Classification
To create an optimal microclimate in the building, a calorific heating system is used, that is, forced heating using equipment that is installed in air ducts.
Depending on what coolant is used, there are 4 types of heaters:
- Steam - used most often in industrial enterprises where steam production is provided for by technological processes.
- Electric - this option is the easiest to install (you only need a power source to heat the built-in heating elements), but it requires a lot of electricity consumption. The use of an electric heater is considered appropriate only in facilities whose area does not exceed 150 m²

- Water - this type of heater operates on the basis of hot water and is installed in ventilation systems with a rectangular or round cross-section in areas over 150 m². This type of heating is reliable, practical, easy to maintain and inexpensive.

A special feature of the heater is that the composition of the air flow coming from the street should not be sticky, fibrous, or contain solid particles. Permissible dust content is no more than 0.5 mg/m³. Minimum intake air temperature -20 °C.
When choosing a heater, the following factors are taken into account:
- room area;
- weather conditions in a given climate zone;
- ventilation power.
The heater is installed in the inside of the ventilation shaft, so it must correspond to its parameters (configuration and size).
If the performance is low, the device will not be able to warm up the air masses.
If it is not possible to install a heater with the required parameters, then several mechanisms with lower power are mounted in series.
Features of the choice of air heaters and their classification
The heater is installed in ventilation systems under the guise of individual elements, or in combination with a monoblock design. His choice is influenced by factors such as:
- Room size;
- Ventilation power;
- Climatic conditions.
Based on these data, it is already possible to select a ventilation heater for specific requirements. Heaters can be divided into 2 types:

Electric heater for fresh air ventilation
Electric heaters are the simplest option. It does not require complex communication lines, since it only requires a power source to operate. To ensure more efficient heat exchange, heating elements are built in, which contribute to the conversion of electricity into heat. The principle of operation is such that the air coming from the street passes through the heating element, in which it is heated and only after that it passes into the room. This option is effective in areas of no more than 150 m2, since its use in larger spaces is impractical. A significant disadvantage is the high energy consumption;

