Vapor barrier for floors in wooden houses is necessary. Unlike walls and roofs, floors are actively affected by moisture coming from nearby soil, since in wooden houses, generally, the floor is built on small columns of brick or concrete to create a mandatory ventilated space. An additional danger is steam coming from inside the premises. Wood, for all its merits, rots in a humid environment. A reliable barrier that prevents the penetration of moisture into a wooden structure and insulation is a vapor barrier layer.
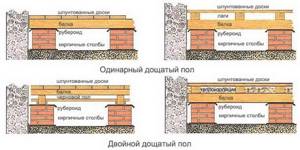
Correct floor design
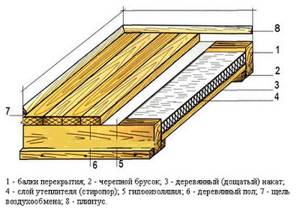
Floors in wooden houses consist of the following structures:
Rough flooring. All wooden products are pre-treated with antiseptics and fire retardants. To re-lay floors during repairs, it is necessary to dismantle the clean covering, remove heat insulators and previously installed hydro- and vapor barrier layers. The existing rough cladding is repaired by replacing damaged boards, cleared of debris and treated with antiseptic and fire retardant compounds.
Sealed waterproofing. We recommend universal materials that provide a combination of hydro, steam and wind protection. The panels are laid with a 10 cm overlap, the joints are sealed using materials recommended by the manufacturer.
Laying logs from wooden blocks (height equal to the insulating layer), pitch 59 cm, which is 1 cm less than the width of most popular insulation materials.
Thermal insulation is placed tightly between the joists; if there are cracks, they are sealed with polyurethane foam.
Laying a vapor barrier on the floor depends on the material used: with a ventilation gap from the insulation or directly on it. It is always indicated in the instructions supplied with the vapor barrier, which will also indicate the method of fastening, sealing joints, and which side to lay the vapor barrier on the floors.
It is important to lay the vapor barrier correctly; failure to do so will lead to the accumulation of moisture in it, loss of thermal insulation properties and even complete destruction. You can be guided by color and roughness: the lighter and smoother one should be located next to the insulation.
The vapor barrier coating must be airtight and extend 10…20 cm onto the walls.
Laying a clean floor.
Step-by-step instructions for installing a vapor barrier
Preparing the subfloor
Before laying a vapor barrier on the floor, it is necessary to treat all wooden base structures (boards, joists, cranial bars) with antiseptic compounds against rot, insects and fungi. If it is decided to install a new vapor barrier in an existing floor covering, the finished floor boards, as well as old heat and vapor barrier materials, are removed. All debris and dust are removed, the wooden elements of the subfloor are primed with antiseptics and installed in place.
Laying vapor barrier on the floor
The first layer of vapor barrier film is laid for vapor and waterproofing, that is, to prevent moisture and steam from the ground from entering the insulation.

A roll of vapor barrier film is unrolled and the sheets are laid on the floor frame. The individual strips are overlapped by 15-20 cm and connected to each other using special double-sided tape or mounting tape. This solution eliminates the occurrence of cracks and gaps through which unnecessary moisture can penetrate into the insulation. The canvas is attached to the joists with a stapler or galvanized nails.
Laying insulation
Insulation with a thickness of at least 50 mm is laid on top of the film, between the joists. These can be polystyrene foam mats, polystyrene foam, mineral wool. The insulation should fit snugly against the joists and vapor barrier film, without creating cracks or gaps.

Installation of the second layer of vapor barrier
The second layer of film plays the role of a direct vapor barrier, creating a barrier for wet steam coming from the room and preventing it from reaching the insulation.

The film is laid on the joists in such a way that a ventilation gap is maintained between the vapor barrier and the finished flooring. The film strips are connected to each other with tape or mounting tape.
Finished flooring
Finished floor boards are mounted on top of the joists, on which the finishing floor covering is subsequently laid, for example, parquet, laminate, linoleum, etc.

