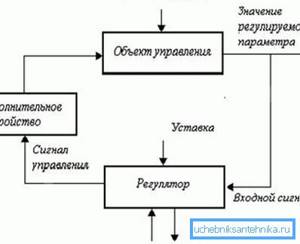
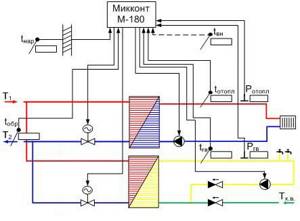
Logical diagram of the system operation.
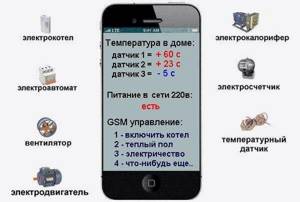
The sensors are pressure and temperature sensors, as well as any additional sensors that allow you to control various processes. The most important are temperature sensors for the supply and return flow of coolant, indoor and outdoor temperature sensors, as well as pressure sensors at the system inlet.
Clip-on temperature sensor.
The role of the controller is played by a low-power computer that reads information from all sensors. A program is recorded on the computer memory card that determines temperature conditions.
The controller compares the received values with the specified ones, and, if necessary, makes a decision to make changes: increasing the coolant supply to one or another circuit, turning off the boiler or switching it to another operating mode, etc.

The controller is assembled without the use of hot cards.
Upon making a decision, the controller sends a control signal to one or another actuator: switching relay, valve or damper servomotor, switch or boiler electronics. Depending on the specified program, the GSM module for heating control can send messages to the owner about a particular event, and after waiting for a response, take certain measures.

Actuator ST 24B.
Heating control in a country house via GSM is carried out using a special module built into the computer.
This module includes the following elements:
- SIM card slot;
Power supply and battery;

Module design with GSM.
Important! Along with the GSM control module, software must be supplied for installation on the mobile phone operating system. The program will help organize remote communication between the controller and operator.
Advantages
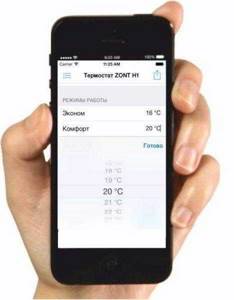
You can easily control the system with your own hands from any distance.
What are the advantages of using an automatic heating control unit?
A modern controller with a communication module allows you to get the following advantages and benefits:
- Fine adjustment of the system in real time allows you to achieve maximum savings at the appropriate level of comfort;
- You can achieve exactly the temperature and climatic parameters of the room that you want, and for this you simply need to set the desired temperature values;
- The instant notification system about emergency conditions and abnormal events significantly increases the reliability and safety of work;
- You have the opportunity to leave the house with the heating running and control its condition from a distance, as well as control operating modes, turn the equipment on or off remotely;
- A winter visit to a country house with the heating turned off requires entering a cold room, heating the unit and waiting several hours for the room to warm up. Now you can give the command to turn on in advance and not waste time.
You just need to take out your phone.
You can assemble and connect the control system yourself - no permits or approvals are required for this. The work is easy to do by following the manufacturer's instructions. The price of the kit can range from 4 to 40 thousand rubles, depending on the configuration and manufacturer.
Important! Most modules have connectors for connecting additional sensors, which can be used to control the opening of windows and doors, listening or surveillance, and other useful functions.
Automatic control unit
Purpose

An automatic control unit is a personal heating point designed to control the parameters of the coolant circulating in the heating system, depending on the temperature in the room, outside, in the supply and return pipelines of the circuit.
In addition, the system allows for protection from emergency situations, switching of equipment operating modes, and GSM heating control. In the event of a breakdown or emergency, the module is able to notify all subscribers included in the mailing list via SMS messages.
But this is not a complete list of functions.
The control unit can supply:
- parameters and operating modes of the circulation pump of the heating system, the specified coolant circulation speed,
- execution and control of maintaining the specified temperature schedule of the supply and return pipelines . This allows you to protect the system from overcooling and overheating,
- Maintaining a given constant pressure difference at the supply and return inputs to the building , which allows all automation to operate normally in normal mode,
- Narrow and uncouth coolant cleaning,
- Visual monitoring of all indicators of system operation : temperature in key areas, pressure difference at the outlet and inlet of the unit, specified operating mode, alarms,
- Remote heating control by phone and via the Internet,
- Remote control of the premises, alarms, gates and entrance doors using additional sensors.

Note! To install such a system, other equipment and the boiler must be adapted for electronic control. Dilapidated frames with mechanical valves will not work with such a scheme.
principle and mechanism of action

Any automatic control system includes sensor units:
- and such Sensors that collect the necessary data in different places of the system,
- processors and controllers, which compare the data received from the sensors with the values dictated by the instruction (program) recorded on the memory card, make a decision and, based on it, issue commands to the executing mechanisms,
- Executing mechanisms, which receive commands from controllers and perform simple actions - close valves and taps, increase the power of units, switch operating modes of heating equipment, make emergency shutdowns of broken components.
The sensors are temperature and pressure sensors, and any additional sensors that allow you to control various processes. The most important are temperature sensors for the supply and return flow of coolant, indoor and outdoor temperature sensors, and pressure sensors at the system inlet.

The role of the controller is played by a low-power computer that reads data from all sensors. A program is recorded on the computer memory card that determines temperature conditions.
The controller compares the received values with the specified ones, and, if necessary, makes a decision to make transformations: increasing the coolant supply to one or another circuit, turning off the boiler or switching it to another operating mode, etc.