Water heater for fresh air ventilation
Water heaters are a practical and reliable option that is more suitable for rooms over 150 m2. They do not require any maintenance and are considered cheap to use. Their effectiveness is interconnected with the presence of automation in control. With their help, you can easily equalize the air temperature, as they are equipped with a thermostat. The principle of operation is based on the fact that air enters through a special air intake mesh and passes to filters, where it is cleaned of dust and harmful substances. Then it passes into the heater, where it is heated by the heat that comes from the main water.
Operating principle and design of a water heater
A heater is a device used to heat air. According to the principle of operation, it is a heat exchanger that transfers energy from the coolant to the flow of the supply jet. It consists of a frame inside which tubes are located in dense rows, connected in one or more lines. A coolant circulates through them - hot water or steam. The air, passing through the cross-section of the frame, receives thermal energy from the hot tubes, due to which it is transported through the ventilation system already heated, without creating the possibility of condensation forming or cooling the premises.
Types of heating devices for supply ventilation
All heaters for supply ventilation can be divided into two main groups:
- Using coolant.
- Not using coolant.
The first group includes water and steam heaters, the second - electric. The fundamental difference between them is that the devices of the first group only organize the transfer of thermal energy supplied to them in finished form, while the devices of the second group create heat within themselves independently. In addition, water and steam heaters are divided into plate heaters, which have greater efficiency but poorer performance, and spiral-rolled heaters, which are now used almost everywhere.
There are also heating devices, often classified in these groups, for example, a gas heater. The burning gas heats the air flow passing through the glow zone, preparing it for use in ventilation or air heating systems. The use of such devices is not widespread, since the use of gas in industrial workshops is associated with a lot of dangers and has many restrictions.
There are also waste oil heaters. The heat generated by burning waste is used. For large rooms such devices do not have sufficient power, but for small auxiliary areas they are quite suitable.
Organization of supply ventilation with air heating: everything you need to know.
We install plastic air ducts for ventilation: advantages and disadvantages.
Ventilation in the bathroom and toilet: selection and installation of an exhaust fan.
Pros and cons of using
The advantages include:
- High efficiency.
- Simplicity of the device, reliability.
- Compact, can be placed in small spaces.
- Low maintenance (water and steam appliances practically do not need it).
Disadvantages include:
- The need for coolant or connection to the power supply network.
- Independence of work - equipment for air supply is required.
- Stopping the supply of electricity or coolant means stopping the system.
Both the advantages and disadvantages of the devices are determined by the design and do not depend on external factors.
Features and nuances of the technological process of installing supply ventilation with air heating
Installation of supply ventilation is not difficult for a professional. In principle, the technological process does not have many difficulties. First of all, to prevent condensation, you need to insulate the area before the entrance to the device using roll insulation.
Air ducts must be fixed to the wall or ceiling. To avoid unnecessary vibration, it is recommended to attach vibration round inserts between the installation and the network. Supply ventilation with heating and cooling of air should be located so that the ventilation grilles are directed to places of maximum concentration of people.
It is much easier to install equipment in a simple apartment or private house. For this purpose, compact installations with small dimensions are used. If the room has plastic windows, it means that natural ventilation is impossible, and therefore you will have to install a forced supply model.
A heated supply valve can be mounted either in the wall or in the ceiling, it all depends on the design of the room and the personal preferences of the owner.
Connection
The supply of air masses can be carried out in one of two options:
- Left version: the mixing unit and automatic control are installed on the left side, water is supplied from the top, outflow is at the bottom.
- Right execution: the indicated mechanisms are on the right, the water supply tube is at the bottom, the “return” is at the top.
The tubes are placed on the side where the air valve is installed.
Water heaters are divided into 2 types according to the type of valve:
- two-way – when connected to a general heating supply;
- three-way – with a closed method of heat supply (for example, when connected to a boiler).
The type of valve is determined by the characteristics of the system supplying heat. These include:
- Type of system.
- Water temperature at the beginning of the process and during outflow.
- With central water supply, the difference between the pressure in the water supply and outflow pipes.
- When autonomous - the presence or absence of a pump installed on the inflow circuit.
The installation diagram must provide for the inadmissibility of installation in the following cases:
- with vertical pipe inlet and outlet;
- with top air intake.
Such restrictions are due to the possibility of snow masses entering the equipment inflow and further leakage of melt water into the electronic unit.
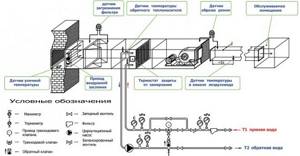
Place of installation of a duct heater for supply ventilation in the air exchange system (if there is a possibility of the temperature dropping below normal, it is obligatory to install an anti-freeze thermostat)
To avoid malfunctions of the automation unit, the temperature sensor must be located in the inside of the air blowing element at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the inflow mechanism.
The principle of operation of supply ventilation with a heater
To ensure optimal air flow from the street into the living space, forced ventilation is used. When it’s warm outside, there are no particular difficulties with this; you just need to choose a sufficiently powerful ventilation that will be enough for a particular room. In the cold season, everything is more complicated, since the influx of cold air can significantly cool the room. For this purpose, air heaters are used that are installed on the supply ventilation. In this case, it will be useful to know what a ventilation heater is and what it provides.