Materials used for vapor barrier
The following materials are used to construct vapor barrier layers:
Various roll films:
- polyethylene;
- polypropylene;
- with a reflective layer (food grade aluminum foil);
- reinforced and unreinforced.
A ventilation gap is required. The films are fragile, so they must be laid very carefully so as not to tear.
Diffuse membranes:
- one-sided, allowing air to pass through only on one side;
- double sided;
- single or multilayer;
- with anti-condensation layer.
Ventilation gap is optional. These are the highest quality, but expensive vapor barriers.
It is up to you to decide which vapor barrier to choose for the floor, but saving can lead to unexpected costs.
A high-quality vapor barrier will ensure the durability of the floor and will help maintain a comfortable climate in a wooden house.
The most ordinary non-insulated floor in a wooden house, the hydro and vapor barrier of which is done according to the rules, will last a long time. Wood, which in this case is not affected by moisture, will be in satisfactory condition even after 10-20 years of operation.
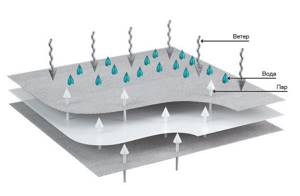
If you have an insulated floor in a wooden house, hydro and vapor barrier is necessary in order to protect the insulation from two unfavorable factors.
The first factor is moisture from the cold basement or subfloor, which will be released from the soil in the form of steam.
The second factor is water vapor from the interior of the house. If you think that steam only comes out of the house upwards, then you are mistaken. Steam from the interior escapes in all directions, through the ceiling, walls and even through the floor.
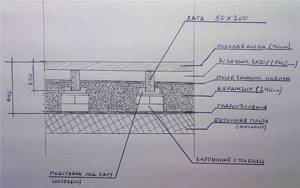
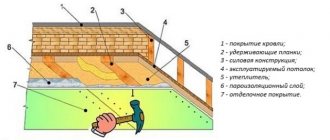
So, a diagram of a cake with waterproofing and vapor barrier for the floor in a wooden house (from top to bottom):
- Finished floor/floor covering.
- Vapor barrier.
- Rough floor.
- Lathing under the subfloor.
- Floor joists.
- Insulation in the floor covering.
- Waterproofing.
- Support for waterproofing (lower subfloor).
In this case, the vapor barrier can be attached both to the subfloor sheathing and to the subfloor itself. Sometimes you have to see a diagram when a vapor barrier is attached between the sheathing and the floor joists. In this case, you will always have a wet sheathing.
See more on this topic on our website:
- All types of internal insulation in a wooden house It is rare when during the construction of a house its insulation is not carried out. Even if insulation materials are not used at the time of construction itself, it is possible to insulate the walls inside the house, as well.
How to insulate walls with mineral wool in a wooden house from the inside The construction of residential buildings made of wood is gaining more and more popularity due to a number of specific reasons. If some people are interested in wooden houses because of aesthetics.
How to insulate a roof, attic, attic, gable in a wooden house Modern houses made of natural materials, despite their high cost, are quite in demand, since they have a number of advantages in comparison with their counterparts.
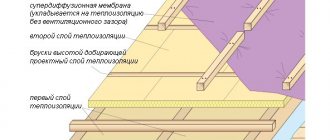
What is a superdiffusion membrane
A water-windproof, vapor-permeable membrane is a non-woven fabric made of “breathable” material. Consists of one or more layers. The structure of the membrane looks like a large number of microscopic cone-shaped holes. They provide the material with one-sided vapor permeability and resistance to moisture.
The superdiffusion membrane has high vapor permeability - at least 1000 g/m². That is, per day it is capable of passing a liter of water per square meter of its area. It is advisable to use it in all insulated roofs and insulated frame walls. Such membranes are excellent for frame construction, where the requirements for the condition of the insulation are very strict.
When installing the roof, the membrane can be laid directly on the insulation, without a gap. This means you can save on installation and materials for the counter-lattice. Among other advantages of “breathable” material, we note:
- UV resistance;
- resistance to mechanical damage;
- maintaining a comfortable microclimate in the house.
The disadvantages of a hydro-windproof membrane include, perhaps, its higher cost compared to simple films that do not have high vapor permeability. However, we generally do not recommend using such films in insulated roofs and facades, since they do not “breathe”. Otherwise, the membrane is an almost ideal material.
When is floor windproofing needed?
Floor wind protection is made on the basis of the same materials as roof wind protection. Most often, the wind protection of the floor serves as its waterproofing. The whole question is what kind of floor design is provided for by the project. Owners of a monolithic concrete floor have nothing to worry about - air penetrates through concrete very poorly and wind certainly does not penetrate. Brick houses are also quite reliably protected from blowing. But frame and wooden buildings very often allow the wind to pass through the floor level.
If we talk about the order of installation, then first there is a subfloor (joists in wooden houses), waterproofing, a layer of insulation, a special lathing, a layer of wind protection, and only then the finished floor on a specially constructed base. In frame houses this foundation is made of oriented stranded slabs, and in wooden houses it is made of plywood or any other strong and smooth sheet material. The finished floor can also be plank with laminate or parquet laid.
Windproof materials market news
Despite criticism of windproof films and membranes, they are in demand among the population and the construction industry. Therefore, manufacturers tried to eliminate the shortcomings and released materials with new properties to the market.
Nowadays there are quite a lot of windproof materials on sale with low flammability and even completely non-flammable: non-flammable windproof membrane DELTA®-FAS NG; “Izospan AF”, “Izospan AF+” and others.
So if you want to improve the fire safety of your home, it is worth spending money on more expensive, but also more reliable materials.
A completely new product was Izoplat slabs, which are sheets of heat-insulating material with wind protection, sound insulation and insulation properties. They are made from softwood fibers without the use of any adhesive, so they are absolutely harmless.
Plates differ favorably from films in that they have stable geometric dimensions that do not change over time. Therefore, once correctly installed, they will serve for a long time: cold bridges do not form between them, they cannot be torn by the wind or destroyed by the touch of a sharp object. In this case, a slab with a thickness of 25 mm in terms of thermal insulation corresponds to a wooden wall with a thickness of 90 mm. The material is perfect for use in cold and humid climates.
When planning the construction of a frame house, where the comfort of living in it depends entirely on the insulation, it is worth making sure that it is reliably protected from any adverse influences that destroy its structure and reduce its thermal protection characteristics. Therefore, for wind protection, it is better to choose high-quality materials that are guaranteed to be worth the money spent.
Choosing wind protection for the floor
As a rule, wind protection for floors has special waterproofing properties and is made on the basis of the most common materials - polyethylene and polypropylene. Among the variety of choices of windproof materials, I advise you to take a closer look at more expensive and effective solutions, because, ultimately, the cost of the material itself cannot be compared with the cost of the house. On the other hand, proper windproofing of the floor saves money on heating the room.