Upon making a decision, the controller sends a control signal to one or another precise device: a switching relay, a valve or damper servomotor, a switch or boiler electronics. Depending on the specified program, the GSM module for heating control can send messages to the owner about this or that event, and after waiting for a response, take certain measures.

Heating control in a country house via GSM is carried out using a special module built into the computer.
This module includes the following elements:
- Slot for SIM card switching,
- Power supply and battery,
- GSM modem,
- Antenna connector,
- LAN port for connecting to an Internet provider,
- CPU,
- Memory card,
- USB connector for configuration and setup,
- LED indicators or liquid crystal display,
- A contact group with outputs and inputs for collecting data and sending control signals.

Note! Along with the module for GSM control, software must be supplied for installation on the cell phone OS. The program will help organize the operator and remote communication of the controller.
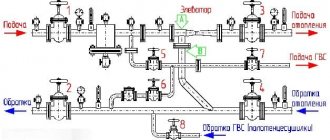
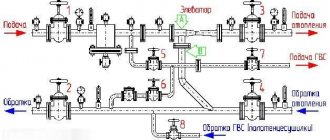
Elevator heating unit - what is it? Scheme and principle of operation
No one will argue that the heating system is one of the most important life support systems of any home, both a private house and an apartment. If we talk about apartments, centralized heating often predominates in them; in private houses, autonomous heating systems are most often found. In any case, the design of the heating system requires close attention. For example, in this article we will talk about such an important element as the elevator heating unit, the purpose of which is not known to everyone. Let's figure it out.
Automation of heating of a private house
Heating system installations for private houses are equipped with automation systems; as a rule, they are closed and come with a set of all necessary sensors and regulators.
The main tasks that automation of heating of a private house solves are:
- control of heating boiler operation;
- providing comfortable living conditions;
- saving fuel and operating equipment in optimal mode.
Setting up an automation system for home heating systems is often quite simple and is carried out either by the owner of the building or by the organization that installed the system itself.
What is an elevator heating unit and what is it used for?
In order to clearly understand the structure and purpose of the elevator unit, you can go into an ordinary basement of a multi-story building. There, among the other elements of the thermal unit, you can find the required part.
Elevator heating unit
Let's consider a schematic diagram of the coolant supply to the heating system of a residential building. Hot water is supplied through pipelines to the house. It is worth noting that there are only two pipelines, of which:
- 1- supply (supplies hot water to the house);
- 2-reverse (removes the coolant that has released heat back to the boiler room);
Water heated to a certain temperature from the thermal chamber enters the basement of the building, where shut-off valves are installed on the pipelines at the entrance to the heating unit. Previously, gate valves were installed everywhere as shut-off valves; now they are gradually being replaced by ball valves made of steel. The further path of the coolant depends on its temperature.
In our country, boiler houses operate according to three main thermal regimes:
If the water in the supply pipeline is heated to no more than 95 0 C, then it is simply distributed throughout the heating system using a manifold equipped with control devices (balancing valves). If the temperature of the coolant is above 95 0 C, then according to current standards such water cannot be supplied to the heating system. You need to cool it down. This is where the elevator unit comes into play. It is worth noting that the elevator heating unit is the cheapest and simplest way to cool the coolant.
Design and principle of operation of a heating elevator
At the entry point of the heating network pipeline, usually in the basement, a node that connects the supply and return pipes catches your eye. This is an elevator - a mixing unit for heating a house. The elevator is manufactured in the form of a cast iron or steel structure equipped with three flanges. This is an ordinary heating elevator; its operating principle is based on the laws of physics. Inside the elevator there is a nozzle, a receiving chamber, a mixing neck and a diffuser. The receiving chamber is connected to the “return” using a flange. Superheated water enters the elevator inlet and passes into the nozzle. Due to the narrowing of the nozzle, the flow speed increases and the pressure decreases (Bernoulli's law). Water from the return line is sucked into the area of low pressure and mixed in the mixing chamber of the elevator. The water reduces the temperature to the desired level and at the same time the pressure decreases. The elevator operates simultaneously as a circulation pump and mixer. This is briefly the principle of operation of an elevator in the heating system of a building or structure.
Thermal unit diagram
Adjustment of the coolant supply is carried out by the elevator heating units of the house.
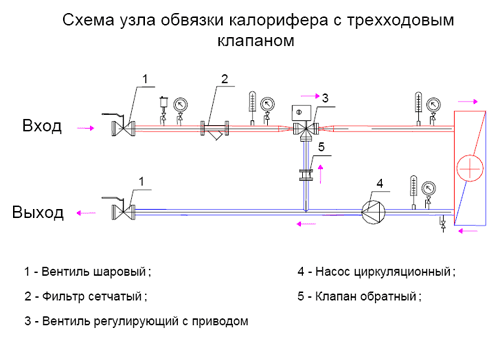
The elevator is the main element of the heating unit and needs piping. The control equipment is sensitive to contamination, so the piping includes dirt filters that are connected to the “supply” and “return”. The elevator harness includes:
- mud filters;
- pressure gauges (inlet and outlet);
- temperature sensors (thermometers at the elevator inlet, outlet and return);
- valves (for preventive or emergency work).
This is the simplest circuit option for adjusting the temperature of the coolant, but it is often used as the basic device of a thermal unit.
The basic elevator heating unit for any buildings and structures provides regulation of the temperature and pressure of the coolant in the circuit. The advantages of using it for heating large objects, houses and high-rise buildings:
- reliability due to the simplicity of the design;
- low cost of installation and components;
- absolute energy independence;
- significant savings in coolant consumption up to 30%.
But while there are undeniable advantages of using an elevator for heating systems, the disadvantages of using this device should also be noted:
- the calculation is done individually for each system;
- a mandatory pressure drop is required in the heating system of the facility;
- if the elevator is unregulated, then it is impossible to change the parameters of the heating circuit.
Elevator with automatic adjustment
Currently, elevator designs have been created in which the nozzle cross-section can be changed using electronic adjustment.
This elevator has a mechanism that moves the throttle needle. It changes the lumen of the nozzle and as a result the coolant flow changes. Changing the lumen changes the speed of water movement. As a result, the mixing ratio of hot water and water from the “return” changes, thereby achieving a change in the temperature of the coolant in the “supply”. Now it’s clear why water pressure is needed in a heating system. The elevator regulates the flow and pressure of the coolant, and its pressure drives the flow in the heating circuit.
Operating principle of the elevator heating unit and diagram
With the help of an elevator, the temperature of the superheated water drops to the calculated temperature, after which the prepared coolant is sent to the heating devices. The operating principle of the elevator unit is based on mixing superheated coolant from the supply pipeline with cooled water from the return pipe.
The diagram of the elevator assembly below clearly shows that the elevator performs 2 functions at once, which makes it possible to increase the overall efficiency of the heating system:
- Works as a circulation pump;
- Performs mixing function;
Elevator unit diagram
The advantage of the elevator is its simple design and, despite this, high efficiency. Its cost is low. It does not require an electrical connection to operate.
It is worth mentioning the disadvantages of this element:
- There is no possibility of regulating the outlet water temperature;
- The pressure difference between the supply and return pipelines should not fall outside the range of 0.8-2 Bar;
- Only accurate calculation of every detail of the elevator guarantees its efficient operation;
Today, elevators are still widely used in heating units of residential buildings, since the efficiency of their operation does not depend on changes in thermal and hydraulic conditions in heating networks. In addition, the elevator unit does not require constant supervision, and to adjust it, it is enough to select the correct nozzle diameter. It is worth remembering that the entire selection of elevator unit elements should be trusted only to specialists who have the appropriate permits.
Elevator diagram
Main components of the heating automation system
- temperature (indoor, outdoor, coolant) and pressure sensors, which provide a constant supply of information about the state of the heating system;
- thermostats (setters, thermostats) that regulate the coolant supply;
- drives and actuators (valves, circulation and make-up pumps, frequency regulators) perform the function of regulatory and safety mechanisms that ensure reliable and trouble-free operation of the system.
- automation panels (controllers, expansion modules) that control the heating system
What does the elevator unit consist of?
- Jet elevator;
- Nozzle;
- Resolution camera;
In addition, the elevator unit includes the so-called “elevator piping”, consisting of control pressure gauges, thermometers, and shut-off valves. Recently, elevators have appeared equipped with an electric drive to regulate the diameter of the nozzle. Such an elevator allows you to automatically regulate the temperature of the coolant entering the heating system. However, such models are not yet widely used due to the low degree of reliability.
Three way valve
If it is necessary to divide the coolant flow between two consumers, a three-way heating valve is used, which can operate in two modes:
- constant mode;
- variable hydraulic mode.
A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water.
The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection, a three-way valve on a heating system can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits. The ball valve is mainly used for:
- adjusting the temperature of heated floors;
- adjusting battery temperature;
- distribution of coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are almost equivalent, but with three-way shut-off valves it is more difficult to regulate the temperature smoothly.
AUU - effective saving of thermal energy