Heater for fresh air ventilation
When a heater is used for supply ventilation, it is possible to ensure an influx of fresh air from the street into the room, which will be heated to a comfortable temperature to maintain the microclimate. The heater is designed to warm up the incoming air by passing the latter through heating elements.
Strapping methods
The piping is a frame made of reinforcement, with the help of which the flow of hot water is regulated. The piping unit helps to monitor the performance of the supply ventilation heater, control it and maintain the desired temperature in the building. The location of the piping units is determined by the installation location, air exchange diagram, and technical parameters of the equipment. There are 2 installation options:
- Recirculated air masses are mixed with supply air.
- Only indoor air is recirculated according to a closed principle.
Taking this into account, there are 2 methods of strapping:
- 2-way valves - with uncontrolled reverse water flow;
- 3-way valves - when controlling water flow in a boiler room or boiler room.
Some produce piping units of various modifications, which are entire sets consisting of valves (balancing and check valves, two and three-way), pumps, bypasses, ball valves, pressure gauges, and cleaning filters.
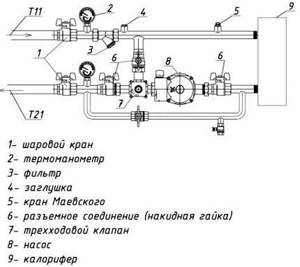
Scheme of piping heater units for supply ventilation. (Ball valves installed at the inlet and outlet allow you to shut off the water, and a thermomanometer allows you to control temperature and pressure)
If natural ventilation is well established, then there are much more opportunities for successful operation of the equipment. The correct choice of piping in such cases is effective both for heating large areas in production and for private houses and cottages.
The heater used for ventilation is usually connected to the heating system directly at the air intake point. If forced ventilation is in effect, the air heater can be installed anywhere. Air heaters for supply ventilation allow you to create a comfortable temperature regime in both industrial and residential premises. It is only important to correctly decide on the choice of coolant, which will be the most effective (with minimal costs and maximum performance) under certain conditions. An automated system - such as a supply ventilation control panel with a water heater - will make the use of heating devices for supply ventilation convenient and safe.
Don't miss: Knauf mineral wool: types and features
Application
Air supply units with a low-power water heater are installed:
- in apartments,
- cottages.
- small offices
- in heating systems of private cottages, houses,
- warehouses
- in shops.
The use of air supply units with a water heater provides a comfortable microclimate for people. They can breathe pollutant-free air at an acceptable temperature, free from smoke, dust particles, allergens and other microscopic debris. The air is not dried as it passes through the unit. Air-conditioning units with a water heater are especially recommended for installation in places where there are people with allergies or diseases of the respiratory system.
Types of heaters
There are several types of air heaters used in different areas and conditions.
Let's take a closer look at them:
Mermen
The most common group of devices, characterized by high efficiency, safety and ease of operation. They use hot water as a coolant, coming from the central heating network, hot water supply or from their own boiler. A water heater for fresh air ventilation is the most convenient and economical solution, allowing you to perform the assigned tasks with minimal maintenance or repair costs. The only drawback of the device is the need to connect to the coolant supply system, which creates certain difficulties at the installation stage and prevents quick transfer to another location.
Steam
Steam devices are complete analogues of water devices and in practice differ from them only in the type of coolant. The only difference between steam devices is the greater thickness of the tube walls - 2 mm versus 1.5 for water ones. This is due to the high pressure in the system, requiring reinforced channels for circulation. Otherwise, the devices are identical and have the same operating rules and requirements.
Electrical
An electric heater for supply ventilation does not require a coolant supply, since the heating source is electric current. Connecting such devices is much simpler, which makes them mobile and easy to use, but high energy costs limit the use of this group. Most often, they are installed for local heating when performing one-time work, and are used as emergency or temporary heat sources.
Selection of industrial air heaters
Having decided on the primary heating source, we select the type of air heater. The first question is under what conditions and within what temperature conditions it will work. The second is the degree of contamination of the coolant and air. If the operation of heat exchangers occurs under poor conditions with air temperatures from -20°C and below, it makes sense to opt for TVV, KP and KFB air heaters. These are bimetallic heaters, in which a metal pipe with aluminum fins is used as a heat exchange element (similar to KSk and KPSk). Their fundamental difference is as follows:
