A one-time replacement is enough to avoid having to think about the thermostat for several years.
Basic thermostat malfunctions
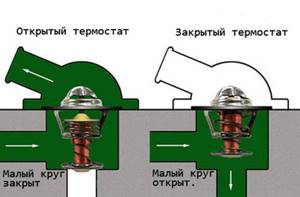
The thermostat is a fairly simple device that rarely fails. If you have problems with your thermostat, they are most often associated with the following reasons:
- The valve for switching the liquid circulation from a large to a small circle has stopped closing tightly. Because of this, immediately after starting the engine, antifreeze circulates in a complete large circle, which is why warming up to an operating temperature of 90 degrees Celsius takes many times longer than with a working thermostat;
- The fluid circulation switch valve is stuck closed. In such a situation, the sensor to open it is triggered, but the damper cannot move. This leads to the fact that the antifreeze continues to circulate in a small circle even after the engine has warmed up. Accordingly, the engine parts do not receive the necessary cooling, and it overheats.
The thermostat is not expensive, but it is not to blame for all problems with engine cooling. That is why, before replacing the thermostat, you need to make sure that it is faulty.
What is it, the purpose of the device
A car thermostat is the main component of the cooling system. Its main purpose is to control temperature indicators with the subsequent redistribution of antifreeze or antifreeze throughout a large or small circulation circle. While the engine is warming up, the system's safety valve is in the closed position and the fluid is in a small circle. Because of this, the engine warms up faster.
After reaching the required temperature, to avoid overheating, the safety valve is activated, and the antifreeze passes into a large circle. Coolant is supplied through the radiator, significantly improving engine cooling.

Where is the thermostat installed in a car?
The thermostatic mechanism is small in size, making it invisible among other parts under the hood. But that doesn't make it any less significant. The small system occupies a position between the small and large circle of movement of the cooling component.
In general, you can drive with a non-working car thermostat, but this will affect the performance of the car’s internal combustion engine. It will quickly overheat and wear will increase. You can replace the system unit yourself (in separate machines). If the engine compartment of a particular model is unknown, it is better to trust competent specialists, because there are valuable components nearby that can be damaged.
Attention! A car thermostat is a special-purpose device that maintains engine temperature in the required range. This function is achieved with coordinated and fully functional operation of the thermostat and timely phase transition.
Blocking the radiator function ensures that the engine reaches its maximum temperature. This is necessary to fully disclose the characteristics of the power unit. Such conditions help reduce the intensity of its wear.
The main functional element is the valve. It operates at temperatures between 70 and 92 degrees Celsius. The exact indicator is determined after clarifying the specific design and the required operating mode of the car engine.
Thermal service thermostat
The manual thermostat is installed directly on the radiator and significantly saves heat.
Signs of thermostat malfunction often include accumulated sediment in the refrigeration system. Scale appears on the heat-sensitive element after it has lost its rustiness, and it begins to react incorrectly to temperature changes in the cooling medium, or even stops responding altogether.
Possible reasons for this breakdown: leakage of water from the cooling unit, untimely replacement of the cooling unit, possible jamming of the thermostat in the open position, in which the cooling unit will constantly circulate along the large circuit. The other reason is that the engine has to warm up for a long time to the temperature of the engine, which is often simply beyond its reach. And when the thermostat is stuck in the closed position, the circulation will only be small, which will inevitably lead to overheating of the engine.