Diffusion membrane windproofing is recognized today as the most effective wind protection with high vapor permeability. With a high value of vapor permeability of the material, it perfectly resists wind pressure and has good waterproofing properties, which is very important when constructing a floor next to the ground. Constant evaporation makes floor wind protection an extremely important element in the overall protection of the building and insulation from mold formation.
Hydro-windproof vapor-permeable membrane BIGBAND M 135
The membrane density indicator is 135 g/m2. Extremely resistant to mechanical damage and exposure to wind and precipitation. Extends the life of the building as a whole. Thanks to the increased density and increased strength of the material, it is not afraid of possible falling of the tool and ruptures, which greatly facilitates installation.

Advantages:
- increased strength;
- easy installation;
- high vapor permeability – 2600 g/m2;
- hydro- and windproof;
- laid on the insulation without a ventilation gap, which allows saving on the counter-lattice;
- European quality control.
Areas of use:
- warm and cold pitched roof;
- walls with external insulation/frame walls;
- ventilated facade.
Wind protection parameters for the floor
Among the main parameters of wind protection are the vapor permeability of the material and the resistance to penetration of liquid under pressure. It is better to choose the first parameter at the level of 500 g/sq.m. This is a rather serious parameter, which is shown only by high-quality diffusion membranes made in Europe. But it’s better not to skimp on floor windproofing. The second parameter is determined by the withstand pressure of the water column per 1 sq.m. surface area. For good wind insulation, it is 1-1.5 m. Important parameters are the roll’s tensile and tensile resistance. It is better to choose these parameters at the level of 400 N.