1. Increased area for coolant passage. A particularly important factor for operation in conditions of low outdoor temperatures. The possibility of contamination with dirt, and in the case of steam air heaters, with scale, is reduced. Which, firstly, extends their overall service life; secondly, when the coolant is contaminated, it prevents complete blocking of the internal section and, accordingly, freezing of the heat exchanger; thirdly, the thermal characteristics are stable over a longer period of time. 2. The thickness of the aluminum fin of these air heaters is greater than that of KSk and KPSk, which contributes to less mechanical deformation of the heating element during transportation and operation. And the increased pitch of the aluminum fins contributes to less clogging of the interfin space with dirt and dust, and accordingly, a decrease in aerodynamic drag
This has a positive effect when operating heaters in buildings with increased dust and air pollution, and, which is again important, when operating in conditions of low temperatures, where the recommended mass velocity in the frontal section when selecting heaters is up to 3.5 kg/m2*s. 3
Less hydraulic resistance.
All of the above factors contribute to the fact that for many years, mining enterprises have chosen to create process heat - water heaters TVV and steam KP, and for the layout of air heating installations heaters KFB 10 A4, which have significant advantages under poor operating conditions in regions with low temperatures modes.
Delivery of purchased industrial air heaters to customers is carried out both on a self-pickup basis and by our company’s vehicles. It is widely practiced to send equipment by freight forwarding companies, and air heaters are delivered to local terminals of transport companies free of charge.
Criteria for selecting air heaters
When choosing a heater, in addition to heat output, air volume output and heat exchange surface, you need to decide on the criteria listed below.
With or without fan
The main task of a heater with a fan is to create a warm air flow to heat the room. Pulling air through the plates of the tubes is the function of a fan. In the event of an emergency situation with a fan failure, the circulation of water through the tubes must be stopped.
In the absence of a fan, the capabilities of the heater are limited; such devices today are ineffective and are only slightly superior to radiators. In essence, they become a convector, creating convection currents and thermal radiation.
Tube shape and material
The basis of the heating element of the heater is a steel tube from which the section grille is assembled. There are three tube design options:
- smooth tube - ordinary tubes are located next to each other, heat transfer is the lowest possible;
- plate - plates are pressed onto smooth tubes to increase the heat transfer area.
- bimetallic - steel or copper tubes with a wound aluminum tape of complex shape. Heat transfer in this case is most effective; copper tubes are more thermally conductive.
Minimum required power
To determine the minimum heating power, you can use a fairly simple calculation, given in the comparative calculation between radiators and air heaters earlier. But since air heaters not only emit thermal energy, but also circulate air with a fan, there is a more accurate way to determine power, taking into account the tabular coefficients. For a car showroom with dimensions 50x20x6 m:
- Car showroom air volume V = 50*20*6 = 6,000 m3 (needs to be heated in 1 hour).
- Outside temperature Tul = -20⁰C.
- Temperature in the cabin Tcom = +20⁰C.
- Air density, p = 1.293 kg/m3 at average temperature (-20⁰C +20⁰C)/2 = 0. Specific heat capacity of air, s = 1009 J/(kg*K) at outside temperature -20⁰C - from the table.
- Air capacity G = L*p = 6,000*1.293 =7,758 m3/hour.
- Minimum power according to the formula: Q (kW) = G/3600*c*(Tcom - Tul) = 7758/3600*1009*40 = 86.976 kW.
- Taking into account a power reserve of 15%, the minimum required heating capacity = 100.02 kW.
There are many methods for relatively accurate calculations. But for specific projects it is better to contact heating engineers or specialized companies.
Power calculation
Before you start choosing a heater, you should calculate the main indicators, such as the power and temperature of the air flows at the outlet of the installation. In addition, it is necessary to take into account a number of characteristics depending on the use of different types of power and the number of phases. So, when connecting an electric heater with a power of 5 kW, it is necessary to arrange a three-phase connection.
The maximum allowed current consumption is calculated using the formula I=P/U, where P denotes power and U is the voltage in the power supply network. For single-phase connections, U is equal to 220, and for three-phase connections – to 660 V.
In addition to electrical calculations, it is necessary to find out the temperature of the supply flows when using a heater of a particular power. The formula used for calculation is T=2.98xP/L, where L means the system performance, and P is the power of the electrical element. Standard indicators for the power of air heaters for apartments and private houses are considered to be values from 1 to 5 kW, despite the fact that the power of devices installed in the ventilation systems of large industrial enterprises is 5-50 kW.
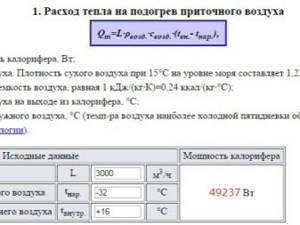
Differences in air heaters by tube type
Heating heaters may differ in the type of tubes used to transfer heat. The following models of such devices are distinguished:
- Smooth tube - products consist of a large number of thin hollow pipes.
- Plate devices have fins, which significantly increases their heat transfer.
- Bimetallic - such products use tubes made of copper and aluminum. Copper ones transfer heat, and collectors are made of aluminum.