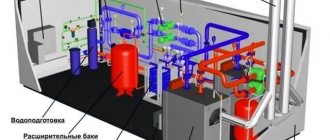
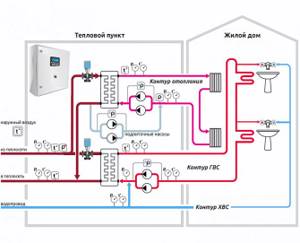
An automated control unit is a set of equipment and devices designed to provide automatic regulation of temperature and coolant flow, which is carried out at the input of each building in accordance with the temperature schedule required for an individual building. Adjustments can also be made according to the needs of the residents.
Water heater piping unit.
Among the advantages of the ACU, when compared with elevator and thermal units that have a fixed cross-section of the passage opening, is the possibility of varying the amount of coolant, which depends on the temperature of the water in the return and supply pipelines.
An automated control unit is usually installed alone for the entire building, which distinguishes it from an elevator unit, which is mounted on each section of the house.
In this case, the installation is carried out after the unit that takes into account the thermal energy of the system.
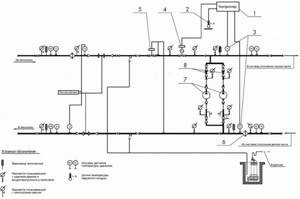
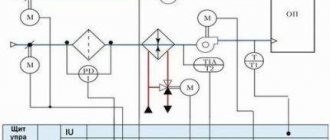
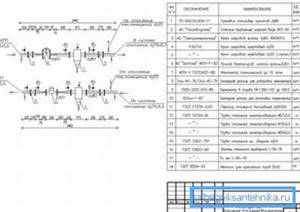
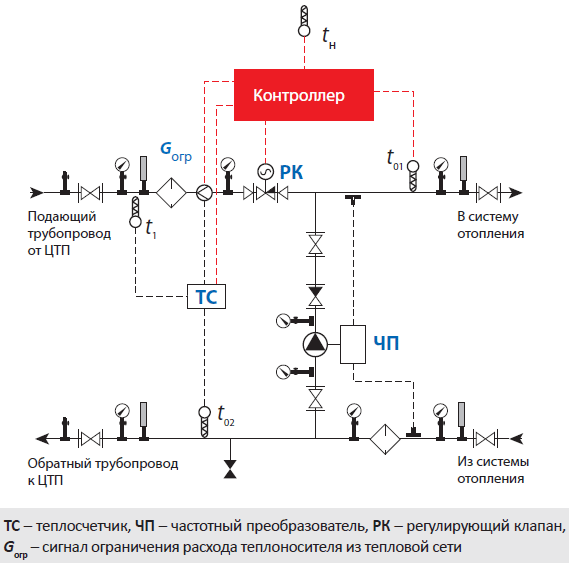
Image 1. Schematic diagram of an ACU with mixing pumps on a jumper for temperatures up to ACU t = 150–70 ˚C with one- and two-pipe heating systems with thermostats (P1 – P2 ≥ 12 m water column).
The automated control unit is represented by a diagram illustrated in PICTURE 1. The diagram provides: an electronic unit (1), which is represented by a control panel; outdoor temperature level sensor (2); temperature sensors in the coolant in the return and supply pipelines (3); valve for regulating flow, equipped with a gear drive (4); valve for adjusting the differential pressure (5); filter (6); circulation pump (7); check valve (8).
As the diagram shows, the control unit fundamentally consists of 3 parts: network, circulation and electronic.
The network part of the ACU includes a coolant flow regulator valve with a gear drive, a differential pressure regulator valve with a spring control element and a filter.
The circulation part of the control unit includes a mixing pump with a check valve. A pair of pumps are used for mixing. In this case, pumps must be used that satisfy the requirements of the automatic unit: they must operate alternately with a cycle of 6 hours. Their operation should be monitored by a signal from a sensor that is responsible for the pressure difference (the sensor is installed on the pumps).
Rules and regulations applied in heat supply systems of MKD
The organization of the heat supply system of an apartment building is strictly regulated by legislative acts and SanPiN norms.
So, according to SanPiN 2.1.4.2496-09:
“The temperature of hot water at water points, regardless of the heat supply system used, must be no lower than 60 °C and no higher than 75 °C.”
The temperature of hot water must be more than 60 degrees Celsius to disinfect it from viruses and bacteria, which can survive at lower temperatures, but die at values above this figure.
On the other hand, using water heated above 75 degrees is unacceptable, as it can lead to burns.
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 6, 2011 N 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings”:
1. The heating system must provide the standard air temperature:
a. in residential premises - not lower than +18 °C (in corner rooms +20 °C);
b. in areas with the coldest five-day temperature -31 °C and below +20 °C (in corner rooms from +22 °C);
c. in other premises, in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on technical regulation.
2. The heating system must ensure an acceptable excess of the standard temperature of no more than 4 °C;
3. The permissible decrease in standard temperature at night (from 0.00 to 5.00 hours) is no more than 3°C;
4. Reducing the air temperature in a living room during the daytime (from 5.00 to 0.00 hours) is not allowed.
Advantages and principle of operation of the automatic unit
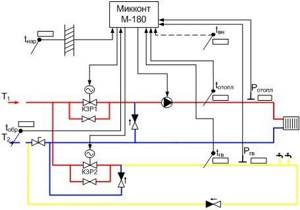
Heating and hot water control unit according to an open circuit.
The electronic part of the control unit includes an electronic unit or the so-called control panel. It is designed to provide automatic control of pumping and thermal mechanical equipment to maintain the required temperature schedule. With its help, the hydraulic schedule is maintained, which should form the basis of the heating system of the entire building.
The electronic part also contains an ECL card, which is intended for programming the controller, the latter is responsible for the thermal mode. The system also includes an outdoor temperature sensor, which is installed on the northern façade of the building. Among other things, there are temperature sensors for the coolant itself in the return and supply pipelines.
Heating automation system design
The equipment and algorithms of the heating system automation project are carried out using the technology of the heating system developers. A typical project composition may be as follows:
- Common data;
- Structural diagrams, if necessary;
- System programming task;
- Functional automation diagrams for each of the subsystems - automation panels will be assembled according to them;
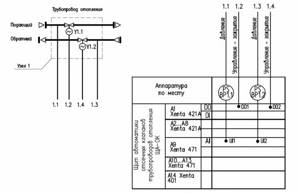
- Communication diagrams of automation system controllers;
- Connection diagrams with related automation systems;
- Diagrams of external connections for automation panels (in fact, this is a table of connections);
- Schematic electrical diagrams of automation panels, pump motors, valve controls;
- Schematic diagrams of power supply for automation panels;
- Layout of equipment and wiring of automation systems;
- Cable magazines;
- Installation diagrams;
- Specification of equipment and wiring.
Errors during the implementation of an automatic node
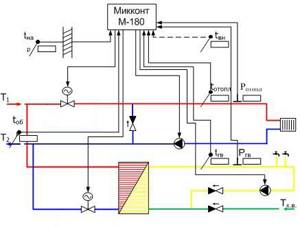
Control unit for heating and hot water supply according to an independent heating circuit and hot water supply according to a closed circuit.
Errors can occur even at the time of planning and subsequent organization of work on the implementation of a heating system. Certain mistakes are often made when choosing a technical solution. You should not miss the rules for installing an individual heating point. Ultimately, at the time of installation of the heating control unit, duplication of the functionality of the equipment that is installed in the central heating center may occur; this, in turn, contradicts the rules for operating heating installations. Thus, installing heating control units with a balancing valve can lead to high hydraulic resistance in the system, which will entail the need to replace or reconstruct thermal and mechanical equipment.
Non-comprehensive installation of heating control units can also be called a mistake, which will certainly disrupt the established thermal and hydraulic balance in intra-block networks. This will cause deterioration in the performance of the heating system of almost every connected building. It is necessary to make thermal adjustments during operation of the heating equipment.
Often errors occur during the input of the heating control unit at the design stage. This is due to the lack of working designs, the use of a standard design, devoid of calculations, linking and selection of equipment to certain conditions. The consequence is a violation of heat supply regimes.
System operating modes. Work in the building automation and dispatch system
Heating control systems can operate in the following modes.
Manual mode . In this case, setting operating modes, switching equipment from primary to backup and many other functions are carried out manually by the operator, and it does not matter whether he presses buttons on the automation panel or on the PC, this is manual mode.
Automatic offline mode . In this case, the operator turns the system on and off; subsequently, the system operates according to a given algorithm and transmits information about its state to the operator or dispatcher.
Automatic as part of an automated building management system. In this mode, the operation of the heating system is synchronized with other life support systems of the building; the operator or dispatcher does not take part in the control.
Additional requirements when putting the heating control unit into operation
Heating and hot water control unit according to an independent circuit.
The selected installation diagrams for heating control units may not correspond to the required ones, which negatively affects the heat supply. It also happens that at the time of commissioning the system, the technical conditions used do not correspond to the real parameters. This may lead to the wrong choice of node scheme.
At the time of commissioning the automation unit, it should be taken into account that the heating system may have previously undergone major repairs and reconstruction, during which the circuit could have been changed from a single-pipe to a two-pipe. Problems may arise when the calculation of a unit is made for a system that existed before reconstruction.
The system commissioning process should be carried out outside of winter so that the system can be launched in a timely manner.
Scheme of an automated control unit for the heating system (AHU) of a house.
It should be remembered that air temperature sensors must be mounted on the north side, which is necessary for correct temperature setting; in this case, solar radiation will not be able to affect the heating of the sensor.
During the commissioning process, backup power to the node must be provided, which will help avoid stopping the central heating system during a power outage. It is necessary to carry out adjustment and adjustment work, as well as noise reduction measures, and maintenance of the unit must take place. It should be noted that failure to comply with one or more rules may lead to the system not warming up, and the lack of muffling equipment will lead to uncomfortable noise.
The implementation of the control unit must be accompanied by verification of the issued technical specifications; they must correspond to the actual data. And technical supervision must be carried out at each stage of work. After all work on the system has been completed, maintenance of the unit should begin, which is carried out by a specialized organization. Otherwise, downtime of expensive equipment of an automated unit or its unqualified maintenance can lead to failure and other negative consequences, including loss of technical documentation.
Installation Features
Installation of a heat metering unit in an apartment building is divided into several main stages:
- Study and analysis of the object.
- Creation and approval of the project.
- Assembly and adjustment.
- Organization of monitoring.
- Providing a diagram of the heating unit of an apartment building to the heating supply organization and obtaining an operating permit.
The cost of the procedure depends on the characteristics of the object and can vary significantly. If it is necessary to replace the thermal energy metering unit, the sequence of actions is approximately the same. The most critical stage is the development of the project and selection of equipment. Naturally, the installation of thermal energy metering units must be carried out with maximum care and precision. However, if the initial calculations turn out to be erroneous, even high-quality, expensive devices will not provide the required accuracy of readings.