Wind protection technology
We will provide instructions on attaching different types of insulation: sheet and roll wind protection.
Wall insulation with rigid boards
Sheet materials are attached after the installation of insulation is completed. It is necessary to ensure that all surfaces are dry and clean; make sure that the protective impregnation of the frame is completely dry.
Sequence of installation of windproof sheets:
- Cut the material into sheets of suitable size. Vertical joints of adjacent slabs must run along the frame posts.
- Determine the orientation of the material - the rough side goes inward, and the smooth surface goes outward.
- Secure the sheets with wide-headed dowels. The approximate density of fixation is 5 pieces per 1 sq. m.
Installation of a diffuse membrane
To attach a roll-up windbreak, you need to prepare:
- diffuse film - when calculating the footage of covering material, the area of windows and doors is not taken into account;
- construction stapler and staples;
- stationery knife;
- thick, wide tape.
It is advisable to enlist the support of one or two assistants. The procedure for installing wind protection:
- Determine the front side of the membrane. Typically, the manufacturer applies the appropriate markers directly to the vapor-permeable fabric.
- Roll out the first strip along the wall from the bottom side. You should not strain the material too much, but sagging is also unacceptable. It is optimal if you can assemble a fold 1 cm high.
- Attach the film to the wooden frame using a stapler and cut off the remainder with a utility knife.
- Roll out the second strip, observing an overlap of 10-15 cm on the first row, and “shoot” it with a stapler.
- Repeat similar steps until the walls are completely filled.
- Tape the horizontal joint lines of the diffuse membranes with tape.
The final stage is attaching vertical slats to create a ventilation gap. The frequency of placement of the bars depends on the type of facade.
Installation of windproof film on the floor
Installation of such a film is similar to installation of film on the roof. The difference is that the sheathing is pre-attached to the insulation sheathing using self-tapping screws. The windproof film itself is attached to the sheathing using special roofing felt nails, as well as other waterproofing fasteners. The film is laid overlapping with an overlap of 10-15 cm on each side. All connections between the film and the sheathing are additionally waterproofed with special mastic or film.
The site uses modern web technologies and your browser (web browser) does not support them. To work with the site, update your browser or install any of the recommended ones:
Consequences of refusing vaporization
A lack of understanding of the importance of vapor barrier for a roof often leads to attempts to save money or speed up the construction process. Many users believe that the material can be installed later if the need arises
Other owners rely too much on ventilation. They are confident that increased air exchange in the attic will help remove moist air and solve all problems. However, in practice, the lack of vapor protection affects the same way. Condensation appears, the heat insulator gets wet, and the rafters rot.
The biggest danger is that the process proceeds quite smoothly. The owner observes the condition of the attic for a week and draws conclusions about the normal condition of the insulation pie. The cladding is installed, the room is finished and put into operation. This deprives the user of the ability to control the condition of the materials hidden behind the skin. When destructive processes become apparent, the problem becomes critical. Usually a major overhaul or complete replacement of rafters, roofing, and other roof support elements is required.