Attention ! Caloriferous smooth-tube heating is the least efficient, but the cost of such products is noticeably lower.
Differences in air heaters by installation method
Household and industrial air heaters can have the following placement options:
- Wall.
- Ceiling.
- Floor.

Some models can also be built into a forced ventilation system, which allows you to maximize the efficiency of this heating method.
Installation Tips
Heaters with sensors in the greenhouse maintain the desired temperature
The water heater is installed in rooms connected to the central heating main. When installing yourself, you should follow the recommendations of specialists:
- The diagonal of the heater depends on the bending characteristics of the channels, the type of damper and structural elements.
- To protect the heater from freezing, installation is carried out in rooms with a temperature not lower than 0 degrees.
- Before installation, it is necessary to inspect the plates and tubes for integrity.
- Weld-on flanges are easiest to connect end-to-end.
- Direct-flow air vent valves are located at the top of the outlet and supply manifolds.
- The joints between the device and the ventilation system are sealed.
- Wall-mounted models are installed by fastening the console with two self-tapping screws.
Connection diagram and control
Electric heaters must be connected in compliance with all safety requirements. The connection diagram for the electric heater is as follows: when you press the “Start” button, the engine starts and the heater ventilation is turned on. At the same time, the engine is equipped with a thermal relay, which, if there is a problem with the fan, instantly opens the circuit and turns off the electric heater. It is possible to turn on the heating elements separately from the fan by closing the blocking contacts. To ensure rapid heating, all heating elements are turned on simultaneously.
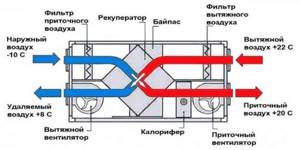
To increase the safety of the electric heater, the connection diagram includes an emergency indicator and a device that prevents the heating elements from turning on when the fan is turned off. In addition, experts recommend including automatic fuses in the circuit, which should be placed in the circuit together with the heating elements. But installing automatic machines on fans, on the contrary, is not recommended. The heater is controlled from a special cabinet located near the device. Moreover, the closer it is located, the smaller the cross-section of the wire connecting them can be.