When a heating unit is installed in a private house, the coordination scheme may be slightly different. In any case, going through the authorities on your own will require serious time investment. As a rule, the installation of thermal energy metering units includes this service. Decide for yourself what is preferable to you - pay a little extra or save through your own efforts. However, keep in mind that it is much easier for experienced representatives of a construction organization to obtain permission than for an individual.
Automation of heat metering units makes it possible to organize remote data collection from meters, which greatly simplifies facility monitoring. UUTE maintenance should be trusted to professionals. Independence in this matter, as in the installation of heat metering units in Moscow, can lead to significant financial losses. If equipment breakdown is not noticed in time, repairs may take a long time, and all this time you will be overpaying for unused heat. If you are interested in whether it is possible to install UUTE on the heating unit of your home and other questions on this topic, you can get answers to them on our website.
Effective use of an automated heating control unit
An example of a diagram of a control unit for heating systems and heat supply installations.
The use of the unit will be most effective in cases where the house has subscribed elevator units of heating systems that are directly connected to the city heat main networks. Such use will also be effective in the conditions of end houses connected to central heating stations, where there are insufficient pressure drops in the central heating system with the obligatory installation of central heating pumps.
The efficiency of use is also noted in houses that are equipped with gas water heaters and central heating; such buildings may also have a decentralized hot water supply.
It is recommended to install automated units comprehensively, covering all non-residential and residential buildings that were connected to the central heating point. Installation and delivery, as well as subsequent acceptance into operation of the entire system and associated equipment of the unit must be carried out simultaneously.
It should be noted that with the installation of an automated unit, the following measures will be effective:
- Converting the central heating station, which has a dependent connection scheme for individual heating systems, to one that will be independent. In this case, installing an expansion membrane tank at a heating point will also be effective.
- Installation in a central heating substation, which is characterized by a dependent circuit for connecting equipment similar to an automated control unit.
- Carrying out the adjustment of intra-block central heating networks with the installation of throttle diaphragms and design nozzles at the input and distribution nodes.
- Converting dead-end hot water systems to circulation circuits.
The operation of exemplary automated units has shown that the use of automatic control units in conjunction with balancing valves, thermostatic valves and the implementation of insulation measures can save up to 37% of thermal energy, providing comfortable living conditions in each of the premises.
Types of heating systems
Heating systems are classified according to the following criteria.
According to the type of heat exchange between the heater and the environment:
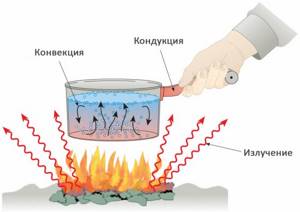
Convective heating . In this case, the transfer of thermal energy occurs along with the movement of volumes of hot and cold air: the warm air flow rushes upward, the cold air flows down. Due to the heat transfer mechanism, convective heating is impossible through any impenetrable barriers, incl. transparent.
Radiant heating . This is a type of heating in which heat is transferred by radiation. From the Sun to the Earth or from the heated surface to the observer.
Convective-radiant heating . Mixed mechanism. Most heating devices (radiators, convectors, heated floors and walls) transfer heat in this particular way; the optimal option is when there is an approximately equal (50/50) ratio of convective and radiant heat.
By type of coolant:
Water heating . Today the most common type of heating, which comes in the following types:
- Radiator heating, in which the following types of radiators can be used: cast iron, steel, aluminum, bimetallic, stone, ceramic, as well as convectors.
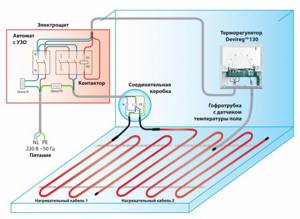
- Warm water floor. In this case, heating communications are laid under the floor covering.
- Baseboard heating. In this case, each section of the warm baseboard is a small convector with a casing, and installation is carried out like installing a regular radiator.