Windproof membrane Ondutis
There are many types of materials used to provide wind protection for a wooden house. Among them, Ondutis films should be highlighted. They go on sale in rolls 1.5 m wide. One roll contains 50 m of material. They choose based on the purpose of use, cost and parameters.
If you need an economical option, then you should pay attention to the windproof film Ondutis A100. It perfectly combines cost and quality. Suitable for both external walls and roofing. Has the following technical characteristics:
- Weight 1 m 2 - 90 g;
- A 5 cm strip can withstand a longitudinal tensile load of more than 125 N/mm 2, and a transverse tensile load of more than 100;
- Heat and frost resistant. It behaves well in the temperature range of −40 - +80 degrees C.
- Over the course of a day, the film transmits 3500 g of water vapor per 1 m2.
- Included in the group of normally combustible building materials, i.e. flue gases reach a temperature of no more than 450 degrees C.
Ondutis A120 is also suitable for wind protection of a wooden house. If we compare the technical characteristics of this membrane with Ondutis A100, here they are higher:
- Weight 1 m 2 - 110 g;
- Tensile strength, if we take the same 5 cm strip - R = 140 and 110 N/mm 2 along and across, respectively.
- Vapor permeability - 3.3 kg/m2.
- It is used in the temperature range −40 - +80 degrees C.
- It is possible to use Ondutis A120 as the main wind protection for walls for up to 3 months.
But perhaps the main advantage of Ondutis films is their long service life, ease of installation and environmental safety.
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
Pile foundations have gained widespread popularity due to their relatively low price and the ability to be used in poor soil conditions. Such structures are quickly installed and can be used for almost any type of structure. Insulation of the floor pie in a frame house on stilts has its own characteristics that must be taken into account in order to avoid problems during further operation.
What types of membranes are there?
There are a huge number of windproof films on sale. They all differ both in price and quality. If you don’t want to take risks on your home, then don’t skimp. A high-quality membrane cannot be cheap.
I can divide films into three types:
- Cheap membranes look very similar to covering material; I would not use them at home. Seal up a shed or a garage, or use it as a flooring under loose insulation on horizontal surfaces.
- More expensive and high-quality windproof films with different surface structures and high density. I used this one for the walls of the house, brand Ondutis A120.