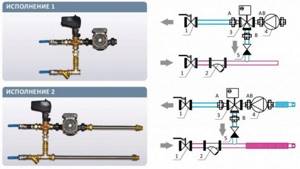
When choosing a water heater connection diagram, you need to focus on the placement of mixing units and units with automation. So, if these units are located to the left of the air valve, then a left-hand design is implied, and vice versa. For each version, the location of the connecting pipes corresponds to the air intake side with the installed valve.
There are a number of differences between left and right placement. So, with the right-hand version, the water supply tube is located at the bottom, and the “return” tube is located at the top. In left-sided circuits, the supply pipe enters from the top, and the outflow pipe is located at the bottom.
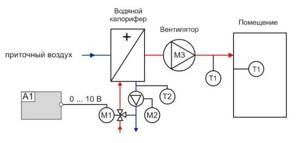
When installing a heater, it is necessary to install a piping unit necessary to monitor the performance of the device and protect it from freezing. Piping nodes are the reinforcement frames that regulate the flow of hot water into the heat exchanger. Piping of water heaters is done using two- or three-way valves, the choice of which depends on the type of heating system. Thus, in circuits heated by a gas boiler, it is recommended to install a three-pass model, while for systems with central heating, a two-pass model is sufficient.
Don't miss: Gypsum stucco fireplace - style, type, shape, DIY
Controlling a water heater involves regulating the thermal power of heating devices. This is made possible by the process of mixing hot and cold water, which is carried out using a three-way valve. When the temperature rises above a set value, the valve releases a small portion of cooled liquid into the heat exchanger, which is taken at the outlet.
To increase the efficiency of the system, it is recommended to include a circulation pump in the connection diagram. The device is installed at the outlet of the heat exchanger, which allows it to work with already cooled glycol solution or water.

In addition, the installation diagram of water heaters does not provide for the vertical arrangement of inlet and outlet pipes, as well as the location of the air intake at the top. Such requirements are due to the risk of snow getting into the air duct and melt water flowing into the automation. An important element of the connection diagram is the temperature sensor. To obtain correct readings, the sensor must be placed inside the air duct in the blowing section, and the length of the flat section must be at least 50 cm.

Connecting a water heater
Air flow using a water heater can be performed in two versions, right and left. It depends on where the mixing unit and the automation unit are located. When the air supply unit is considered from the air valve side, then:
- Left-hand execution means that the automatic unit and mixing unit are located on the left side;
- Right-hand execution means that the automatic unit and mixing unit are located on the right side.
In each version, the connecting pipes are located on the air intake side, where the air valve is installed. Depending on the version, there are the following features:
- In the right-hand versions, the supply tube is located at the bottom, and the “return” tube is located at the top;
- In left executions everything is different. The supply is at the top and the outflow is at the bottom.
Because in air supply installations using water heaters, a mixing unit is required, the latter must contain a 2 or 3 way valve. You need to select a valve based on the parameters of the heat supply system. For individual circuits of autonomous heating systems, which can be a gas boiler, a three-way valve is required. If the air handling unit is connected to a central heating system, then a two-way valve is required. To summarize, the choice of valve depends on:
- System type;
- Temperatures of supply and return water;
- Pressure drop between the supply and return pipes if the system is central;
- Is there a separate pump on the ventilation supply circuit if the system is autonomous?
When installing a circuit with a water heater, installation in a position where the input and output pipes are located vertically is prohibited. Also, installation should not be carried out if the air intake is located at the top. This is due to the fact that snow can get into the inflow of the installation and melt there, which threatens water penetration into the automation. In order for the temperature controllers to work correctly, it is necessary to place the temperature sensor inside the air duct exhaust so that the area is even in length at least 50 cm from the inlet installation.
You should also know that:
- It is prohibited to install an air supply unit 100 – 3500 m3/h if the motor axis is vertical;
- It is prohibited to install air supply units where they may be exposed to moisture or chemically active substances;
- It is prohibited to use the air handling unit where there is direct influence of precipitation on the installation;
- It is prohibited to block access for servicing installations;
- To install the air handling unit in a heated room and avoid condensation on the supply air duct, it is necessary to use only a thermally insulated air duct.
There is nothing particularly complicated in installing air heaters; you just need to follow the rules and observe safety precautions. Sometimes it is better to entrust this matter to professionals and be sure that all work is completed taking into account all requirements.
Source
Installation and operation
Installation of air heaters in home supply and ventilation systems can be done independently. Household air heaters are small in size and quite lightweight. However, before carrying out work, you should still check the strength of the wall or ceiling. The strongest bases are concrete and brick surfaces, the average ones are wooden, and plasterboard partitions are completely unsuitable supports for hanging devices.
Installation of the heater begins with the installation of a bracket or frame that has a number of compatible holes for mounting the device. Then the device itself is installed on them and pipes equipped with a set of shut-off valves or a mixing unit are connected.
If technical capabilities allow, it is recommended to connect part of the unit before placing the heater on the wall.