- Water infrared heating (“warm ceiling”). When installing such a system, a large infrared panel is attached to the ceiling, which is a heat source.
- Combined systems: include elements of the above heating systems.
Air heating . Air systems include systems in which the coolant is heated air. In supply ventilation, such systems can be local or distributed.
In local systems, heating and air supply are carried out directly in the heated room using heating and heating and ventilation devices.
In distributed systems, air is heated in an air heating unit and supplied to rooms through ducts.
In addition, there is fire-air heating, in which heat comes from stoves and fireplaces. With this type of heating, the coolant is either practically absent, or it is hot flue gases.
Heating systems without coolant.
- Electric heating systems. In such systems, electrical energy, converted into heat, heats the room rather than the coolant, for example, electric fireplaces, infrared electric panels, electric radiators or floors.
- Gas systems. In such systems, heat is generated by the combustion of a gas-air mixture. An example is gas fireplaces. picture of galley heating
Heating control systems
As a result of the advancement of modern technologies, everyone can turn their home into a “smart home”. Thus, coordinating the heating of your home using the Internet or GSM cellular network is becoming increasingly popular. Manually adjusting the temperature when heating a room is not always effective. Automatic thermostats used in some homes are also becoming irrelevant today due to limited functionality.
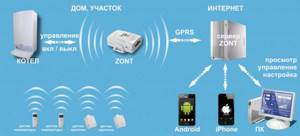
The advantage of using GSM administration is that problems with organizing such control do not arise when using any heating equipment. Almost all modifications of such units available on the market are capable of performing additional tasks. They can remotely transmit information to the homeowner's mobile phone and change room temperature settings. To implement such functions, mechanisms equipped with a GSM controller are used. It is a multi-purpose control element included in the structure of a “smart home” with automation of familiar functions.
Heating control system elements
The heating control unit is a set of elements combined into a single circuit. Their selection becomes key to ensuring the efficiency of the system. Items may have different characteristics. The main indicator of their effectiveness is the possibility of forming multilateral communication between the control unit, the owner and the heating elements.