I bought this membrane
This is the best thing that I have held in my hands that is available for sale in our city. Of course not Tyvek, but still a pretty thick film. (If there was, Tyvek would have taken it)
- Superdiffusive membranes. These films are used for insulated pitched roofs. They absolutely do not allow water to pass through from the outside to the inside, and easily release steam to the outside. Often made in multilayers to obtain appropriate properties. Well, of course, you can also use them on walls. They are absolutely not blown by the wind.
Building design features
When erecting a building on screw piles, it is necessary to take into account that the house does not have a basement or basement, but there is a ventilated underground. Such foundations are used mainly in swampy areas, so another important factor during operation will be the increased humidity of the space under the house.
When building a house on screw foundations, it is important to pay great attention to the performance characteristics of the insulation and additional layers.
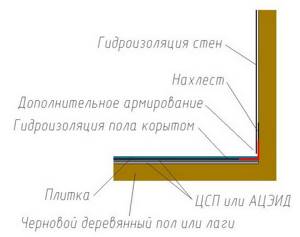
Waterproofing and vapor barrier will serve as reliable protection for thermal insulation material and interior spaces from high humidity, neglect of which will soon lead to serious problems.
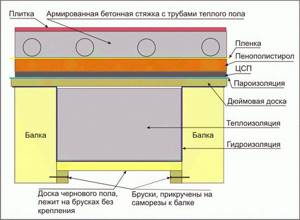
Frame house floor composition
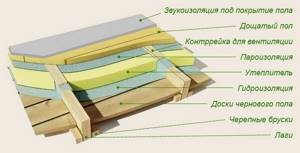
To build a ceiling over a ventilated space, you will need to lay the layers in the following order:
- load-bearing wooden frame (with a subfloor that “bears” insulation);
- a layer of vapor-permeable wind protection (to protect the insulation from “weathering”);
- thermal insulation material;
- steam and waterproofing;
- finished floor construction (board + finished floor).
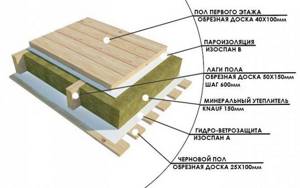
Floor insulation scheme for a house on stilts
All materials for a building on screw foundations must be laid in this order. Some sources indicate the erroneous installation of vapor barrier on the cold air side, but this makes no sense. Steam forms in a warm room and settles on colder surfaces, thus forming condensation. To prevent condensation from penetrating into the thermal insulation layer and reducing the degree of protection of the building from the cold, a vapor barrier is provided.
Why is insulation necessary?
The need for thermal insulation material is not always clear to a person far from construction. From the point of view of the future owner of the house, it is much easier to start from the load-bearing capacity of the structure.
Neglect of thermal insulation standards can lead to the following problems during the operation of the building:
- condensation on the surface of the floor in the technical underground;
- decreased building energy efficiency and increased heating costs;
- High humidity leads to wood rotting, mold and mildew, as a result of which wooden structures quickly fail and require expensive repairs.
Insulating the floor in a frame house allows you to avoid these troubles and ensure a long service life of the building and all its individual structures.
Insulation materials
Attention should be paid not only to the insulation material, but also to vapor barrier, waterproofing and wind protection.
Choice of insulation
Various materials can be used as a thermal insulation layer. It is important to consider the possibility of operation in conditions of high humidity. The most rational solutions are the following options:
Mineral wool insulation. Mineral wool has many advantages, including non-flammability and high thermal insulation characteristics. Not subject to biological influences. The disadvantages include the fact that if water gets on the material, it sags and loses its properties. Compared to other types, this insulation has a fairly high cost. Mineral wool is produced in the form of rolls and slabs. For the floor of a house on screw foundations, it is better to use slab insulation, since it has greater rigidity. Depending on the type of raw material, stone, glass and slag wool are distinguished. It is important that when working with material, builders must have protective equipment: overalls, gloves, a mask.
Polyfoam is attractive in price and has good thermal protection properties. It is worth considering that when exposed to low temperatures and high humidity, it can crumble into small balls. Such damage leads to a violation of the building’s thermal protection. If polystyrene foam is used, it is important to carefully protect it from moisture penetration.
Extruded polystyrene foam (known to everyone as “Penoplex” ) is very similar in appearance to polystyrene foam, but lacks its main disadvantages. The material has higher strength and low water absorption. Thanks to this, you don’t have to worry about its destruction at low temperatures. In addition, extruded polystyrene foam is produced with special additives that allow it to fall into the group of non-combustible materials. The thermal protection characteristics of the above three materials are almost identical.
Another cheap option for insulating the floor of a house on screw piles is expanded clay . It is inferior in thermal insulation properties to all other materials, but is affordable. It is non-flammable and easy to use. It consists of round-shaped transverse clay particles.
What materials are used for floor vapor barrier?
It is convenient to use various films as vapor barrier materials for wooden floors, which, due to their structure, do not allow steam and water to pass through. You can select the type of vapor barrier from the list:
Polyethylene film
The most famous and inexpensive vapor barrier is polyethylene film, which is sold in wide rolls. Since polyethylene sheets themselves are quite fragile and tear easily, they are reinforced with fabric or thin reinforcing mesh.

Reinforced films can be perforated or non-perforated. The first type, due to micro-holes, is characterized by a fairly high vapor permeability (Sd = 1 - 2 m). This means that the perforated films allow some amount of steam to pass through. Therefore, in damp rooms such films are more often used in waterproofing systems. A completely different matter is non-perforated polyethylene with vapor permeability values Sd = 40 - 80 m, which serves as an excellent barrier even for fine vapor.
Aluminum Laminated Polyethylene Film
There is another type of film - polyethylene sheets with an aluminum reflective layer. In addition to high vapor barrier properties (Sd = 200 m), this material also has thermal insulating qualities, reflecting infrared radiation and retaining heat indoors. This type of vapor barrier for a wooden floor is most often used for very humid or hot rooms, where it is important to maintain the existing microclimate. These can be kitchens, showers, baths and saunas.

Polypropylene film
Compared to polyethylene, polypropylene is more durable. Materials with an anti-condensation layer, which have low vapor permeability (Sd = 50 -100 m) and prevent the formation of condensation on the inner surface of the film, are considered especially high-quality.