The heat exchanger is connected to the heating system circuit using fittings or welding. The welded method is more preferable, however, if there is a flexible connection, its use is impossible. After connecting, it is recommended to treat all connections with a heat-resistant sealant, and before carrying out the first testing, remove air accumulations from the channels, check the valves and adjust the position of the blind guides.
After successful testing and commissioning of ventilation, it is important to follow a number of rules that will extend the service life of the installation and make operating the system simple and safe.
- It is necessary to regularly monitor the air condition in the room.
- The temperature of the liquid in water appliances should not be allowed to rise above 190 degrees.
- The operating pressure of the system should be monitored and not allowed to rise above 1.2 MPa.
- The first start of the system, as well as turning on the heater after a long break, must be done very carefully. Heating should be increased gradually, no more than 30 degrees per hour.
- When operating water appliances, the indoor air temperature must not be allowed to drop below 0 degrees. Otherwise, the water in the pipes will freeze and rupture the system.
- When installing electric heaters in rooms with high humidity, the moisture protection level of the device must correspond to class IP 66.

The correct choice of heater for the supply ventilation system will ensure uniform and effective heating of the incoming air masses and make staying in the room pleasant and comfortable.
System installation
On the balcony side, the circuit changed, the input muffler was removed, and another G5 filter was installed in front of the fan instead. There is a valve on the main ventilation channel, bypassing the heaters; in winter mode it is closed - the air will flow through the heaters.

With the help of a janitor, a hole was made in the wall onto the balcony. It's good that walls are easy to break down. The inside is foam concrete, then 15 cm of polystyrene foam and facing the floor with bricks. The layout of the apartment made it possible to create a small storage room measuring 50x50 cm in the corner near the balcony.

The task was complicated by the fact that it was necessary to place the muffler (length 110 cm, diameter 30 cm) after the heater. Because of this, the installation turned out to be very tight.
Using a drill, some kind of thing and a round bend, I cut into the main ventilation duct, which runs under my ceiling. To the left of the new insert you can see the air conditioner's air intake for recirculation. Installed a silencer. It weighs about 5 kg, so it rests on supports.

I tried on the air heaters. Everything fits in smoothly, the margin is only a couple of centimeters. The distance between electric and water turned out to be too small - at least two diameters are needed. This was one of my serious mistakes.
I insulated the corner and the flap with 2 cm foam foam and foamed the hole. The heaters are connected using quick-release clamps FK 200 Fast clamp. The clamps are simply fantastic, they allow you to remove any assembly in a few seconds, plus they isolate vibration noise from the fan.

KSK
Heaters KSK-3, produced at the company T.S.T.

The model range of domestically produced KSK water heaters includes 2/3/4-row devices that differ in performance and size
Specifications:
- coolant temperature at the inlet (outlet) – +150 °C (+70 °C);
- inlet air temperature – from -20 °C;
- working pressure – 1.2 MPa;
- maximum temperature – +190 °C;
- service life – 11 years;
- working resource – 13,200 hours.
External parts are made of carbon steel, heating elements are made of aluminum.
Teplomash TW and MW series

Water heaters Teplomash KEV TW/MW with a heat power range from 3.1 to 31 kW and an air capacity from 600 to 3000 m3/hour for TW; for MW heat power from 11.7 to 120 kW, air power from 3000 to 7000 m3/hour. Coolant temperature up to +150°C, operating ambient temperature: from -10°C to +40°C. The TW series is made in a metal case, and the MW series in a plastic case.
Cost: from 18,000 rub.
Galletti AREO
Galletti AREO heater made in Italy.