The basis of the system is a special electronic unit that has 1 or several slots (sockets) for installing conventional SIM cards for cellular communications
Almost any GSM complex operates with the participation of the same elements, which may differ only in the basic configuration and controller resources.
Typical configuration of elements of the GSM heating coordination system:
- connecting wires;
- several temperature meters;
- GSM controller;
- leak detector;
- electronic key scanner;
- access control mechanism;
- GSM signal reception and broadcast antenna;
- accumulator battery;
- an ethernet adapter that provides interaction with other elements;
- blocks intended for connection to the boiler;
Repair and maintenance of heating systems
Depending on the source of heat supply, repair and maintenance of heat supply systems in an apartment building is carried out differently.
With a centralized heat supply system, maintenance is carried out annually, which includes the following activities:
· Hydraulic testing of thermal units, heating networks, heating systems, hot water supply systems;
· Flushing the heating system;
· Inspection of heat consumption systems equipment;
· Diagnostics, repair and maintenance of thermal energy metering unit;
· Current repairs of heat consumption systems;
· Washing of heat exchange equipment.
With a local decentralized heat supply system:
· Maintenance of boiler equipment;
· Hydraulic testing of thermal units, heating systems, hot water supply systems;
· Annual flushing of the heating system;
· Inspection of heat consumption systems equipment (checking pressure gauges, thermometers, packing gland seals on valves);
· Routine repair of heat consumption systems (in accordance with defect reports);
· Washing of heat exchange equipment;
· Inspection and audit of heat exchange equipment, pumping equipment;
· Pressure pumping in the expansion tank;
· Maintenance and repair of gas equipment.
With an individual decentralized heat supply system, a set of works is carried out necessary to maintain the heat supply system equipment in operational condition:
· Checking the heating and hot water system for tightness;
· Checking safety valves;
· Cleaning filters;
· Pressure pumping in the expansion tank;
· Monitoring of pumping equipment.
Mandatory measures in this case also include maintenance of gas equipment.
Control unit "TR-102"
For example, consider one of the most popular modifications of GSM systems today. Its main purpose is to maintain temperature in 4 zones. It occurs in a cyclic mode thanks to the thermostat. This displays the current administration area.