Polypropylene films may not have an anti-condensation layer, but in this case, condensation often forms on their surface, which is located in close proximity to the insulation.
What tasks are assigned to wind protection?
There is a misconception that wall insulation compensates for wind insulation and resists moisture penetration. However, thermal insulation and wind protection are in no way substitutes for each other.
The direct purpose of the insulating layer is to prevent wind from penetrating into the room
Particular attention is paid to preventing blowing at the joints and corners of the structural elements of the house. Wind protection increases the thermal efficiency of a frame house - no cold comes through the cracks, and heat costs through the walls and roof are minimal
In addition to the main function, the wind barrier is assigned additional tasks:
Insulation protection. Insulation ensures the removal of vapors from the room, preventing the accumulation of moisture inside the insulating layer
The absence of dampness is an important condition for maintaining the thermal insulation qualities of the insulation. Frame ventilation. Normal air circulation prevents rotting of the wooden elements of a frame house.
The wind protection of the under-roof space additionally serves as a water barrier, reducing the risk of leaks during rain and melting snow.
How to properly lay sheet windbreaks
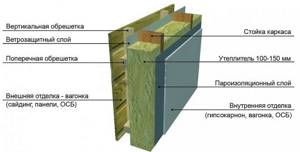
If we are talking about the most popular frame construction today, then we should adhere to the correct sequence of wall layers. For example, after the finishing material inside the house there should be a vapor barrier and insulation. After them comes the lathing for the ventilation gap and only then the layers of wind protection and facade finishing.

Healthy! It is worth clarifying that some windproofing materials are also vapor permeable and can even be used as additional insulation. In this case, some layers of the wall can be abandoned.
The general algorithm for installing sheet wind protection is as follows:
First you need to make sure that all surfaces are dry. The same applies to impregnations. Then the complete installation of thermal insulation is carried out
If mineral wool sheets are used, it is important to ensure that they fit tightly together. At the next stage, the wind protection sheets are cut so that they are installed vertically (in height). It can also be mounted horizontally, but this is not very convenient. The sheets should be laid with the rough side down (if there is one)
This will greatly simplify subsequent finishing work. The sheets are fastened with dowels (it is recommended to choose those with larger caps). As a rule, at least 5 fasteners are required for 1 “square”.
Of course, each specific material has its own nuances. However, regardless of whether roll or sheet material is chosen, novice builders often make a number of mistakes.
Why do you need a windproof layer?
Moisture and windproof films protect the surface of the insulation from water and moisture, from mechanical damage, and also prevent heat loss due to longitudinal filtration of air in the insulation. Protection is especially important during slanting rain, then the insulation is abundantly wetted and, if there is no ventilated gap that quickly dries the surface, there is a risk of freezing of the walls. Wet insulation loses up to 90% of the energy saving characteristics declared by the manufacturer. The vapor barrier film must be laid with the smooth side facing out.
Peculiarities
Wind protection of walls plays an important role in any construction. The need for its arrangement is explained by the fact that heat tends to leave the building; there are several reasons for this.
- Infiltration is the flow of heated air through cracks, as well as cracks and pores in the walls and floor.
- Ventilation - even the most durable thermal insulation materials have micropores, so air masses spread throughout the entire internal volume of the insulation. This reduces its functionality; this figure can reach 90%.

That is why it is extremely important to use wind protection, thanks to which you can regulate the temperature in the room. In addition, the wind and moisture protective film prevents the appearance of fungi and mold that are dangerous to life and health, which invariably appear when condensation occurs
There is an opinion that wind protection and vapor barrier are the same thing, but this is not so. The materials have a similar effect, however, the differences between them are very significant.
A vapor barrier is needed to protect the insulation layer from wet condensation coming from the room. It is used in construction as an addition to thermal insulation coating. Wind protection is indispensable in situations where it is necessary to protect the structure from the adverse effects of wind, precipitation and other weather phenomena. Ventilated facades have the property of allowing steam to pass through, so liquid in the form of condensation does not accumulate inside the insulation and maintains its functional characteristics.