Galletti AREO water heaters are capable of both heating the premises being treated and cooling the space in hot weather
The models are equipped with a fan, a copper-aluminum heat exchanger and a drainage tray.
Specifications:
- power in heating mode – from 8 kW to 130 kW;
- power in cooling mode – from 3 kW to 40 kW;
- water temperature – + 7°C +95 °C;
- air temperature – from 10°C to + 40°C;
- working pressure – 10 bar;
- number of fan speeds – 2/3;
- electrical safety class – IP 55;
- motor protection.
In addition to the devices of the listed brands, on the market of heaters and water air heaters you can find models of the following brands: Teplomash, 2VV, Fraccaro, Yahtec, Tecnoclima, Kroll, Pakole, Innovent, Remko, Zilon.
Ballu BHP-W3

Domestic water fan heaters with a single-row copper-aluminum heat exchanger (W) for economical heating with three operating modes. Coolant temperature up to +150°C, maximum thermal power – 24.55 kW, air heating up to +23°C. Plastic housing (mounted or wall-mounted), attractive design, low noise level. Developed in the Netherlands, manufactured in China. This is one of the best options for both domestic needs and the industrial sector when the budget is not limited.
Cost: from 19,000 rub.
Electric heater
The electric heater chosen was Systemair CB 200-3.0. The power of this heater is enough to heat 200 m3/hour from -20 °C to + 18 °C.
- minimum air flow - 170 m3/hour
- three separate sections of 1 kW
- The heater is equipped with automatic bimetallic overheating protection (normally closed contact) and additional overheating protection with manual restart.

I divided it into two sections 1 + 2 kW:
- a 1 kW section will operate in water + electricity mode (priority on water), the electric heater will be connected automatically if the water heater cannot cope. This section is controlled via a solid-state relay.
- the 2 kW section is controlled by the PULSER Controller. Its temperature sensor is installed after the electric heater, but before the water heater. This mode turns on at night - electricity + water (priority on electricity). Two 2 kW sections will heat the air as much as they can, the rest will be heated by a water heater.
There were fears that the solid-state relay would overheat in the heater housing, but it turned out that it was practically cold. Just in case, a standard fire sensor (operation temperature 70 °C) with normally closed contacts was additionally installed in the heater housing.

Volcano
The Volcano mini water fan heater is a compact device from the Polish brand Volcano, characterized by practicality and ergonomic design. The air flow direction is adjusted using controlled blinds.

One Volcano mini fan heater is capable of generating as much heat as a dozen conventional bimetallic radiators made up of ten sections
Specifications:
- power within the range - 3-20 kW;
- maximum productivity – 2000 m³/h;
- heat exchanger type – double row;
- protection class – IP 44;
- maximum coolant temperature – 120 °C;
- maximum working pressure – 1.6 MPa;
- internal volume of the heat exchanger – 1.12 l;
- guide blinds.
Volcano water fan heaters are designed to heat the air in domestic and industrial premises using water coolant.
Classic KSk-3 and KSk-4

Water heaters with thermal elements made of tubes with bimetallic and aluminum fins in a spiral-rolling manner. It is used to heat air with water at temperatures up to +190°C, supplied by circulation pumps under pressure up to 1.2 MPa (12 bar). The range of air productivity is from 2000 to 2500 m3/hour, for heat for KSk-3 - from 37 to 556.4 kW; for KSk-4 – from 43.4 to 648.1 kW. The main advantage is the affordable price due to its simple design, domestic production and simple appearance.
Cost: from 9,000 rub.
Sources
- https://VentingInfo.ru/oborudovanie/kalorifer
- https://klimatlab.com/ventilyaciya/kondicionirovanie/kalorifer-vodyanoj-dlya-pritochnoy.html
- https://GradusPlus.com/radiatory-otopleniya/vidy/kalorifery/
- https://stroy-podskazka.ru/ventilyaciya/pritochnaja-kalorifer/
- https://www.tproekt.com/kalorifery-otopleniya/
- https://sovet-ingenera.com/vent/oborud/kalorifer-vodyanoj-dlya-pritochnoj-ventilyacii.html
[collapse]