It will not be possible to remotely control the simplest energy-independent heat generators that do not have electronic systems.
The TR-102 unit performs the following functions:
- blocking control of unnecessary areas;
- cyclical temperature control in 4 thermal zones;
- displaying information on an integrated indicator with LEDs;
- setting up the unit using a computer or keys on the front panel of the unit;
- transferring information about regulated zones to a computer via an open communication protocol;
- saving configurations after power failures or unauthorized logins;
The presented heating control unit does not depend on power outages. An additional advantage of this system is the bimetallic sensor for thermoregulation, which is user programmable.
Conditions for using the TR-102 block:
- storage is carried out at temperatures from -45 to +70 °C;
- operation is possible at temperatures from -35 to +55 °C;
In this case, the standard atmospheric pressure should be from 84 to 106.7 kPa, and the air humidity should be 30–80%.
Heating control methods
Remote throttling may differ in the method of data transfer. The key here may be the standard functionality of the transmitting panel, as well as the capabilities of the owner’s phone. Receiving information via SMS is the simplest thing the device should do. There are modifications of control units that have an integrated module for messages sent to control and configure functions. Such messages have a specific format. This method of coordinating boiler functions is considered the most common.

In normal mode, the automated heating system control unit acts as a remote control with a thermostat and monitors the maintenance of the set temperature in the rooms
Important! Effective remote administration of heat supply can be carried out by knowing the level of error in the indicators. Please note that the information received in the message may differ from the actual information.
Errors in system performance:
- electronic modifications of temperature meters by ±0.5° C;
- shut-off and control valves – from 0.2 ° C to 0.5 ° C.
Heat exchanger based models
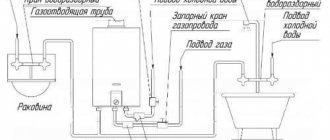
There is another type of heating unit for a private house - based on a heat exchanger.
In this case, a special heat exchanger is attached to the device, which separates the liquid from the heating main from the liquid in the room. This function is necessary for additional preparation of the coolant using various additives and filtering devices. The scheme expands the possibilities for regulating the pressure and temperature of the coolant inside the building. Thus, heating costs for the building are significantly reduced. Thermostatic valves must be used to mix water at different temperatures. Such systems interact normally with aluminum radiators, but in order for the latter to last as long as possible, it is necessary to carefully select the coolant, abandoning low-quality raw materials. Of course, keeping track of the quality of the liquid is problematic, so it is better to abandon this material, giving preference to bimetallic or cast iron radiators.
The DHW connection diagram involves the use of a heat exchanger. This method provides many advantages, including :
- 1. Possibility of adjusting water temperature.
- 2. Possibility of changing the pressure of the hot coolant.
Unfortunately, many management companies do not monitor the coolant temperature, and sometimes even lower it by several degrees. The average consumer will hardly notice such changes, but on the scale of an entire home, this means saving impressive amounts of money.
Heating control devices
Programmers and thermostats
The key parts of the heating control system are thermostats and programmers. They are electronic devices, in some modifications equipped with a control panel, which helps control the operation of the boiler. In addition, such a device allows you to synchronously change the indicators in two connected components.
In addition, an additional function of the programmers is adjustment using SMS from a cell phone or commands transmitted via the Internet.
You can select a suitable modification of this device based on a set of basic characteristics, which may include:
Control via the Internet occurs in the same way, only through a different communication channel between the homeowner and the electronic unit in the house
- remote communication between components using radio transmitters;
- operation of radiators (depending on the settings) can be in comfortable, normal or economical mode;
- the number of connected circuits can be increased by connecting additional modules;
- heating control via mobile phone;
- data transfer via SMS, etc.
These functional features make the presented elements quite convenient and in demand.
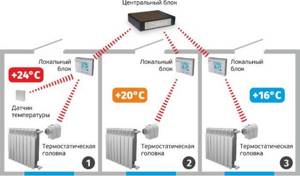
Zone devices
Such heat supply control elements are installed directly on radiators and boilers. In this case, adjustment by the system is carried out via Internet connection. These devices are represented by electronic thermostats. They are capable of changing the water temperature in each individual battery or the system as a whole. The differences between these thermostats are their ease of installation and affordable price. At the same time, the complexity of setting up the system is reduced, especially since they do not require a separate control cabinet. Zone devices allow the use of several thermostats that are connected to one control unit.
Heating remote control modules
The function of remote control of the heating network can be provided by special modules included in the package with shut-off and control valves and programmers.
The number of additional functions of the devices is limited by the number of connected sensors and executive relays of the electronic heating control unit itself
Internet management
Control using the Internet block is as convenient as SMS control. It features the following features:
- installation of specific software systems into a smartphone, laptop or other gadget;
- simple interface that can be easily combined with Android or Windows OS;
- unlike SMS blocks, restrictions on the number of connected users have been removed;
- Parameters are adjusted where there is access to the Internet (you do not need to use roaming for this).
When traveling abroad, experts advise not to use roaming functions to regulate heat supply via the GSM system, as this can be fraught with large financial costs. In this case, the right decision would be to entrust control of the heating system to friends you trust.
The operation of heating radiators can be controlled using local devices, represented by mechanical temperature controllers. They cannot connect to electronic controls. Their only advantage is their low cost.
Advantages and disadvantages of air heating
To make a choice, consider the features of using such systems in private homes:
Heating of a private house, the fireplace acts as a heating element.
Estimated service life is 30 years. Usually, after a couple of years, the costs of VO are fully repaid to the owners. No leaks or risk of pipe freezing, high efficiency, no intermediate transmission elements and low energy consumption. Fans can “cooperate” with a conventional stove and supply warm air to all rooms. A well-known example is fireplace air heating of a private house. Filters and ionizers can purify the air of odors and eliminate harmful particles. The system creates an optimal microclimate, producing additional air humidification or drying, depending on the characteristics of the climate and the room. In the summer, you can cool the room using air ducts with additional draft that supply cool air. If you are not at home, the system operates at a minimum and quickly increases the temperature when necessary. The main disadvantage is the need for power supply to the forced circulation system and the need for backup power if power outages are expected. Support for installing the system is laid only during the construction of a building or complex repairs are carried out with subsequent installation. VO is quite demanding in terms of repair and maintenance; with regular use, it is difficult to carry out a full modernization.
GSM heating control scheme "smart home"
Usually you can install the system yourself. This requires checking the condition and analyzing the capabilities of existing equipment. It is also important to correctly select the missing components. Typically, a set of control devices is built from a single block, which is the connecting link between all components of the heat supply.

Control systems based on coolant temperature control operate regardless of current conditions
It must be installed subject to the following conditions:
- The control unit should be located at a distance of no more than 300 meters from the user. To increase the distance, radio-controlled modifications are purchased, coordination is connected via the Internet or cell phone.
- The use of a controller based on heat supply control boards ensures the installation of additional functions.
- A careful selection of the location in the house for installation of the control unit is carried out.
General provisions
2.1. Use of the TeploProekt website by the User means acceptance of this Privacy Policy and the terms of processing of the User’s personal data.
2.2. In case of disagreement with the terms of the Privacy Policy, the User must stop using the TeploProekt website.
2.3. This Privacy Policy applies to the TeploProekt website. The site does not control and is not responsible for third party sites that the User can access via links available on the TeploProekt website.
2.4. The Administration does not verify the accuracy of the personal data provided by the User.
Air conditioning control
In addition to monitoring heat supply, GSM devices allow remote control of the air conditioning system. This is done using IR or Wi-Fi modules (requires connection to a phone or personal computer), as well as GSM controllers.
Internet control
In summer, air conditioners or systems consisting of several units are often used as cooling tools. So, in ordinary apartments you can lower the temperature in a short time by using the “turbo” function. But in buildings where, for example, servers are located, there must be round-the-clock air cooling. The uninterrupted operation of powerful equipment provokes the release of heat. In such a situation, constant monitoring of microclimatic indicators in the room allocated for this equipment is required. Such processes cannot be carried out manually. For this purpose there is remote control. This is done using devices for remote monitoring of indicators in the room.
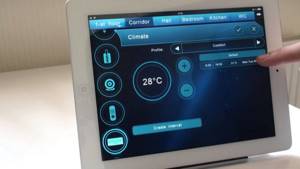
Weather-dependent regulation is considered the most progressive and effective, since it allows you to quickly respond to changing environmental conditions
In the case when an Internet network is present at the facility, the unit for remote control of the functions of the air conditioning complex can be launched using gadgets running on the Android or iOS OS. Such devices are climate modules designed to interact with modern air conditioners. They provide the ability to remotely regulate the operating mode. To do this, a special program for GSM communication is installed in the gadget. The general thermoregulation scheme includes a laptop, telephone or personal computer and an adapter connected to the air conditioner. To transmit information, Wi-Fi or an infrared protocol can be used as an additional component for remote control of the air conditioning system.
SMS control
It is most convenient to remotely coordinate the parameters of home air conditioners using messages. It is not only convenient, but also profitable. Used appliances can be turned off remotely to save energy. Such technologies are used in devices included in the Smart Home. GSM controllers are suitable for premises where there is no Internet network. In this case, thermal sensors are used for correct operation. Operating modes are regulated using software that is installed both in control units and in communication devices. Thus, you can change the power of the compressor, the speed of rotation of the fan motor, etc.
Computer control
For industrial systems, computer control of VRF air conditioners via a network is best suited. In this case, remote communication protocols are used.
When connecting a remote control module, the following problems can be solved:
- excessive energy consumption;
- 24-hour climate control;
- reduction of equipment service life;
- consumption of human resources, etc.
In addition, a positive aspect of using GSM coordination of air conditioning systems is to provide comfortable conditions for workers and visitors of offices, entertainment centers, etc.

Author, specialist in the field of IT and new technologies.
Received higher education in fundamental computer science and information technology at Moscow State University named after M.V. Lomonosov. After that, he became an expert in a well-known online publication. After a while, I decided to try writing articles on my own. He runs a popular blog on YouTube and shares interesting information from the world of technology.